双目摄像头标定及矫正
- 棋盘格标定板
- 标定
- 矫正
棋盘格标定板
本文使用棋盘格标定板,可以到这篇博客中下载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39330520/article/details/107864568
标定
要进行标定首先需要双目拍的棋盘格图片,20张左右,由于本文的双目摄像头嵌入在开发板底板中,并且使用的是ros进行开发,所以对于大部分人拍照这里是没有参考价值的,对于也是使用ros开发的小伙伴,需要写一个节点发布双目摄像头的图像数据,然后再写一个节点订阅双目摄像头数据进行拍照保存。本文重点也不在拍照,对于其他小伙伴可以直接搜索一些适用的拍照方法,只要能获得到图片即可。
左摄像头图片如下:

右摄像头图片如下:
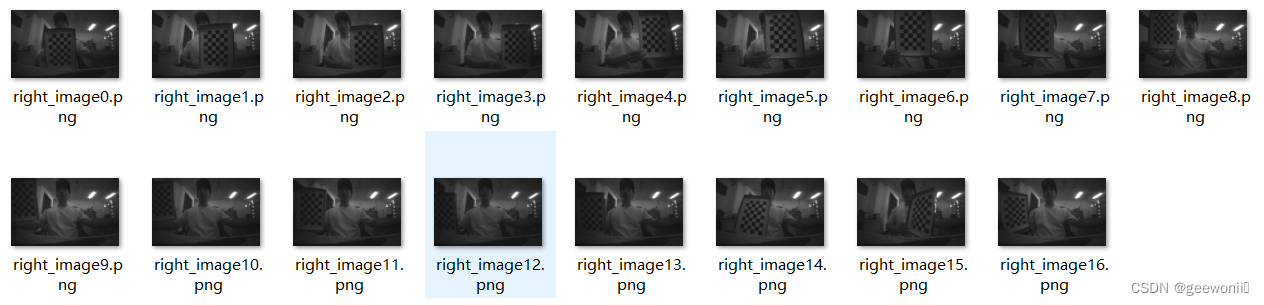
由于摄像头底层代码有问题,所以图像很暗,但不影响标定。
标定代码如下:
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
import itertools
import yaml# 定义文件夹路径
left_folder = "C:/new_pycharm_project/yolov10-main/shuangmu_left_pic"
right_folder = "C:/new_pycharm_project/yolov10-main/shuangmu_right_pic"# 获取图像文件列表并排序
left_images = sorted(os.listdir(left_folder))
right_images = sorted(os.listdir(right_folder))# 确保左右相机图像数量一致
assert len(left_images) == len(right_images), "左右相机图像数量不一致"# 加载两个摄像头图片文件夹并将里面的彩图转换为灰度图
def load_images(folder, images):img_list = []for img_name in images:img_path = os.path.join(folder, img_name)frame = cv2.imread(img_path)if frame is not None:gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)img_list.append((frame, gray))else:print(f"无法读取图像: {img_path}")return img_list# 检测棋盘格角点
def get_corners(imgs, pattern_size):corners = []for frame, gray in imgs:ret, c = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, pattern_size) #ret 表示是否成功找到棋盘格角点,c 是一个数组,包含了检测到的角点的坐标if not ret:print("未能检测到棋盘格角点")continuec = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray, c, (5, 5), (-1, -1),(cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 0.001)) #cv2.cornerSubPix 函数用于提高棋盘格角点的精确度,对初始检测到的角点坐标 c 进行优化corners.append(c) #将优化后的角点坐标 c 添加到 corners 列表中# 绘制角点并显示vis = frame.copy()cv2.drawChessboardCorners(vis, pattern_size, c, ret)new_size = (1280, 800)resized_img = cv2.resize(vis, new_size)cv2.imshow('Corners', resized_img)cv2.waitKey(150)return corners# 相机标定
def calibrate_camera(object_points, corners, imgsize):cm_input = np.eye(3, dtype=np.float32)ret = cv2.calibrateCamera(object_points, corners, imgsize, cm_input, None)return retdef save_calibration_to_yaml(file_path, cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, R, T, E, F):data = {'camera_matrix_left': {'rows': 3,'cols': 3,'dt': 