文章目录
- 1. 为什么学习string类?
- 1.1 C语言中的字符串
- 1.2 两个面试题(暂不做讲解)
- 2. 标准库中的string类
- 2.1 string类(了解)
- 2.2 auto和范围for
- 3. 查看技术文档
- 4. string的访问
- 5. 如何读取每个字符呢?
- 6. auto语法糖(C++11)
- 7. 范围for 语法糖(C++11)
- 8. reserve
- 9. resize
- 10. Modifiers
- insert,erase(偶尔使用)
- replace(偶尔使用)
- 11. find
- 12.c_str,rfind,find_first_not_of
- 13. 需要掌握的部分
1. 为什么学习string类?
1.1 C语言中的字符串
C语言中,字符串是以'\0'结尾的一些字符的集合,为了操作方便,C标准库中提供了一些str系列的库函数,但是这些库函数与字符串是分离开的,不太符合OOP的思想,而且底层空间需要用户自己管理,稍不留神可能还会越界访问。
1.2 两个面试题(暂不做讲解)
字符串相加
在OJ中,有关字符串的题目基本以string类的形式出现,而且在常规工作中,为了简单、方便、快捷,基本都使用string类,很少有人去使用C库中的字符串操作函数。
2. 标准库中的string类
2.1 string类(了解)
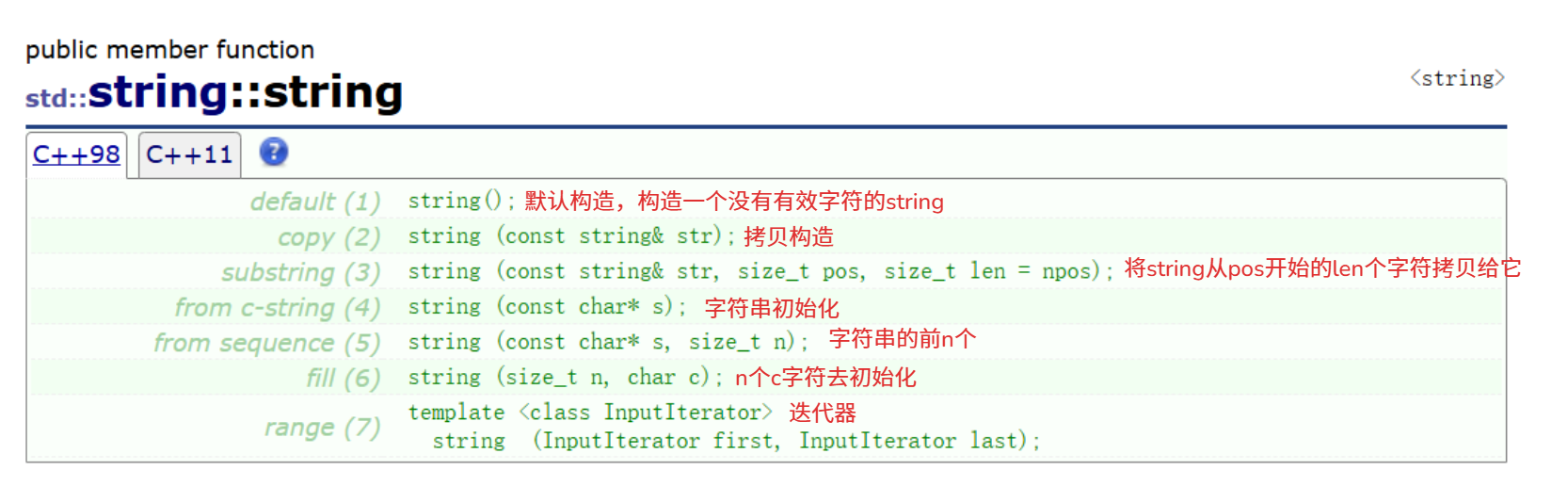
string类的文档介绍
在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
2.2 auto和范围for
auto关键字
在这里补充2个
C++11的小语法,方便我们后面的学习。
在早期
C/C++中auto的含义是:使用auto修饰的变量,是具有自动存储器的局部变量,后来这个不重要了。C++11中,标准委员会变废为宝赋予了auto全新的含义即:auto不再是一个存储类型指示符,而是作为一个新的类型指示符来指示编译器,auto声明的变量必须由编译器在编译时期推导而得。用
auto声明指针类型时,用auto和auto*没有任何区别,但用auto声明引用类型时则必须加&当在同一行声明多个变量时,这些变量必须是相同的类型,否则编译器将会报错,因为编译器实际只对第一个类型进行推导,然后用推导出来的类型定义其他变量。
auto不能作为函数的参数,可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用
auto不能直接用来声明数组
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int func1()
{return 10;
}
// 不能做参数
void func2(auto a)
{}
// 可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用
auto func3()
{return 3;
}
int main()
{int a = 10;auto b = a;auto c = 'a';auto d = func1();// 编译报错:rror C3531: “e”: 类型包含“auto”的符号必须具有初始值设定项auto e;cout << typeid(b).name() << endl;cout << typeid(c).name() << endl;cout << typeid(d).name() << endl;int x = 10;auto y = &x;auto* z = &x;auto& m = x;cout << typeid(x).name() << endl;cout << typeid(y).name() << endl;cout << typeid(z).name() << endl;auto aa = 1, bb = 2;// 编译报错:error C3538: 在声明符列表中,“auto”必须始终推导为同一类型auto