模型构造
回顾一下感知机。
nn.Sequential():定义了一种特殊的module。
torch.rand():用于生成具有均匀分布的随机数,这些随机数的范围在[0, 1)之间。它接受一个形状参数(shape),返回一个指定形状的张量(Tensor)。
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
# 定义网络结构
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(20, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(256, 10))
# 生成随机数[0,1),大小为2x20
X = torch.rand(2, 20)
# 输入网络
net(X)torch.nn.functional.relu():ReLU激活函数
# 自定义MLP模块
class MLP(nn.Module):def __init__(self): #初始化类与参数super().__init__() #父类Module的initself.hidden = nn.Linear(20, 256) #隐藏层self.out = nn.Linear(256, 10) #输出层def forward(self, X): #进行前向传播return self.out(F.relu(self.hidden(X)))# 实例化MLP类,然后在每次调用前向传播函数的时候调用这些层
net = MLP() # 实例化的时候,()里面的参数是init中的参数
net(X) # 调用的时候,()里面的参数是forward中的参数.values(): 返回一个字典中所有值
# 自定义顺序块
class MySequential(nn.Module):def __init__(self, *args):super().__init__()for block in args:self._modules[block] = blockdef forward(self, X):for block in self._modules.values():X = block(X)return Xnet = MySequential(nn.Linear(20, 256), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(256, 100))
net (X)torch.mm:矩阵乘法
# 隐藏层固定的MLP
class FixedHiddenMLP(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.rand_weight = torch.rand((20, 20), requires_grad = False) #权重固定无需进行训练self.linear = nn.Linear(20, 20)def forward(self, X):X = self.linear(X)X = F.relu(torch.mm(X, self.rand_weight) + 1)X = self.linear(X)while X.abs().sum() > 1:X /= 2return X.sum()net = FixedHiddenMLP()
net(X)# 混合嵌套MLP
class NestMLP(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(20, 64), nn.ReLU(),nn.Linear(64, 32), nn.ReLU())self.linear = nn.Linear(32, 16)def forward(self, X):return self.linear(self.net(X))chimera = nn.Sequential(NestMLP(), nn.Linear(16, 20), FixedHiddenMLP())
chimera(X)参数管理
state_dict:一个Python字典,将每一层的参数映射成Tensor张量,只包含具有可学习参数的层,例如卷积层(Conv2d)和全连接层(Linear)。权重和偏置就是Linear层的状态。
import torch
from torch import nn
# 关注具有隐藏层的多感知机
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4, 8), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(8,1))
X = torch.rand(size = (2, 4))
net(X)
# 参数访问
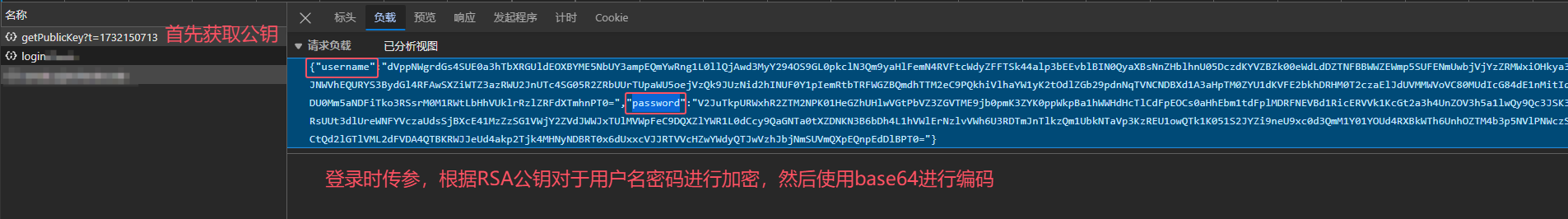
print(net[2].state_dict()) #net[2]拿到的是最后的输出层
bias:偏置,包括参数值和梯度值
bias.data:访问参数值
bias.grad:访问梯度值
named_parameters():返回一个包含元组的迭代器,每个元组包含两个元素,参数的名称和参数的值。
# 目标函数
print(type(net[2].bias))
print(net[2].bias)
print(net[2].bias.data) # 参数值
net[2].weight.grad == None # 梯度值# 一次性访问所有参数
print(*[(name, param.shape) for name, param in net[0].named_parameters()])
print(*[(name, param.shape) for name, param in net.named_parameters()])
# ReLU没有参数所以拿不出
net.state_dict()['2.bias'].data
# 通过名字获取想要的参数
![]()


net.add_module(name, module): 添加每一层,并且为每一层增加了一个单独的名字。
# 从嵌套块收集函数
def block1():return nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4, 8), nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(8, 4), nn.ReLU())def block2():net = nn.Sequential()for i in range(4):net.add_module(f'block{i}', block1())return netrgnet = nn.Sequential(block2(), nn.Linear(4, 1))
rgnet(X)
print(rgnet)
torch.nn.init模块中的所有函数都用于初始化神经网络参数,因此它们都在torch.no_grad()模式下运行,autograd不会将其考虑在内。
nn.init.normal_(tensor, mean=0.0, std=1.0): 将tensor变成指定mean和std正态分布
torch.nn.init.zeros_(tensor): 将tensor置零