'd','data': cameraMatrix_l.flatten().tolist()},'dist_coeff_left': {'rows': 1,'cols': 5,'dt': 'd','data': distCoeffs_l.flatten().tolist()},'camera_matrix_right': {'rows': 3,'cols': 3,'dt': 'd','data': cameraMatrix_r.flatten().tolist()},'dist_coeff_right': {'rows': 1,'cols': 5,'dt': 'd','data': distCoeffs_r.flatten().tolist()},'R': {'rows': 3,'cols': 3,'dt': 'd','data': R.flatten().tolist()},'T': {'rows': 3,'cols': 1,'dt': 'd','data': T.flatten().tolist()},'E': {'rows': 3,'cols': 3,'dt': 'd','data': E.flatten().tolist()},'F': {'rows': 3,'cols': 3,'dt': 'd','data': F.flatten().tolist()}}with open(file_path, 'w') as file:yaml.dump(data, file, default_flow_style=False)print(f"Calibration parameters saved to {file_path}")img_left = load_images(left_folder, left_images) #img_left是个列表,存放左摄像头所有的灰度图片。
img_right = load_images(right_folder, right_images)
pattern_size = (8, 5)
corners_left = get_corners(img_left, pattern_size) #corners_left的长度表示检测到棋盘格角点的图像数量。corners_left[i] 和 corners_right[i] 中存储了第 i 张图像检测到的棋盘格角点的二维坐标。
corners_right = get_corners(img_right, pattern_size)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()# 断言,确保所有图像都检测到角点
assert len(corners_left) == len(img_left), "有图像未检测到左相机的角点"
assert len(corners_right) == len(img_right), "有图像未检测到右相机的角点"# 准备标定所需数据
points = np.zeros((8 * 5, 3), dtype=np.float32) #创建40 行 3 列的零矩阵,用于存储棋盘格的三维坐标点。棋盘格的大小是 8 行 5 列,40 个角点。数据类型为 np.float32,这是一张图的,因为一个角点对应一个三维坐标
points[:, :2] = np.mgrid[0:8, 0:5].T.reshape(-1, 2) * 21 #给这些点赋予实际的物理坐标,* 21 是因为每个棋盘格的大小为 21mmobject_points = [points] * len(corners_left) #包含了所有图像中棋盘格的三维物理坐标点 points。这里假设所有图像中棋盘格的物理坐标是相同的,因此用 points 复制 len(corners_left) 次。
imgsize = img_left[0][1].shape[::-1] #img_left[0] 是左相机图像列表中的第一张图像。img_left[0][1] 是该图像的灰度图像。shape[::-1] 取灰度图像的宽度和高度,并反转顺序,以符合 calibrateCamera 函数的要求。print('开始左相机标定')
ret_l = calibrate_camera(object_points, corners_left, imgsize) #object_points表示标定板上检测到的棋盘格角点的三维坐标;corners_left[i]表示棋盘格角点在图像中的二维坐标;imgsize表示图像大小
retval_l, cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, rvecs_l, tvecs_l = ret_l[:5] #返回值里就包含了标定的参数print('开始右相机标定')
ret_r = calibrate_camera(object_points, corners_right, imgsize)
retval_r, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, rvecs_r, tvecs_r = ret_r[:5]# 立体标定,得到左右相机的外参:旋转矩阵、平移矩阵、本质矩阵、基本矩阵
