ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架

工具库:text_analysis_tools - 中文文本分析工具包
tags: [文本分析,文本分类,文本聚类,关键词,情感分析,文本纠错]
工具包功能覆盖:文本分类、文本聚类、文本相似性、关键词抽取、关键短语抽取、情感分析、文本纠错、文本摘要、主题关键词、同义词、近义词、事件三元组抽取
GitHub: https://github.com/murray-z/text_analysis_tools

工具:Redpanda Console - 开源的数据流处理工具
tags: [数据流]
Redpanda Console(前身是 Kowl),搭配可视化 UI,可用于快速管理和调试 Kafka/Redpanda 工作负载。
GitHub: https://github.com/redpanda-data/console


工具语言:Enso - 具有视觉和文本双重表示的交互式编程语言
tags: [计算机视觉,自然语言处理,编程语言]
‘Enso - Hybrid visual and textual functional programming.’
GitHub: https://github.com/enso-org/enso


工具框架:nvim-compleet - Neovim自动补全框架
tags: [代码补全,自动补全]
‘nvim-compleet - A Neovim autocompletion framework written in Rust’ by Riccardo Mazzarini
GitHub: https://github.com/noib3/nvim-compleet

工具模型:ClipCap-Chinese - 基于ClipCap的看图说话Image Caption模型
tags: [看图说话,图像字幕,image caption]
GitHub: https://github.com/yangjianxin1/ClipCap-Chinese

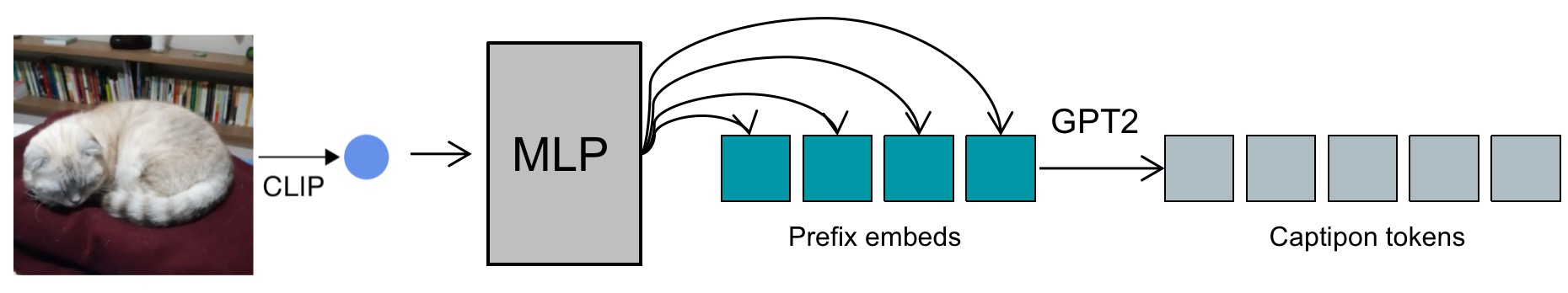
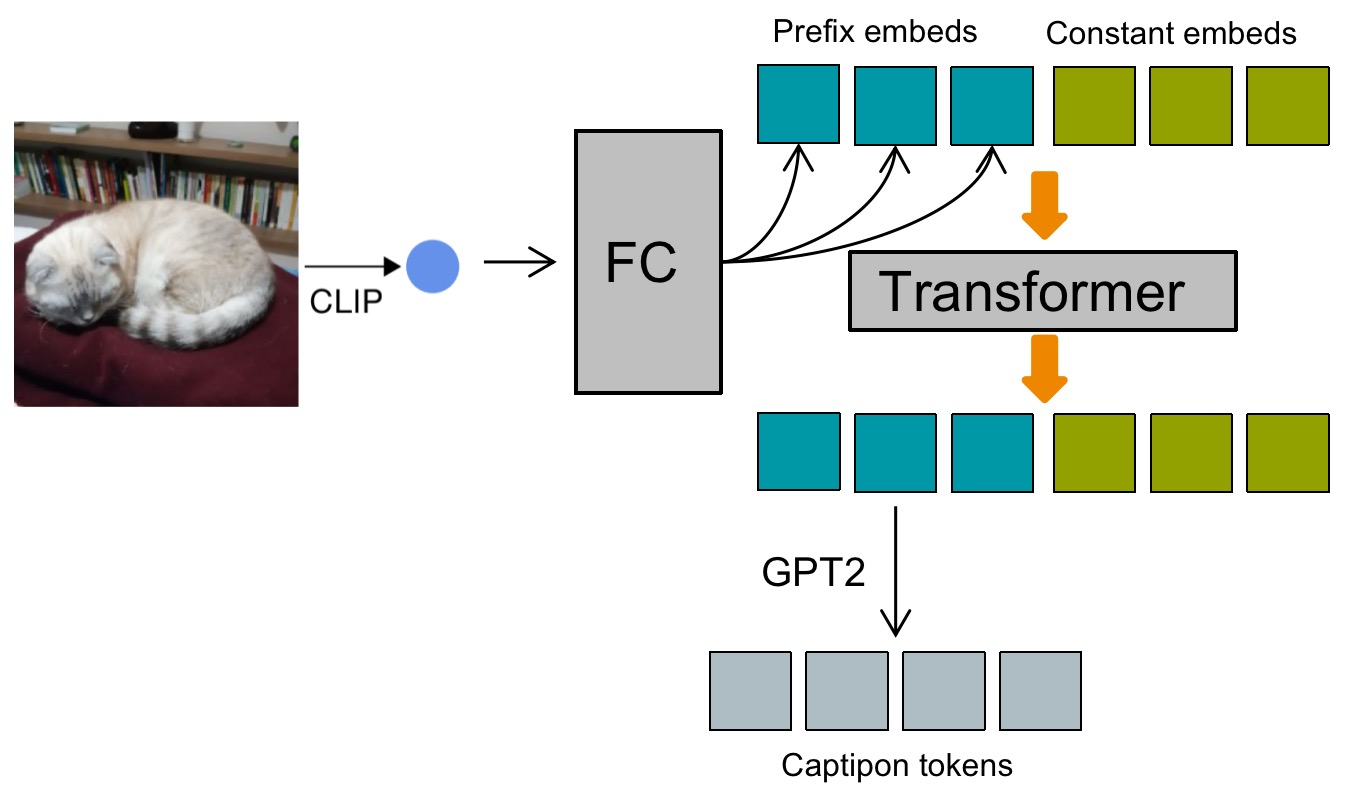

工具库:Dagger - 用于CI/CD pipeline的可移植开发套件
tags: [CI/CD,可移植开发]
‘Dagger - A portable devkit for CI/CD pipelines’
GitHub: https://github.com/dagger/dagger

2.项目&代码

Kaggle机器学习 / 数据科学 / 数据可视化 / 深度学习入门 Notebook推荐
tags: [数据科学,机器学习,数据可视化,深度学习,notebook,代码]
Data ScienceTutorial for Beginners

https://www.kaggle.com/code/kanncaa1/data-sciencetutorial-for-beginners
Machine Learning Tutorial for Beginners

https://www.kaggle.com/code/kanncaa1/machine-learning-tutorial-for-beginners/notebook
Python Data Visualizations
https://www.kaggle.com/code/benhamner/python-data-visualizations/notebook
Scikit-Learn ML from Start to Finish

https://www.kaggle.com/code/jeffd23/scikit-learn-ml-from-start-to-finish/notebook
TensorFlow deep NN
https://www.kaggle.com/code/kakauandme/tensorflow-deep-nn/notebook
3.博文&分享

资源分享:《如何做研究》北京交通大学系统与网络实验室收集的关于科研学习指南的资料。
tags: [科研,研究,指南]
GitHub: http://fangvv.github.io/Homepage/exp.html
4.数据&资源

数据集:UrbanNav - 开源城市定位算法基准测试多感官数据集
tags: [数据集,城市数据,定位数据]
‘UrbanNav:An Open-sourced Multisensory Dataset for Benchmarking Positioning Algorithms Designed for Urban Areas’ by PolyU Intelligent Positioning And Navigation Lab
GitHub: https://github.com/IPNL-POLYU/UrbanNavDataset




资源列表:以人为本AI阅读清单,重点是计算机视觉
tags: [AI资源,计算机视觉]
‘A reading list for some interesting papers on Human-centered AI, with a focus on computer vision - a reading list for human-centered AI’ by human-centeredAI
GitHub: https://github.com/human-centeredAI/awesomeHAI

