命名空间(namespace)的目的:对标识符的名称进行本地化,以避免命名冲突或者名字污染
#include<stdio.h>
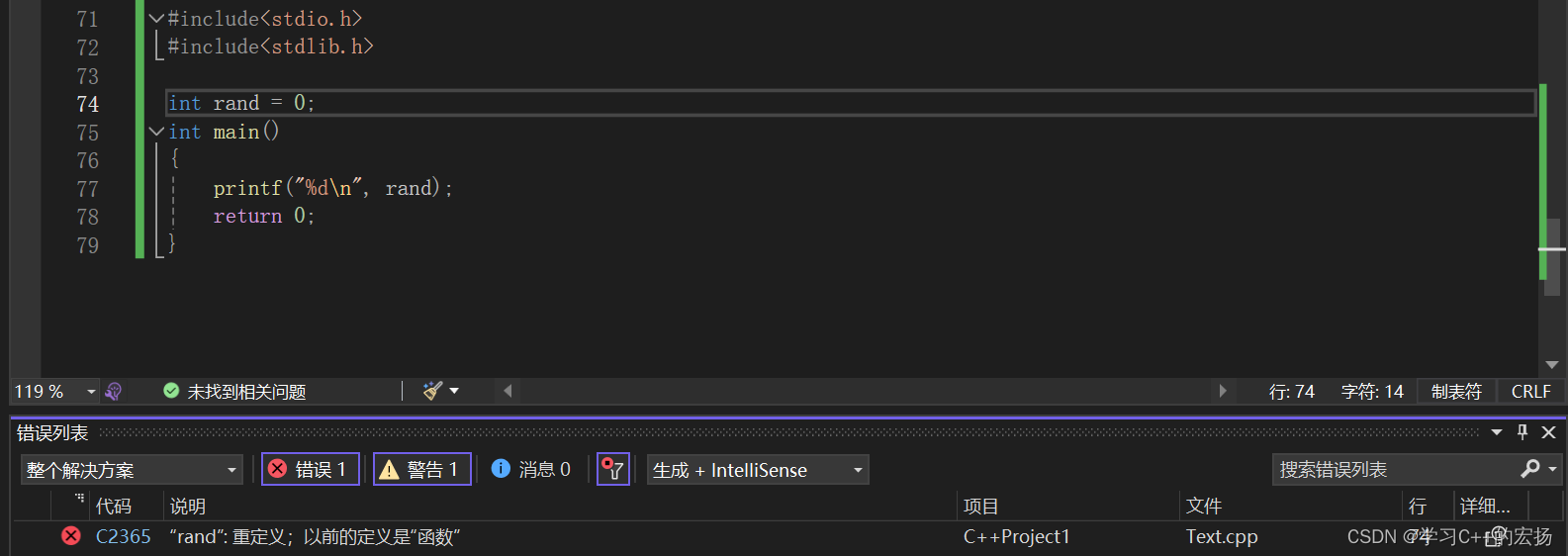
#include<stdlib.h>int rand = 0;
int main()
{
//C语言没有办法解决类似这种的命名冲突,而C++提出了namespace来解决printf("%d\n", rand);return 0;
}
命名空间的定义,需要使用namespace关键字,后面跟空间命名名字,然后接一对{}即可,{}中即为命名空间的成员
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>namespace bit
{int rand = 10;int ADD(int x, int y){return x + y;}struct Node{struct Node* next;int val;};
}namespace N1
{int a = 0;int b = 1;int ADD(int x, int y){return x + y;}namespace N2{int c = 2;int d = 3;int SUM(int x, int y){return x - y;}}
}//命名空间可以嵌套
int main()
{printf("%d\n", rand);printf("%d\n",bit::rand);return 0;
}
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//同一个工程允许多个相同名称的命名空间,编译器最后会将相同的命名空间合并到一起
//一个工程中的也会合并到一起
//text.h
//namespace bit
//{
// int rand = 10;
// struct Node
// {
// struct Node* next;
// int val;
// };
//}
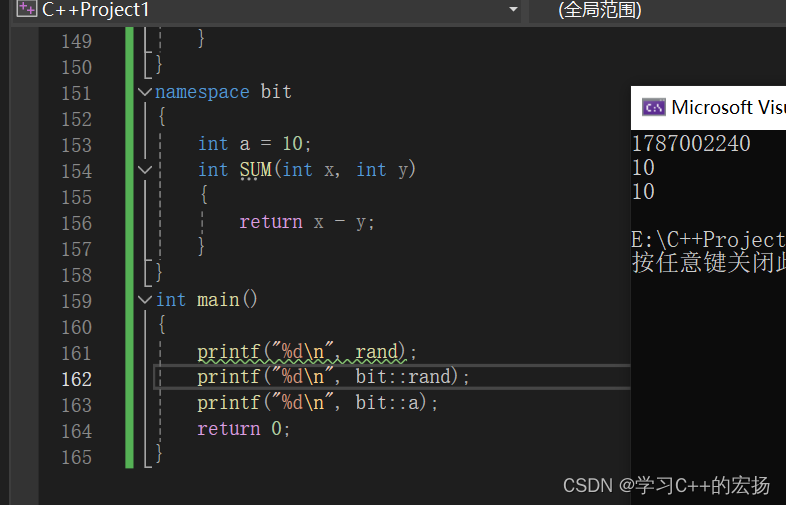
namespace bit
{int rand = 10;int ADD(int x, int y){return x + y;}
}
namespace bit
{int a = 10;int SUM(int x, int y){return x - y;}
}
int main()
{printf("%d\n", rand);printf("%d\n", bit::rand);printf("%d\n", bit::a);return 0;
}
注意:一个命名空间就定义了一个新的作用域,命名空间中的所有内容都局限于改命名空间中
命名空间的三种使用方式
#include<stdio.h>
//#include<stdlib.h>
namespace bit
{int rand = 10;int a = 20;int ADD(int x, int y){return x + y;}
}
int main1()
{//加命名空间名称及作用域限定符printf("%d\n", bit::rand);return 0;
}using bit::a;
int main2()
{//使用using命令将命名空间中某个成员引入printf("%d\n", a);return 0;
}using namespace bit;
int main()
{//使用using namespace 命名空间名引入printf("%d\n", bit::rand);printf("%d\n", a);
