✨✨ 欢迎大家来到景天科技苑✨✨
🎈🎈 养成好习惯,先赞后看哦~🎈🎈
🏆 作者简介:景天科技苑
🏆《头衔》:大厂架构师,华为云开发者社区专家博主,阿里云开发者社区专家博主,CSDN全栈领域优质创作者,掘金优秀博主,51CTO博客专家等。
🏆《博客》:Python全栈,前后端开发,小程序开发,人工智能,js逆向,App逆向,网络系统安全,数据分析,Django,fastapi,flask等框架,linux,shell脚本等实操经验,网站搭建,数据库等分享。所属的专栏:微信小程序开发零基础教学,难点与应用实战总结
景天的主页:景天科技苑
文章目录
- flex布局
- 1.什么是Flex布局
- 2.flex布局的好处
- 3.flex布局中的概念
- 容器样式属性
- 1.flex-direction
- 有4个参数值(如下图)
- 强调
- 2.flex-wrap
- 3.flex-flow
- 4.justify-content
- 1.justify-content: flex-start(左对齐:默认值)
- 2.justify-content: flex-end;右对齐
- 3.justify-content: center; 居中
- 4.justify-content: space-between;两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等
- 5.justify-content: space-around;每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍
- 6.justify-content: space-evenly;项目与项目之间,项目与边框之间的间隔都相等
- 5.align-items
- 1.align-items:flex-start;交叉轴的起点对齐
- 2.align-items:flex-end;交叉轴的终点对齐
- 3.align-items:center;交叉轴的中点对齐
- 4.align-items:baseline;项目的第一行文字的基线对齐
- 5.align-items:stretch;(默认值)如果项目未设置高度或设为 auto,将占满整个容器的高度
- 6.align-content属性
- 1.flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐
- 2.flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐
- 3.center:与交叉轴的中点对齐
- 4.space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布
- 5.space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等
- 6.stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴
- 项目样式属性
- 1.order属性
- 2.flex-grow属性
- 1.均匀分布
- 2.中间占两倍,两边一样大
- 3.flex-shrink属性
- 1.等比例缩小
- 2.为0的情况
- 4.flex-basis属性
- 5.flex属性
- 6.align-self属性
flex布局
flex 是一种布局方式,跟微信小程序没有必然联系
以下几种页面方式都可以使用flex布局
- web前端
- 微信小程序
- uniapp
1.什么是Flex布局
-
布局的传统解决方案,基于盒状模型,依赖 display 属性 + position 属性 + float 属性。它对于那些特殊布局非常不方便,比如,垂直居中就不容易实现
-
Flex 是 Flexible Box 或 flexbox 的缩写,意为"弹性布局",用来为盒状模型提供最大的灵活性
-
任何一个容器都可以指定为 Flex 布局。
.box{ display: flex;
}
- 行内元素也可以使用 Flex 布局。
.box{ display: inline-flex;
}
2.flex布局的好处
- 简单易懂:与传统的布局方式相比,Flex布局的语法和理解起来更加简单,容易上手。
- 弹性和自适应:Flex布局能够自动适应不同尺寸的屏幕,让页面更具有弹性。
- 等高布局:Flex布局可以方便地实现多列等高布局。
- 对齐和排序:Flex布局支持各种对齐方式,包括水平和垂直对齐,并且可以通过设置order属性对子元素进行排序。
- 可以与传统布局结合使用:Flex布局并不是完全取代传统的布局方式,它可以与传统布局方式结合使用,实现更灵活的布局效果
