药物研发的过程和意义
- 1. 药物研发过程简介
- 2. 药物发现
- 2.1 Target Discovery
- 2.2 Target Validation
- 2.3 Lead Compound Identification
- 2.4 Lead Optimization
- 3. 临床前药物开发
- 4. 药物设计的意义
- 5. 药物研发案例:卡托普利
- 参考资料
1. 药物研发过程简介
现代药物的研发是一个从基因到药物的研究过程,通常经历药物研究和药物开发两大阶段,需要耗费1-3年时间和2亿美元。药物研究阶段起始于新靶标的发现(Target Discovery),从基因研究开始,研究人员依靠大量实验数据获得与疾病相关的基因,进一步发现相应的蛋白,然后寻找与疾病相关的药物靶标,再对它们进行靶标验证(Target Validation)。
研究人员在这个基础上,运用结构生物学手段,解析靶标的三维结构,发现和优化先导化合物(Lead Compound Identification and Optimization),获得成药性比较好的候选药物。先导化合物的发现和优化是创新药物研究成败的关键。
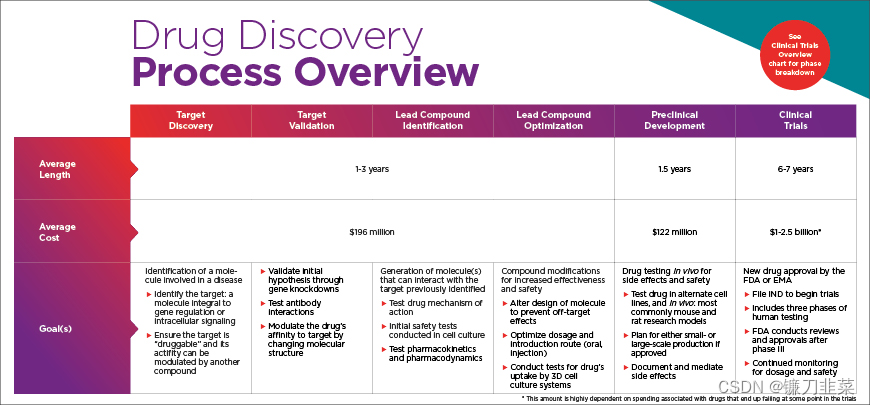
图1 药物研究到开发的过程
2. 药物发现
2.1 Target Discovery
During the first phase, known as target discovery, in vitro research is performed to identify targets involved in specific diseases. A target is usually a molecule integral to gene regulation or intracellular signaling, such as a nucleic acid sequence or protein. In order to decide on which target to focus research efforts, one needs to ensure that the molecule is “druggable” — that its activity can be modulated by an exogenous compound.
在第一阶段,即靶点发现阶段,进行体外研究以确定涉及特定疾病的靶点。 靶标通常是基因调控或细胞内信号传导不可或缺的分子,例如核酸序列或蛋白质。 为了决定将研究工作集中在哪个目标上,需要确保该分子是“可成药的”——它的活性可以被外源性化合物调节。
2.2 Target Validation
After selecting a potential target, researchers must demonstrate that it is involved in the progression of a given disease and that its activity can be regulated. Conducting careful and precise target validation experiments is essential for the success of drug development in the following stages.
在选择了一个潜在的目标后,研究人员必须证明它参与了特定疾病的进展,并且其活动是可以调节的。 进行仔细和精确的目标验证实验对于以下阶段药物开发的成功至关重要。
2.3 Lead Compound Identification
Lead compound identification is the process of identifying or creating a compound that can interact with the target previously selected. Researchers can conduct screening experiments to identify possible naturally-occurring compounds that can be re-purposed as drugs. Alternatively, synthetic compounds can be designed that will both target the predicted target while not interfering with other cellular processes. In addition to testing the mechanism of action of the drug, initial safety tests are conducted in cell culture. Both the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the drug are also tested — how it is metabolized and how it affects various bodily functions, respectively.