资源列表:MLOPs Primer - MLOPs入门资源汇编
tags: [MLOP,资源列表]
‘MLOPs Primer - A collection of resources to learn about MLOPs.’ by DAIR.AI
GitHub: https://github.com/dair-ai/MLOPs-Primer

5.研究&论文

可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
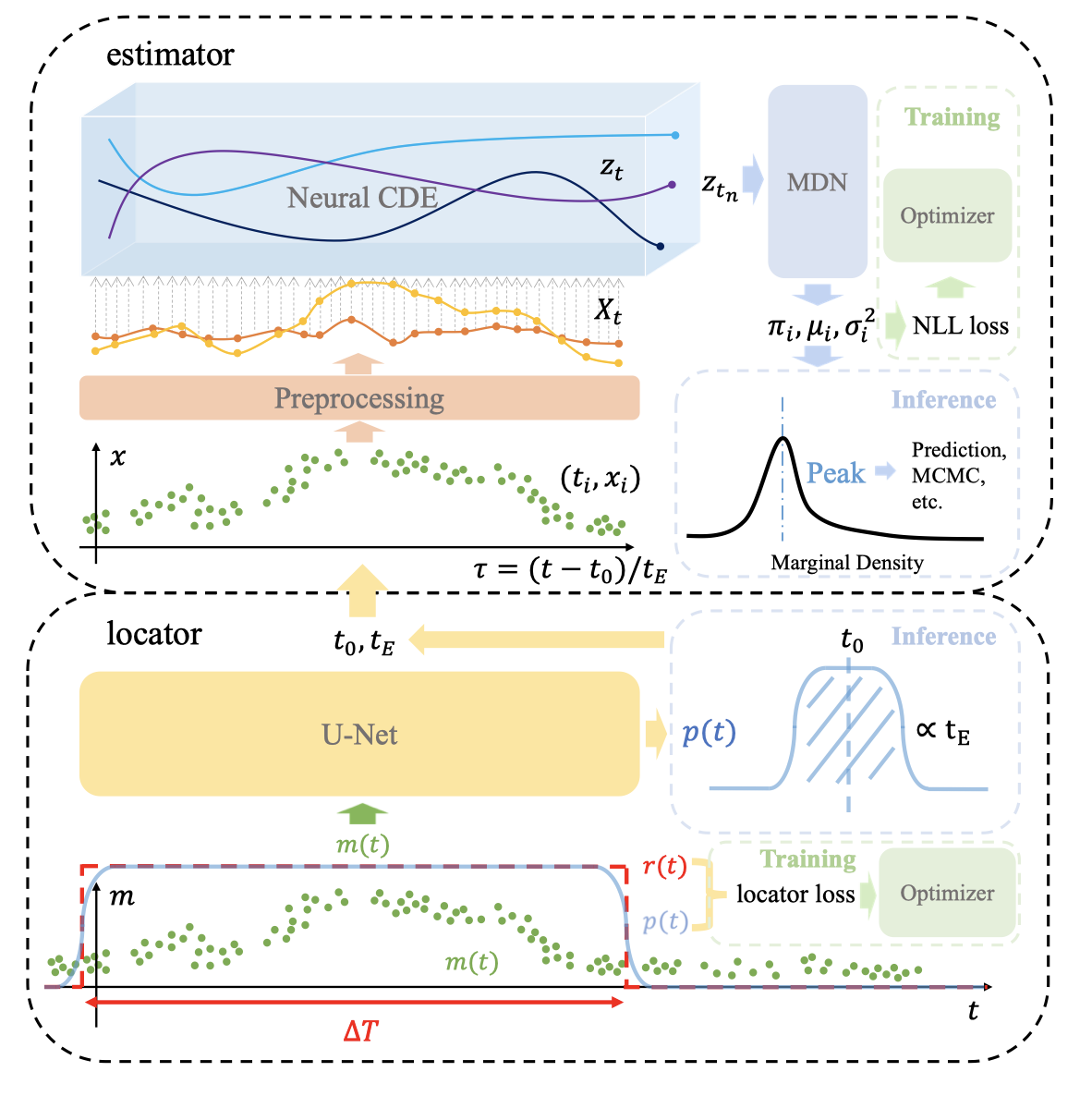
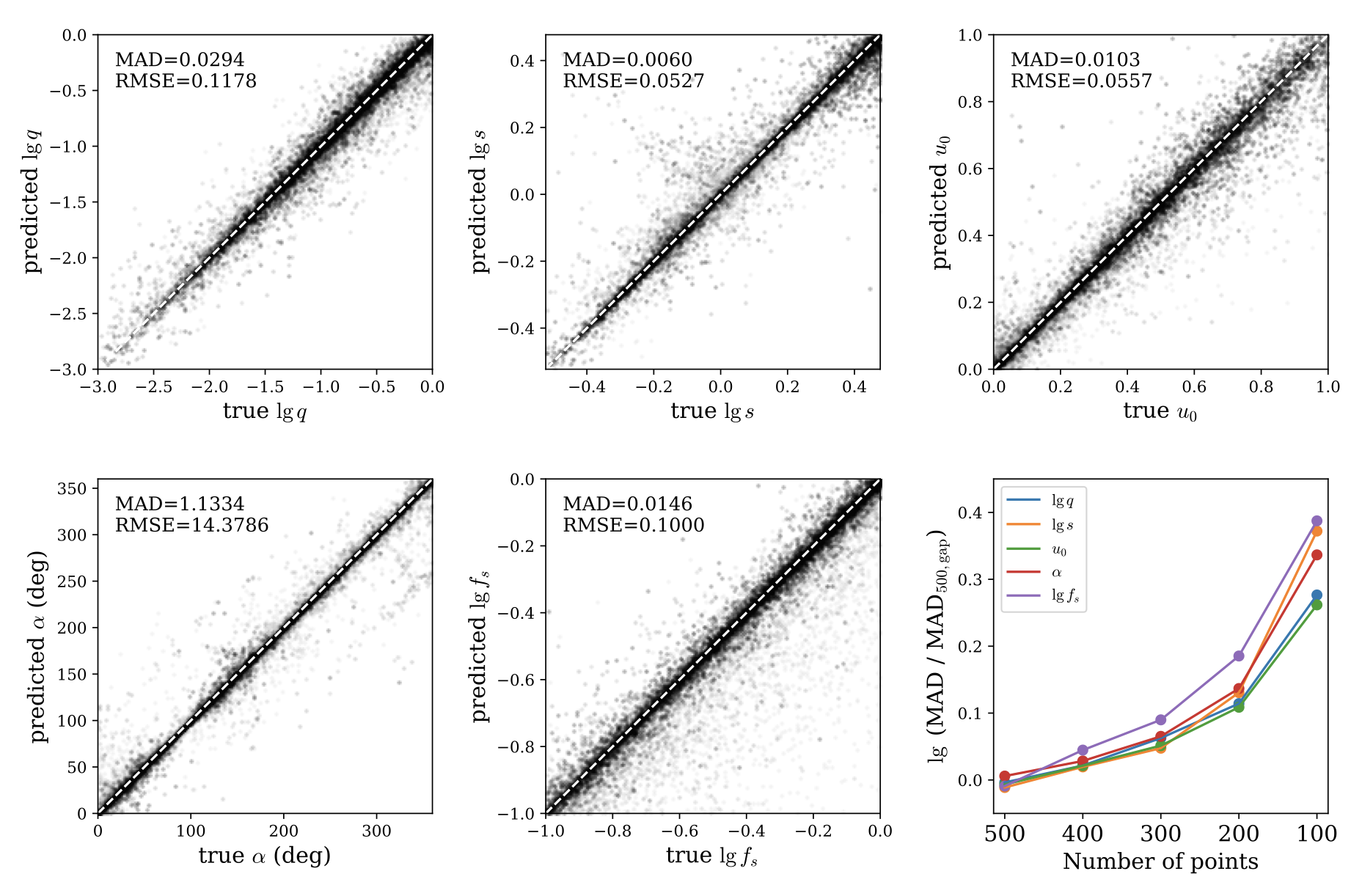
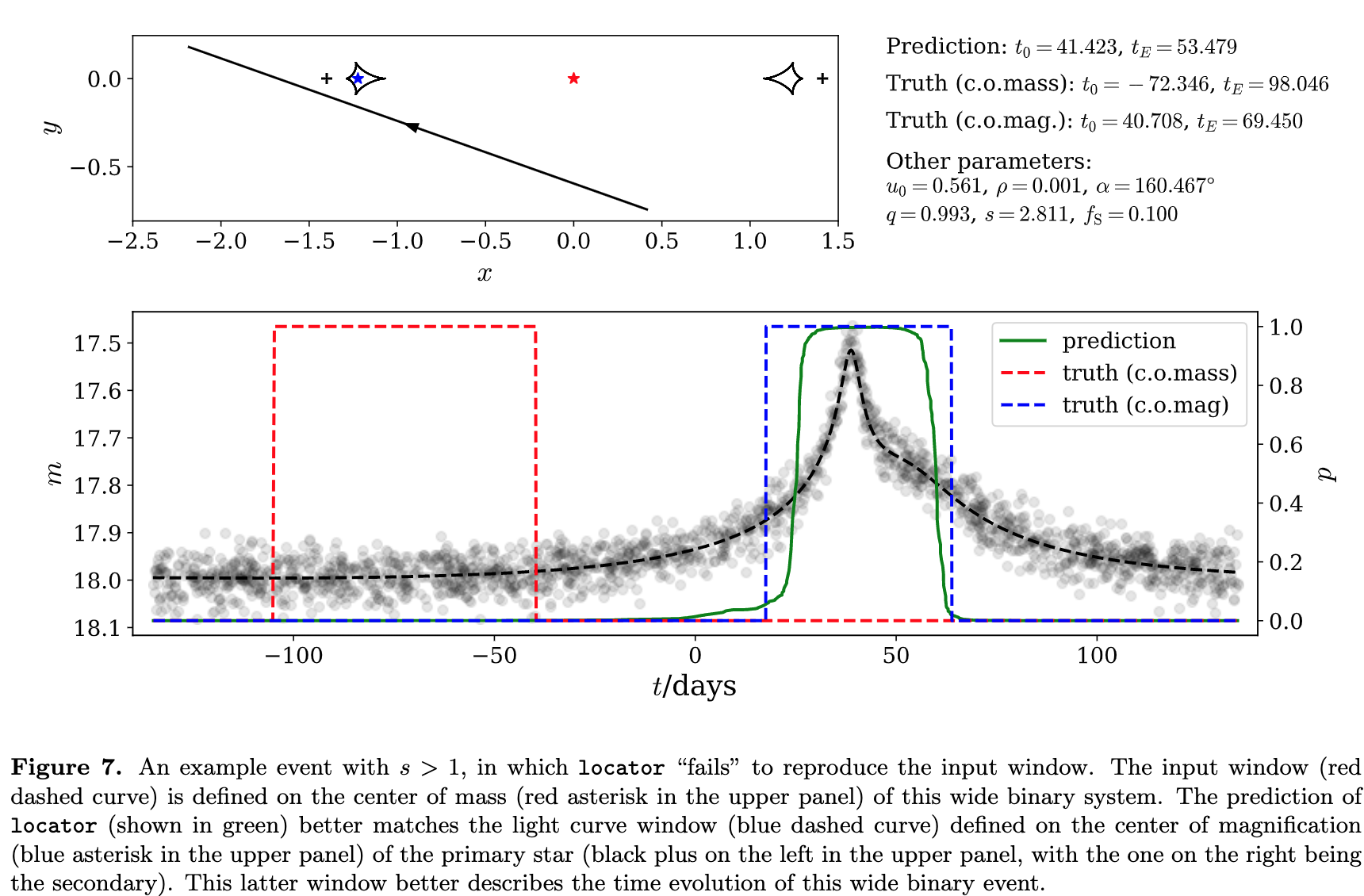
论文:MAGIC: Microlensing Analysis Guided by Intelligent Computation
论文标题:MAGIC: Microlensing Analysis Guided by Intelligent Computation
论文时间:16 Jun 2022
所属领域:时间序列
对应任务:时间序列
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08199
代码实现:https://github.com/JasonZHM/magic-microlensing
论文作者:Haimeng Zhao, Wei Zhu
论文简介:The key feature of MAGIC is the introduction of neural controlled differential equation, which provides the capability to handle light curves with irregular sampling and large data gaps. / MAGIC 的关键特性是引入了神经控制的微分方程,它提供了处理不规则采样和大数据间隙的光变曲线的能力。
论文摘要:The modeling of binary microlensing light curves via the standard sampling-based method can be challenging, because of the time-consuming light curve computation and the pathological likelihood landscape in the high-dimensional parameter space. In this work, we present MAGIC, which is a machine learning framework to efficiently and accurately infer the microlensing parameters of binary events with realistic data quality. In MAGIC, binary microlensing parameters are divided into two groups and inferred separately with different neural networks. The key feature of MAGIC is the introduction of neural controlled differential equation, which provides the capability to handle light curves with irregular sampling and large data gaps. Based on simulated light curves, we show that MAGIC can achieve fractional uncertainties of a few percent on the binary mass ratio and separation. We also test MAGIC on a real microlensing event. MAGIC is able to locate the degenerate solutions even when large data gaps are introduced. As irregular samplings are common in astronomical surveys, our method also has implications to other studies that involve time series.
由于光变曲线计算耗时且高维参数空间中的病理似然性景观,通过基于标准采样的方法对二元微透镜光变曲线进行建模可能具有挑战性。在这项工作中,我们提出了 MAGIC,它是一个机器学习框架,可以有效、准确地推断具有真实数据质量的二元事件的微透镜参数。在 MAGIC 中,二元微透镜参数分为两组,分别用不同的神经网络进行推断。 MAGIC 的主要特点是引入了神经控制的微分方程,它提供了处理不规则采样和大数据间隙的光变曲线的能力。基于模拟的光变曲线,我们表明 MAGIC 可以在二元质量比和分离上实现百分之几的分数不确定性。我们还在一个真实的微透镜事件中测试了 MAGIC。即使引入了大的数据间隙,MAGIC 也能够定位退化的解决方案。由于不规则采样在天文调查中很常见,我们的方法也对其他涉及时间序列的研究产生影响。
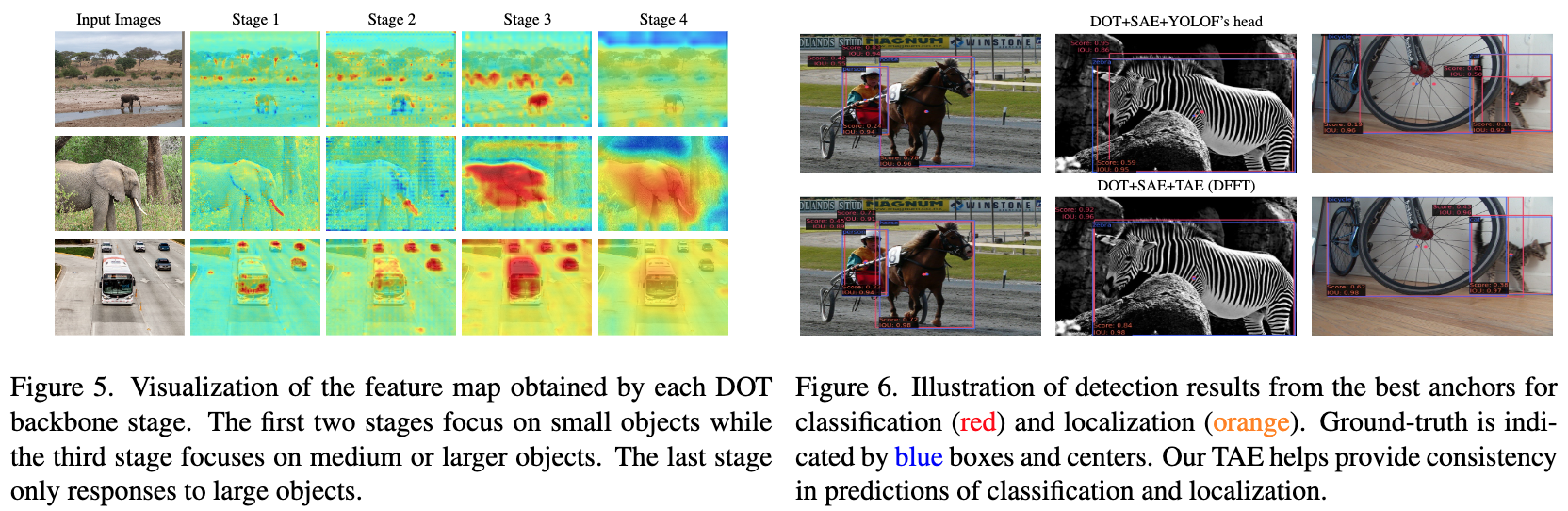
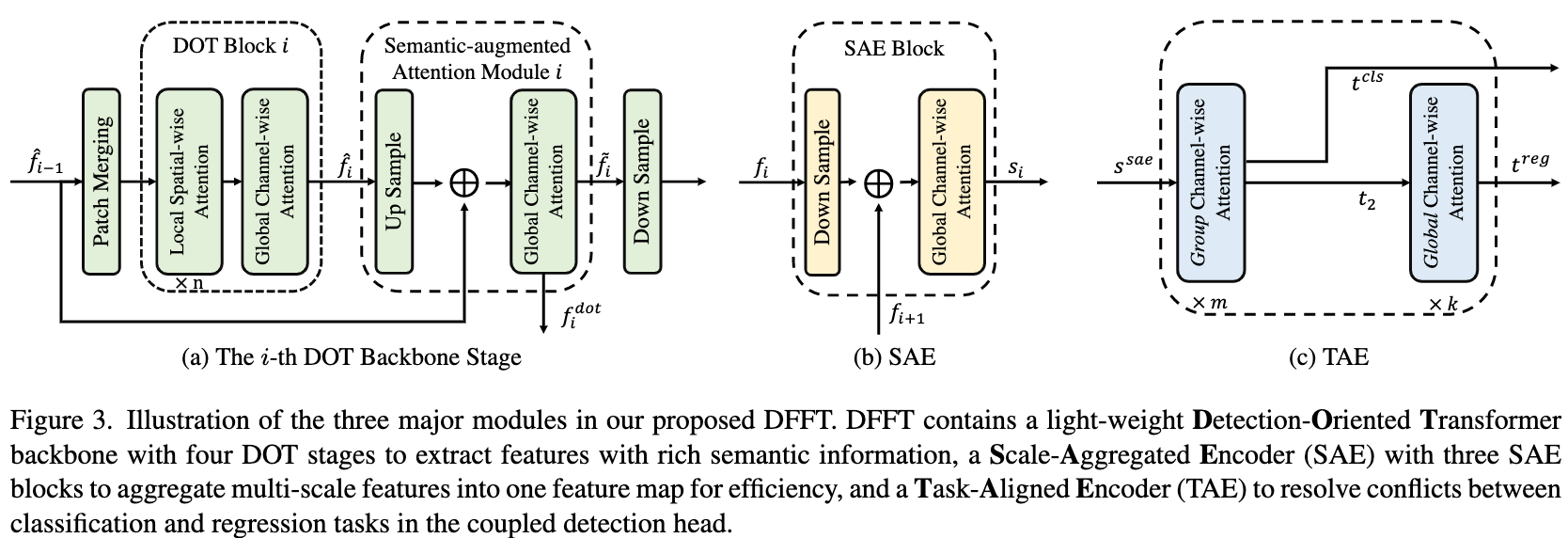
论文:Efficient Decoder-free Object Detection with Transformers
论文标题:Efficient Decoder-free Object Detection with Transformers
论文时间:14 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:object-detection,Object Detection,目标检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.06829
代码实现:https://github.com/Pealing/DFFT
论文作者:Peixian Chen, Mengdan Zhang, Yunhang Shen, Kekai Sheng, Yuting Gao, Xing Sun, Ke Li, Chunhua Shen
论文简介:A natural usage of ViTs in detection is to replace the CNN-based backbone with a transformer-based backbone, which is straightforward and effective, with the price of bringing considerable computation burden for inference. / ViTs 在检测中的一个自然用法是用基于transformer的主干替换基于 CNN 的主干,这简单有效,但代价是为推理带来了相当大的计算负担。
论文摘要:Vision transformers (ViTs) are changing the landscape of object detection approaches. A natural usage of ViTs in detection is to replace the CNN-based backbone with a transformer-based backbone, which is straightforward and effective, with the price of bringing considerable computation burden for inference. More subtle usage is the DETR family, which eliminates the need for many hand-designed components in object detection but introduces a decoder demanding an extra-long time to converge. As a result, transformer-based object detection can not prevail in large-scale applications. To overcome these issues, we propose a novel decoder-free fully transformer-based (DFFT) object detector, achieving high efficiency in both training and inference stages, for the first time. We simplify objection detection into an encoder-only single-level anchor-based dense prediction problem by centering around two entry points: 1) Eliminate the training-inefficient decoder and leverage two strong encoders to preserve the accuracy of single-level feature map prediction; 2) Explore low-level semantic features for the detection task with limited computational resources. In particular, we design a novel lightweight detection-oriented transformer backbone that efficiently captures low-level features with rich semantics based on a well-conceived ablation study. Extensive experiments on the MS COCO benchmark demonstrate that DFFT_SMALL outperforms DETR by 2.5% AP with 28% computation cost reduction and more than 10x fewer training epochs. Compared with the cutting-edge anchor-based detector RetinaNet, DFFT_SMALL obtains over 5.5% AP gain while cutting down 70% computation cost.
视觉transformer(ViTs)正在改变目标检测方法的格局。 ViT 在检测中的一个自然用途是用基于transformer的主干替换基于 CNN 的主干,这简单有效,但代价是为推理带来了相当大的计算负担。更微妙的用法是 DETR 系列,它消除了在对象检测中对许多手工设计组件的需求,但引入了需要超长收敛时间的解码器。因此,基于 Transformer 的目标检测无法在大规模应用中流行。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了一种新颖的无解码器完全基于transformer(DFFT)的目标检测器,首次在训练和推理阶段都实现了高效率。我们通过围绕两个入口点将目标检测简化为仅编码器的基于锚点的单级密集预测问题:1)消除训练效率低下的解码器并利用两个强大的编码器来保持单级特征图预测的准确性; 2)探索计算资源有限的检测任务的低级语义特征。特别是,我们设计了一种新颖的轻量级面向检测的 Transformer 主干,它基于精心设计的消融研究有效地捕获具有丰富语义的低级特征。在 MS COCO 基准上进行的大量实验表明,DFFT_SMALL 比 DETR 高出 2.5% AP,计算成本降低了 28%,训练 epoch 减少了 10 倍以上。与尖端的基于锚的检测器 RetinaNet 相比,DFFT_SMALL 获得了超过 5.5% 的 AP 增益,同时降低了 70% 的计算成本。



