前言
Interface Class是在SystemVerilog 2012版本中引入的,但目前在验证中几乎很少采用,大多数验证工程师要么不知道它,要么没有看到使用它的任何好处,这使得Interface Class成为一个未被充分使用和不被重视的特性。本文将举两个Interface Class的使用例子,在这些例子中,Interface Class提高了验证环境的灵活性和质量,同时进一步提高了其可维护性和可调试性。
示例1:观察者设计模式
Interface Class用于观察者设计模式(Observer Design pattern)。观察者模式允许你定义一种订阅机制, 可在对象事件发生时通知多个 “观察” 该对象的其他对象。例如验证环境中monitor需要采集interface上的信息,将其组合成某种transaction数据结构,并将其发送给感兴趣的各方组件,例如scoreboard和checker。在这里,monitor也称作publisher,scoreboard和checker称作subscriber或listener。如下图所示。
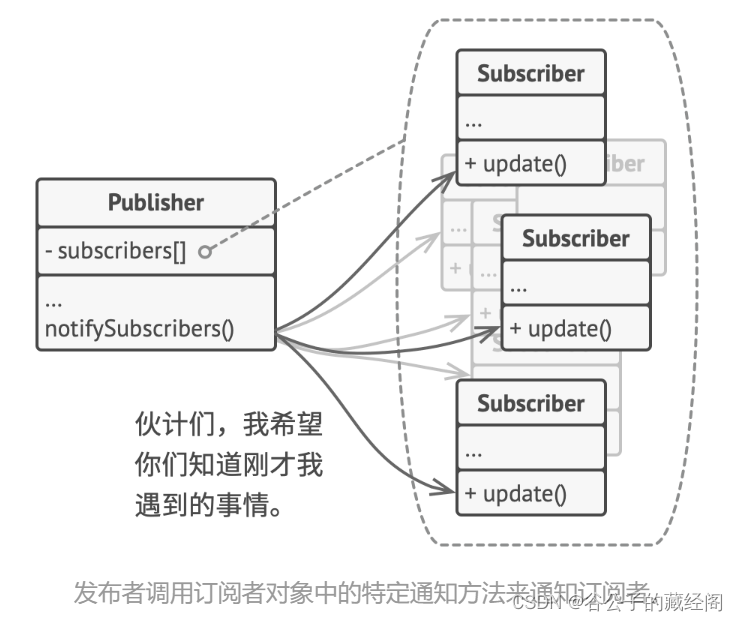
图1 观察者设计模式
UVM方法学通过TLM analysis port开发了观察者模式,提供了在publisher和subscriber之间创建连接的方法,实现一对多的连接。这种方式在现在验证环境中大量使用了,但也有许多限制:
- 限制一:这种方式的组件连接是静态的,它们通常在connect_phase就确定了,并且只有uvm_component可以参与连接。
- 限制二:这种通信方式仅限于一种类型的单个事务传输。
- 限制三:subscriber需要多个analysis port时需要求助于UVM宏,或者创建子层次结构来监听transaction。
使用Interface Class实现的观察者模式完美解决了所有这三个问题。下图提供与UVM analysis port非常相似功能的实例。
interface class resolve_listener;pure virtual function void new_resolve(txn_resolve resolve);
endclass : resolve_listenerclass monitor extends uvm_component;local resolve_listener m_resolve_listeners[$];function void add_listener(resolve_listener listener);m_resolve_listener.push_back(listener);endfunctionvirtual task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);forever begintxn_resolve resolve = get_next_resolve();foreach(m_resolve_listeners[i])m_resolve_listeners[i].new_resolve(resolve);endendtaskendclass : monitorclass resolve_checker extends uvm_component implements resolve_listener;virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);super.connect_phase(phase);m_config.monitor.add_listener(this);endfunctionvirtual function void new_resolve(txn_resolve resolve);if (resolve.is_abort())`uvm_fatal(get_name(), "Aborts are not expected")endfunctionendclass : resolve_checker图2 使用Interface Class实现通信
首先这个实例使用了动态连接,subscribers可以在仿真过程中的任何时间点向publisher注册自己(并不限制于connect_phase阶段),并开始订阅transactions。另外,这个实例也允许UVM sequence等非uvm_component直接订阅monitor、BFM和checker等的transactions。下面为reactive sequence直接利用monitor监控到的接口行为产生其它动作的例子,这样的写法使得reactive sequence更容易编写。维护和理解,而不需要借助于sequencer和sequence之间错综复杂的通信通道。
task run_sequence();m_done = 0;m_config.monitor_l1l2.add_listener(this);wait(m_done);m_config.monitor_l1l2.remove_listener(this);
endtaskvirtual function void new_l1l2_request(txn_l1l2 req);// Wait until a request to upgrade line from shared to exclusive is seen and// send a snoop request to steal the line awayif (!m_done && l1l2.req_type() == READ_UNIQUE_HIT_SHARED) beginsend_snoop(SNOOP_INVALIDATE, l1l2.req_address());m_done = 1;end
endfunction图3 使用观察者模式直接订阅monitor的事件
第二个是subscriber和publisher之间的接口并不局限于单个transaction传输。接口函数new_resolve(…)可以传递任何可能对subscriber有用的附加信息,如下面new_resolve新的函数参数。
pure virtual function void new_resolve(txn_uop uop, txn_resolve resolve);图4 new_resolve新定义
最后,subscriber可以订阅多个publisher的消息,因为Interface Class允许多继承,下图的例子是order检查器一方面订阅正在进行的微操作(micro operation),另一方面订阅了ACE协议口发出的请求,并检查它们是否是以正确的顺序进行。这样生成的代码比使用UVM analysis port更干净和直接得多,那个函数做什么很清楚。