先导化合物识别是识别或创建可以与先前选择的目标相互作用的化合物的过程。 研究人员可以进行筛选实验,以确定可能的天然化合物,这些化合物可以重新用作药物。 或者,可以设计合成化合物,既可以靶向预测的靶标,又不干扰其他细胞过程。 除了测试药物的作用机制外,还在细胞培养中进行了初步的安全性测试。 还测试了药物的药代动力学和药效学——分别是如何代谢以及如何影响各种身体功能。
2.4 Lead Optimization
Once a compound (or compounds) have been identified, they need to be optimized for efficacy and safety. The design of synthetic molecules can be altered to prevent off-target binding, making them less likely to interact with molecules other than the target. Additionally, the optimal dosage and introduction route (oral, injection) is tested on two- and three-dimensional cell culture platforms.
一旦确定了一种(或多种)化合物,就需要对其功效和安全性进行优化。 可以改变合成分子的设计以防止脱靶结合,使它们不太可能与目标以外的分子相互作用。 此外,在二维和三维细胞培养平台上测试了最佳剂量和引入途径(口服、注射)。
This stage also includes safety testing prior to introduction into multiple in vivo animal models in the following preclinical development stage. Animal models such as mice and rats can be used at this stage, however some tests for safety are first conducted in vitro.
此阶段还包括在以下临床前开发阶段引入多个体内动物模型之前的安全性测试。 在这个阶段可以使用小鼠和大鼠等动物模型,但是首先在体外进行一些安全性测试。