3.flex布局中的概念
-
采用 Flex 布局的元素,称为 Flex 容器(flex container),简称"容器"。它的所有子元素自动成为容器成员,称为 Flex 项目(flex item),简称"项目"
- 容器和项目:container、item
-
容器默认存在两根轴:水平的主轴(main axis)和垂直的交叉轴(cross axis)
- 主轴和交叉轴:main axis、cross axis
-
主轴的开始位置(与边框的交叉点)叫做main start,结束位置叫做main end;交叉轴的开始位置叫做cross start,结束位置叫做cross end。
- 起始位置:
main start 主轴起始位置
cross start 侧轴起始位置 - 结束位置:
main end 主轴结束位置
cross start 侧轴结束位置
- 起始位置:
-
项目默认沿主轴排列。单个项目占据的主轴空间叫做main size,占据的交叉轴空间叫做cross size
- 主轴尺寸
- 侧轴尺寸
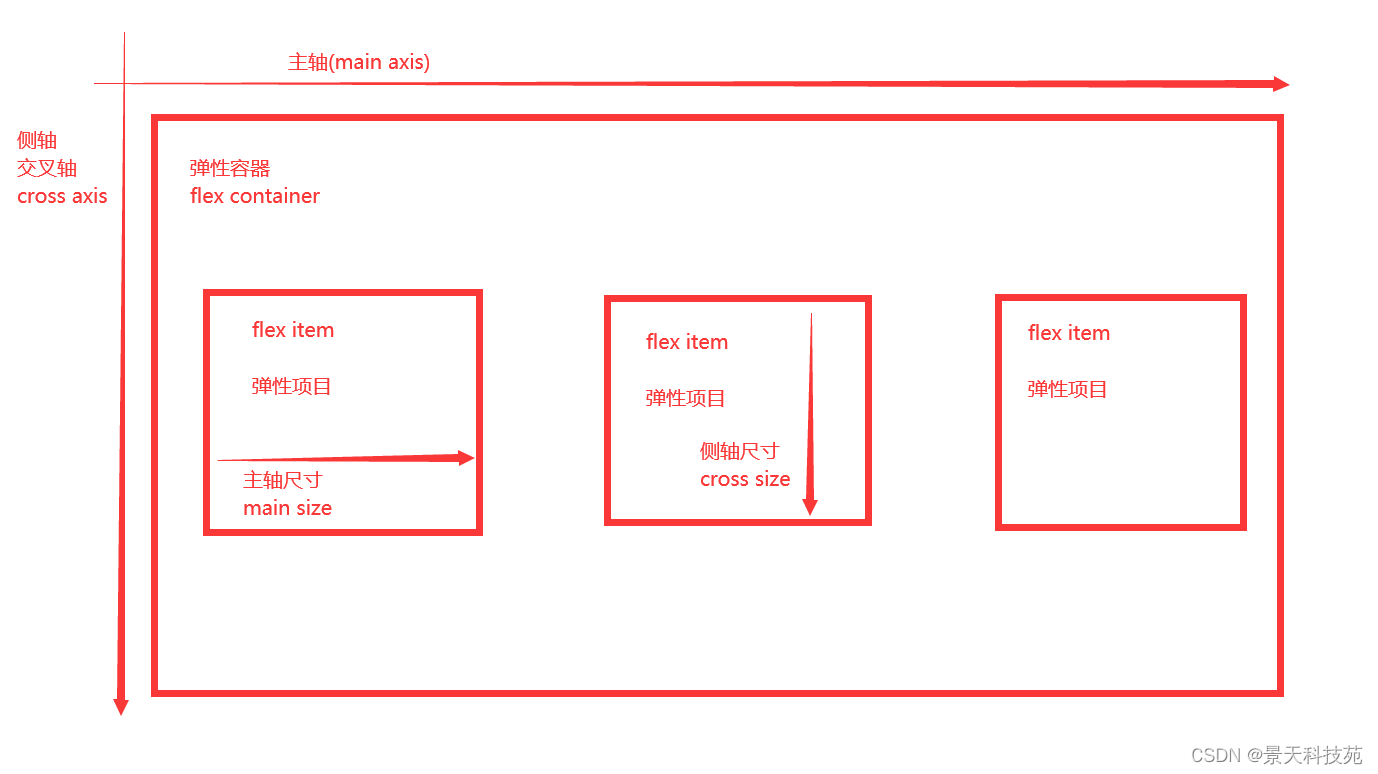
容器样式属性
- flex-direction:决定主轴的方向。
- flex-wrap:如果一条轴线排不下,如何换行。
- flex-flow:flex-direction 属性和 flex-wrap 属性的简写属性。
- justify-content:定义项目在主轴上的对齐方式。
- align-items:定义项目在交叉轴上如何对齐。
- align-content:定义了多根轴线的对齐方式。如果项目只有一根轴线,该属性不起作用。
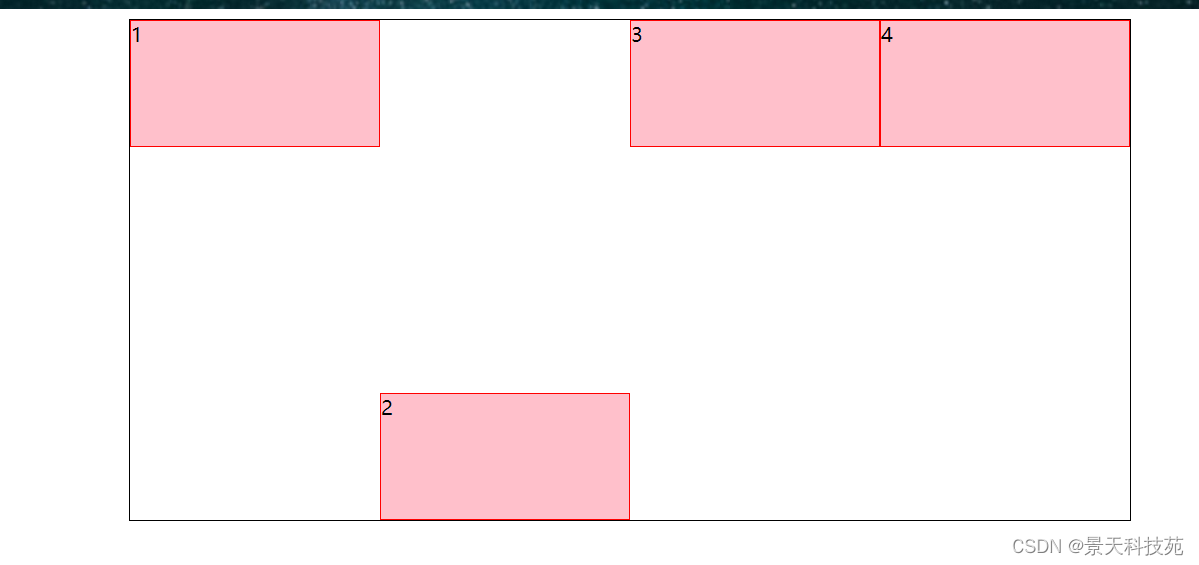
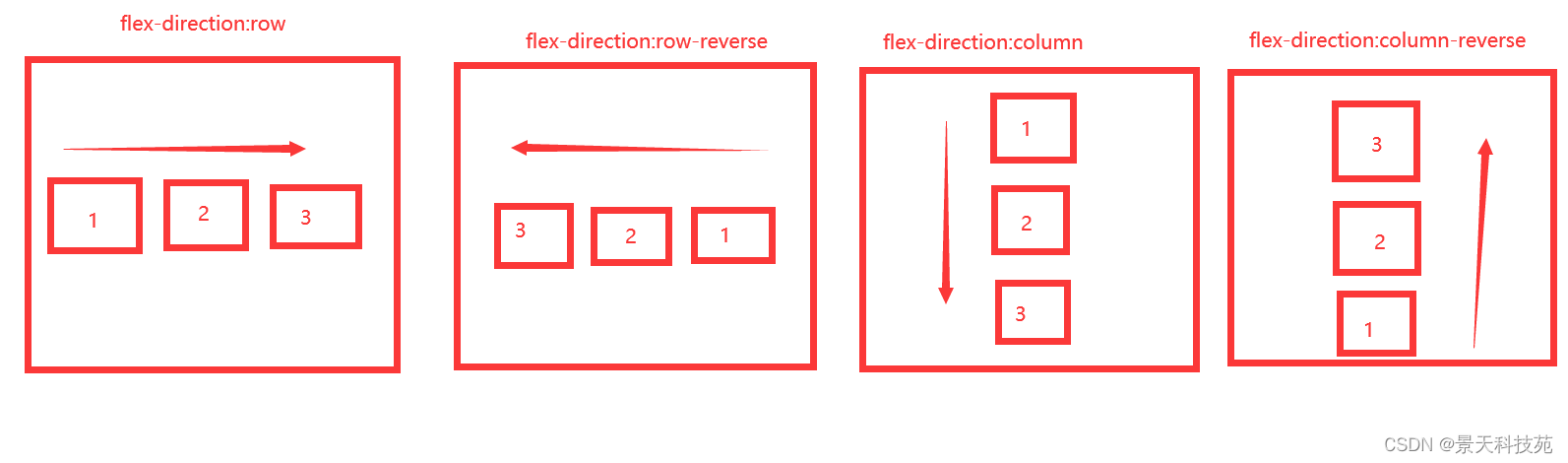
1.flex-direction
- flex-direction属性决定主轴的方向(即项目的排列方向)
有4个参数值(如下图)
- row(默认值):主轴为水平方向,起点在左端。
- row-reverse:主轴为水平方向,起点在右端。
- column:主轴为垂直方向,起点在上沿。
- column-reverse:主轴为垂直方向,起点在下沿。
强调
使用 flex-direction属性后,因为主轴的位置发生了改变,使用和主轴或交叉轴有关的属性之前一定要确定好主轴的位置
代码展示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用flex弹性布局,把这个容器设置为flex布局 */display: flex;/* row(默认值):主轴为水平方向,起点在左端。 */flex-direction: row; /* row-reverse column column-reverse */}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div></div>
</body>
</html>
效果
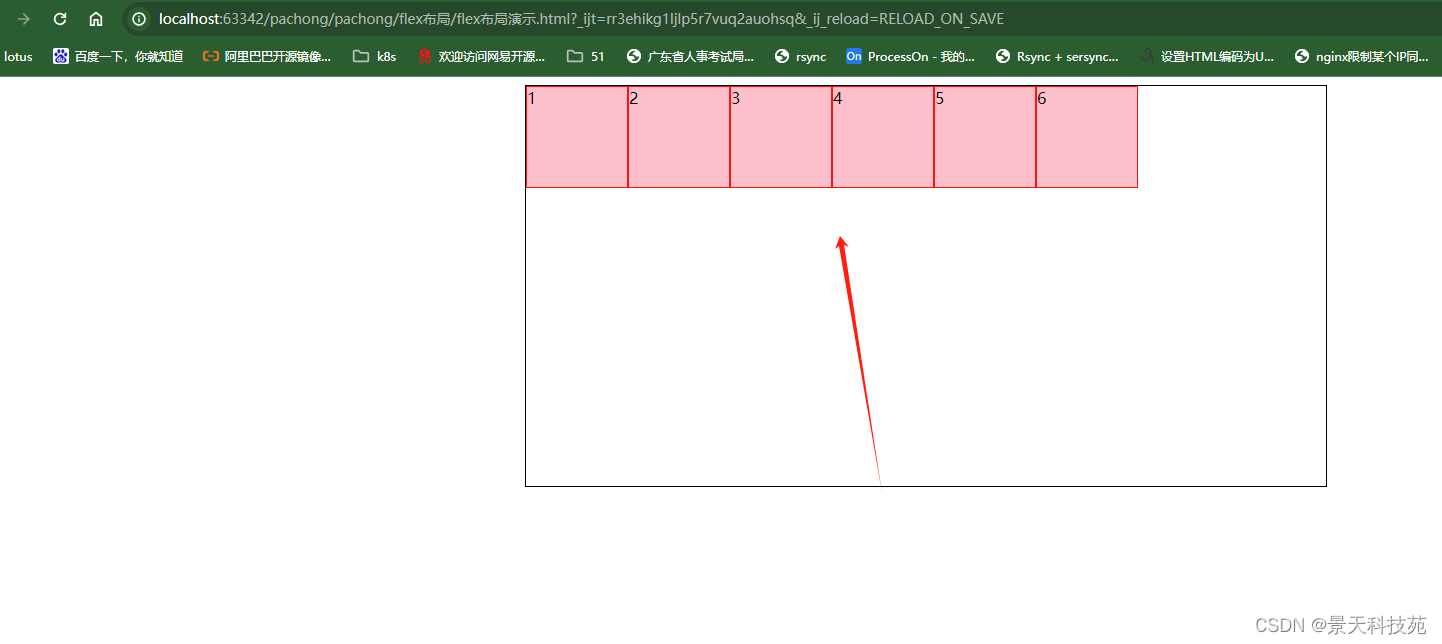
2.flex-wrap
-
默认情况下,项目都排在一条线(又称"轴线")上。flex-wrap属性定义,如果一条轴线排不下,如何换行。
-
flex-wrap 属性规定flex容器是单行或者多行,同时横轴的方向决定了新行堆叠的方向 默认不换行
-
有3个参数值 flex-wrap: nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse;
- nowrap 不换行
- wrap 换行,第一行在上方
- wrap-reverse 换行,第一行在下方
代码展示
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box{width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto;/* 把这个容器设置为flex布局*/display: flex;flex-direction: row; /* row row-reverse column column-reverse *//* */flex-wrap: wrap-reverse; /*nowrap | wrap | wrap-reverse;*/}.box>div{width: 100px;height: 100px;background: pink;border: 1px solid red;}</style></head>
