文章目录
- 1.进程间通信
- 2.进程间通信方式
- 2.1 管道---匿名管道
- 2.2 使用管道---管道测试接口(代码实现)
- 3.进程池
- 3.1 进程池的原理图
- 3.2 进程池的代码实现
- 4.命名管道
- 4.1 有名管道通信
- 4.2 有名管道通信的代码实现
- 5.共享内存
- 5.1 共享内存原理
- 5.2 共享内存的代码实现
- 6.共享内存
- 7.代码
1.进程间通信
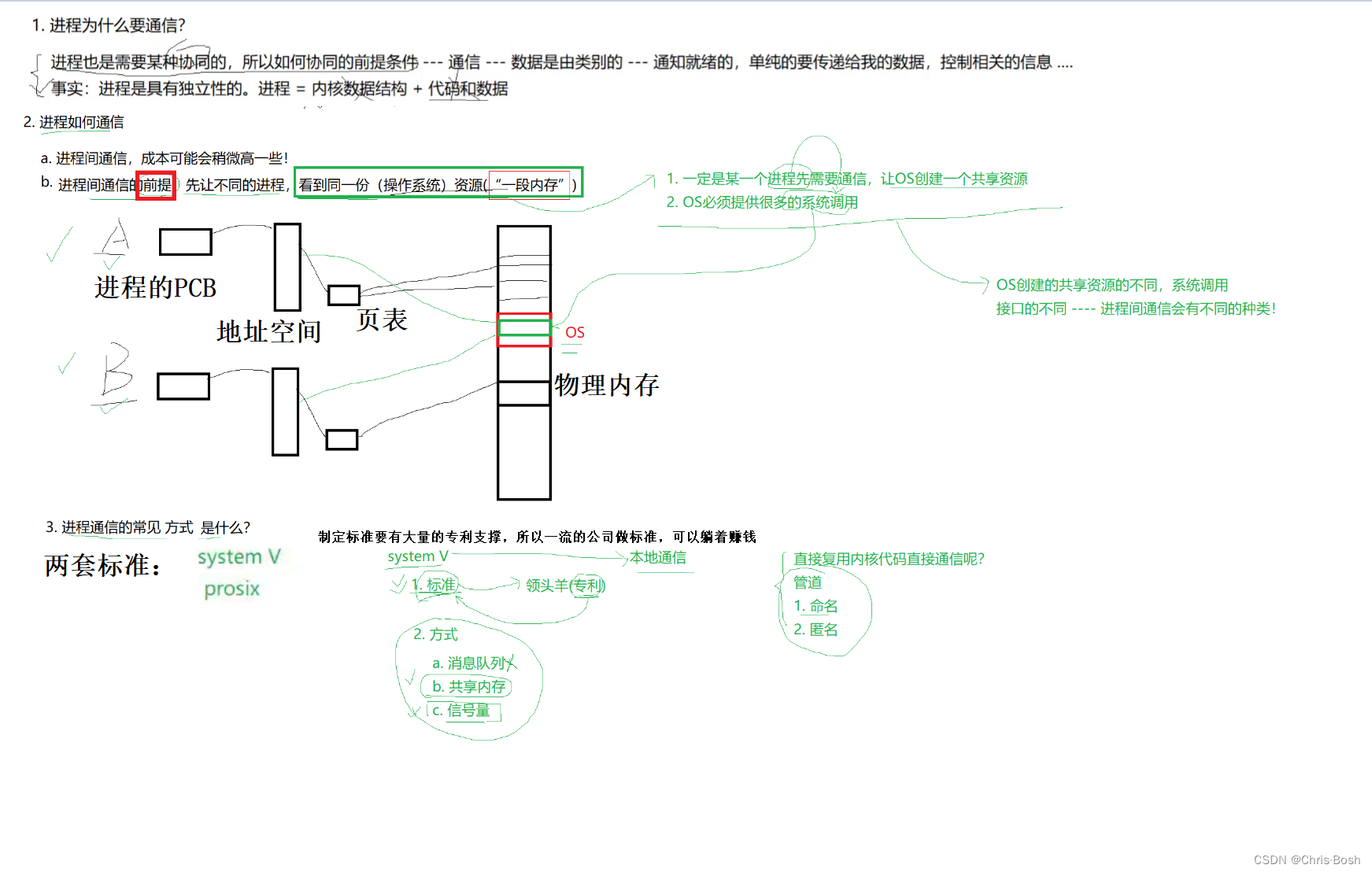
2.进程间通信方式
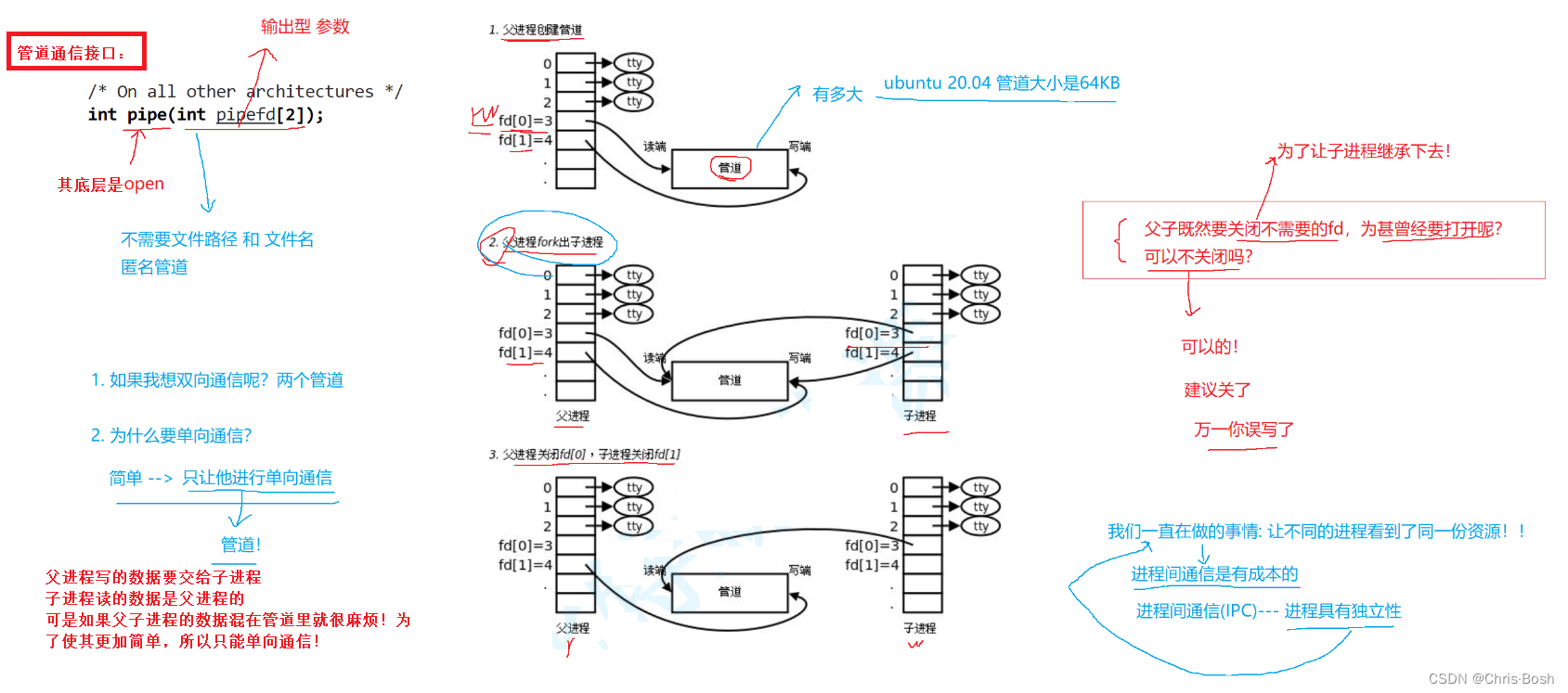
2.1 管道—匿名管道
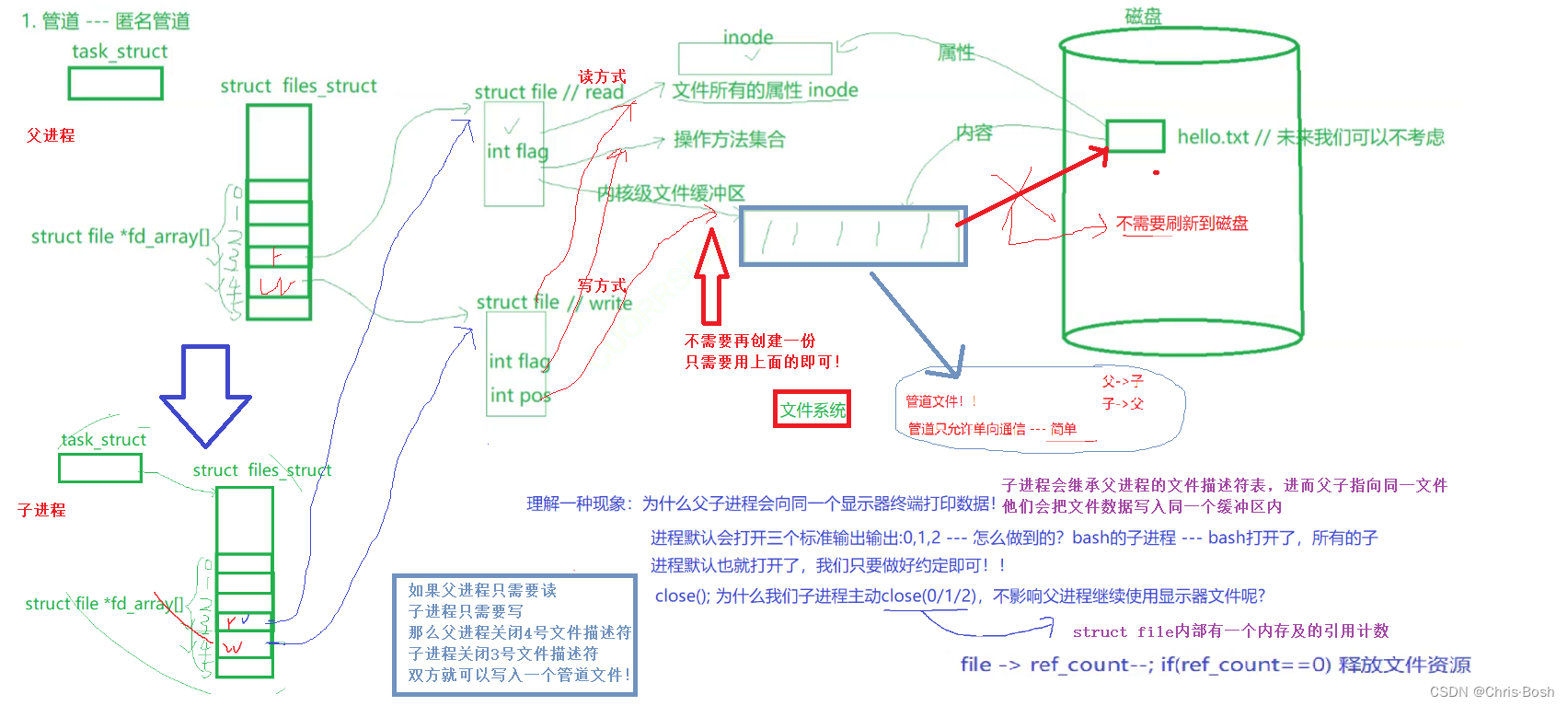
根据上面对匿名管道的基本描述,那么还有两个问题:
①既然父子进程要关闭不需要的fd(文件描述符),那为什么曾经要打开?可以不关闭fd嘛?
②既然不需要刷新到磁盘,那么需要重新设计通信接口嘛?
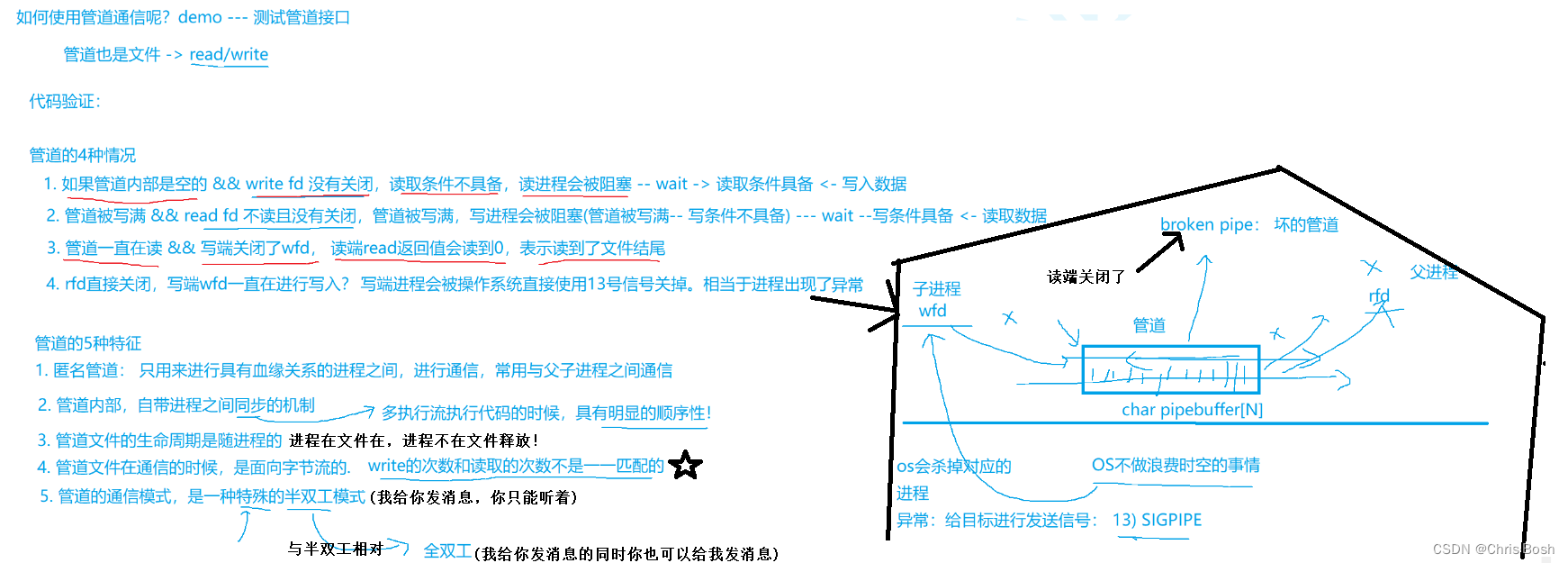
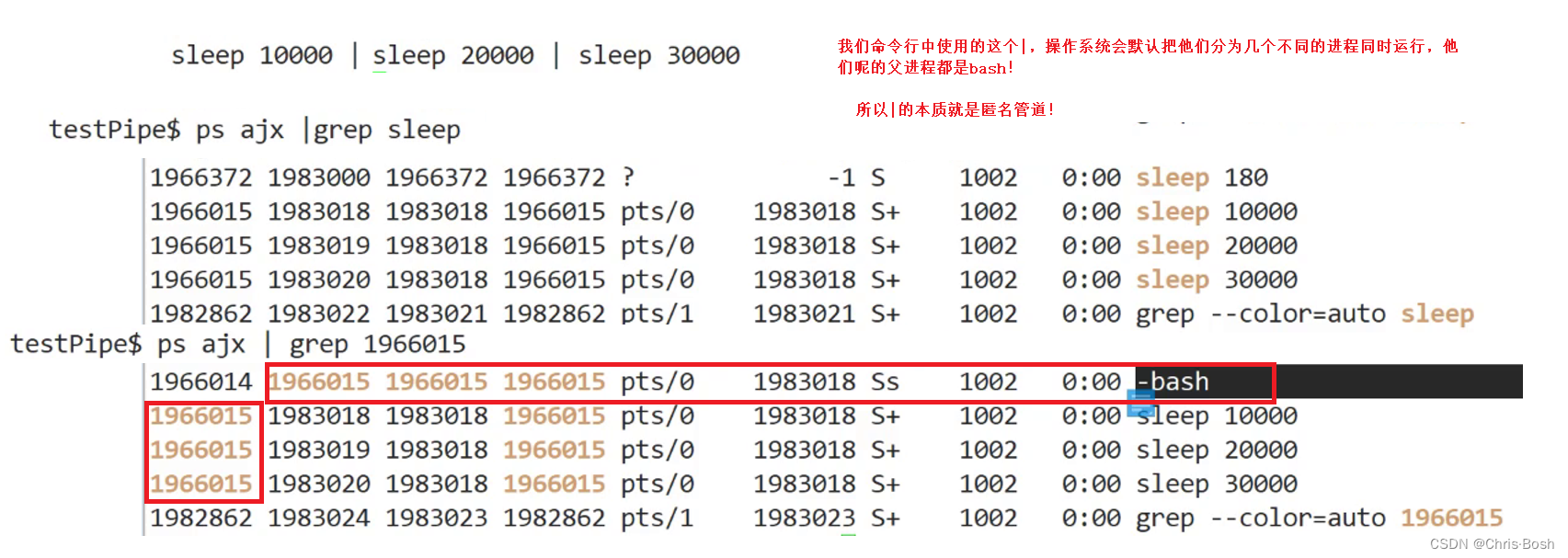
2.2 使用管道—管道测试接口(代码实现)
makefile:
testpipe: testpipe.cppg++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11
.PHONY:clean
clean:rm -f testpipe
testpip.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cerrno> // errno.h
#include <cstring> // string.h
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>const int size = 1024;std::string getOtherMessage()