}
C++输入&输出
#include<iostream>
//std是C++标准库的命名空间名,C++将标准库的定义都放到这个命名空间中
using namespace std;
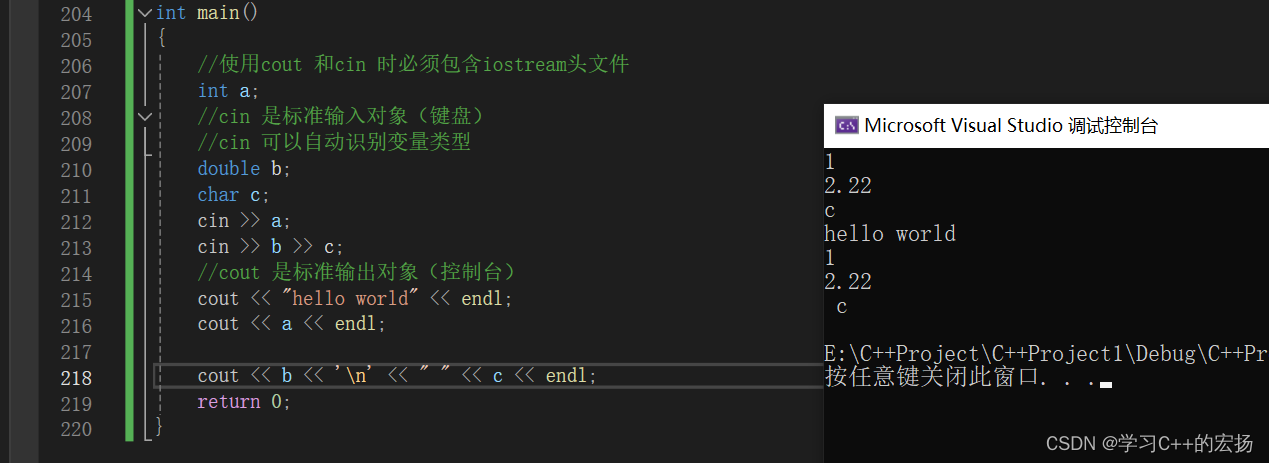
int main()
{//使用cout 和cin 时必须包含iostream头文件 int a;//cin 是标准输入对象(键盘)//cin 可以自动识别变量类型double b;char c;cin >> a;cin >> b >> c;//cout 是标准输出对象(控制台)cout << "hello world" << endl;cout << a << endl;cout << b << '\n' << " " << c << endl;return 0;
}
std 命名空间的使用惯例:std 是 C++ 标准库的命名空间,如何展开 std 使用更合理呢?1. 在日常练习中,建议直接 using namespace std 即可,这样就很方便。2. using namespace std 展开,标准库就全部暴露出来了,如果我们定义跟库重名的类型 / 对象 / 函数,就存在冲突问题。该问题在日常练习中很少出现,但是项目开发中代码较多、规模大,就很容易出现。所以建议在项目开发中使用,像 std::cout 这样使用时指定命名空间 +using std::cout 展开常用的库对象 / 类型等方式。
缺省参数
缺省参数概念:是声明或定义函数时为函数的参数指定一个缺省值。在调用该函数时,如果没有指定实 参则采用该形参的缺省值,否则使用指定的实参。
#include<iostream>using namespace std;void Fun(int a = 0)
{cout << a << endl;
}int main()
{Fun();//0Fun(1);//1return 0;
}缺省参数类型

#include<iostream>
#include"a.h"
using namespace std;
//半缺省类型
//注意
//1. 半缺省参数必须从右往左依次来给出,不能间隔着给void Fun(int a, int b = 20, int c = 30)
{cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b = " << b << endl;cout << "c = " << c << endl;
}int main1()
{Fun(1, 2, 3);//1 2 3//Fun(1, ,3);//erro//Fun(, ,3);//erro//Fun();//erroFun(1, 2);//1 2 30Fun(1);//1 20 30return 0;
}//2. 缺省参数不能在函数声明和定义中同时出现
void Fun1(int a = 10 , int b = 20, int c = 30)
{cout << "a = " << a << endl;cout << "b = " << b << endl;cout << "c = " << c << endl;
}
//3. 缺省值必须是常量或者全局变量
//4. C语言不支持(编译器不支持)












![[蓝桥杯真题]买二赠一](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/4a6bbb0728808c08e430ed348bd60d73.png)