<body><div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div><div>7</div><div>8</div><div>9</div><div>10</div><div>11</div></div></body>
</html>
效果
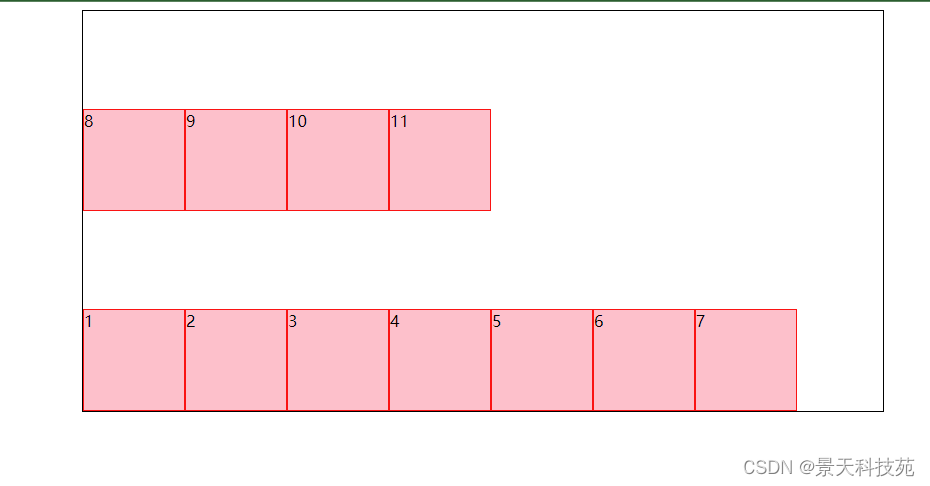
3.flex-flow
- flex-flow属性是flex-direction属性和flex-wrap属性的简写形式,默认值为row nowrap。
.box { flex-flow: flex-direction || flex-wrap;
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;/*flex-flow: row nowrap;*/flex-flow: column wrap;/*flex-flow: row nowrap;*/}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div><div>7</div><div>8</div><div>9</div></div>
</body>
</html>
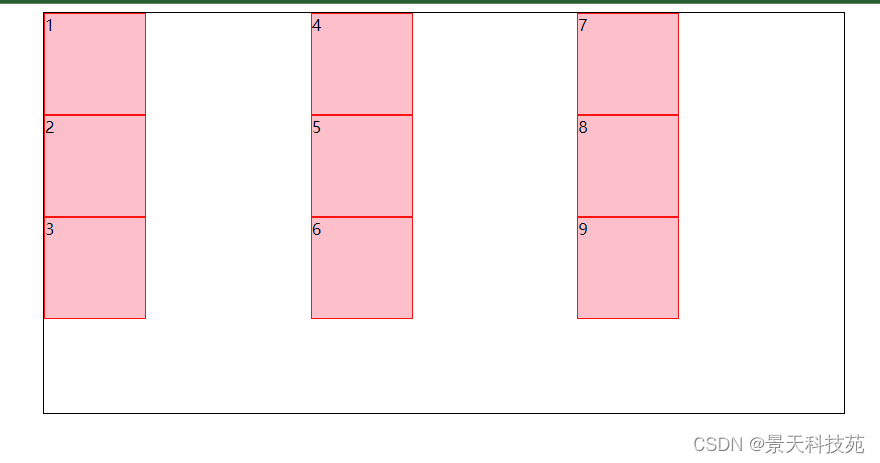
4.justify-content
- justify-content属性定义了项目在主轴上的对齐方式
- 有6个参数值,具体对齐方式与轴的方向有关。下面假设主轴为从左到右
justify-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | space-evenly;- flex-start(默认值):左对齐
- flex-end:右对齐
- center: 居中
- space-between:两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等。
- space-around:每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍。
- space-evenly:项目与项目之间,项目与边框之间的间隔都相等
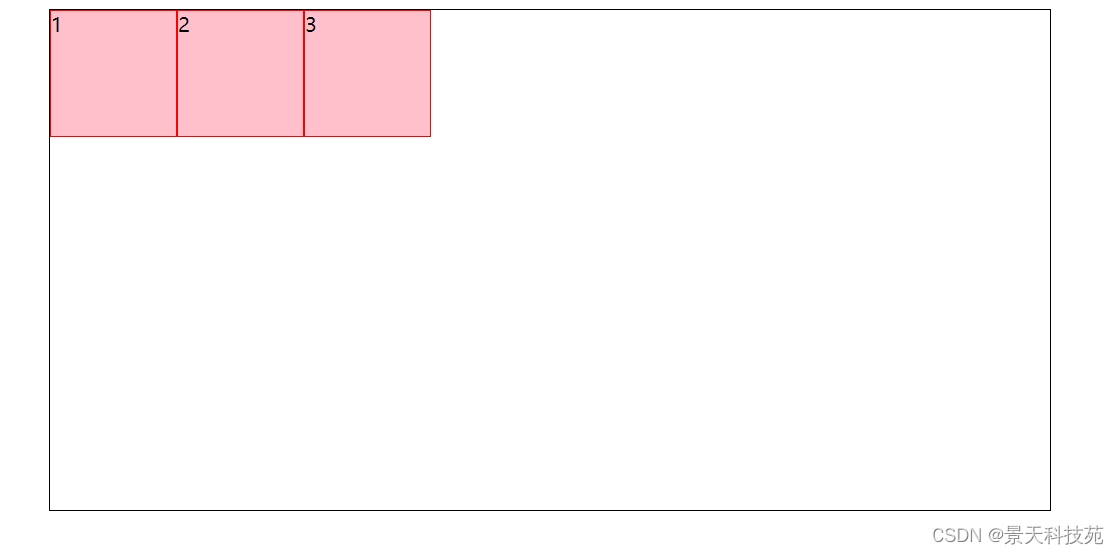
1.justify-content: flex-start(左对齐:默认值)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row wrap;justify-content: flex-start}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div>
</body>
</html>

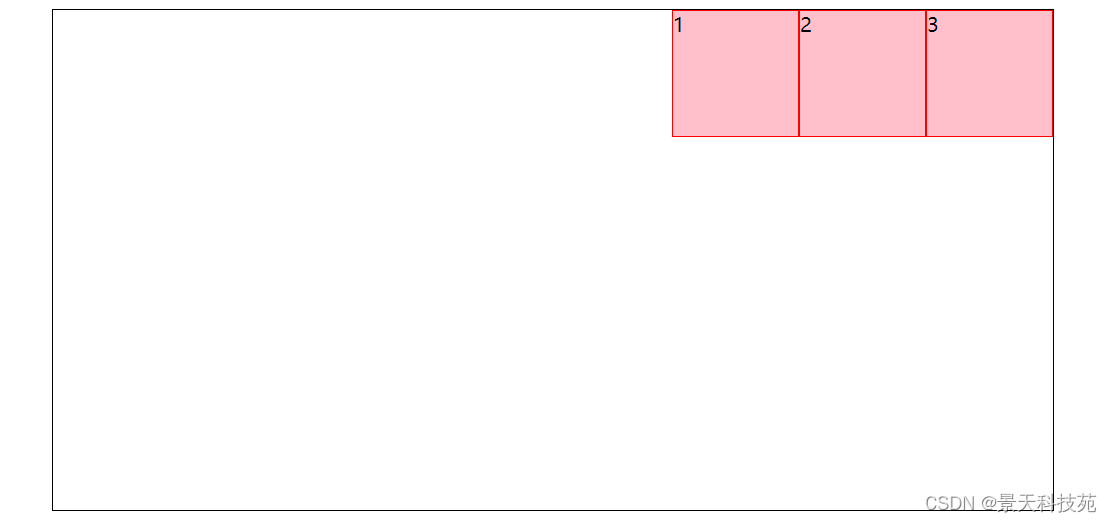
2.justify-content: flex-end;右对齐

3.justify-content: center; 居中

4.justify-content: space-between;两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等
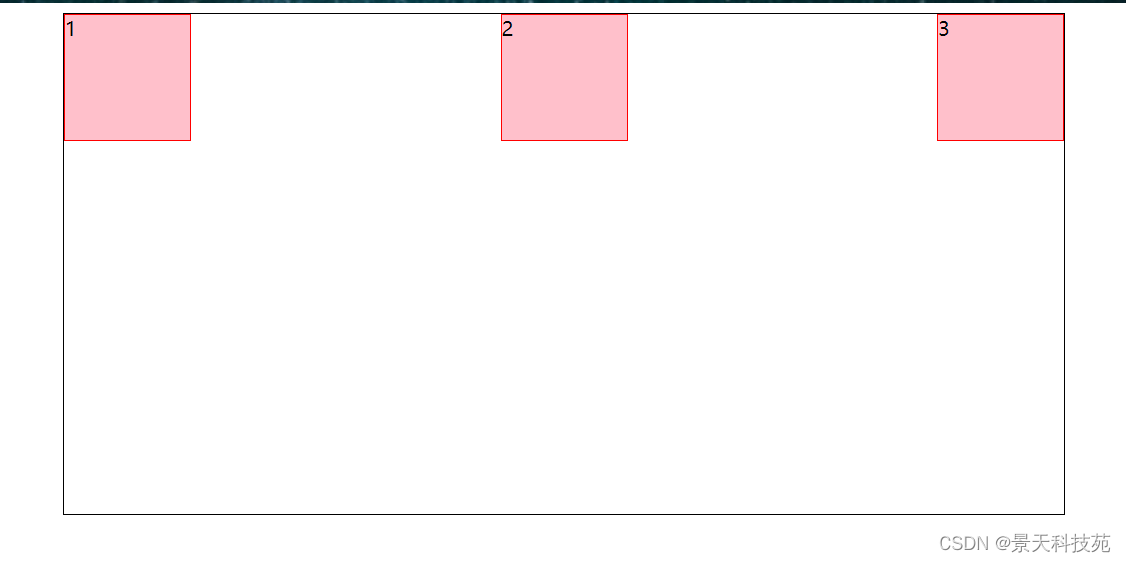
5.justify-content: space-around;每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍

6.justify-content: space-evenly;项目与项目之间,项目与边框之间的间隔都相等
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row wrap;justify-content: flex-start;/* 左对齐 */justify-content: flex-end;/* 右对齐 */justify-content: center;/* 居中 */justify-content: space-between;/* 两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等 */justify-content: space-around;/*每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍*/justify-content: space-evenly;/*项目与项目之间,项目与边框之间的间隔都相等*/}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div>