{static int cnt = 0;std::string messageid = std::to_string(cnt); // stoi -> string -> intcnt++;pid_t self_id = getpid();std::string stringpid = std::to_string(self_id);std::string message = "messageid: ";message += messageid;message += " my pid is : ";message += stringpid;return message;
}// 子进程进行写入
void SonProcessWrite(int wfd)
{std::string message = "father, I am your son process!";while (true){std::string info = message + getOtherMessage(); // 这条消息,就是我们子进程发给父进程的消息write(wfd, info.c_str(), info.size()); // 写入管道的时候,没有写入\0, 有没有必要?没有必要sleep(1);}
}// 父进程进行读取
void FatherProcessRead(int rfd)
{char inbuffer[size]; // c99 , gnu g99while (true){ssize_t n = read(rfd, inbuffer, sizeof(inbuffer) - 1); // sizeof(inbuffer)->strlen(inbuffer);if (n > 0){inbuffer[n] = 0; // == '\0'std::cout << "father get message: " <<inbuffer << std::endl;}else if (n == 0){// 如果read的返回值是0,表示写端直接关闭了,我们读到了文件的结尾std::cout << "client quit, father get return val: " << n << " father quit too!" << std::endl;break;}else if(n < 0){std::cerr << "read error" << std::endl;break;}}
}int main()