print('开始立体标定')
criteria_stereo = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 30, 1e-5)
ret_stereo = cv2.stereoCalibrate(object_points, corners_left, corners_right,cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l,cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r,imgsize, criteria=criteria_stereo,flags=cv2.CALIB_FIX_INTRINSIC)
ret, _, _, _, _, R, T, E, F = ret_stereo# 输出结果
print("左相机内参:\n", cameraMatrix_l)
print("左相机畸变系数:\n", distCoeffs_l)
print("右相机内参:\n", cameraMatrix_r)
print("右相机畸变系数:\n", distCoeffs_r)
print("旋转矩阵 R:\n", R)
print("平移向量 T:\n", T)
print("本质矩阵 E:\n", E)
print("基本矩阵 F:\n", F)
print("标定完成")# 保存标定结果
save_calibration_to_yaml('calibration_parameters.yaml', cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, R, T, E, F)# 计算重投影误差
def compute_reprojection_errors(objpoints, imgpoints, rvecs, tvecs, mtx, dist):total_error = 0total_points = 0for i in range(len(objpoints)):imgpoints2, _ = cv2.projectPoints(objpoints[i], rvecs[i], tvecs[i], mtx, dist)error = cv2.norm(imgpoints[i], imgpoints2, cv2.NORM_L2) / len(imgpoints2)total_error += errortotal_points += len(imgpoints2)mean_error = total_error / total_pointsreturn mean_error# 计算并打印左相机和右相机的重投影误差
print("左相机重投影误差: ", compute_reprojection_errors(object_points, corners_left, rvecs_l, tvecs_l, cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l))
print("右相机重投影误差: ", compute_reprojection_errors(object_points, corners_right, rvecs_r, tvecs_r, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r))# 立体矫正和显示
def stereo_rectify_and_display(img_l, img_r, cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, R, T):img_size = img_l.shape[:2][::-1]# 立体校正R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, _, _ = cv2.stereoRectify(cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, img_size, R, T)map1x, map1y = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, R1, P1, img_size, cv2.CV_32FC1)map2x, map2y = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, R2, P2, img_size, cv2.CV_32FC1)# 图像矫正rectified_img_l = cv2.remap(img_l, map1x, map1y, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)rectified_img_r = cv2.remap(img_r, map2x, map2y, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)# 显示矫正后的图像combined_img = np.hstack((rectified_img_l, rectified_img_r))cv2.imshow('Rectified Images', combined_img)cv2.imwrite("stereo_jiaozheng.png",combined_img)cv2.waitKey(0)cv2.destroyAllWindows()# 加载并矫正示例图像