cc = 3, dd = 4.0;// 编译报错:error C3318: “auto []”: 数组不能具有其中包含“auto”的元素类型auto array[] = { 4, 5, 6 };return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{std::map<std::string, std::string> dict = { { "apple", "苹果" },{ "orange", "橙子" }, {"pear","梨"} };// auto的用武之地//std::map<std::string, std::string>::iterator it = dict.begin();auto it = dict.begin();while (it != dict.end()){cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;++it;}return 0;
}
3. 查看技术文档
网址:https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/

#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;int main()
{string s1;//构造一个没有有效字符的stringstring s2("1111122222");//字符串初始化string s3("1111111111", 3);//字符串的前3个初始化string s4(100, 'x');//100个x字符初始化string s5(s2, 4, 3);//将string从pos开始的len个字符拷贝给它string s6(s2, 4);//没有传第三个参数就拷贝到s2的结束string s7(s2, 4, 20);//传递的第三个参数比剩下的字符长,就拷贝到结束cout << s1 << endl;//(什么都不打印)cout << s2 << endl;//1111122222cout << s3 << endl;//111cout << s4 << endl;//xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxcout << s5 << endl;//122cout << s6 << endl;//122222cout << s7 << endl;//122222return 0;
}
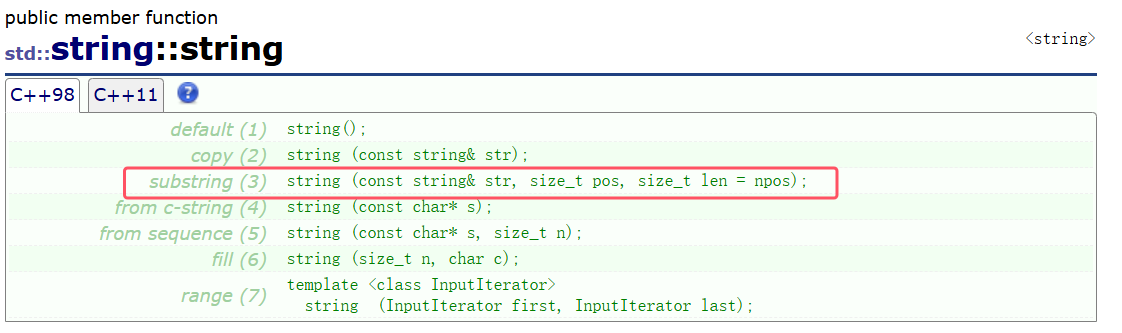


这个npos是string里面的一个静态成员变量,所以在这里可以做缺省参数,他给的是-1,其实他不是-1,是整形的最大值。因为这里他的类型是size_t也就是unsigned int。
所以第三个参数不写就会一直走下去,因为是整型的最大值。所以会走到字符串结束。
4. string的访问

访问第pos位置的字符。
string为了和C兼容,末尾是添加了\0的。string是在STL之前就有的,所以有的接口会比较繁琐。
operator[]的底层类似于
class string
{
public:char& operator[] (size_t pos){assert(pos < _size);//防止越界return _str[pos];}
private:char* _str;size_t _size;size_t _capacity;
};
这里面牛逼的地方在于是传引用返回,而不是传值返回。
- 这样做有一个好处,如果想修改一个字符,就可以直接修改。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;int main()
{string s2("1111122222");//字符串初始化cout << s2 << endl;//1111122222//s2.operator[](0) = 'x';s2[0] = 'x';cout << s2 << endl;//x111122222return 0;