{// 1. 创建管道int pipefd[2];int n = pipe(pipefd); // 输出型参数,rfd, wfdif (n != 0){std::cerr << "errno: " << errno << ": "<< "errstring : " << strerror(errno) << std::endl;return 1;}// pipefd[0]->0->r(嘴巴 - 读) pipefd[1]->1->w(笔->写)std::cout << "pipefd[0]: " << pipefd[0] << ", pipefd[1]: " << pipefd[1] << std::endl;sleep(1);// 2. 创建子进程pid_t id = fork();if (id == 0){std::cout << "子进程关闭不需要的fd了, 准备发消息了" << std::endl;sleep(1);// 子进程 --- write// 3. 关闭不需要的fdclose(pipefd[0]);SonProcessWrite(pipefd[1]);close(pipefd[1]);exit(0);}std::cout << "父进程关闭不需要的fd了, 准备收消息了" << std::endl;sleep(1);// 父进程 --- read// 3. 关闭不需要的fdclose(pipefd[1]);FatherProcessRead(pipefd[0]);close(pipefd[0]);int status = 0;pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0);if (rid > 0){std::cout << "wait child process done, exit sig: " << (status&0x7f) << std::endl;std::cout << "wait child process done, exit code(ign): " << ((status>>8)&0xFF) << std::endl;}return 0;
}
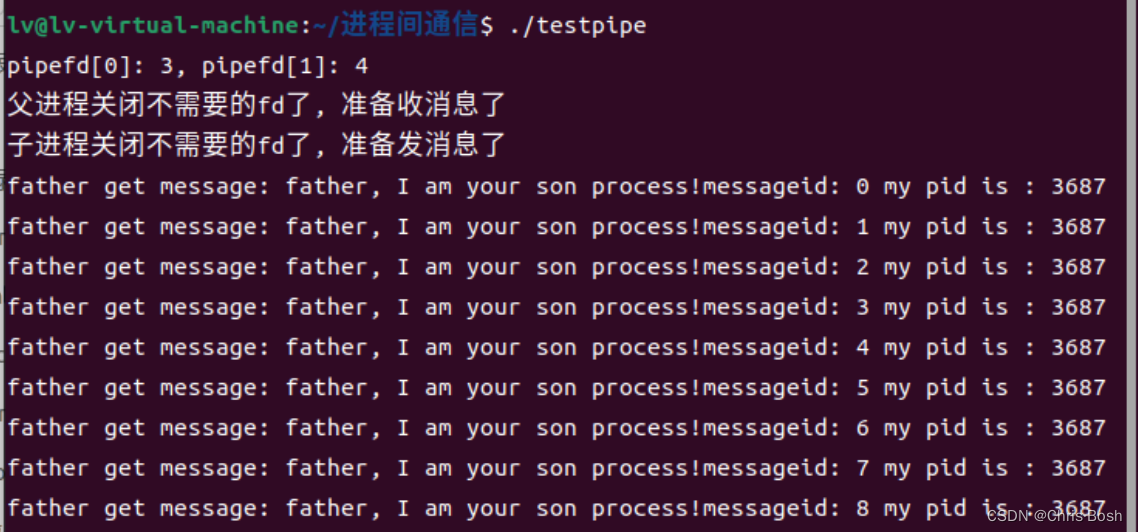
可以看到父进程收消息,子进程发消息。这就是一个简单的管道的例子!