论文:Pythae: Unifying Generative Autoencoders in Python – A Benchmarking Use Case
论文标题:Pythae: Unifying Generative Autoencoders in Python – A Benchmarking Use Case
论文时间:16 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Reconstruction,图像重建
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08309
代码实现:https://github.com/clementchadebec/benchmark_VAE
论文作者:Clément Chadebec, Louis J. Vincent, Stéphanie Allassonnière
论文简介:In recent years, deep generative models have attracted increasing interest due to their capacity to model complex distributions. / 近年来,深度生成模型因其对复杂分布建模的能力而引起了越来越多的兴趣。
论文摘要:In recent years, deep generative models have attracted increasing interest due to their capacity to model complex distributions. Among those models, variational autoencoders have gained popularity as they have proven both to be computationally efficient and yield impressive results in multiple fields. Following this breakthrough, extensive research has been done in order to improve the original publication, resulting in a variety of different VAE models in response to different tasks. In this paper we present Pythae, a versatile open-source Python library providing both a unified implementation and a dedicated framework allowing straightforward, reproducible and reliable use of generative autoencoder models. We then propose to use this library to perform a case study benchmark where we present and compare 19 generative autoencoder models representative of some of the main improvements on downstream tasks such as image reconstruction, generation, classification, clustering and interpolation. The open-source library can be found at https://github.com/clementchadebec/benchmark_VAE
近年来,深度生成模型因其对复杂分布建模的能力而引起了越来越多的兴趣。在这些模型中,变分自编码器已广受欢迎,因为它们已被证明具有计算效率并在多个领域产生了令人印象深刻的结果。在这一突破之后,为了改进原始出版物,已经进行了广泛的研究,从而产生了各种不同的 VAE 模型来响应不同的任务。在本文中,我们介绍了 Pythae,一个多功能的开源 Python 库,提供统一的实现和专用框架,允许直接、可重复和可靠地使用生成自动编码器模型。然后,我们建议使用这个库来执行案例研究基准测试,其中我们展示并比较了 19 个生成自动编码器模型,这些模型代表了下游任务的一些主要改进,例如图像重建、生成、分类、聚类和插值。可以在 https://github.com/clementchadebec/benchmark_VAE 找到开源库。