}
但他不是数组,相当于调用s2.operator[](0) = 'x';
这个使用起来很方便,就像数组一样使用。
- 我们想遍历这个
string的每个字符,就可以像数组一样去遍历每个字符。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>using namespace std;int main()
{string s2("1111122222");//字符串初始化cout << s2 << endl;//1111122222s2[0] = 'x';s2[5] = 'x';cout << s2 << endl;//x1111x2222for (size_t i = 0; i < s2.size(); i++){s2[i]++;}cout << s2 << endl;//y2222y3333return 0;
}
- 可以很好的解决越界问题,因为里面有
assert断言

5. 如何读取每个字符呢?
- 下标+
[]
int main()
{//auto ret1 = func2();string s1("hello world");//1. 下标+[]for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){s1[i]++;}for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++){cout << s1[i] << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
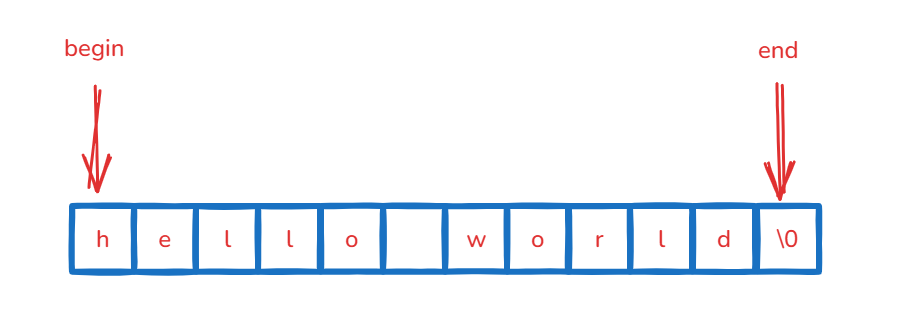
- 迭代器
int main()
{string s1("hello world");//2. 迭代器 -- 像指针一样的对象string::iterator it1 = s1.begin();//begin返回第一个类型的迭代器while (it1 != s1.end())//end返回最后一个数据的下一个位置的迭代器{(*it1)--;//读+修改++it1;}cout << endl;it1 = s1.begin();while (it1 != s1.end()){cout << *it1 << " ";//读++it1;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
迭代器是所有容器通用的,只是在string这里面看起来麻烦点,但是下标+[]不是通用的。
while (it1 != s1.end())这里面推荐写!=,虽然这里用<也可以,但这是因为这里的空间是连续的,但是别的地方不一定可以。
链表的迭代器的定义:
int main() {list<int> lt;lt.push_back(1);lt.push_back(2);lt.push_back(3);lt.push_back(4);list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){cout << *it << " ";//这里的*是运算符重载,不是解引用++it;//这里的++是运算符重载}cout << endl;return 0;
}
打印:
1 2 3 4
6. auto语法糖(C++11)
int main()
{int i = 0;int j = i;// auto会自动推导类型 C++11auto z = i; // z是intauto x = 1.1; // x是doubleauto p = &i; // p是int*int& r1 = i;auto r2 = r1; // r2是int,因为本质上r1是i的引用,改变r1就改变i,r1就是int类型的auto& r3 = r1; // r3是int&//auto r4; // 报错return 0;
}
auto看起来没什么用,那么auto真正的价值是什么呢?