3.进程池
3.1 进程池的原理图
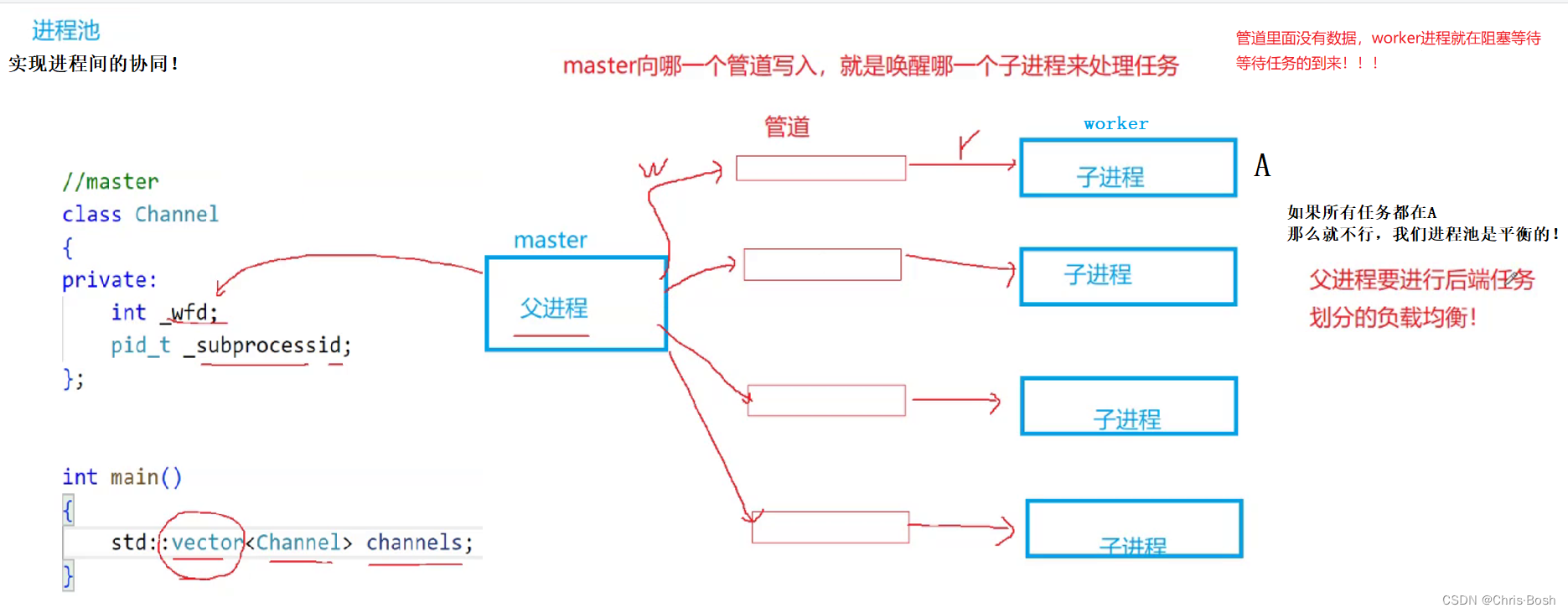
3.2 进程池的代码实现
Makefile:
processpool: ProcessPool.ccg++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11
.PHONY:clean
clean:rm -f processpool
Task.hpp:
#pragma once#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>#define TaskNum 3typedef void (*task_t)(); // task_t 函数指针类型void Print()
{std::cout << "I am print task" << std::endl;
}
void DownLoad()
{std::cout << "I am a download task" << std::endl;
}
void Flush()
{std::cout << "I am a flush task" << std::endl;
}task_t tasks[TaskNum];void LoadTask()
{srand(time(nullptr) ^ getpid() ^ 17777);tasks[0] = Print;tasks[1] = DownLoad;tasks[2] = Flush;
}void ExcuteTask(int number)
{if (number < 0 || number > 2)return;tasks[number]();
}int SelectTask()
{return rand() % TaskNum;
}
ProcessPool.cc:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include "Task.hpp"void work(int rfd){while (true){int command = 0;int n = read(rfd, &command, sizeof(command));if (n == sizeof(int)){std::cout << "pid is : " << getpid() << " handler task" << std::endl;ExcuteTask(command);}else if (n == 0){std::cout << "sub process : " << getpid() << " quit" << std::endl;break;}}}// master
class Channel
{
public:Channel(int wfd, pid_t id, const std::string &name): _wfd(wfd), _subprocessid(id), _name(name){}int GetWfd() { return _wfd; }pid_t GetProcessId() { return _subprocessid; }std::string GetName() { return _name; }void CloseChannel(){close(_wfd);}void Wait(){pid_t rid = waitpid(_subprocessid, nullptr, 0);if (rid > 0){std::cout << "wait " << rid << " success" << std::endl;}}~Channel(){}private:int _wfd;pid_t _subprocessid;std::string _name;
};// 形参类型和命名规范
// const &: 输出
// & : 输入输出型参数
// * : 输出型参数
// task_t task: 回调函数
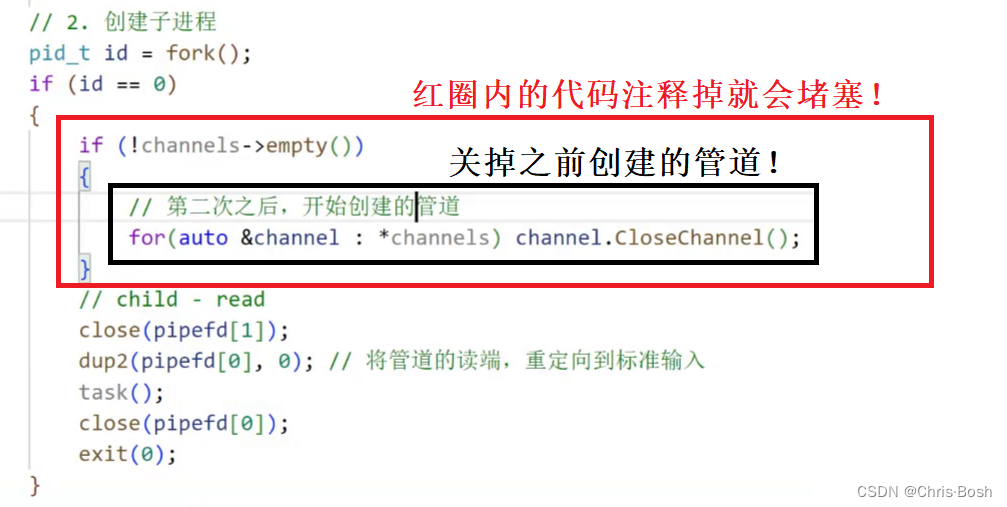
void CreateChannelAndSub(int num, std::vector<Channel> *channels)
