文献来源:Sadik A, Dardani C, Pagoni P, et al. Parental inflammatory bowel disease and autism in children. Nat Med. 2022;28(7):1406-1411. doi:10.1038/s41591-022-01845-9

目录
1.基本信息
2. 主要内容概览:
3. 主要结果
3.1. Study 1: Parental IBD diagnoses and autism in children
3.2. Study 2: Genetic correlation between IBD and autism
3.3. Study 3: Polygenic risk for IBD and broad autistic traits
3.4. Study 4: Causal effect of genetic liability to IBD on autism
4. 结论
Expert opinion
Behind the paper
1.基本信息
期刊:nature medicine
影响因子2021:87
分区:肯定是一区top
机构:英国布里斯托大学
发表时间:2022年7月
一句话介绍:通过多个人群数据分析父母炎症性肠病与子代自闭症的关联和因果:瑞典国家登记数据队列、连锁不平衡分数回归、多基因风险评分、两样本双向孟德尔随机化。
2. 主要内容概览:
文章整体分为四个部分
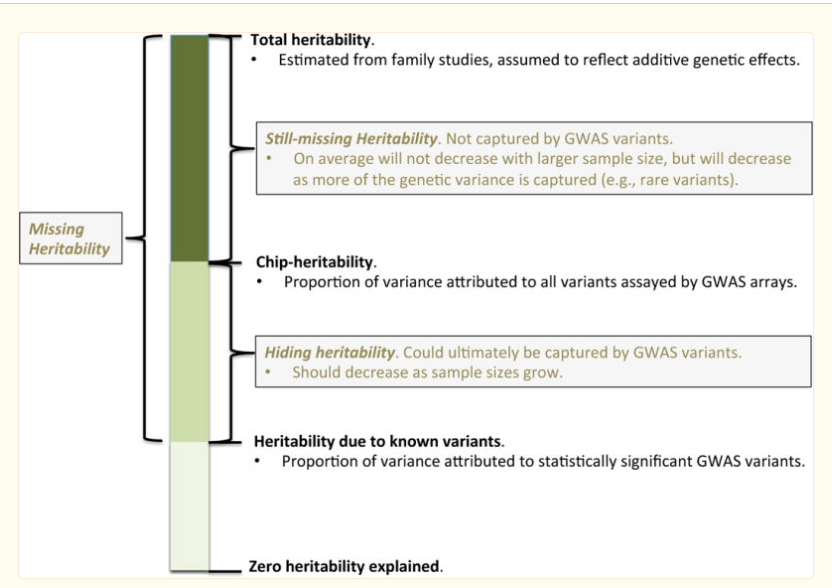
Four complementary studies (Fig. 1 and Table 1) to investigate:
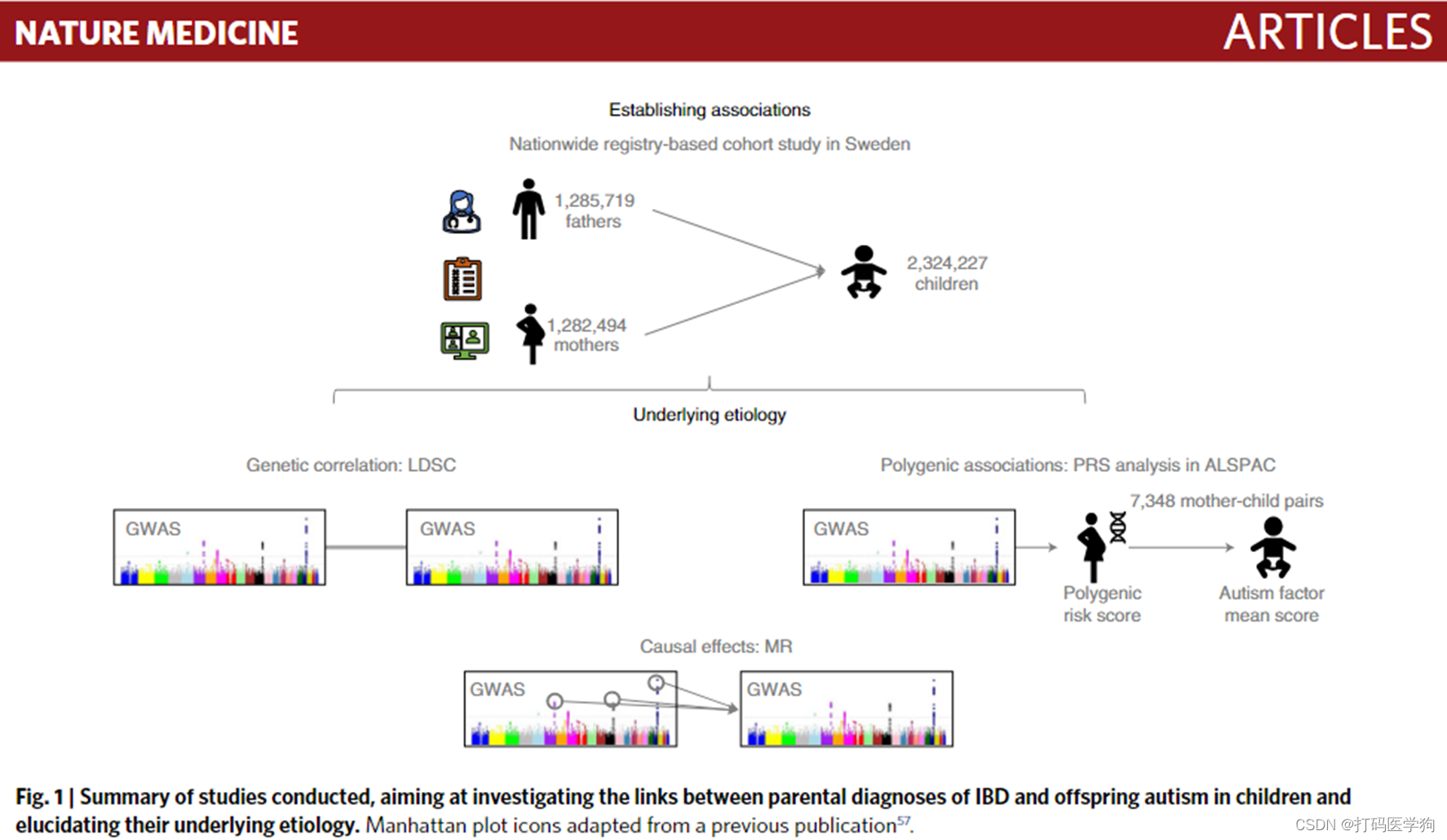