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
auto it = lt.begin();//简化代码,替代写起来长的类型
迭代器比较长的就可以用auto来简化代码。
7. 范围for 语法糖(C++11)
对于一个有范围的集合而言,由程序员来说明循环的范围是多余的,有时候还会容易犯错误。因此
C++11中引入了基于范围的for循环。for循环后的括号由冒号“:”分为两部分:第一部分是范围内用于迭代的变量,第二部分则表示被迭代的范围,自动迭代,自动取数据,自动判断结束。范围
for可以作用到数组和容器对象上进行遍历范围
for的底层很简单,容器遍历实际就是替换为迭代器,这个从汇编层也可以看到。
适用于:容器遍历和数组遍历
自动取容器的数据赋值给左边的对象
自动
++,自动判断结束原理:范围
for底层是迭代器
string s1("hello world");for (auto ch : s1)
{cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;for (auto e : lt)
{cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 修改
for (auto& ch : s1)
{ch++;
}
总结:对
string来说有三种遍历方法:
- 下标+
[]- 迭代器
- 范围
for
之前这么写:
int main(){int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(a)/sizeof(int); i++){cout << a[i] << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
现在这么写:
int main(){int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };for (auto e : a){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
简单多了。
迭代器可以倒着遍历吗?
可以使用反向迭代器,倒着走。
int main()
{string s1("hello world");string::reverse_iterator rit = s1.rbegin();while (rit != s1.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";++rit;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
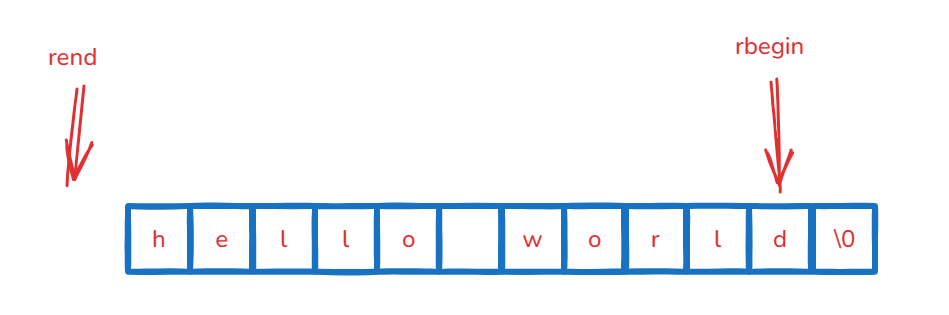
const迭代器
int main(){const string s2(s1);//string::const_iterator it1 = s2.begin();auto it1 = s2.begin();//用auto替代while (it1 != s2.end()){//*it1 += 1;//const_iterator不能给常量赋值,*it1是常量cout << *it1 << " ";++it1;}cout << endl;//string::const_reverse_iterator rit1 = s2.rbegin();auto rit1 = s2.rbegin();//用auto替代while (rit1 != s2.rend()){cout << *rit1 << " ";++rit1;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
迭代器有四种:
iteratorreverse_iteratorconst_iteratorconst_reverse_iterator
8. reserve

代码1:
int main()
{try{string s1("hello world11111");cout << s1.size() << endl;//16cout << s1.length() << endl;//16cout << s1.max_size() << endl;//9223372036854775807cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//31(扩容一次会多扩容一点),capacity没计算\0的空间cout << endl << endl;s1.clear();//把所有数据清除,但是不清除空间cout << s1.size() << endl;//0cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//31//s1[20];//越界了会断言报错s1.at(20);//at会捕获异常}catch (const exception& e){cout << e.what() << endl;//invalid string position}return 0;