</body>
</html>
5.align-items
- align-items属性定义项目在交叉轴上如何对齐。
- align-items: flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch 5个值
- flex-start:交叉轴的起点对齐。
- flex-end:交叉轴的终点对齐。
- center:交叉轴的中点对齐。
- baseline:项目的第一行文字的基线对齐。
- stretch(默认值):如果项目未设置高度或设为 auto,将占满整个容器的高度
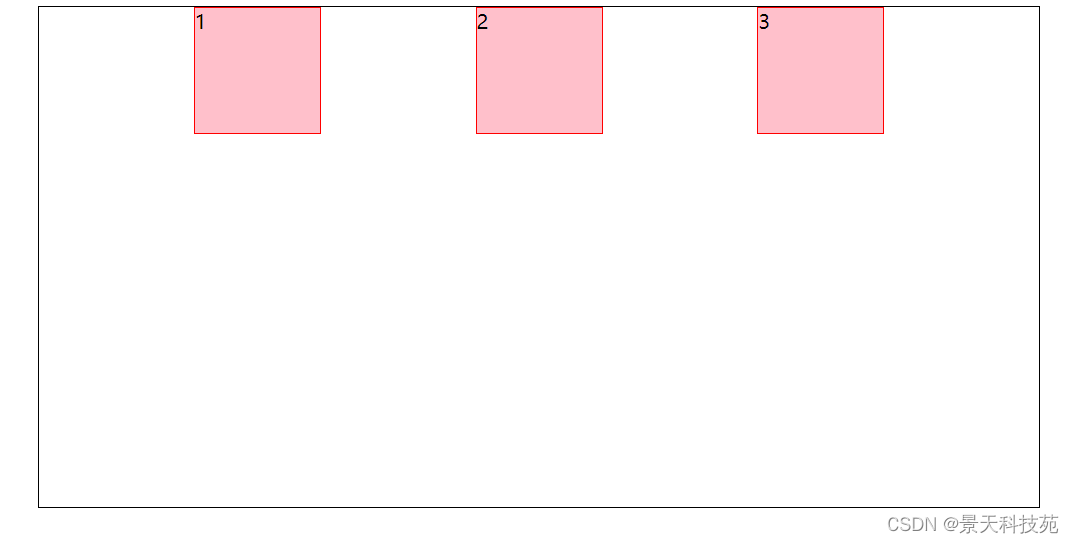
1.align-items:flex-start;交叉轴的起点对齐
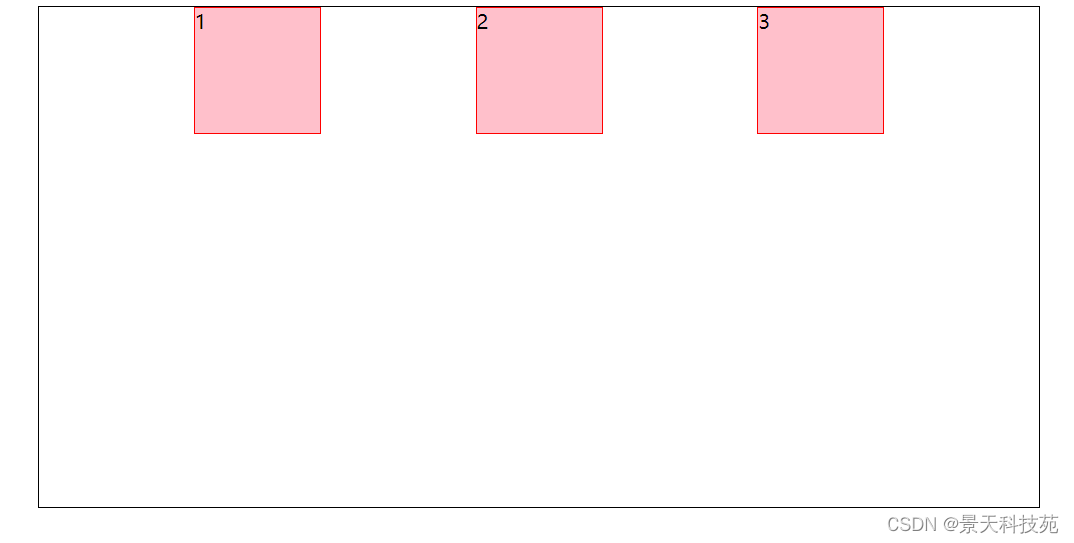
2.align-items:flex-end;交叉轴的终点对齐
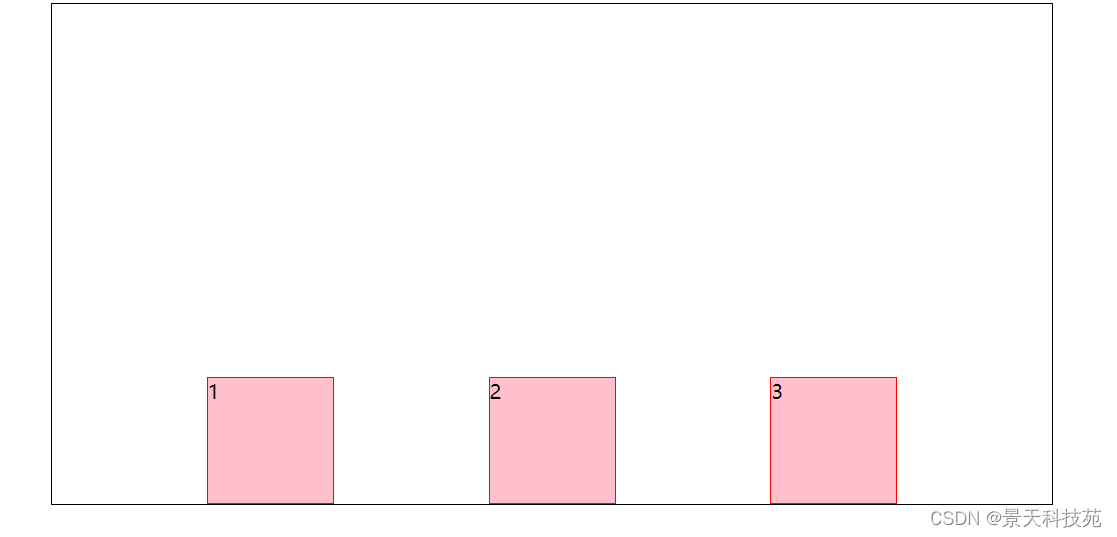
3.align-items:center;交叉轴的中点对齐
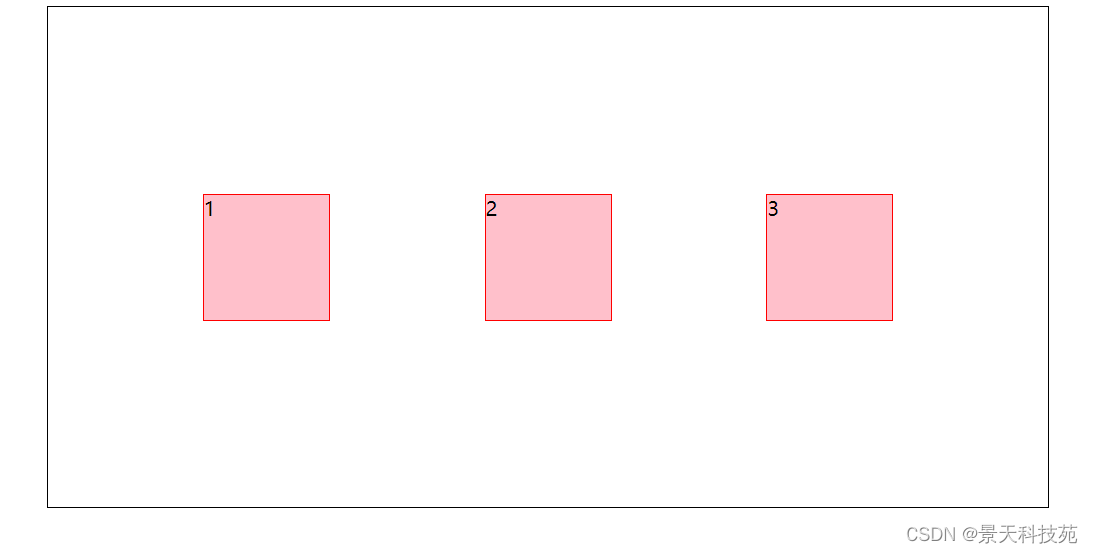
4.align-items:baseline;项目的第一行文字的基线对齐
<style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row wrap;justify-content: flex-start; /* 左对齐 */justify-content: flex-end; /* 右对齐 */justify-content: center; /* 居中 */justify-content: space-between; /* 两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等 */justify-content: space-around; /*每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍*/justify-content: space-evenly; /*项目与项目之间,项目与边框之间的间隔都相等*/align-items: flex-start; /*交叉轴的起点对齐*/align-items: flex-end; /*交叉轴的终点对齐*/align-items: center; /*交叉轴的中点对齐*/align-items: baseline; /*项目的第一行文字的基线对齐*/}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}.box div:nth-child(1) {padding-top: 10px;}.box div:nth-child(2) {padding-top: 15px;}.box div:nth-child(4) {padding-top: 20px;}</style><div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div></div>
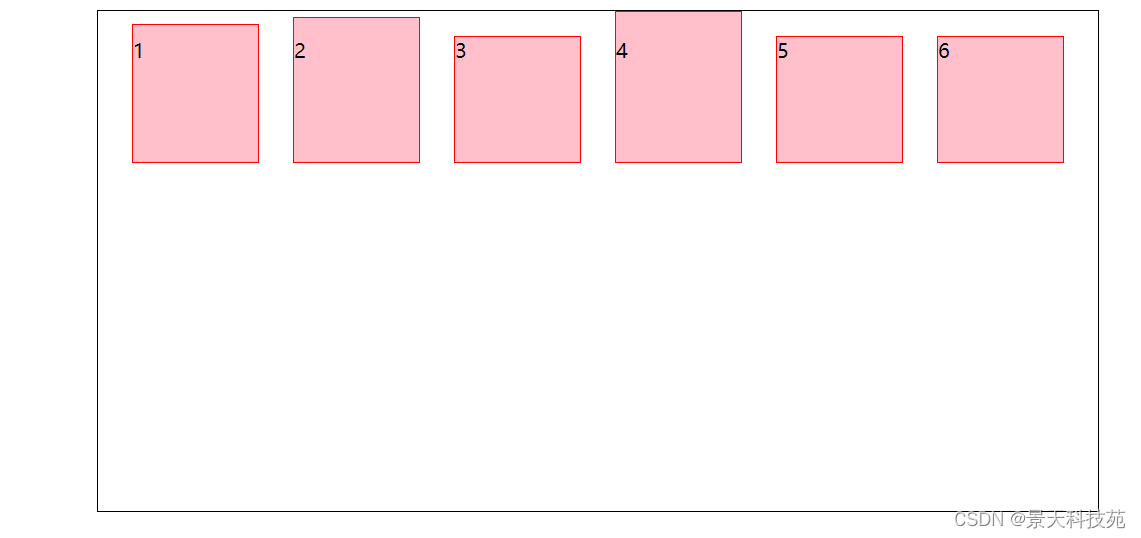
5.align-items:stretch;(默认值)如果项目未设置高度或设为 auto,将占满整个容器的高度
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row wrap;justify-content: flex-start; /* 左对齐 */justify-content: flex-end; /* 右对齐 */justify-content: center; /* 居中 */justify-content: space-between; /* 两端对齐,项目之间的间隔都相等 */justify-content: space-around; /*每个项目两侧的间隔相等。所以,项目之间的间隔比项目与边框的间隔大一倍*/justify-content: space-evenly; /*项目与项目之间,项目与边框之间的间隔都相等*/align-items: flex-start; /*交叉轴的起点对齐*/align-items: flex-end; /*交叉轴的终点对齐*/align-items: center; /*交叉轴的中点对齐*/align-items: baseline; /*项目的第一行文字的基线对齐*/align-items: stretch;; /*默认值)如果项目未设置高度或设为 auto,将占满整个容器的高度*/}.box div {width: 100px;/*height: 100px;*/background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}.box div:nth-child(1) {padding-top: 10px;}.box div:nth-child(2) {padding-top: 15px;}.box div:nth-child(4) {padding-top: 20px;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div></div>