One specific example of a three-dimensional platform is a scaffold developed for the testing of new glaucoma drugs (Torrejon, KY, 2013). Glaucoma can result from increased intraocular pressure in the eye, which is directly related to the outflow of aqueous humor through a structure called the trabecular meshwork. The scaffold developed is a three-dimensional trabecular meshwork which effectively mimics the microenvironment around the eye. By screening drugs first in this 3D in vitro setting, animal models used in the next stage will have better chances of encountering a safe and effective drug.
三维平台的一个具体示例是为测试新的青光眼药物而开发的支架(Torrejon,KY,2013)。 青光眼可能是由眼内压升高引起的,这与房水通过称为小梁网的结构流出直接相关。 开发的支架是一种三维小梁网,可有效模拟眼睛周围的微环境。 通过在这种 3D 体外环境中首先筛选药物,下一阶段使用的动物模型将有更好的机会遇到安全有效的药物。
3. 临床前药物开发
药物开发阶段需要经历**临床前研究(Preclinical Development)和临床一、二、三期研究 (Clinical Trials)**后才能最终上市。
- 临床前研究包括药物合成、体内活性测试、生物利用度、药动学性质以及安全性研究。
- 临床一期研究通常需要对20-80位健康受试者进行药物耐受性和有效剂量的评估。
- 临床二期研究需要对100-300位患者进行初步的药物安全性和疗效的评估。
- 临床三期研究则在多个医疗中心对1000-5000位患者进行药物的有效性、安全性以及长期服用药物后的副作用的评估。
完成前三期研究后,药物可以正式上市。上市后,为了进一步完善药物在人身上的应用评估,还需要投入第四期扩大性临床研究。药物开发的整个阶段一般需要耗费7-9年时间和大概10-26亿美元。
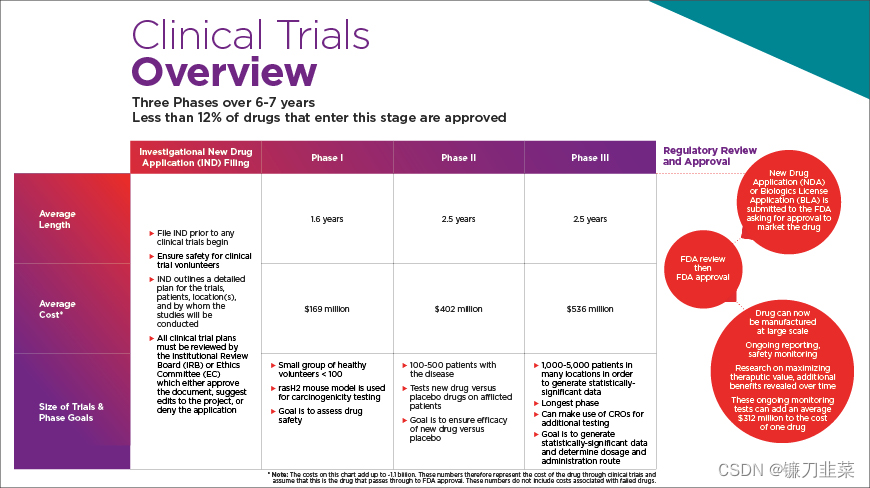
图2. 药物的临床测试阶段
药物开发的临床前阶段涉及在动物模型中进行广泛的测试,以确定该药物对人体试验是否安全,以及它是否能发挥应有的作用。 具体来说,需要监测和解决药物的副作用。
the chances of a drug making it to phase III clinical trials is just 12%