}
代码2:
int main()
{string s1("hello");s1.push_back(',');//尾插s1.push_back('w');cout << s1 << endl;//hello,ws1.append("orld");//尾插字符串cout << s1 << endl;//hello,worlds1.append(10, '!');cout << s1 << endl;//hello,world!!!!!!!!!!string s2("hello bit hello world");s1.append(s2.begin()+6, s2.end());cout << s1 << endl;//hello,world!!!!!!!!!!bit hello worldstring s3("hello");s3 += ',';s3 += "world";cout << s3 << endl;//hello,worldreturn 0;
}
代码3-1:
int main()
{string s1;size_t old = s1.capacity();//记录之前的旧的容量cout << "capacity:" << old << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < 200; i++){s1 += 'x';if (s1.capacity() != old)//如果容量发生变化,就说明扩容了{cout << "capacity:" << s1.capacity() << endl;//capacity:207old = s1.capacity();}}return 0;
}
打印:
capacity:15
capacity:31
capacity:47
capacity:70
capacity:105
capacity:157
capacity:235
差不多是1.5倍扩容
代码3-2:
//reserve 保留 预留
//reverse 反向 翻转
int main()
{string s1;//提前开空间,避免扩容s1.reserve(200);size_t old = s1.capacity();//记录之前的旧的容量cout << "capacity:" << old << endl;for (size_t i = 0; i < 200; i++){s1 += 'x';if (s1.capacity() != old)//如果容量发生变化,就说明扩容了{cout << "capacity:" << s1.capacity() << endl;//capacity:207old = s1.capacity();}}string s3("11111111");string s4("111111112222222222222222222222222222222222222222222");cout << sizeof(s3) << endl;//40return 0;
}
9. resize


int main()
{string s1("11111111111111111111");cout << s1 << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;// 删除// n < sizes1.resize(15);cout << s1 << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;// 插入// size < n < capacitys1.resize(25, 'x');cout << s1 << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;// n > capacitys1.resize(40, 'x');cout << s1 << endl;cout << s1.size() << endl;cout << s1.capacity() << endl;return 0;
}
打印:
11111111111111111111//20个1
20
31
111111111111111//15个1
15
31
111111111111111xxxxxxxxxx//15个1,10个x
25
31
111111111111111xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx//15个1,25个x
40
47

10. Modifiers

insert,erase(偶尔使用)
int main()
{string s1("hello world");s1.insert(5, "xxxx");cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(5, 5);cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(0, 1);cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(s1.begin());cout << s1 << endl;s1.erase(5, 10);cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