</body>
</html>
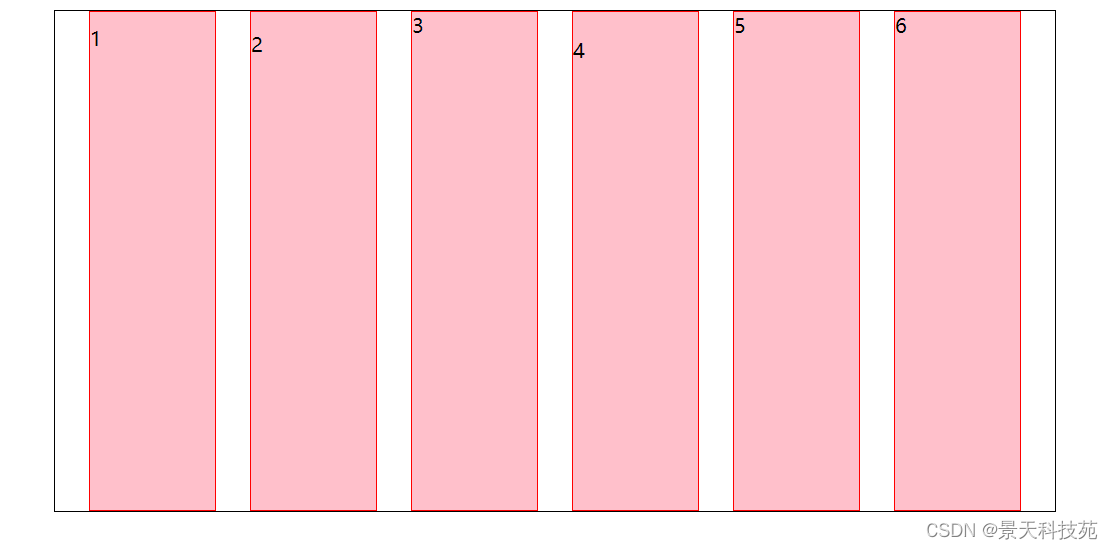
6.align-content属性
-
align-content属性定义了多根轴线的对齐方式。如果项目只有一根轴线,该属性不起作用。
- 必须允许项目换行【flex-wrap: wrap】,使用align-content属性的前提,否则align-content属性不生效
-
align-content: flex-start | flex-end | center | space-between | space-around | stretch; 6个值
flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐。
flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐。
center:与交叉轴的中点对齐。
space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。
space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。
stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。 -
align-content的属性值和前面的都一样, 只需要注意在使用align-content的属性之前一定要加上 flex-wrap: wrap;属性
1.flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐
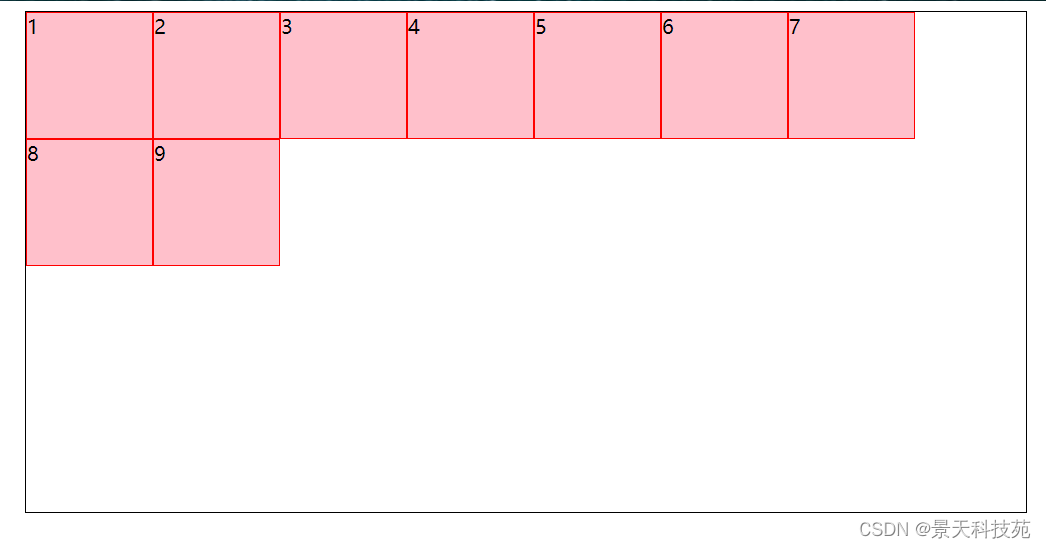
2.flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐
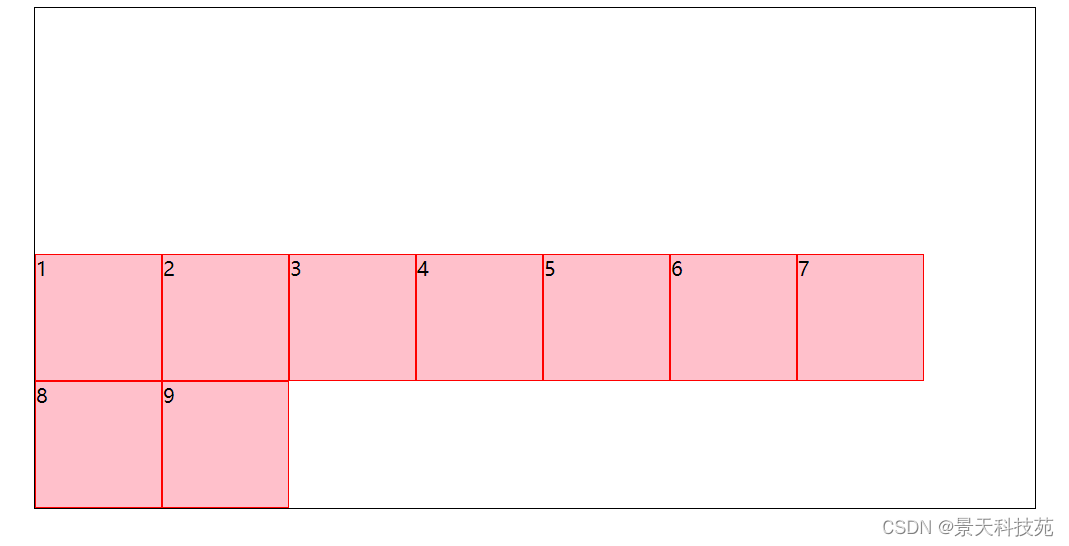
3.center:与交叉轴的中点对齐
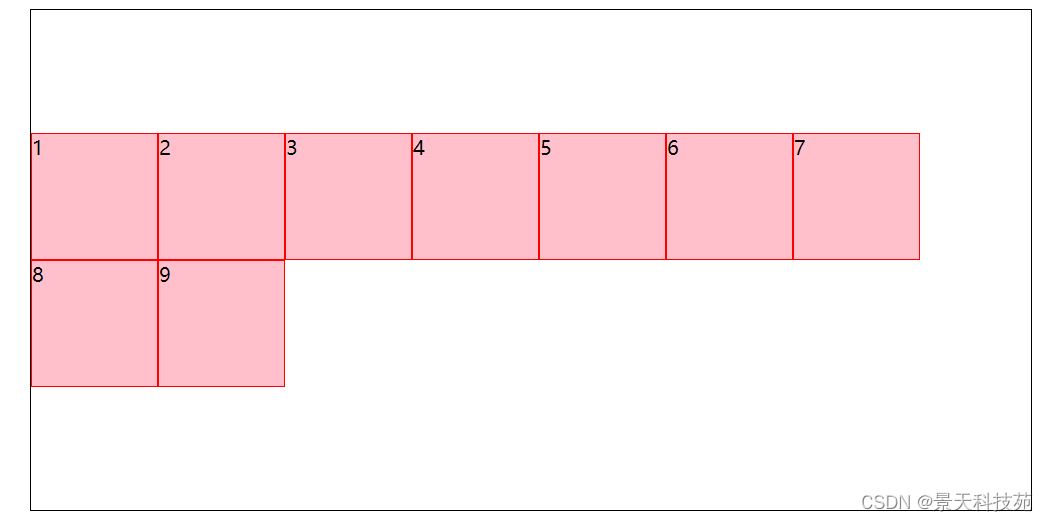
4.space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布
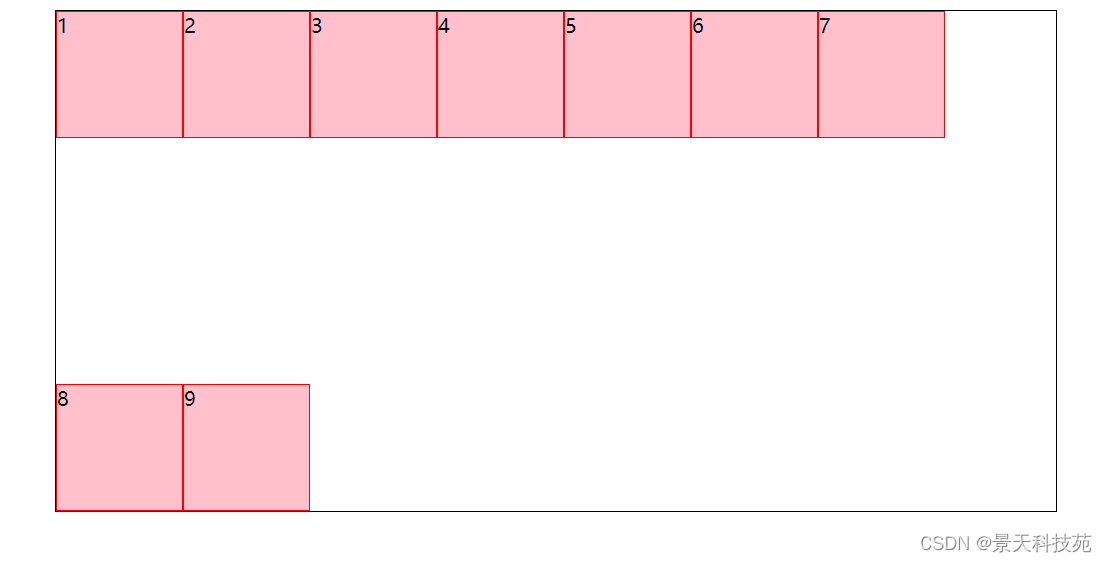
5.space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等
所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍

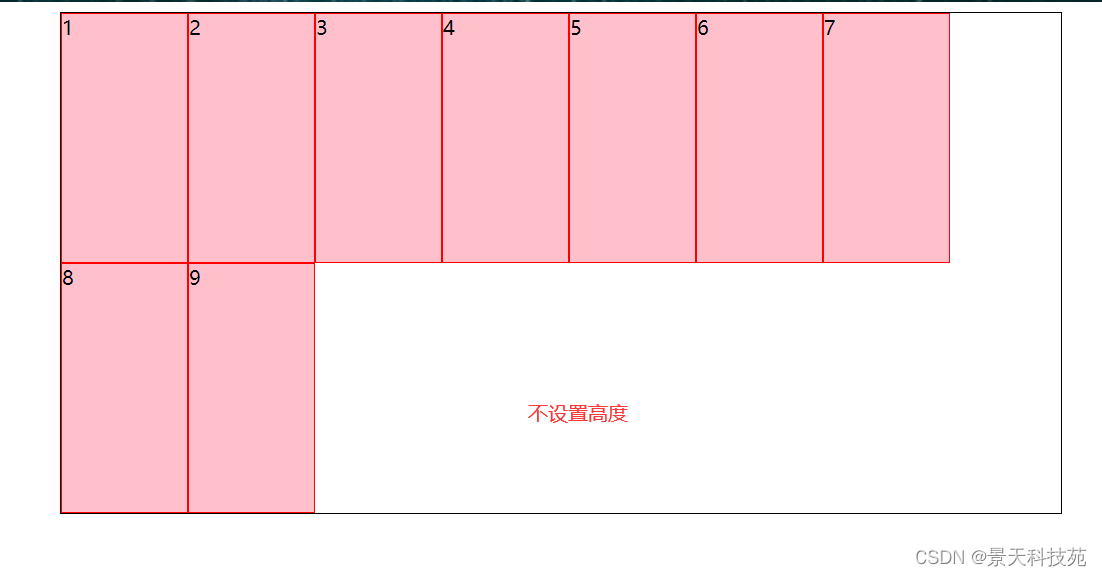
6.stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row wrap;/* flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐。 */align-content: flex-start;/* flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐。 */align-content: flex-end;/* center:与交叉轴的中点对齐。 */align-content: center;/* space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。 */align-content: space-between;/* space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。 */align-content: space-around;/* stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。 */align-content: stretch;}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px; /*align-content: stretch 不设置高度*/background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div><div>7</div><div>8</div><div>9</div></div>