论文:Robust deep learning based protein sequence design using ProteinMPNN
论文标题:Robust deep learning based protein sequence design using ProteinMPNN
论文时间:bioRxiv 2022
所属领域:医疗
对应任务:Drug Discovery,Protein Folding,Protein Function Prediction,Protein Structure Prediction,药物发现,蛋白质折叠,蛋白质功能预测,蛋白质结构预测
论文地址:https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101
代码实现:https://github.com/dauparas/ProteinMPNN
论文作者:J. Dauparas, I. Anishchenko, N. Bennett, H. Bai, R. J. Ragotte, L. F. Milles, B. I. M. Wicky, A. Courbet, R. J. de Haas, N. Bethel, P. J. Y. Leung, T. F. Huddy, S. Pellock, D. Tischer, F. Chan, B. Koepnick, H. Nguyen, A. Kang, B. Sankaran, A. K. Bera, N. P. King, D. Baker
论文简介:While deep learning has revolutionized protein structure prediction, almost all experimentally characterized de novo protein designs have been generated using physically based approaches such as Rosetta. / 虽然深度学习彻底改变了蛋白质结构预测,但几乎所有以实验为特征的从头蛋白质设计都是使用基于物理的方法(如 Rosetta)生成的。
论文摘要:While deep learning has revolutionized protein structure prediction, almost all experimentally characterized de novo protein designs have been generated using physically based approaches such as Rosetta. Here we describe a deep learning based protein sequence design method, ProteinMPNN, with outstanding performance in both in silico and experimental tests. The amino acid sequence at different positions can be coupled between single or multiple chains, enabling application to a wide range of current protein design challenges. On native protein backbones, ProteinMPNN has a sequence recovery of 52.4%, compared to 32.9% for Rosetta. Incorporation of noise during training improves sequence recovery on protein structure models, and produces sequences which more robustly encode their structures as assessed using structure prediction algorithms. We demonstrate the broad utility and high accuracy of ProteinMPNN using X-ray crystallography, cryoEM and functional studies by rescuing previously failed designs, made using Rosetta or AlphaFold, of protein monomers, cyclic homo-oligomers, tetrahedral nanoparticles, and target binding proteins.
虽然深度学习已经彻底改变了蛋白质结构预测,但几乎所有具有实验特征的从头蛋白质设计都是使用基于物理的方法(如 Rosetta)生成的。在这里,我们描述了一种基于深度学习的蛋白质序列设计方法,ProteinMPNN,具有出色的在计算机和实验测试中的表现。不同位置的氨基酸序列可以在单链或多链之间偶联,从而能够应用于当前广泛的蛋白质设计挑战。在天然蛋白质骨架上,ProteinMPNN 的序列恢复率为 52.4%,而 Rosetta 为 32.9%。在训练过程中加入噪声改善了蛋白质结构模型的序列恢复,并产生了更稳健地编码其结构的序列,如使用结构预测算法评估的那样。我们使用 X 射线晶体学、cryoEM 和功能研究通过重做优化以前失败的设计(使用 Rosetta 或 AlphaFold 制作的蛋白质单体、环状同源低聚物、四面体纳米颗粒和靶结合蛋白)证明了 ProteinMPNN 的广泛实用性和高精度。

