本文涉及知识点
二分查找算法合集
C++算法:滑动窗口总结
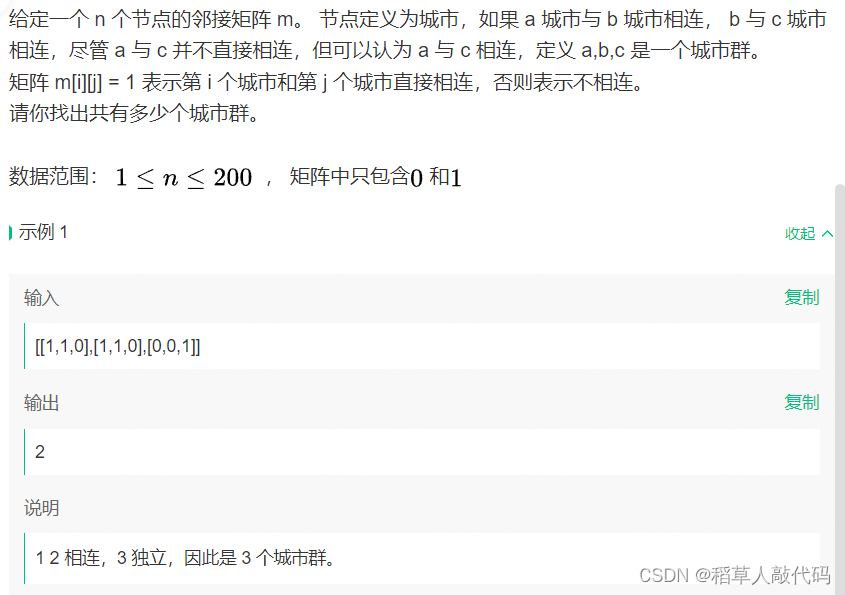
LeetCode 100257找出唯一性数组的中位数
给你一个整数数组 nums 。数组 nums 的 唯一性数组 是一个按元素从小到大排序的数组,包含了 nums 的所有非空子数组中不同元素的个数。
换句话说,这是由所有 0 <= i <= j < nums.length 的 distinct(nums[i…j]) 组成的递增数组。
其中,distinct(nums[i…j]) 表示从下标 i 到下标 j 的子数组中不同元素的数量。
返回 nums 唯一性数组 的 中位数 。
注意,数组的 中位数 定义为有序数组的中间元素。如果有两个中间元素,则取值较小的那个。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:1
解释:
nums 的唯一性数组为 [distinct(nums[0…0]), distinct(nums[1…1]), distinct(nums[2…2]), distinct(nums[0…1]), distinct(nums[1…2]), distinct(nums[0…2])],即 [1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3] 。唯一性数组的中位数为 1 ,因此答案是 1 。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [3,4,3,4,5]
输出:2
解释:
nums 的唯一性数组为 [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3] 。唯一性数组的中位数为 2 ,因此答案是 2 。
示例 3:
输入:nums = [4,3,5,4]
输出:2
解释:
nums 的唯一性数组为 [1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3] 。唯一性数组的中位数为 2 ,因此答案是 2 。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
1 <= nums[i] <= 105
二分查找、滑动窗口
二分窗口
唯一性数组的长度为long long llTotal = (long long)m_c * (1 + m_c) / 2。
令f(x) 等于唯一性数组小于等于x的元素数量。如果f(x) < (llTotal +1)/2 ,则x一定不是解;否则,可能是解。可能是解的最小值便是解minLen。
令检查函数是Check(x)是f(x) >= (llTotal +1)/2 ,则当x < minLen时,Check(x)
{ C h e c k ( x ) = f a l s e x < m i n L e n C h e c k ( x ) = t r u e o t h e r \begin{cases} Check(x) = false && x < minLen \\ Check(x) = true && other \\ \end{cases} {Check(x)=falseCheck(x)=truex<minLenother
寻找第一个符合的元素,故用左开右闭空间。
滑动窗口
用封装类CKeyCount cnt记录[left,right)中不同数的数量。 ∀ \forall ∀left,对应right为以下情况之一:
一,right 为m_c。
二,cnt中的数量超过minLen,如果多个符合,right取最小值。
如果符合情况二(无论是否符合情况一),以left开始,长度小于等于minLen的数量为:right-left-1。
否则,长度小于等于minLen的数量为:right-left。
∀ \forall ∀left,left+1对应的right(令为right1) 只会不变或变大。可以用反证法证明:
因为:righ1 < right。故right1不为m_c,故只能是情况二。即:有minLen+1个元素,那left,righ1至少有minLen+1个元素,故right1或更小的数才是right。和假设矛盾。
代码
核心代码
template<class KEY>
class CKeyCount
{
public:void Add(const KEY& key, int iCount){Cnt[key] += iCount;if (0 == Cnt[key]){Cnt.erase(key);}}std::unordered_map<KEY, int> Cnt;
};namespace NBinarySearch