</body>
</html>
项目样式属性
- 以下6个属性设置在项目上。
-
order:定义项目的排列顺序。数值越小,排列越靠前,默认为 0
-
flex-grow:定义项目的放大比例,默认为 0,即如果存在剩余空间,也不放大
-
flex-shrink:定义了项目的缩小比例,默认为 1,即如果空间不足,该项目将缩小
-
flex-basis:定义了在分配多余空间之前,项目占据的主轴空间(main size)。它的默认值为 auto,即项目的本来大小
-
flex: flex-grow 、 flex-shrink 和 flex-basis 的简写,默认值为 0 1 auto 。后两个属性可选
-
align-self:允许单个项目有与其他项目不一样的对齐方式,可覆盖 align-items 属性。默认值为 auto
-
1.order属性
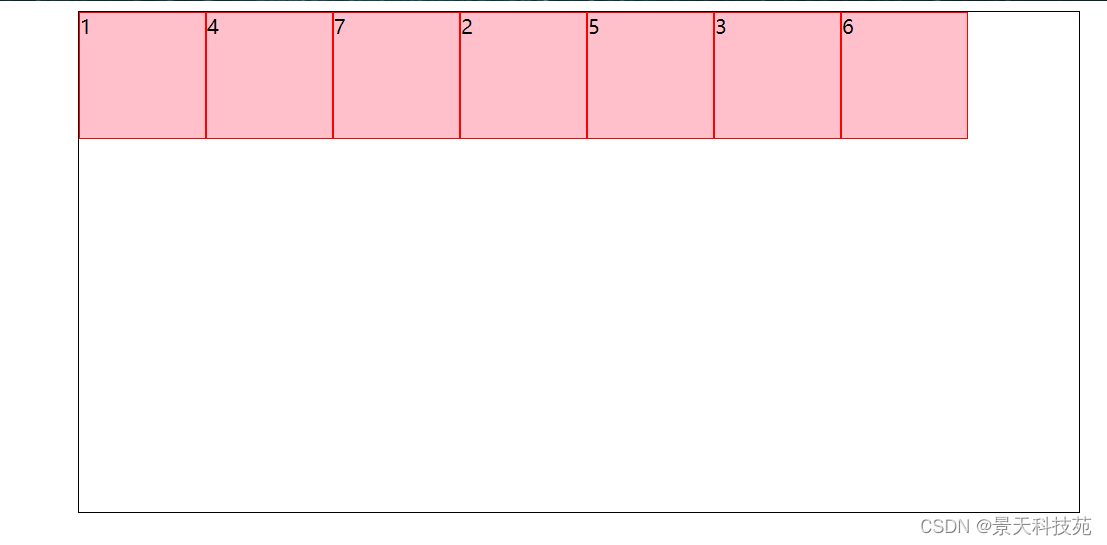
- order属性定义项目的排列顺序。数值越小,排列越靠前,默认为0。
- 使用方式:item { order: integer;}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row wrap;/* flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐。 */align-content: flex-start;/* flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐。 */align-content: flex-end;/* center:与交叉轴的中点对齐。 */align-content: center;/* space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。 */align-content: space-between;/* space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。 */align-content: space-around;/* stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。 */align-content: stretch;}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px; /*align-content: stretch 不设置高度*/background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}.box div:nth-child(1){order: -1;}.box div:nth-child(2){order: 2;}.box div:nth-child(3){order: 4;}.box div:nth-child(4){order: 0;}.box div:nth-child(5){order: 3;}.box div:nth-child(6){order: 7;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div><div>5</div><div>6</div><div>7</div></div>
</body>
</html>

2.flex-grow属性
- flex-grow属性定义项目的放大比例,默认为0,即如果存在剩余空间,也不放大
- item { flex-grow: number; /* default 0 */}
- 如果所有项目的flex-grow属性都为1,则它们将等分剩余空间(如果有的话)。如果一个项目的flex-grow属性为2,其他项目都为1,则前者占据的剩余空间将比其他项多一倍
1.均匀分布