4. 药物设计的意义
迄今,临床上仍有大量疾病缺乏安全有效的治疗药物。这种情况一方面源于新疾病的出现,比如自2019年至今肆虐全球的新型冠状病毒肺炎(COVID-19),另一方面源于对已知疾病缺乏对症的药物,例如癌症。因此,新药的研发非常重要。
新药的发现是一个高投入、长周期、高风险的过程,可谓步步荆棘、道阻且长。在二十世纪早期,药物的发现主要依靠疾病表型筛选,通过偶然发现和随机盲目的大规模筛选来实现。这种方法周期长、效率低。到了二十世纪末期,药物分子设计理论和技术的发展,在很大程度上改善了这一现状。药物化学家以疾病靶标和已知活性化合物的结构、性质及其相互作用等先验知识为指 导,用理性设计的方法取代随机盲目的大规模筛选模式,有目的地开发新药。这种方法节省了新药创新工作中的人力物力,显著提高了新药研发的效率和速度。
5. 药物研发案例:卡托普利
通过经典抗压药"卡托普利"的设计实例来说明药物的研发过程。卡托普利是一款治疗高血压的药物。按照药物研究的流程,第一步就是研究疾病产生的机制并确定合适的药物作用靶标。英国药理学家John Vane通过系统研究发现肾素-血管紧张素系统与高血压的形成密切相关,在比较分析了多个作用靶标之后,确认血管紧张素转化酶(ACE)为降压药物的作用靶标。
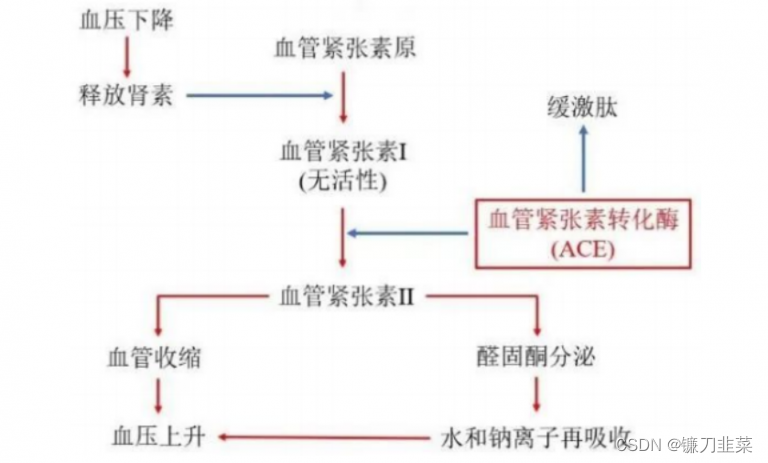
图3. 肾素-血管紧张素-醛固酮系统
确定了靶标之后,第二步就是要寻找能作用于ACE的先导化合物。研究人员在蛇毒中发现了 一种降血压物质,并将其命名为替普罗肽(Teprotide)。
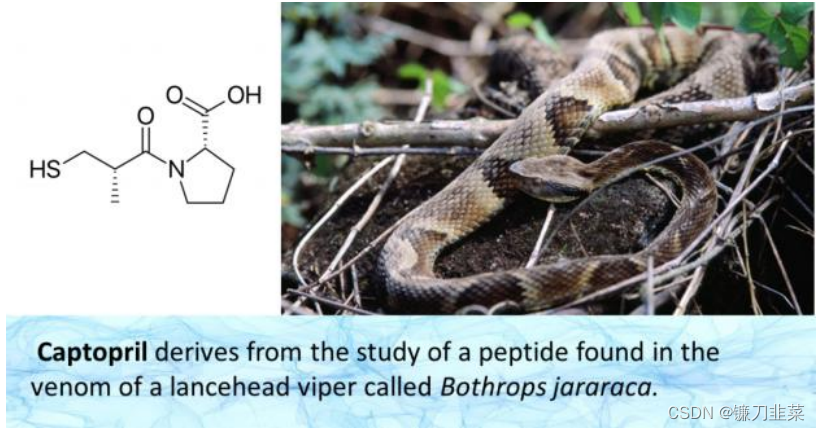
图4. 蛇毒中发现了替普罗泰
与此同时,研究人员还合成了几个替普罗肽的类似肽,并发现C端的氨基酸序列为Phe-Ala-Pro时,其抑制ACE的活性很好。在这个基础之上,研究人员继续研究ACE的结构,并构建了ACE 的活性位点模型,发现了氨基酸残基为L-Pro的羧基烷烃酰基拟肽小分子类似物的抑制活性最好。科研 人员对先导化合物进行了大量的结构修饰,并最终获得卡托普利这个结构简单但抑制活性高的药物,由此开发出一类全新的高血压治疗药物。
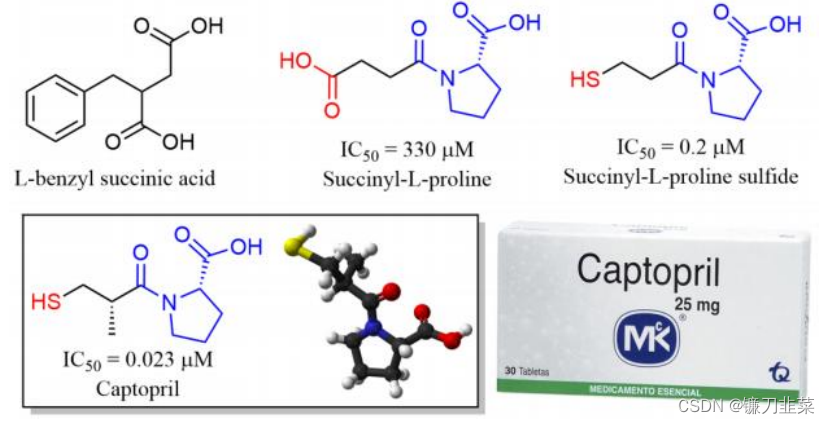
图5. 卡托普利开发过程中代表性的活性化合物
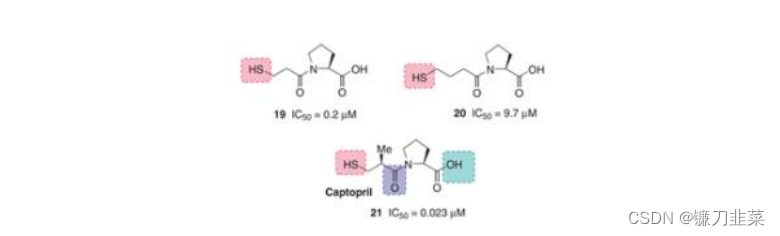
图6. 优化后的结构
参考资料
[1] https://www.taconic.com/taconic-insights/quality/drug-development-process.html
[2] http://www.yinfotek.com/blog