打印:
helloxxxx world
helloworld
elloworld
lloworld
llowo
replace(偶尔使用)
int main()
{string s1("hello world hello bit");cout << s1 << endl;size_t i = s1.find(' ');while (i != string::npos){s1.replace(i, 1, "%%");i = s1.find(' ', i+2);}cout << s1 << endl;string s2;for (auto ch : s1){if (ch != ' ')s2 += ch;elses2 += "%%";}cout << s2 << endl;//s1.swap(s2);return 0;
}
打印:
hello world hello bit
hello%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%world%%hello%%bit
hello%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%world%%hello%%bit
11. find
int main()
{string s1("hello world hello bit");cout << s1 << endl;size_t i = s1.find(' ');while (i != string::npos){s1.replace(i, 1, "%%");i = s1.find(' ', i+2);}cout << s1 << endl;return 0;
}
打印:
hello world hello bit
hello%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%world%%hello%%bit
12.c_str,rfind,find_first_not_of
可以更好地兼容
C的接口


int main()
{string s1("hello world");cout << s1 << endl;//hello worldcout << s1.c_str() << endl;//hello worldstring s2("Test.cpp");FILE* fout = fopen(s2.c_str(), "r");char ch = fgetc(fout);/*while (ch != EOF){cout << ch;ch = fgetc(fout);}*/const char* p1 = "xxxxx";int* p2 = nullptr;cout << (void*)p1 << endl;//00007FF64CEC1648cout << p2 << endl;//0000000000000000//rfindstring s3("test.cpp.zip");size_t pos = s3.rfind('.');if (pos != string::npos){string sub = s3.substr(pos);cout << sub << endl;//.zip}//find_first_not_ofstd::string str("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks.");std::size_t found = str.find_first_not_of("aeiou");while (found != std::string::npos){str[found] = '*';found = str.find_first_not_of("aeiou", found + 1);}std::cout << str << '\n';//**ea*e***e**a*e***e**o*e***i****i***e**e**e****a**e*i****return 0;
}
打印:
hello world
hello world
00007FF64CEC1648
0000000000000000
.zip
**ea*e***e**a*e***e**o*e***i****i***e**e**e****a**e*i****
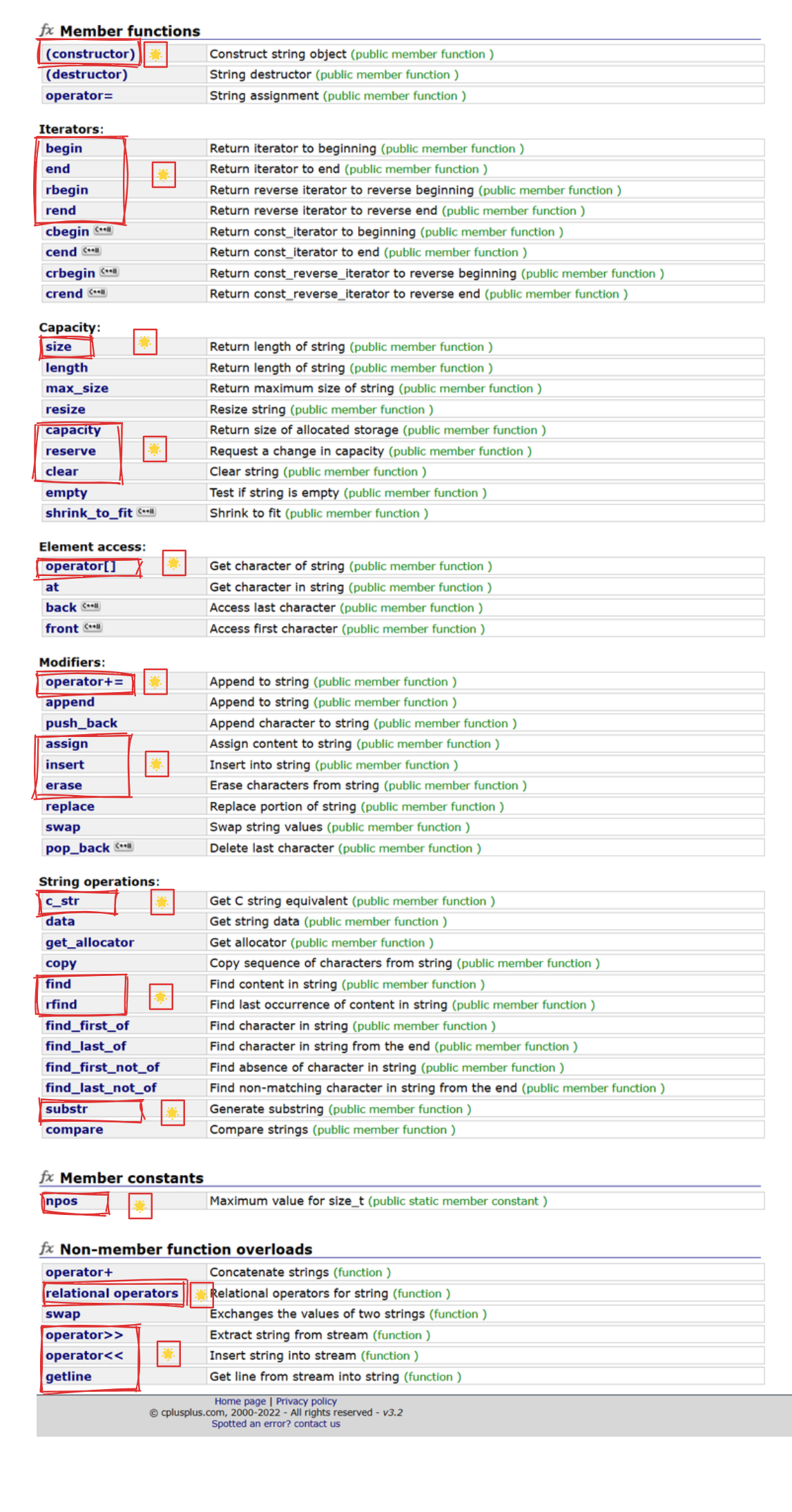
13. 需要掌握的部分





![[单master节点k8s部署]40.安装harbor](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/ca9b0868ccbf4b0790f38cb36f29ed0d.png)