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row wrap;/* flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐。 */align-content: flex-start;/* flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐。 */align-content: flex-end;/* center:与交叉轴的中点对齐。 */align-content: center;/* space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。 */align-content: space-between;/* space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。 */align-content: space-around;/* stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。 */align-content: stretch;}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px; /*align-content: stretch 不设置高度*/background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}.box div:nth-child(1) {flex-grow: 1;}.box div:nth-child(2) {flex-grow: 1;}.box div:nth-child(3) {flex-grow: 1;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div>
</body>
</html>
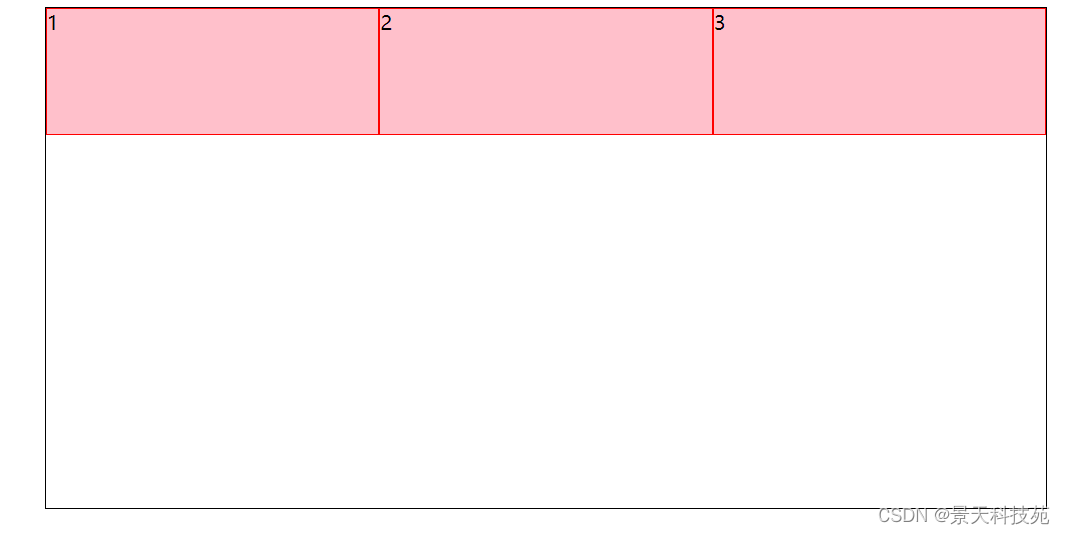
2.中间占两倍,两边一样大
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row wrap;/* flex-start:与交叉轴的起点对齐。 */align-content: flex-start;/* flex-end:与交叉轴的终点对齐。 */align-content: flex-end;/* center:与交叉轴的中点对齐。 */align-content: center;/* space-between:与交叉轴两端对齐,轴线之间的间隔平均分布。 */align-content: space-between;/* space-around:每根轴线两侧的间隔都相等。所以,轴线之间的间隔比轴线与边框的间隔大一倍。 */align-content: space-around;/* stretch(默认值):轴线占满整个交叉轴。 */align-content: stretch;}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px; /*align-content: stretch 不设置高度*/background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}.box div:nth-child(1){flex-grow: 1;}.box div:nth-child(2){flex-grow: 2;}.box div:nth-child(3){flex-grow: 1;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div></div>
</body>
</html>

3.flex-shrink属性
- flex-shrink属性定义了项目的缩小比例,默认为1,即如果空间不足,该项目将缩小
- .item { flex-shrink: number; /* default 1 */}
- 如果所有项目的flex-shrink属性都为1,当空间不足时,都将等比例缩小。如果一个项目的flex-shrink属性为0,其他项目都为1,则空间不足时,前者不缩小
- 负值对该属性无效
1.等比例缩小
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row nowrap;}.box div {width: 400px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}.box div:nth-child(1) {flex-shrink: 1;}.box div:nth-child(2) {flex-shrink: 1;}.box div:nth-child(3) {flex-shrink: 1;}.box div:nth-child(4) {flex-shrink: 1;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div></div>