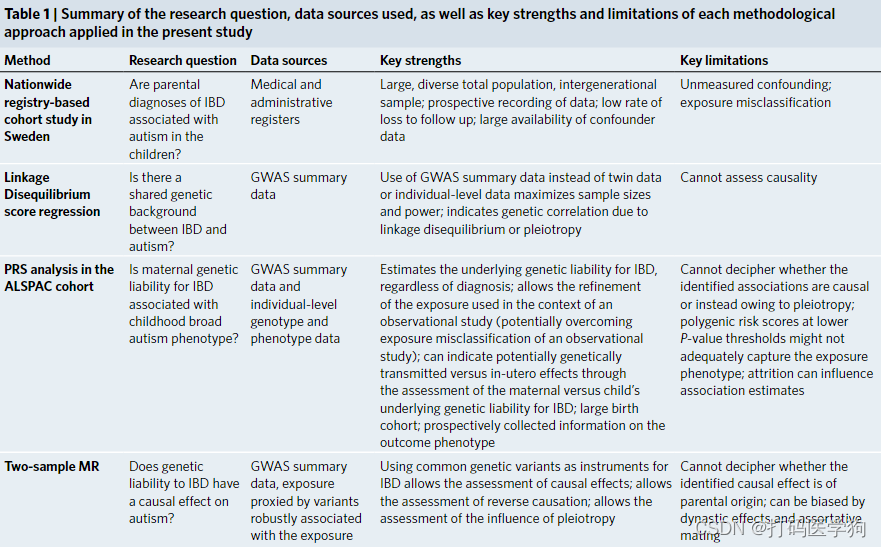
3. 主要结果
3.1. Study 1: Parental IBD diagnoses and autism in children
瑞典国家登记数据队列研究纳排标准
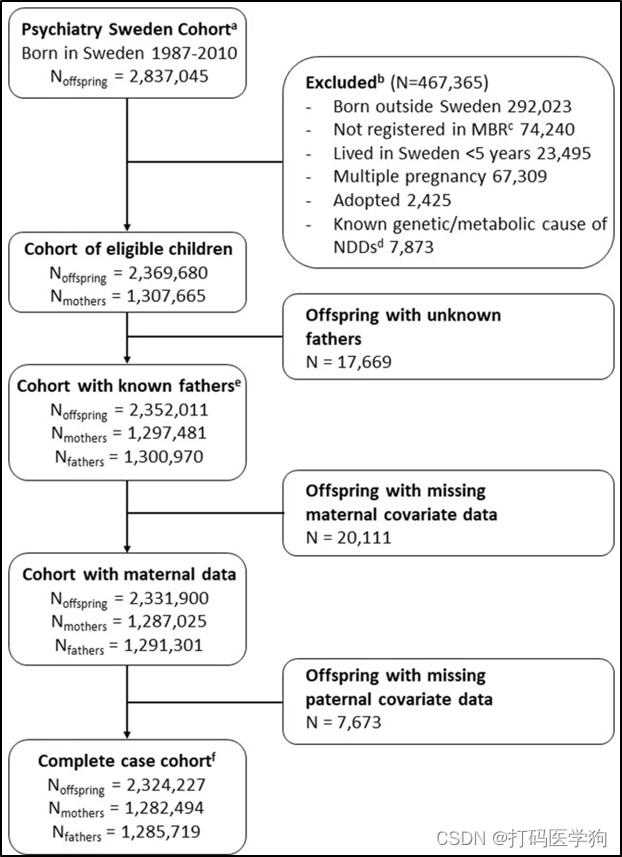
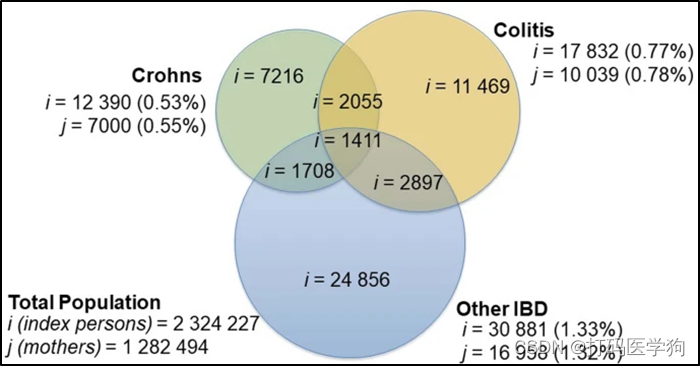
母亲IBD的人群情况(j是母亲的数量,i是这些母亲亲生孩子的数量)
父亲IBD的人群情况(j是父亲的数量,i是这些父亲亲生孩子的数量)
Using logistic regression, we assessed the associations between parental IBD diagnoses and autism in children.