{// BUG? --> fix bugfor (int i = 0; i < num; i++){// 1. 创建管道int pipefd[2] = {0};int n = pipe(pipefd);if (n < 0)exit(1);// 2. 创建子进程pid_t id = fork();if (id == 0){// child - readclose(pipefd[1]);work(pipefd[0]);close(pipefd[0]);exit(0);}// 3.构建一个channel名称std::string channel_name = "Channel-" + std::to_string(i);// 父进程close(pipefd[0]);// a. 子进程的pid b. 父进程关心的管道的w端channels->push_back(Channel(pipefd[1], id, channel_name));}
}// 0 1 2 3 4 channelnum
int NextChannel(int channelnum)
{static int next = 0;int channel = next;next++;next %= channelnum;return channel;
}void SendTaskCommand(Channel &channel, int taskcommand)
{write(channel.GetWfd(), &taskcommand, sizeof(taskcommand));
}void ctrlProcessOnce(std::vector<Channel> &channels)
{sleep(1);// a. 选择一个任务int taskcommand = SelectTask();// b. 选择一个信道和进程int channel_index = NextChannel(channels.size());// c. 发送任务SendTaskCommand(channels[channel_index], taskcommand);std::cout << std::endl;std::cout << "taskcommand: " << taskcommand << " channel: "<< channels[channel_index].GetName() << " sub process: " << channels[channel_index].GetProcessId() << std::endl;
}void ctrlProcess(std::vector<Channel> &channels, int times = -1)
{if (times > 0){while (times--){ctrlProcessOnce(channels);}}else{while (true){ctrlProcessOnce(channels);}}
}void CleanUpChannel(std::vector<Channel> &channels)
{for (auto &channel : channels){channel.CloseChannel();}// 注意for (auto &channel : channels){channel.Wait();}
}// ./processpool 5
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{if (argc != 2){std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " processnum" << std::endl;return 1;}int num = std::stoi(argv[1]);LoadTask();std::vector<Channel> channels;// 1. 创建信道和子进程CreateChannelAndSub(num, &channels);// 2. 通过channel控制子进程ctrlProcess(channels, 5);// 3. 回收管道和子进程. a. 关闭所有的写端 b. 回收子进程CleanUpChannel(channels);return 0;
}
运行结果:
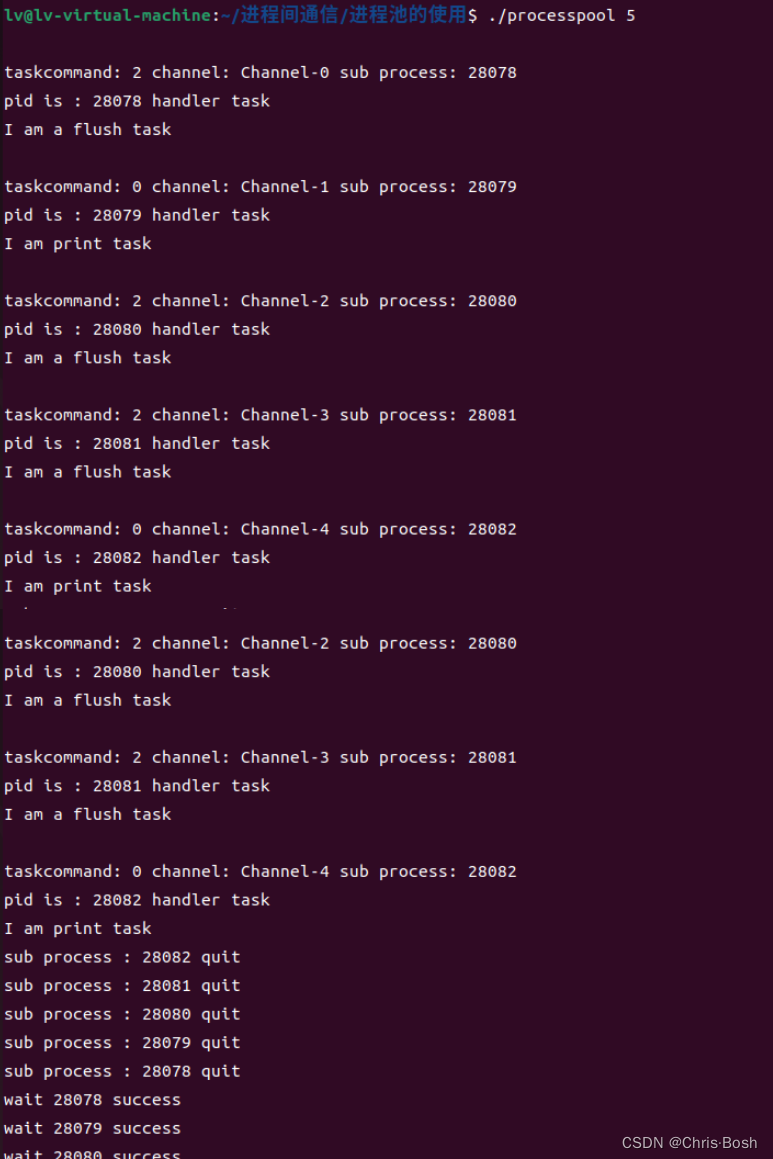
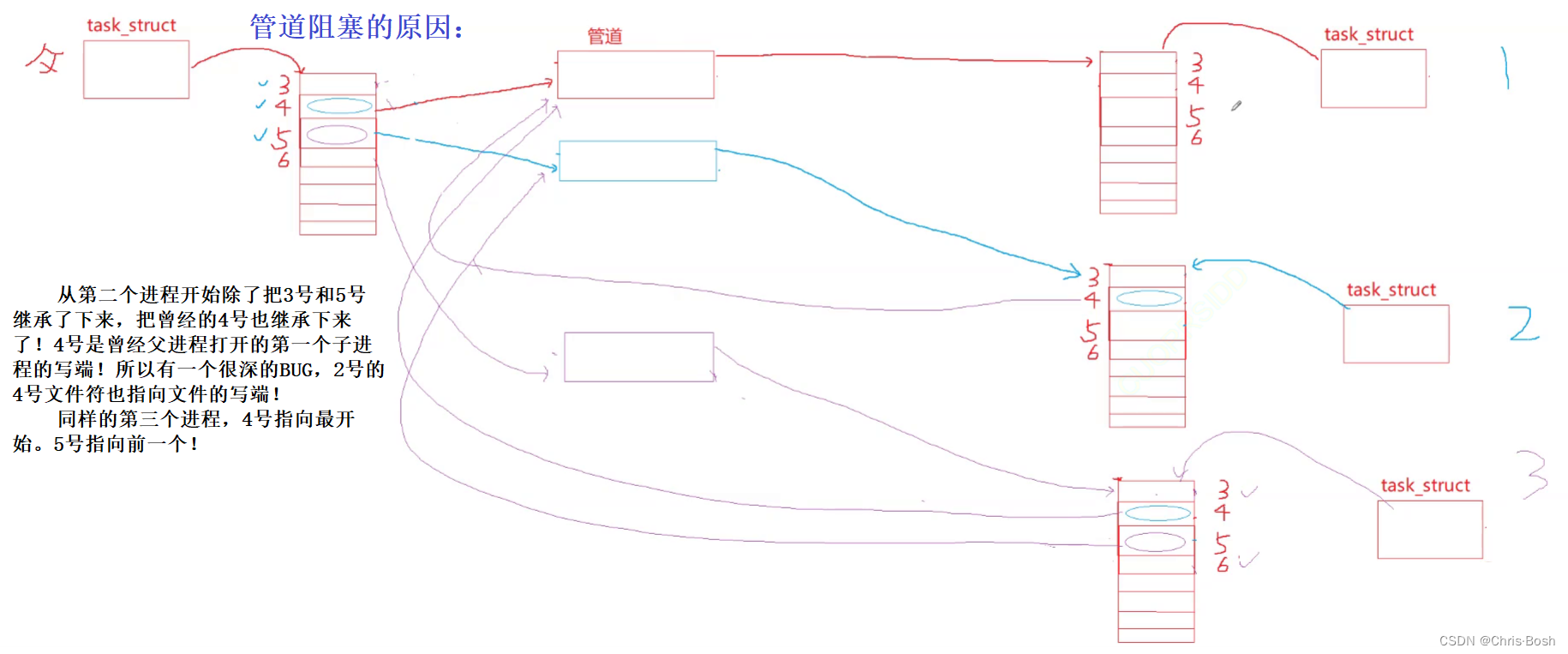
但是代码中void CreateChannelAndSub中有一个 BUG! 这个BUG会造成管道阻塞
那么要如何解决这个BUG呢?