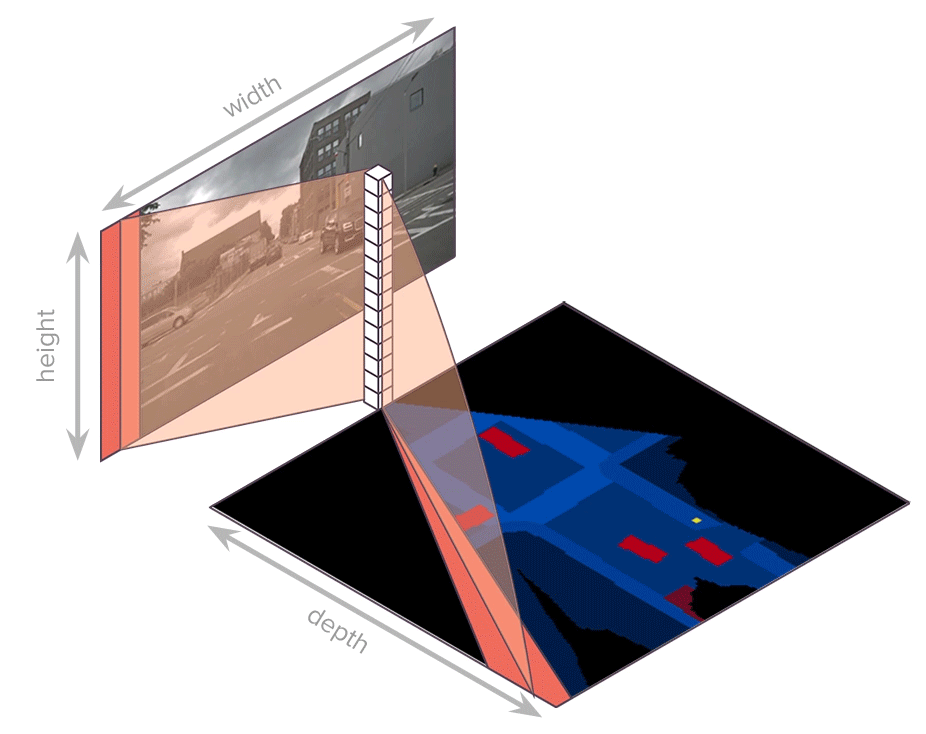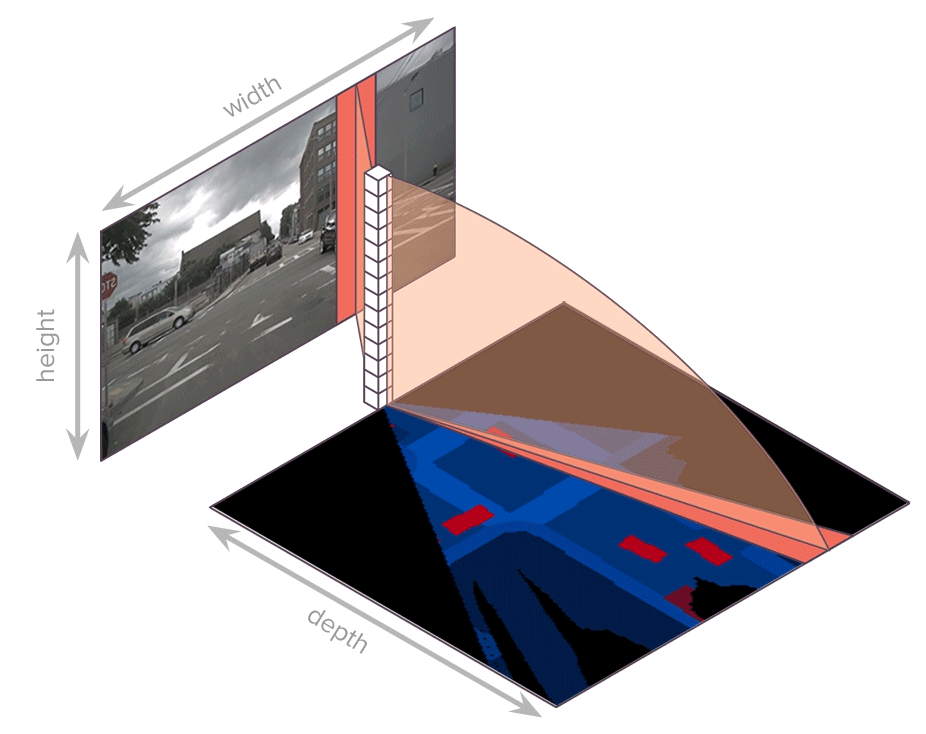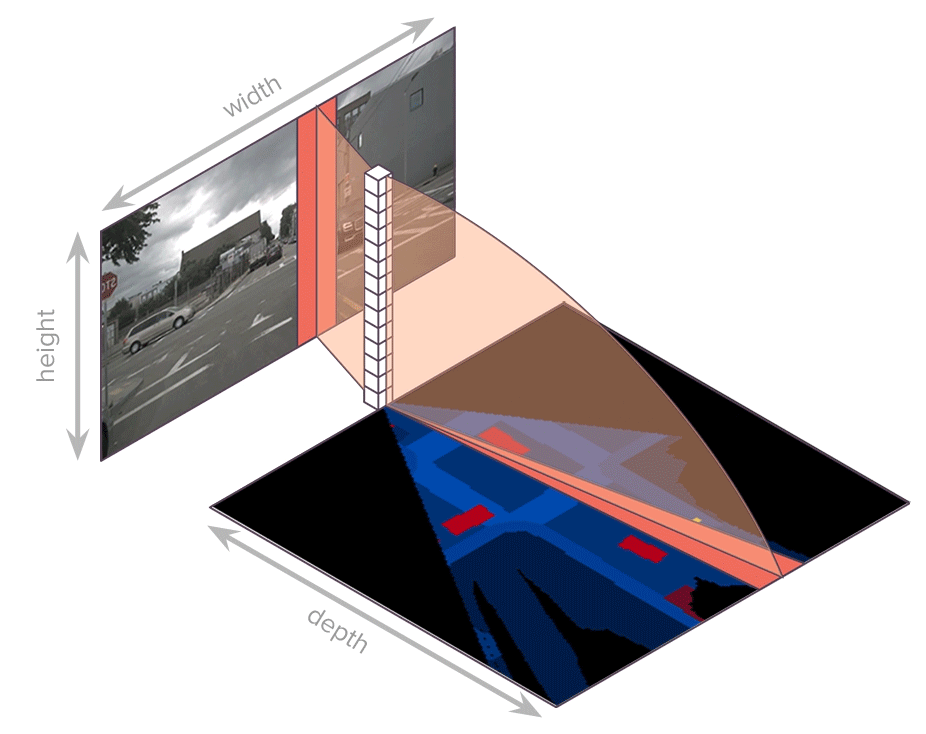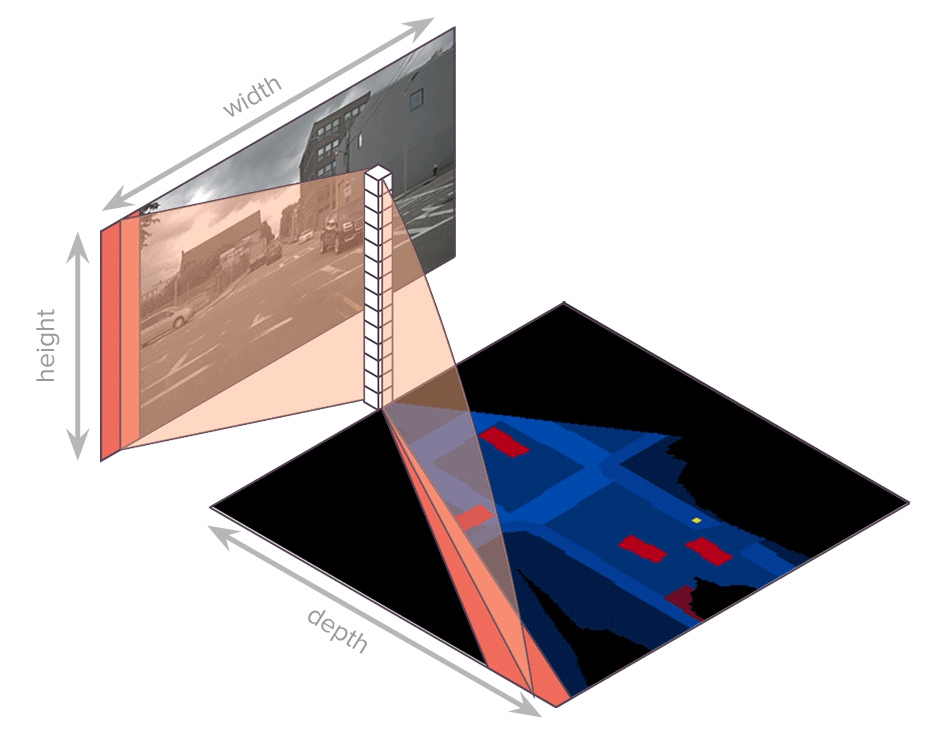
论文:Translating Images into Maps
论文标题:Translating Images into Maps
论文时间:3 Oct 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:视觉映射
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.00966
代码实现:https://github.com/avishkarsaha/translating-images-into-maps
论文作者:Avishkar Saha, Oscar Mendez Maldonado, Chris Russell, Richard Bowden
论文简介:We show how a novel form of transformer network can be used to map from images and video directly to an overhead map or bird’s-eye-view (BEV) of the world, in a single end-to-end network. / 我们展示了如何使用一种新颖的transformer网络形式,在单个端到端网络中将图像和视频直接映射到世界的俯视图或鸟瞰图 (BEV)。
论文摘要:We approach instantaneous mapping, converting images to a top-down view of the world, as a translation problem. We show how a novel form of transformer network can be used to map from images and video directly to an overhead map or bird’s-eye-view (BEV) of the world, in a single end-to-end network. We assume a 1-1 correspondence between a vertical scanline in the image, and rays passing through the camera location in an overhead map. This lets us formulate map generation from an image as a set of sequence-to-sequence translations. Posing the problem as translation allows the network to use the context of the image when interpreting the role of each pixel. This constrained formulation, based upon a strong physical grounding of the problem, leads to a restricted transformer network that is convolutional in the horizontal direction only. The structure allows us to make efficient use of data when training, and obtains state-of-the-art results for instantaneous mapping of three large-scale datasets, including a 15% and 30% relative gain against existing best performing methods on the nuScenes and Argoverse datasets, respectively. We make our code available on https://github.com/avishkarsaha/translating-images-into-maps
我们把瞬时映射问题,即“将图像转换为自上而下的视图”,作为一个翻译问题来处理。我们展示了如何使用一种新颖的transformer网络形式,在单个端到端网络中将图像和视频直接映射到世界的俯视图或鸟瞰图 (BEV)。我们假设图像中的垂直扫描线与通过俯视图中的相机位置的光线之间存在 1-1 对应关系。这让我们可以将图像的映射生成公式化为一组序列到序列的转换。将问题定位为翻译允许网络在解释每个像素的作用时使用图像的上下文。这种基于问题的强大物理基础的受约束公式会导致受限制的transformer网络仅在水平方向上卷积。该结构使我们能够在训练时有效地利用数据,并为三个大规模数据集的瞬时映射获得最先进的结果,包括相对于 nuScenes 上现有最佳性能方法的 15% 和 30% 的相对增益和 Argoverse 数据集。我们在 https://github.com/avishkarsaha/translating-images-into-maps 上提供我们的代码。
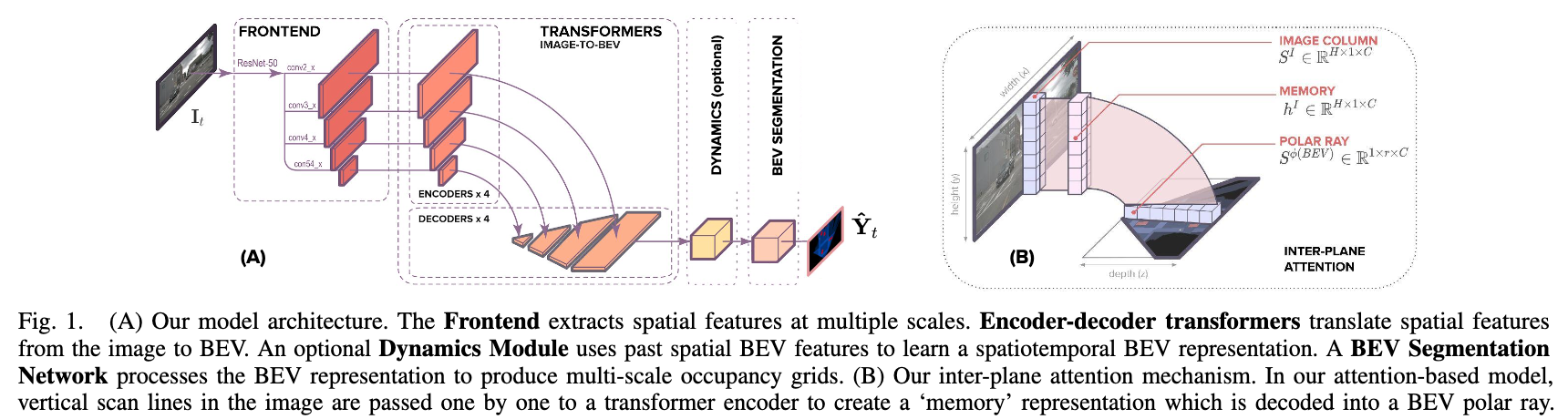