torch.nn.init.constant_(tensor, val): 用val数值填充tensor
# 内置初始化
def init_normal(m):if type(m) == nn.Linear:nn.init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0, std=0.01)nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)net.apply(init_normal)
net[0].weight.data[0], net[0].bias.data[0]def init_constant(m):if type(m) == nn.Linear:nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)net.apply(init_constant)
net[0].weight.data[0], net[0].bias.data[0]
![]()
torch.nn.ini.xavier_uniform_(tensor, gain=1.0
):
# 对某些块应用不同的初始化方法
def xavier(m):if type(m) == nn.Linear:nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)def init_42(m):if type(m) == nn.Linear:nn. init.constant_(m.weight, 42)net[0].apply(xavier)
net[2].apply(init_42)
print(net[0].weight.data[0])
print(net[2].weight.data)
nn.init.uniform_(tensor, val1, val2): 将tensor变成均匀分布
def my_init(m):if type(m) == nn.Linear:print("Init",*[(name, param.shape) for name, param in m.named_parameters()][0])nn.init.uniform_(m.weight, -10, 10)m.weight.data *= m.weight.data.abs() >= 5net.apply(my_init)
net[0].weight[:2]
net[0].weight.data[:]+=1
net[0].weight.data[0,0]=42
net[0].weight.data[0]

# 参数绑定
shared = nn.Linear(8, 8)
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(4, 8), nn.ReLU(), shared, nn.ReLU(), shared, nn.ReLU(), nn.Linear(8, 1))
net(X)
print(net[2].weight.data[0] == net[4].weight.data[0])
net[2].weight.data[0,0] = 100
print(net[2].weight.data[0] == net[4].weight.data[0])自定义层
# 自定义层
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import nnclass CenteredLayer(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super().__init__()def forward(self, X):return X - X.mean()layer = CenteredLayer()
layer(torch.FloatTensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]))
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(8, 128), CenteredLayer())
Y = net(torch.rand(4, 8))
Y.mean()class MyLinear(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_units, units):super().__init__()self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(in_units, units))self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(units,))def forward(self, X):linear = torch.matmul(X, self.weight.data) + self.bias.datareturn F.relu(linear)dense = MyLinear(5, 3)
dense.weight# 使用自定义层直接执行正向传播计算
dense(torch.rand(2,5))
net = nn.Sequential(MyLinear(64, 8), MyLinear(8, 1))
net(torch.rand(2, 64))读写文件
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import funcational as F
# 加载和保存张量
x = torch.arange(4)
torch.save(x, 'x-file')x2 = torch.load("x-file")# 存储一个张量列表,读回内存
y = torch.zeros(4)
torch.save([x, y], 'x-files')
x2, y2 = torch.load('x-files')
(x2, y2)
# 写入或读取字符串映射到张量的字典
mydict = {'x':x, 'y':y}
torch.save(mydict, 'mydict')
mydict2 = torch.load('mydict')# 加载和保存模型参数
class MLP(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.hidden = nn.Linear(20, 256)self.output = nn.Linear(256, 10)def forward(self, x):return self.output(F.relu(self.hidden(x)))net = MLP()
X = torch.randn(size=(2, 20))
Y = net(X)torch.save(net.state_dict(), 'mlp.params')# 实例化了原始多层感知机模型的一个备份
clone = MLP()
clone.load_state_dict(torch.load("mlp.params"))
clone.eval()Y_clone = clone(X)
Y_clone == Y