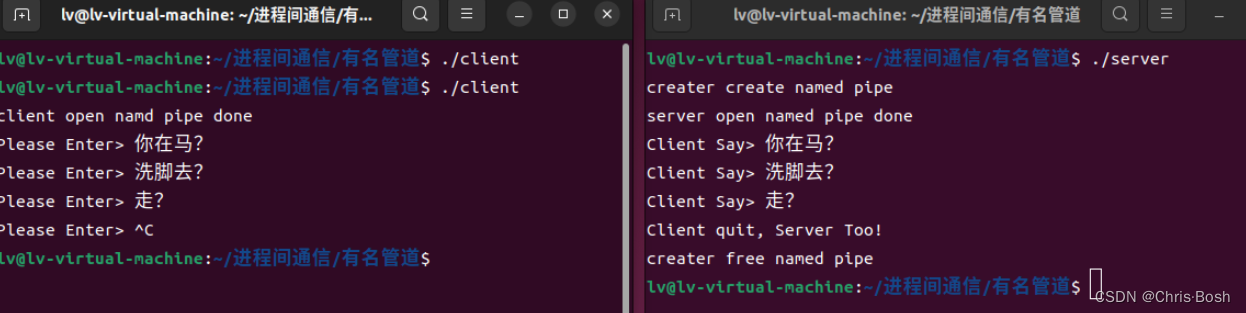
4.命名管道
4.1 有名管道通信
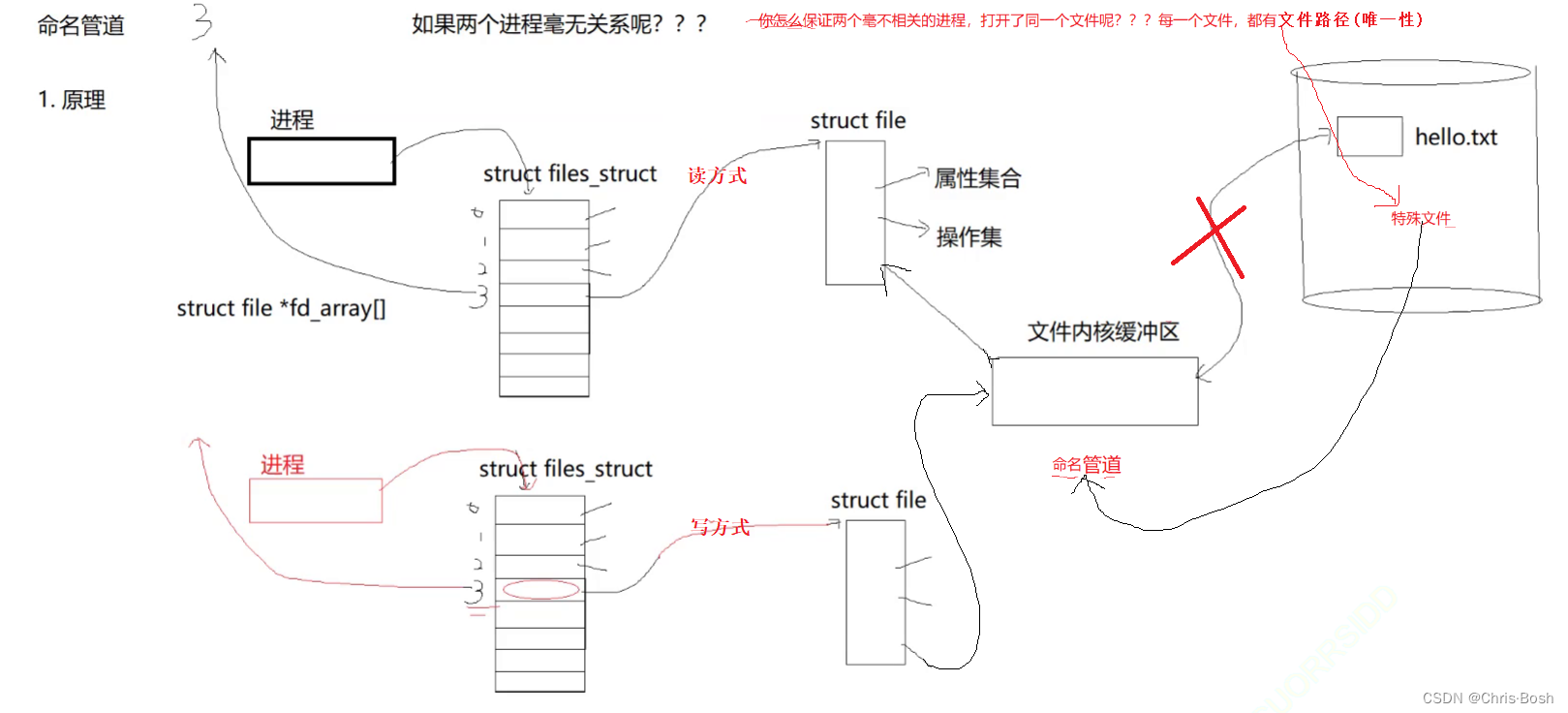
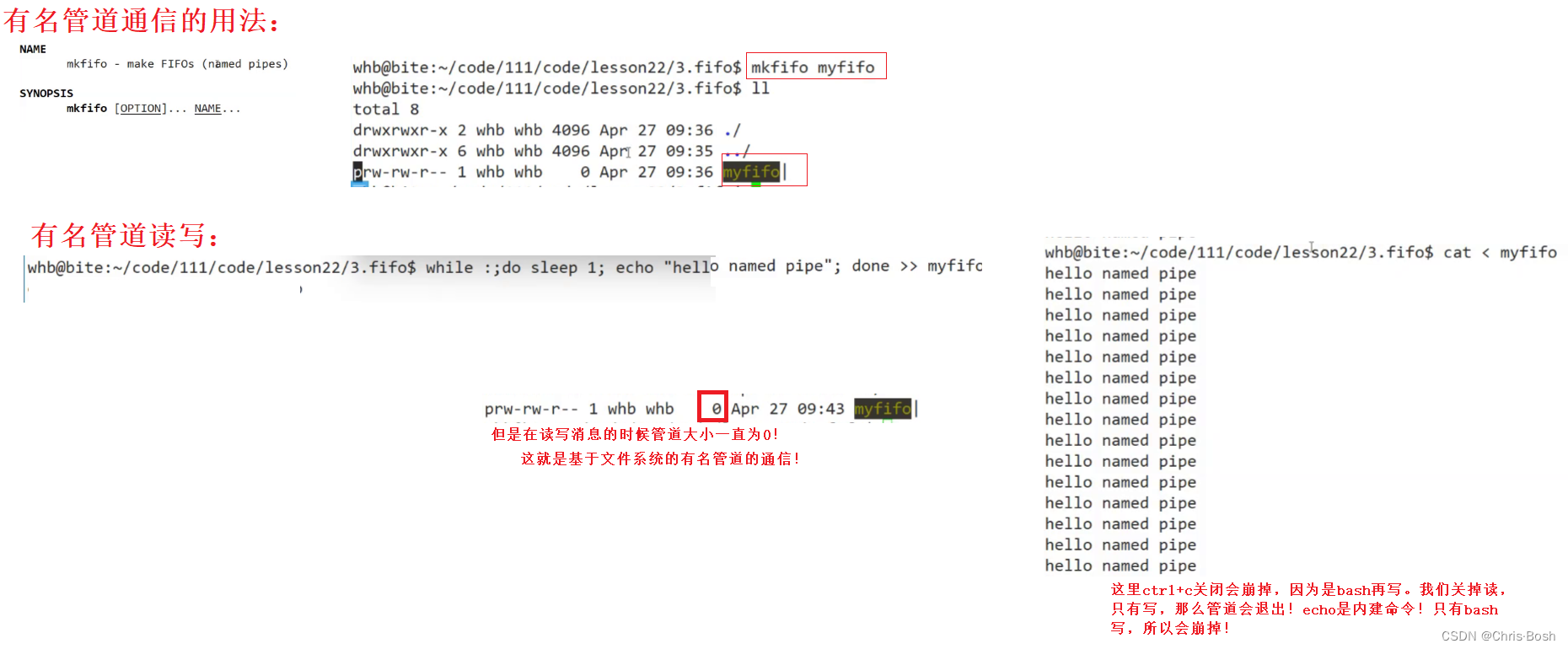
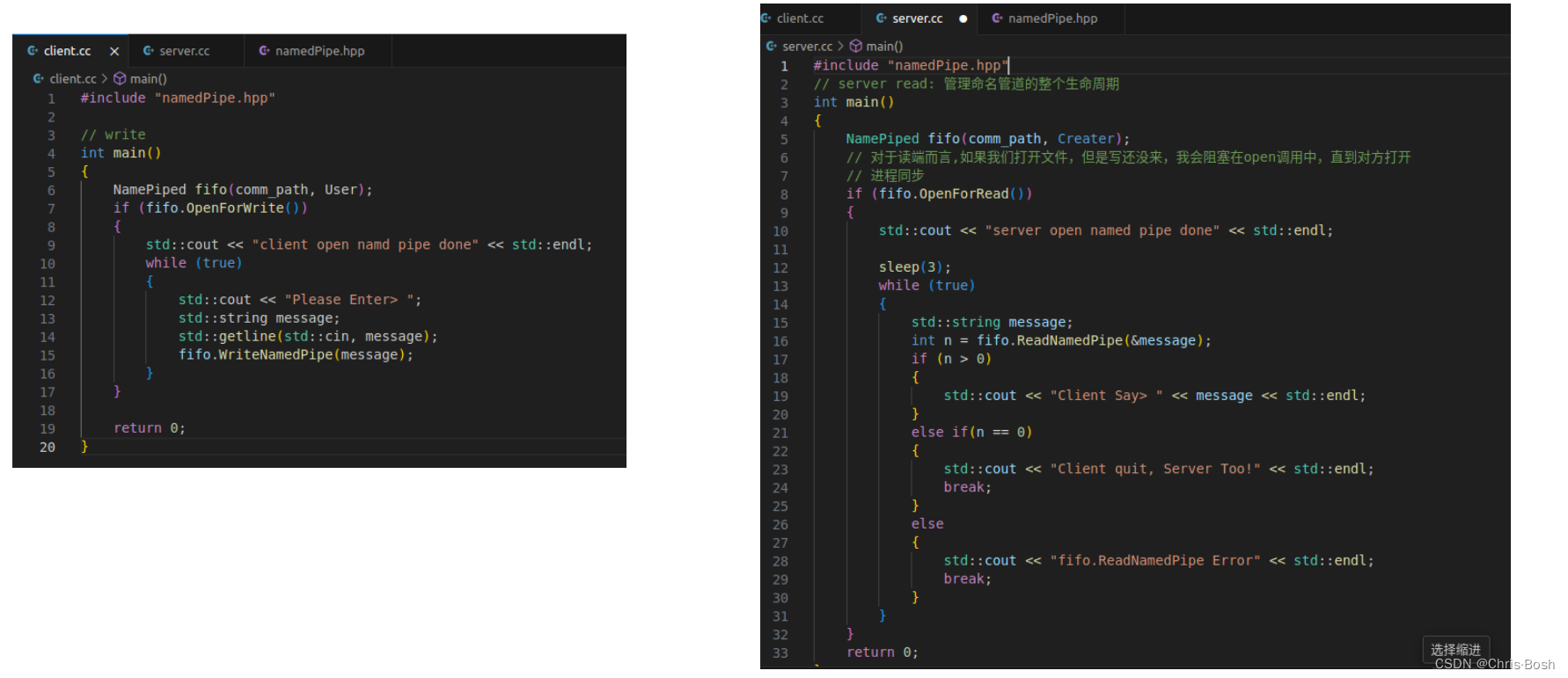
4.2 有名管道通信的代码实现
在代码实现之前有必要认识两个接口函数:

namedPipe.hpp:
#pragma once#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cerrno>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>const std::string comm_path = "./myfifo";
#define DefaultFd -1
#define Creater 1
#define User 2
#define Read O_RDONLY
#define Write O_WRONLY
#define BaseSize 4096class NamePiped
{