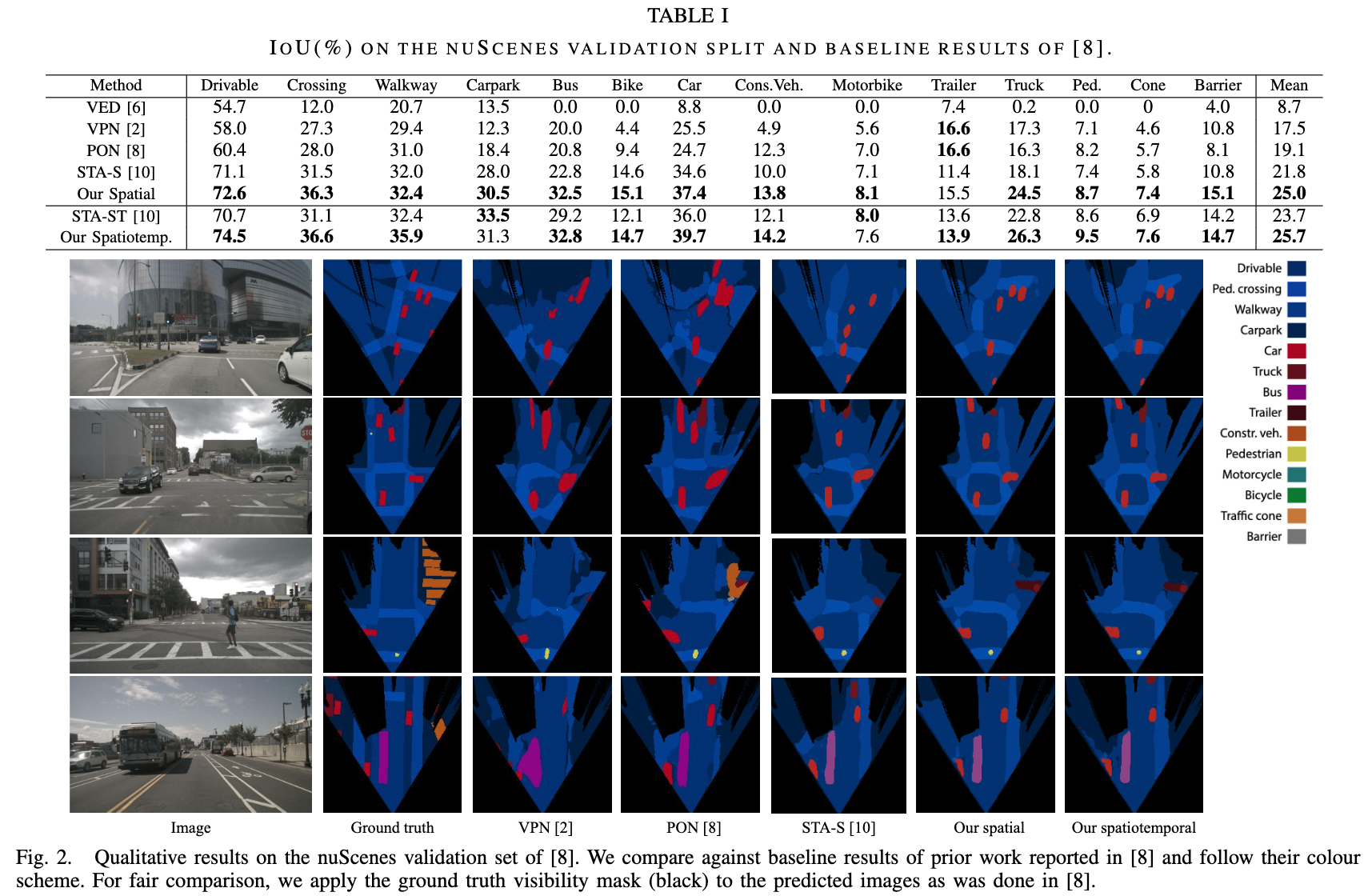
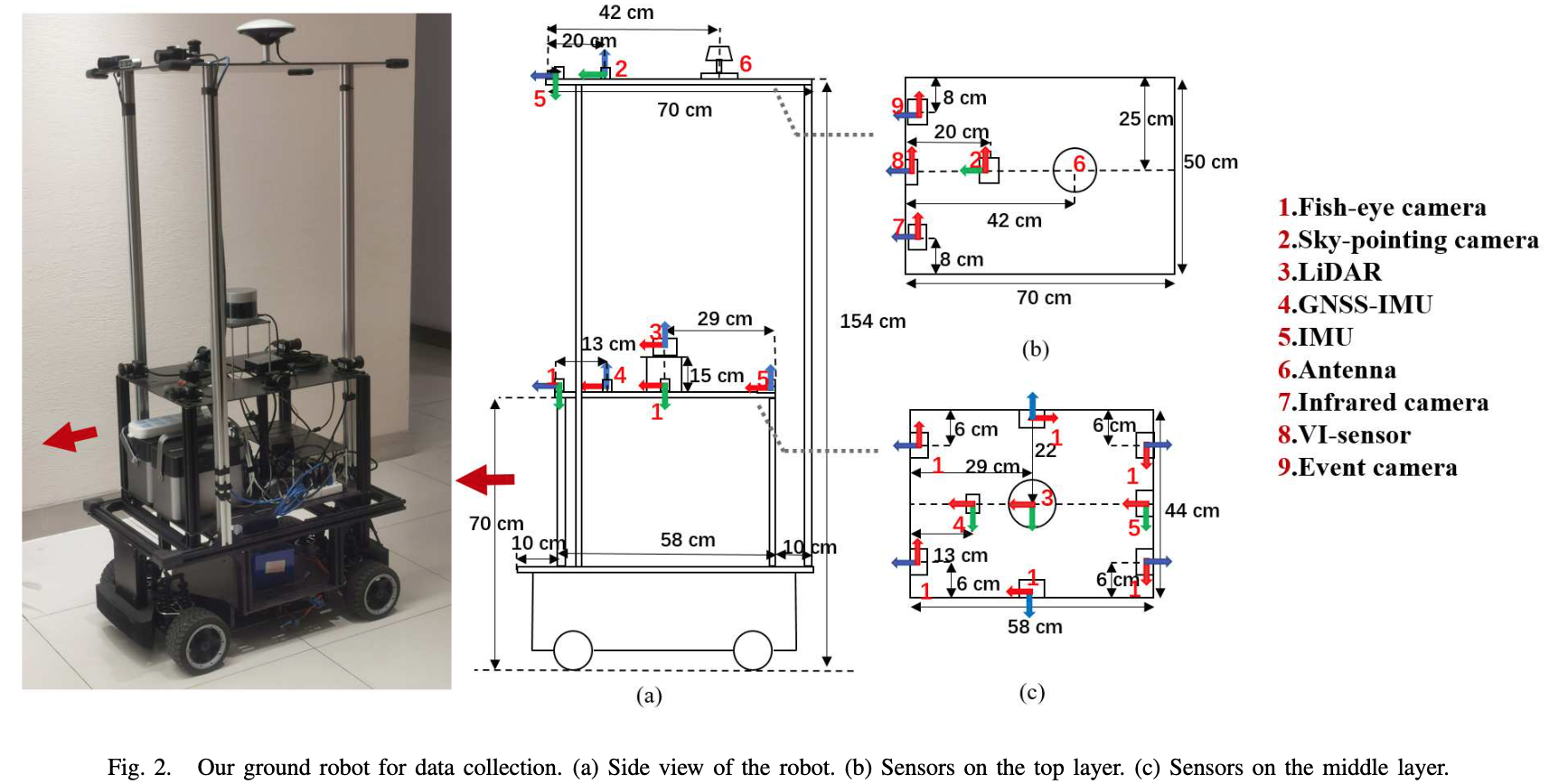
论文:M2DGR: A Multi-sensor and Multi-scenario SLAM Dataset for Ground Robots
论文标题:M2DGR: A Multi-sensor and Multi-scenario SLAM Dataset for Ground Robots
论文时间:19 Dec 2021
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.13659
代码实现:https://github.com/SJTU-ViSYS/M2DGR
论文作者:Jie Yin, Ang Li, Tao Li, Wenxian Yu, Danping Zou
论文简介:We introduce M2DGR: a novel large-scale dataset collected by a ground robot with a full sensor-suite including six fish-eye and one sky-pointing RGB cameras, an infrared camera, an event camera, a Visual-Inertial Sensor (VI-sensor), an inertial measurement unit (IMU), a LiDAR, a consumer-grade Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and a GNSS-IMU navigation system with real-time kinematic (RTK) signals. / 我们介绍 M2DGR:由地面机器人收集的新型大规模数据集,具有完整的传感器套件,包括六个鱼眼和一个指向天空的 RGB 摄像头、一个红外摄像头、一个事件摄像头、一个视觉惯性传感器(VI-sensor)、惯性测量单元 (IMU)、激光雷达、消费级全球导航卫星系统 (GNSS) 接收器和具有实时运动 (RTK) 信号的 GNSS-IMU 导航系统。
论文摘要:We introduce M2DGR: a novel large-scale dataset collected by a ground robot with a full sensor-suite including six fish-eye and one sky-pointing RGB cameras, an infrared camera, an event camera, a Visual-Inertial Sensor (VI-sensor), an inertial measurement unit (IMU), a LiDAR, a consumer-grade Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver and a GNSS-IMU navigation system with real-time kinematic (RTK) signals. All those sensors were well-calibrated and synchronized, and their data were recorded simultaneously. The ground truth trajectories were obtained by the motion capture device, a laser 3D tracker, and an RTK receiver. The dataset comprises 36 sequences (about 1TB) captured in diverse scenarios including both indoor and outdoor environments. We evaluate state-of-the-art SLAM algorithms on M2DGR. Results show that existing solutions perform poorly in some scenarios. For the benefit of the research community, we make the dataset and tools public. The webpage of our project is https://github.com/SJTU-ViSYS/M2DGR
我们介绍了 M2DGR:一种由地面机器人收集的新型大规模数据集,具有完整的传感器套件,包括六个鱼眼和一个指向天空的 RGB 相机、一个红外相机、一个事件相机、一个视觉惯性传感器(VI-sensor)、惯性测量单元 (IMU)、激光雷达、消费级全球导航卫星系统 (GNSS) 接收器和具有实时运动 (RTK) 信号的 GNSS-IMU 导航系统。所有这些传感器都经过了良好的校准和同步,并且同时记录了它们的数据。地面实况轨迹由运动捕捉设备、激光 3D 跟踪器和 RTK 接收器获得。该数据集包括在包括室内和室外环境在内的不同场景中捕获的 36 个序列(约 1TB)。我们在 M2DGR 上评估最先进的 SLAM 算法。结果表明,现有解决方案在某些情况下表现不佳。为了研究社区的利益,我们将数据集和工具公开。我们项目的网页是 https://github.com/SJTU-ViSYS/M2DGR