example_idx = 0
img_l = img_left[example_idx][0]
img_r = img_right[example_idx][0]
stereo_rectify_and_display(img_l, img_r, cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, R, T)
标定完成后会显示一张矫正后的图像。代码重要的地方都给出了注释,主要流程就是分别对左右相机进行标定,然后对两个相机进行联合标定(立体标定),最后得到的参数会保存到yaml文件中:
---
camera_matrix_left:rows: 3cols: 3dt: ddata:- 531.7200210313852- 0- 642.0170539101581- 0- 533.6471323984354- 420.4033045027399- 0- 0- 1
dist_coeff_left:rows: 1cols: 5dt: ddata:- -0.1670007968198256- 0.04560028196221921- 0.0011938487550718078- -0.000866537907860316- -0.00805042100882671
camera_matrix_right:rows: 3cols: 3dt: ddata:- 525.9058345430292- 0- 628.7761214904813- 0- 528.2078922687268- 381.8575789135264- 0- 0- 1
dist_coeff_right:rows: 1cols: 5dt: ddata:- -0.15320688387351564- 0.03439886104586617- -0.0003732170677440928- -0.0024909528446780153- -0.005138400994014348
R:rows: 3cols: 3dt: ddata:- 0.9999847004116569- -0.00041406631566505544- 0.005516112008926496- 0.0003183979929468572- 0.9998497209492369- 0.017333036100216304- -0.005522460079247196- -0.017331014592906722- 0.9998345554979852
T:rows: 3cols: 1dt: ddata:- -55.849260376265015- 2.1715925432988743- 0.46949841441903933
E:rows: 3cols: 3dt: ddata:- -0.012142020481601675- -0.5070637607007459- 2.1630954322858496- 0.1610659204031652- -0.9681187500627653- 55.84261022903612- -2.189341611238282- -55.83996821910631- -0.9800159939787676
F:rows: 3cols: 3dt: ddata:- -2.4239149875305048e-8- -0.0000010085973649868748- 0.0027356495714066175- 3.2013501988129346e-7- -0.0000019172863951399893- 0.05961765359743852- -0.002405523166325036- -0.057046539240958545- 1分别是左相机的内参矩阵、畸变系数,右相机的内参矩阵和畸变系数,两个相机之间的旋转矩阵、平移矩阵、本质矩阵、基本矩阵。
矫正
import cv2
import yaml
import numpy as np# 定义函数读取标定数据