</body>
</html>

2.为0的情况
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row nowrap;}.box div {width: 400px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}.box div:nth-child(1) {flex-shrink: 1;}.box div:nth-child(2) {flex-shrink: 0;}.box div:nth-child(3) {flex-shrink: 1;}.box div:nth-child(4) {flex-shrink: 1;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div></div>
</body>
</html>

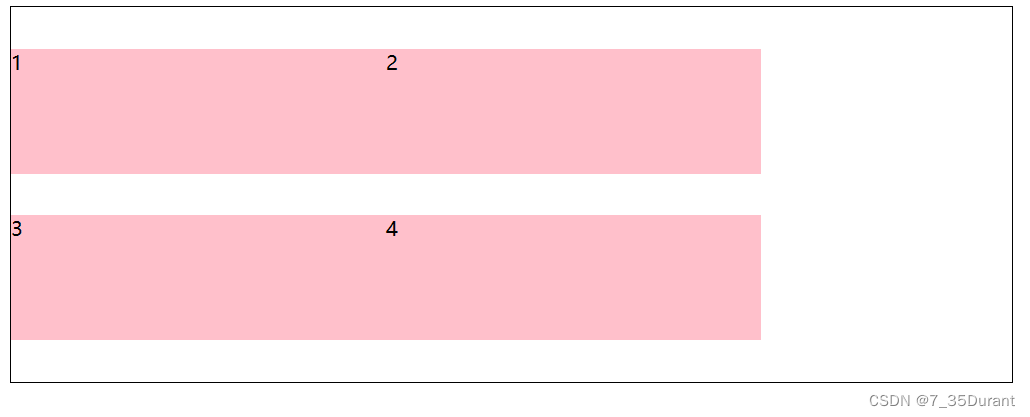
4.flex-basis属性
- flex-basis属性定义了在分配多余空间之前,项目占据的主轴空间(main size)。浏览器根据这个属性,计算主轴是否有多余空间。它的默认值为auto,即项目的本来大小
- .item { flex-basis: length | auto; /* default auto */}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row nowrap;}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;}.box div:nth-child(2) {/* 将项目2的宽度设为200px */flex-basis: 200px;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div></div>
</body>
</html>

5.flex属性
-
flex属性是flex-grow, flex-shrink 和 flex-basis的简写,默认值为 0 1 auto。后两个属性可选。
-
.item { flex: none | [ <‘flex-grow’> <‘flex-shrink’>? || <‘flex-basis’> ]}
-
该属性有两个快捷值:auto (1 1 auto) 和 none (0 0 auto)。
-
建议优先使用这个属性,而不是单独写三个分离的属性,因为浏览器会推算相关值。
-
一般情况下flex属性用于将项目平均占满空间
.box div {/* 使所有项目平均占满空间 */flex: 1;
}

6.align-self属性
- align-self属性允许单个项目有与其他项目不一样的对齐方式,可覆盖align-items属性。默认值为auto,表示继承父元素的align-items属性,如果没有父元素,则等同于stretch
- .item { align-self: auto | flex-start | flex-end | center | baseline | stretch;}
- 该属性可能取6个值,除了auto,其他都与align-items属性完全一致
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>Title</title><style>.box {width: 800px;height: 400px;border: 1px solid black;margin: auto; /* box 居中*//* 使用弹性布局 */display: flex;flex-flow: row nowrap;}.box div {width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: pink;border: 1px solid red;flex: 1;}.box div:nth-child(2) {/* 使第二个项目在交叉轴上终点对齐 */align-self: flex-end;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box"><div>1</div><div>2</div><div>3</div><div>4</div></div>
</body>
</html>