论文:Combining Label Propagation and Simple Models Out-performs Graph Neural Networks
论文标题:Combining Label Propagation and Simple Models Out-performs Graph Neural Networks
论文时间:ICLR 2021
所属领域:图算法
对应任务:Node Classification,Node Property Prediction,节点分类,节点属性预测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.13993
代码实现:https://github.com/CUAI/CorrectAndSmooth , https://github.com/dmlc/dgl/tree/master/examples/pytorch/correct_and_smooth , https://github.com/Chillee/CorrectAndSmoothOGB , https://github.com/sangyx/gtrick/tree/main/benchmark/pyg , https://github.com/xnuohz/CorrectAndSmooth-dgl
论文作者:Qian Huang, Horace He, Abhay Singh, Ser-Nam Lim, Austin R. Benson
论文简介:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are the predominant technique for learning over graphs. / 图神经网络(GNN)是学习图的主要技术。
论文摘要:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are the predominant technique for learning over graphs. However, there is relatively little understanding of why GNNs are successful in practice and whether they are necessary for good performance. Here, we show that for many standard transductive node classification benchmarks, we can exceed or match the performance of state-of-the-art GNNs by combining shallow models that ignore the graph structure with two simple post-processing steps that exploit correlation in the label structure: (i) an “error correlation” that spreads residual errors in training data to correct errors in test data and (ii) a “prediction correlation” that smooths the predictions on the test data. We call this overall procedure Correct and Smooth (C&S), and the post-processing steps are implemented via simple modifications to standard label propagation techniques from early graph-based semi-supervised learning methods. Our approach exceeds or nearly matches the performance of state-of-the-art GNNs on a wide variety of benchmarks, with just a small fraction of the parameters and orders of magnitude faster runtime. For instance, we exceed the best known GNN performance on the OGB-Products dataset with 137 times fewer parameters and greater than 100 times less training time. The performance of our methods highlights how directly incorporating label information into the learning algorithm (as was done in traditional techniques) yields easy and substantial performance gains. We can also incorporate our techniques into big GNN models, providing modest gains. Our code for the OGB results is at https://github.com/Chillee/CorrectAndSmooth
图神经网络(GNN)是图学习的主要技术。然而,对于 GNN 为何在实践中取得成功以及它们是否对于良好性能是必要的,人们知之甚少。在这里,我们展示了对于许多标准的转导节点分类基准,我们可以通过将忽略图结构的浅层模型与两个利用相关性的简单后处理步骤相结合来超越或匹配最先进的 GNN 的性能。标签结构:(i) 一种“误差相关性”,将训练数据中的残差传播到纠正测试数据中的错误;(ii) 一种“预测相关性”,用于平滑对测试数据的预测。我们将此整体过程称为正确和平滑 (C&S),后处理步骤是通过对早期基于图的半监督学习方法的标准标签传播技术的简单修改来实现的。我们的方法在各种基准测试中超过或几乎与最先进的 GNN 的性能相匹配,却有更小量级的参数和数量级级别的运行推理效率提升。例如,我们超过了已知最好的GNN在 OGB-Products 数据集上的性能,参数少 137 倍,训练时间少 100 倍以上。我们的方法的性能突出了如何将标签信息直接结合到学习算法中(就像在传统技术中所做的那样)产生简单而可观的性能提升。我们还可以将我们的技术整合到大型 GNN 模型中,提供适度的收益。我们的 OGB 结果代码位于 https://github.com/Chillee/CorrectAndSmooth