3个Model: model 1是粗模型,model2是调整了一些人口学信息,model3是调整了父亲或目前IBD的情况
结果说明了父母IBD与子代自闭症有关联
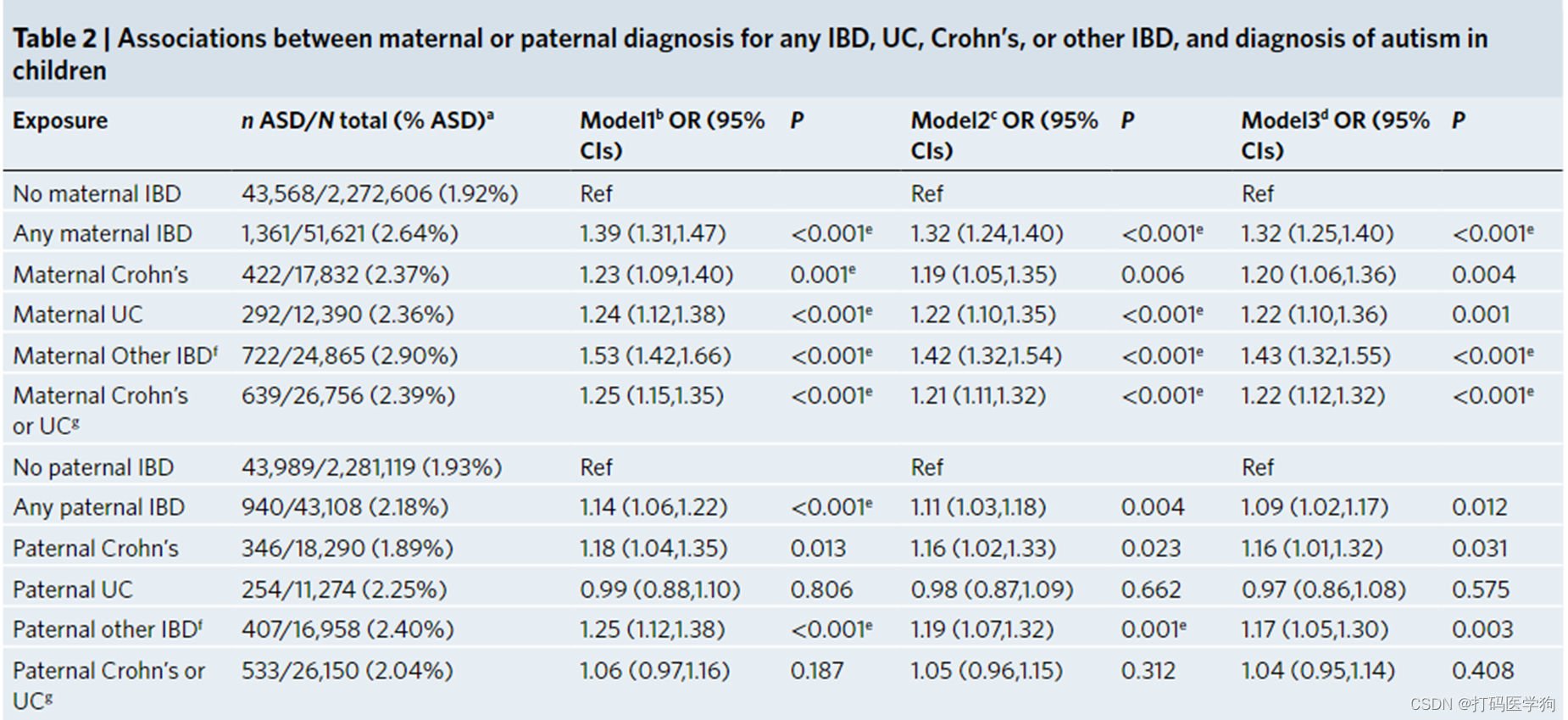
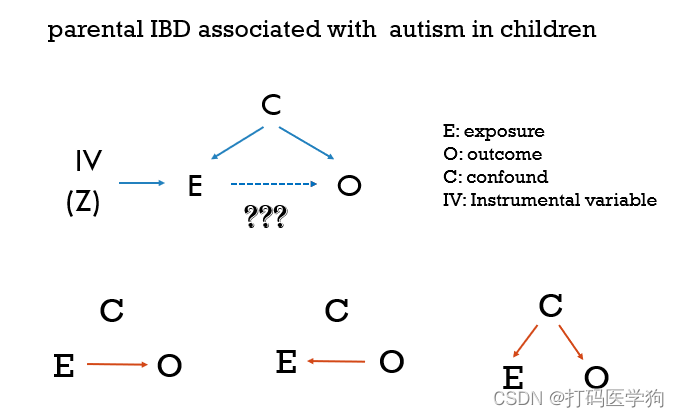
但是有关联不一定是因果关联
3.2. Study 2: Genetic correlation between IBD and autism
这个部分是分析遗传与IBD和自闭症的关联
原文描述的结果:
Linkage disequilibrium score regression (LDSC) allows the estimation of the genetic correlation between complex traits such as IBD and autism by utilizing GWAS summary data.