{template<class INDEX_TYPE, class _Pr>INDEX_TYPE FindFrist(INDEX_TYPE left, INDEX_TYPE rightInclue, _Pr pr){while (rightInclue - left > 1){const auto mid = left + (rightInclue - left) / 2;if (pr(mid)){rightInclue = mid;}else{left = mid;}}return rightInclue;}template<class INDEX_TYPE, class _Pr>INDEX_TYPE FindEnd(INDEX_TYPE leftInclude, INDEX_TYPE right, _Pr pr){while (right - leftInclude > 1){const auto mid = leftInclude + (right - leftInclude) / 2;if (pr(mid)){leftInclude = mid;}else{right = mid;}}return leftInclude;}
}class Solution {
public:int medianOfUniquenessArray(vector<int>& nums) {m_c = nums.size();long long llTotal = (long long)m_c * (1 + m_c) / 2;auto Can = [&](int iMinLen) {CKeyCount<int> cnt;long long llCnt = 0;for (int left = 0, right = 0; left < m_c; left++) {for (; (right < m_c)&& (cnt.Cnt.size() <= iMinLen); right++) { cnt.Add(nums[right],1);}llCnt += right - left - (cnt.Cnt.size() > iMinLen) ;cnt.Add(nums[left], -1);}return llCnt >= (llTotal+1) / 2;};const int iRet = NBinarySearch::FindFrist(-1, m_c, Can);return iRet;}int m_c;
};
测试用例
template<class T>
void Assert(const vector<T>& v1, const vector<T>& v2)
{if (v1.size() != v2.size()){assert(false);return;}for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++){assert(v1[i] == v2[i]);}
}template<class T>
void Assert(const T& t1, const T& t2)
{assert(t1 == t2);
}int main()
{vector<int> nums;{Solution slu;nums = { 1 };auto res = slu.medianOfUniquenessArray(nums);Assert(1, res);}{Solution slu;nums = { 4,3,5,4 };auto res = slu.medianOfUniquenessArray(nums);Assert(2, res);}{Solution slu;nums = { 1,2,3 };auto res = slu.medianOfUniquenessArray(nums);Assert(1, res);}{Solution slu;nums = { 3,4,3,4,5 };auto res = slu.medianOfUniquenessArray(nums);Assert(2, res);}}

扩展阅读
视频课程
有效学习:明确的目标 及时的反馈 拉伸区(难度合适),可以先学简单的课程,请移步CSDN学院,听白银讲师(也就是鄙人)的讲解。
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/38771
如何你想快速形成战斗了,为老板分忧,请学习C#入职培训、C++入职培训等课程
https://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/6176
相关下载
想高屋建瓴的学习算法,请下载《喜缺全书算法册》doc版
https://download.csdn.net/download/he_zhidan/88348653
| 我想对大家说的话 |
|---|
| 《喜缺全书算法册》以原理、正确性证明、总结为主。 |
| 闻缺陷则喜是一个美好的愿望,早发现问题,早修改问题,给老板节约钱。 |
| 子墨子言之:事无终始,无务多业。也就是我们常说的专业的人做专业的事。 |
| 如果程序是一条龙,那算法就是他的是睛 |
测试环境
操作系统:win7 开发环境: VS2019 C++17
或者 操作系统:win10 开发环境: VS2022 C++17
如无特殊说明,本算法用**C++**实现。