论文:Multi-Graph Fusion Networks for Urban Region Embedding
论文标题:Multi-Graph Fusion Networks for Urban Region Embedding
论文时间:24 Jan 2022
所属领域:图算法
对应任务:Crime Prediction,犯罪预测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.09760
代码实现:https://github.com/wushangbin/mgfn
论文作者:Shangbin Wu, Xu Yan, Xiaoliang Fan, Shirui Pan, Shichao Zhu, Chuanpan Zheng, Ming Cheng, Cheng Wang
论文简介:Human mobility data contains rich but abundant information, which yields to the comprehensive region embeddings for cross domain tasks. / 人类流动性数据包含丰富的信息,这产生了跨领域任务的综合区域嵌入。
论文摘要:Learning the embeddings for urban regions from human mobility data can reveal the functionality of regions, and then enables the correlated but distinct tasks such as crime prediction. Human mobility data contains rich but abundant information, which yields to the comprehensive region embeddings for cross domain tasks. In this paper, we propose multi-graph fusion networks (MGFN) to enable the cross domain prediction tasks. First, we integrate the graphs with spatio-temporal similarity as mobility patterns through a mobility graph fusion module. Then, in the mobility pattern joint learning module, we design the multi-level cross-attention mechanism to learn the comprehensive embeddings from multiple mobility patterns based on intra-pattern and inter-pattern messages. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on real-world urban datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed MGFN outperforms the state-of-the-art methods by up to 12.35% improvement.
从人类流动数据中学习城市区域的嵌入可以揭示区域的功能,然后实现相关但不同的任务,例如犯罪预测。人类移动数据包含丰富但丰富的信息,这产生了跨域任务的综合区域嵌入。在本文中,我们提出了多图融合网络(MGFN)来实现跨域预测任务。首先,我们通过移动图融合模块将具有时空相似性的图整合为移动模式。然后,在移动模式联合学习模块中,我们设计了多级交叉注意机制,以基于模式内和模式间消息从多个移动模式中学习综合嵌入。最后,我们对现实世界的城市数据集进行了广泛的实验。实验结果表明,所提出的 MGFN 比最先进的方法提高了 12.35%。


我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。

- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处
- 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~