Using the latest GWAS summary statistics on IBD (N cases = 25,042; N controls = 34,915), Crohn’s (N cases = 12,194; N controls = 28,072), UC (N cases = 12,366; N controls = 33,609), and autism (N cases = 18,381; N controls = 27,969), we performed LDSC. We found no evidence of a genetic correlation between genetic liability to autism and IBD, UC, or Crohn’s
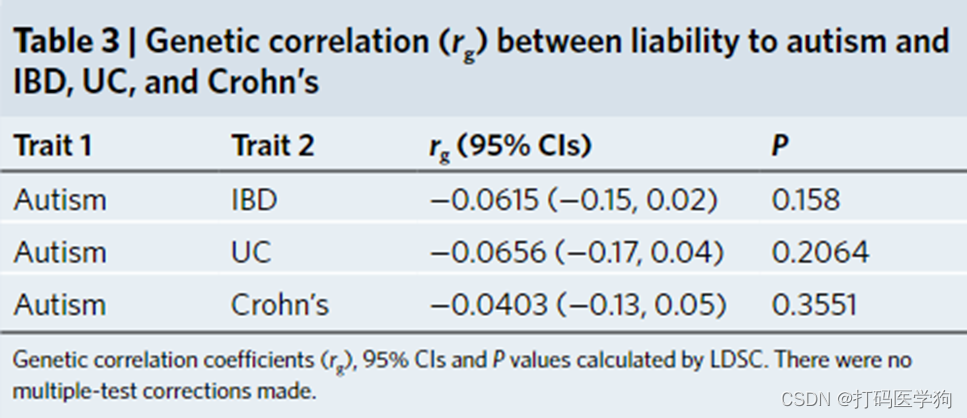
也就是说本部分没有发现自闭症的遗传倾向与 IBD、 UC 或克罗恩病之间存在遗传相关性的证据
3.3. Study 3: Polygenic risk for IBD and broad autistic traits
Polygenic Risk Score (PRS) approaches enable the estimation of an individual’s underlying genetic liability to a complex trait. PRSs require individual-level genotype data, and are calculated as the sum of the individual’s risk alleles, weighted by the effect sizes of each variant identified in the GWAS of the trait.
Study sample derivation and characteristics for the PRS analyses in ALSPAC.
Maternal PRS for IBD and broad autistic traits in children
Maternal polygenic risk for UC and Crohn’s was associated with a higher autism factor mean score in the child (UC: βPRS = 0.02; 95%CIs: 0.003 to 0.05; P = 0.03; Crohn’s: βPRS = 0.03; 95%CIs: 0.01 to 0.05; P = 0.004).