class ordering_checker extends checker implements uop_listener, ace_listener;local txn_uop m_ordered_uops[$];// Register ourselves with micro-op and ACE agentsvirtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);super.connect_phase(phase);m_config.uop_agent.add_listener(this);m_config.ace_agent.add_listener(this);endfunction// On commits, record micro-ops that need to be orderedvirtual function void new_commit(txn_uop uop, txn_commit commit);if (commit.is_clean() && uop.is_ordered())m_ordered_uops.push_back(uop);endfunction// On ACE requests, compare address and sizevirtual function void new_ace_req(ace_req ace_request);txn_uop uop;if (!ace_request.needs_to_be_ordered())return;uop = m_ordered_uops.pop_front();check(ace_request.addr().equals(uop.addr()) && (ace_request.size() == uop.size()),{"ACE request seen doesn¿t match the oldest micro-op: ", uop.covert2string()});endfunctionendclass : ordering_checker图5 checker订阅两个不同的monitor的事件
在某些情况下,用于复杂checker的subscriber的Interface Class定义了许多函数,但并非所有函数都在每个subscriber中用到。一种解决方案是将Interface Class分解为更小的类,但这需要向订阅所有events的subscriber添加额外代码。可以使用一个优雅的解决方案,也就是引入中间层类,中间层类为Interface Class的所有函数提供了空的实现,允许子类只覆盖它需要的函数,如下图所示。
class uop_listener_mixin(type T = uvm_component) extends T implements uop_listener;virtual function void new_resolve(txn_uop uop, txn_resolve resolve);endfunctionvirtual function void new_commit(txn_uop uop, txn_commit commit);endfunctionvirtual function void new_issue(txn_uop uop);endfunctionvirtual function void uop_flush(txn_uop uop, flush_cause_e cause);endfunctionendclass : uop_listener_mixinclass uop_checker extends uop_listener_mixin#(checker);virtual function void new_issue(txn_uop uop);check_uop(uop);endfunctionendclass : uop_checker图6 在Interface Class中使用中间层
这种方式的一大优点是,仍然允许中间层继承多个Interface Class,进而订阅多个接口的transactions。order检查器的声明可以写成如下图所示。
class strongly_ordered_checker extends uop_listener_mixin#(l1l2_listener_mixin #(checker));图7 中间层的嵌套使用
示例2:多继承
在SystemVerilog中缺乏真正的多继承,我们可以使用Interface Class来绕过这个限制,我们以Arm指令类为例。下图左边为带地址的指令,比如load和store指令,右边为不带地址的操作,比如data barrier指令中的DMB和DSB等。但如果引入了Load-Acquire(LDAR)和Store-Release(STLR)指令呢(LDAR和STLR指令的行为就像是二合一指令,它们即是load/store,也是barrier)?那么它们在下图中该处于什么位置呢?
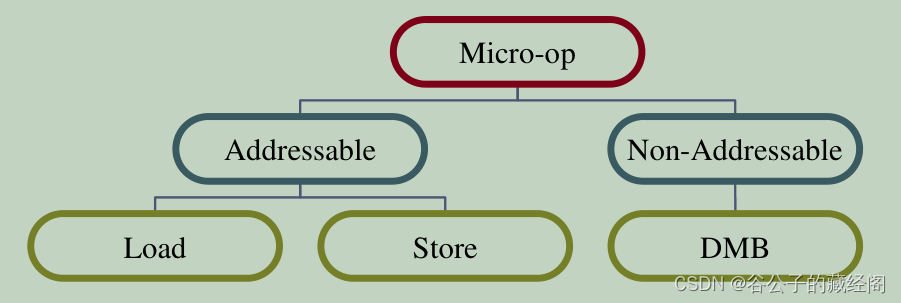
图8 CPU指令集的典型类层次划分
如果支持类多继承的话,LDAR可以从load和data barrier类继承。但缺乏类多继承的情况下,大多数类层次结构只允许LDAR继承自load,并且要么将所有特定于barrier的函数放在共同基本类中,要么在任何地方编写特殊代码来处理此问题,这样会导致代码更难以维护。
然而,有了Interface Class一切就好办了,它允许我们做一些类似于多继承的实现。我们可以定义一个Barrier Interface Class,它声明描述Barrier行为的函数,然后让Dat啊Barrier、LDAR和STLR类实现它。现在,判断一个指令是否是Barrier只需要做一次$cast检查就好了。
interface class barrier;// Return 1 if this barrier affects the given uop in a given directionpure virtual function bit affects_uop(txn_uop uop, dir_e direction);// Perform age comparison between a barrier and a uoppure virtual function bit is_barrier_older(txn_uop uop);//...
endclass : barrierclass barrier_checker;function void check_out_of_order_resolve(txn_uop first, txn_uop second);barrier bar;if ($cast(bar, second) && bar.affects_uop(first, YOUNGER))`uvm_fatal(get_name(), "Uop bypassed a barrier it isn¿t allowed to.")endfunction
endclass :barrier_checker图9 Barrier Interface Class的使用示例
这种方式可以用于指令类层次结构中的其它指令,比如exclusive指令、atomic指令等等。
总结
本文两个Interface Class用例都会使得验证环境开发更加容易,观察者模式使得transaction传递更加清晰和灵活,这对激励质量有特别积极的影响,sequence可以直接根据monitor中的事件自适应调整激励。多继承模式简化了类的层次结构,使每个类的职责有更清晰的划分。