private:bool OpenNamedPipe(int mode){_fd = open(_fifo_path.c_str(), mode);if (_fd < 0)return false;return true;}public:NamePiped(const std::string &path, int who): _fifo_path(path), _id(who), _fd(DefaultFd){if (_id == Creater){int res = mkfifo(_fifo_path.c_str(), 0666);if (res != 0){perror("mkfifo");}std::cout << "creater create named pipe" << std::endl;}}bool OpenForRead(){return OpenNamedPipe(Read);}bool OpenForWrite(){return OpenNamedPipe(Write);}// const &: const std::string &XXX// * : std::string *// & : std::string & int ReadNamedPipe(std::string *out){char buffer[BaseSize];int n = read(_fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));if(n > 0){buffer[n] = 0;*out = buffer;}return n;}int WriteNamedPipe(const std::string &in){return write(_fd, in.c_str(), in.size());}~NamePiped(){if (_id == Creater){int res = unlink(_fifo_path.c_str());if (res != 0){perror("unlink");}std::cout << "creater free named pipe" << std::endl;}if(_fd != DefaultFd) close(_fd);}private:const std::string _fifo_path;int _id;int _fd;
};
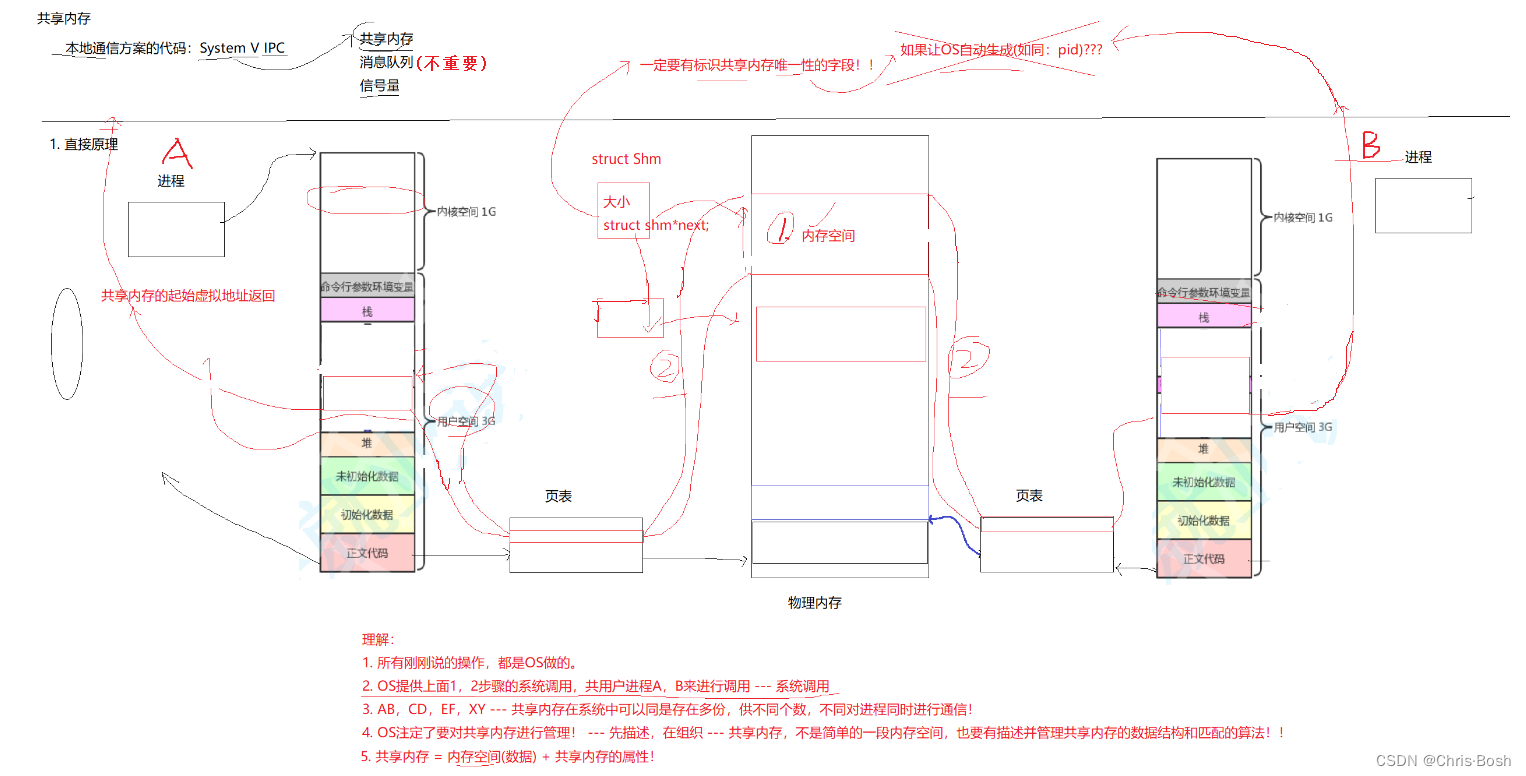
5.共享内存
5.1 共享内存原理
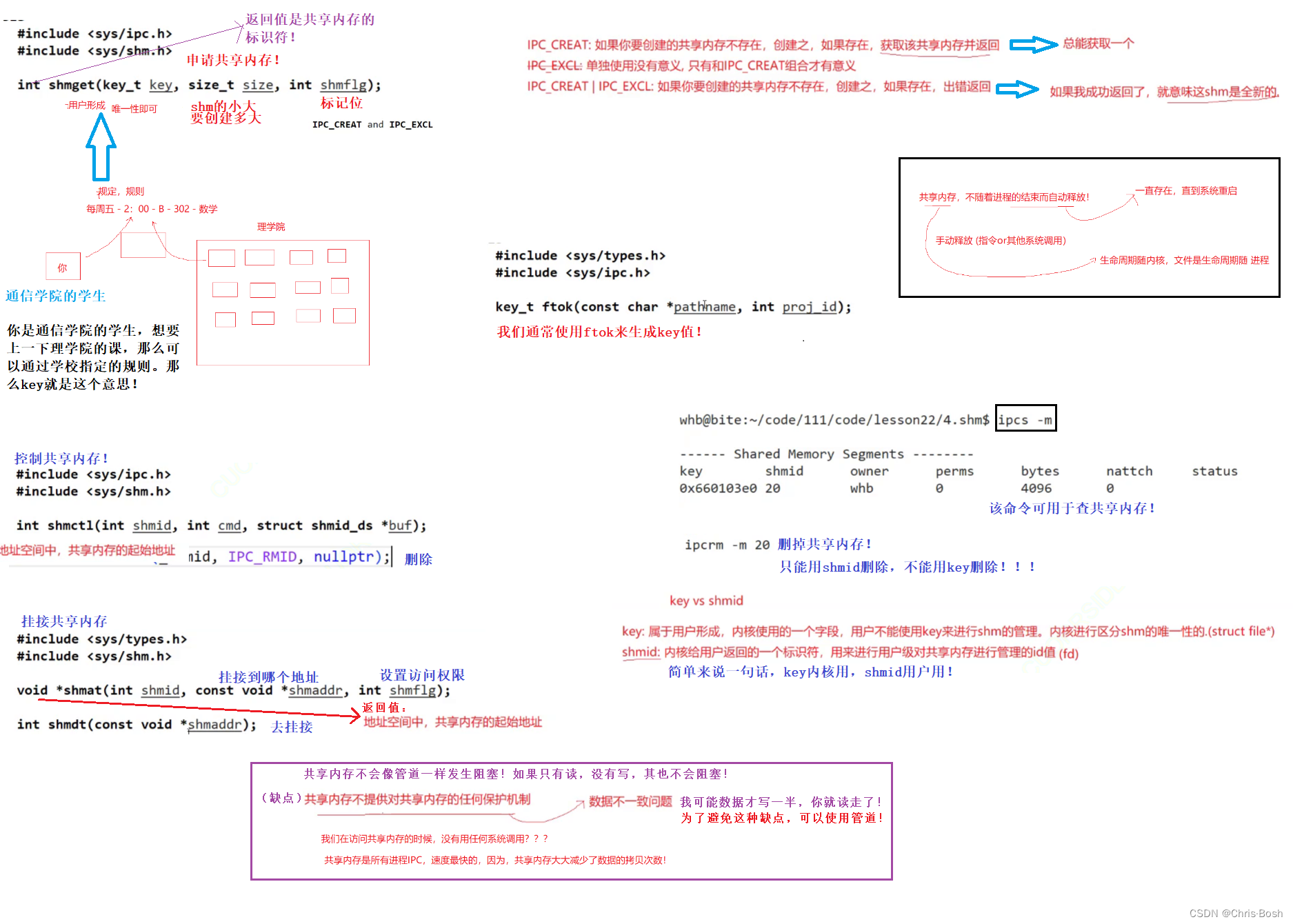
5.2 共享内存的代码实现
在代码实现之前,需要了解其的一些接口和指令用法:
其代码量庞大,这里便不在展示。
将在本文最后将代码打包!
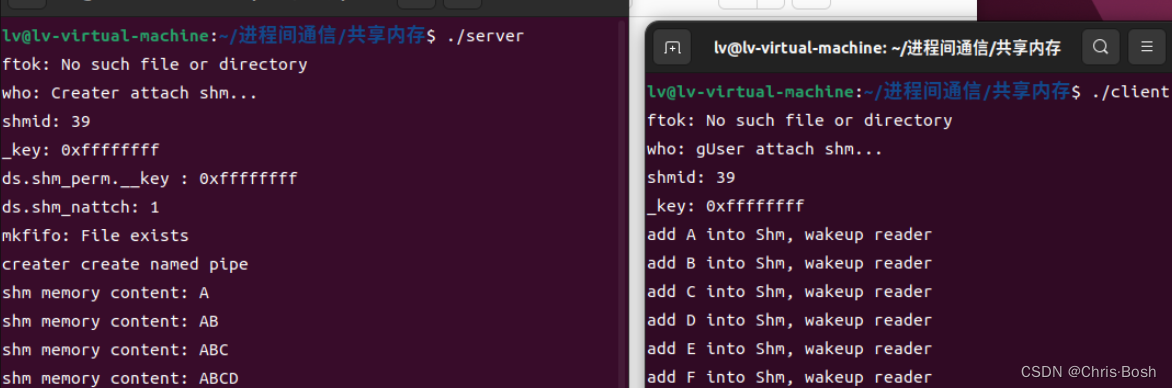
6.共享内存

7.代码
以上内容的代码在如下:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1my0GlYsC-h4phn5bX9BxqA
提取码:lyds