The effect size of the association between maternal polygenic risk for IBD and autism factor mean score, was comparable with that of UC and Crohn’s, although CIs crossed the null (βPRS = 0.02; 95%CIs: −0.004 to 0.040; P = 0.1; R2 = 0.06)
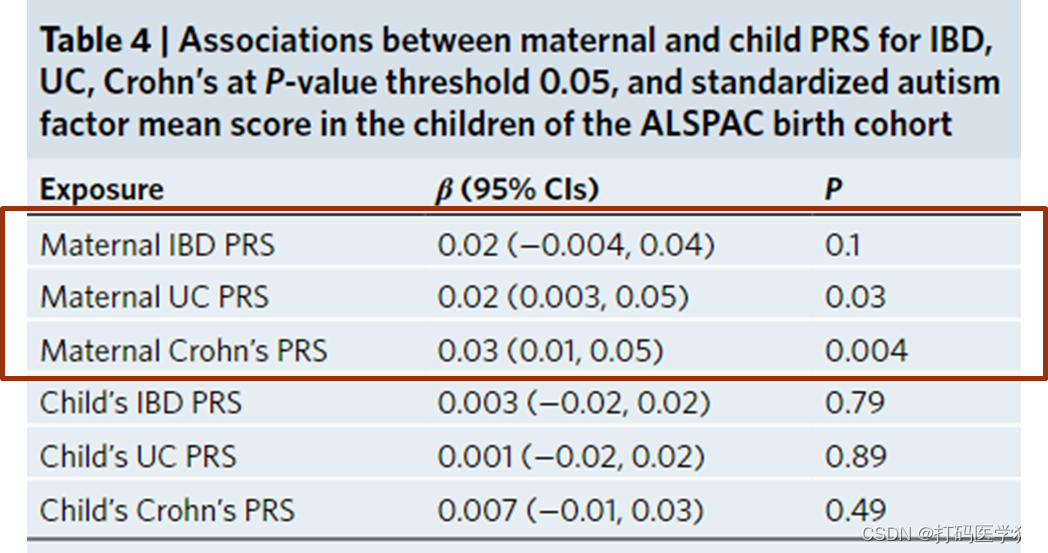
这就说明母亲 UC 和克罗恩病的多基因风险与儿童较高的自闭症因子平均评分相关
Child’s PRS for IBD and broad autistic traits
There was no evidence of associations between a child’s PRS for IBD, UC, Crohn’s, and autism mean factor score in children (IBD: βPRS = 0.003; 95%CIs: −0.02 to 0.02; P = 0.79; R2 = 0.05; UC: βPRS = 0.001; 95%CIs: −0.02 to 0.02; P = 0.89; R2 = 0.05; Crohn’s: βPRS = 0.007; 95%CIs: −0.01 to 0.03; P = 0.49; R2 = 0.05)
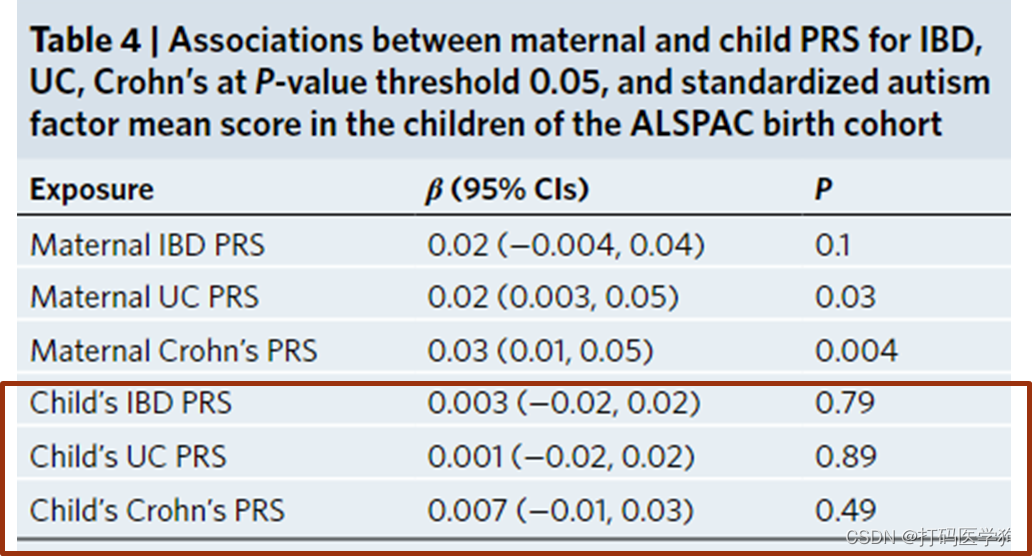
然而,子代UC 和克罗恩病的多基因风险与儿童较高的自闭症因子平均评分不相关
3.4. Study 4: Causal effect of genetic liability to IBD on autism
作者先做了MR的介绍:主要是强调MR的因果推断优势,而这点PRS则没有
MR is a causal inference approach that can overcome limitations of observational and PRS approaches .
MR is based on the principles of instrumental variables analyses, utilizing germline genetic variants as instruments for exposures to assess their causal effects on outcomes of interest.
In contrast to PRS approaches that estimate associations, under certain assumptions that the instruments should satisfy, MR can generate unbiased causal effect estimates.