def read_calibration_data(calibration_file):with open(calibration_file, 'r') as f:calib_data = yaml.safe_load(f)cameraMatrix_l = np.array(calib_data['camera_matrix_left']['data']).reshape(3, 3)distCoeffs_l = np.array(calib_data['dist_coeff_left']['data'])cameraMatrix_r = np.array(calib_data['camera_matrix_right']['data']).reshape(3, 3)distCoeffs_r = np.array(calib_data['dist_coeff_right']['data'])R = np.array(calib_data['R']['data']).reshape(3, 3)T = np.array(calib_data['T']['data']).reshape(3, 1)return cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, R, T# 定义函数对图像进行矫正
def rectify_images(left_image_path, right_image_path, calibration_file):# 读取标定数据cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, R, T = read_calibration_data(calibration_file)# 读取左右图像img_left = cv2.imread(left_image_path)img_right = cv2.imread(right_image_path)# 获取图像尺寸(假设左右图像尺寸相同)img_size = img_left.shape[:2][::-1]# 立体校正R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, roi1, roi2 = cv2.stereoRectify(cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l,cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r,img_size, R, T)# 计算映射参数map1_l, map2_l = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrix_l, distCoeffs_l, R1, P1, img_size, cv2.CV_32FC1)map1_r, map2_r = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(cameraMatrix_r, distCoeffs_r, R2, P2, img_size, cv2.CV_32FC1)# 应用映射并显示结果rectified_img_l = cv2.remap(img_left, map1_l, map2_l, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)rectified_img_r = cv2.remap(img_right, map1_r, map2_r, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)# 合并图像显示combined_img = np.hstack((rectified_img_l, rectified_img_r))cv2.imshow('Rectified Images', combined_img)cv2.waitKey(0)cv2.destroyAllWindows()# 设置路径和文件名
left_image_path = "C:/new_pycharm_project/yolov10-main/shuangmu_left_pic/left_image0.png"
right_image_path = "C:/new_pycharm_project/yolov10-main/shuangmu_right_pic/right_image0.png"
calibration_file = "C:/new_pycharm_project/yolov10-main/calibration_parameters.yaml"# 调用函数进行图像矫正
rectify_images(left_image_path, right_image_path, calibration_file)结果对比:
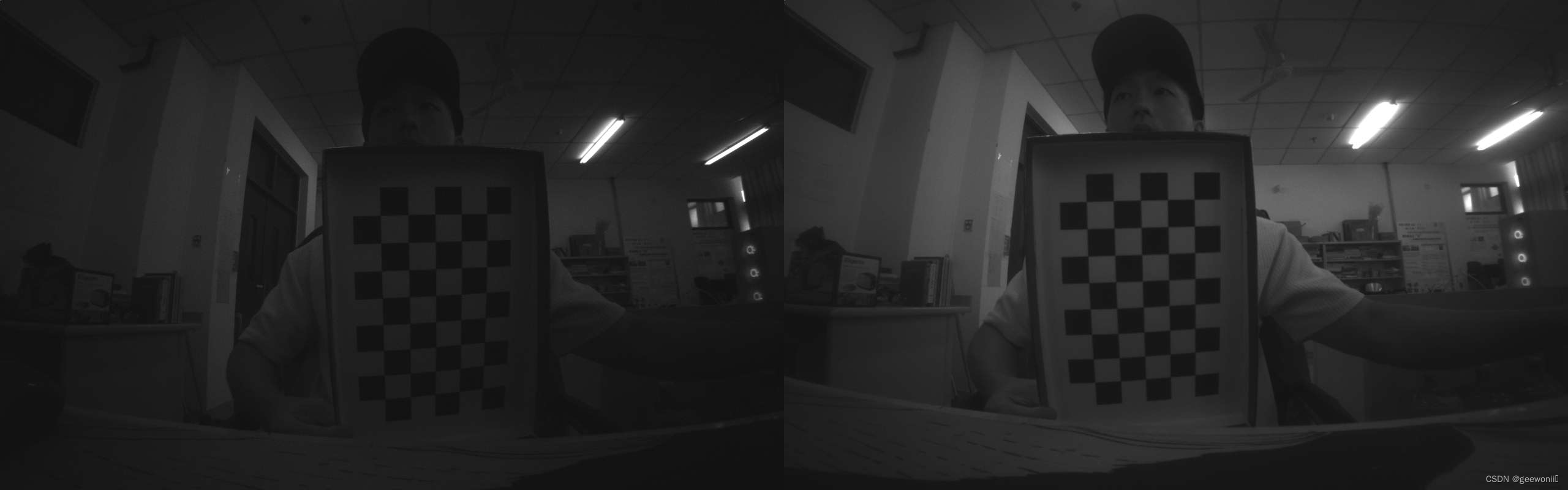
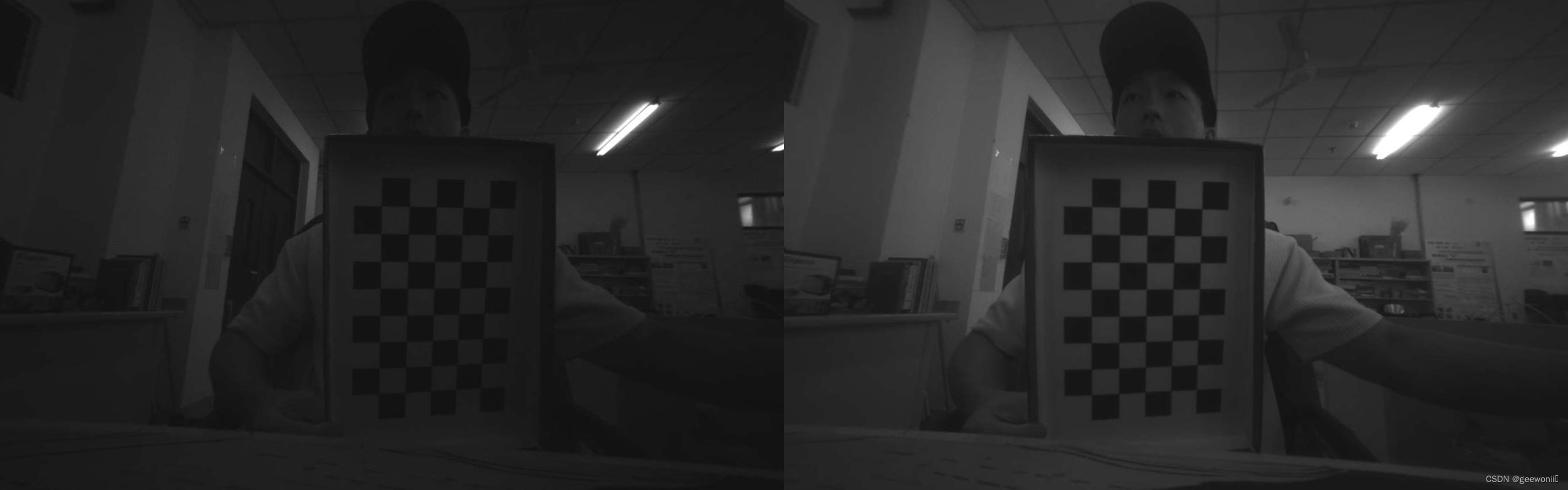


第一张是矫正前的左右相机图像,第二张是矫正后的。可以看到去除了畸变,并且两图像基本出于同一水平线。

![[JS]对象](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/d11c90b3175d4a4d3bb29625a244659a.png)



![[leetcode]avoid-flood-in-the-city 避免洪水泛滥](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/5c18fecf8b124fa2ad3d4b199869ba12.png)