更多MR内容以后有空梳理
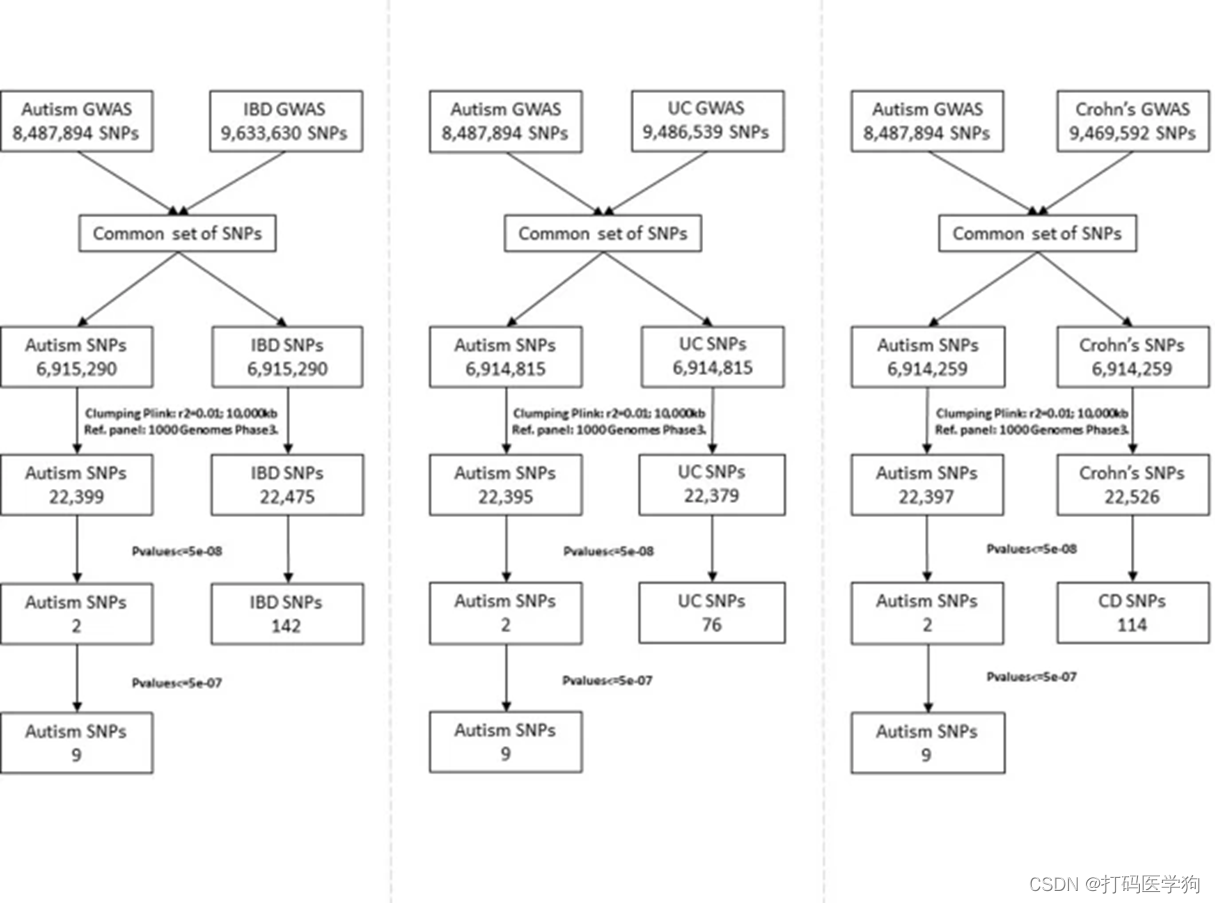
然后作者进行如下的工具变量的筛选
Within a two-sample MR framework, we extracted common genetic variants robustly associated (P ≤ 5.0−8) with IBD, Crohn’s, and UC using the latest available GWAS summary data, and assessed their causal effects on 18,381 autism cases and 27,969 controls of the PGC and the iPSYCH consortia.
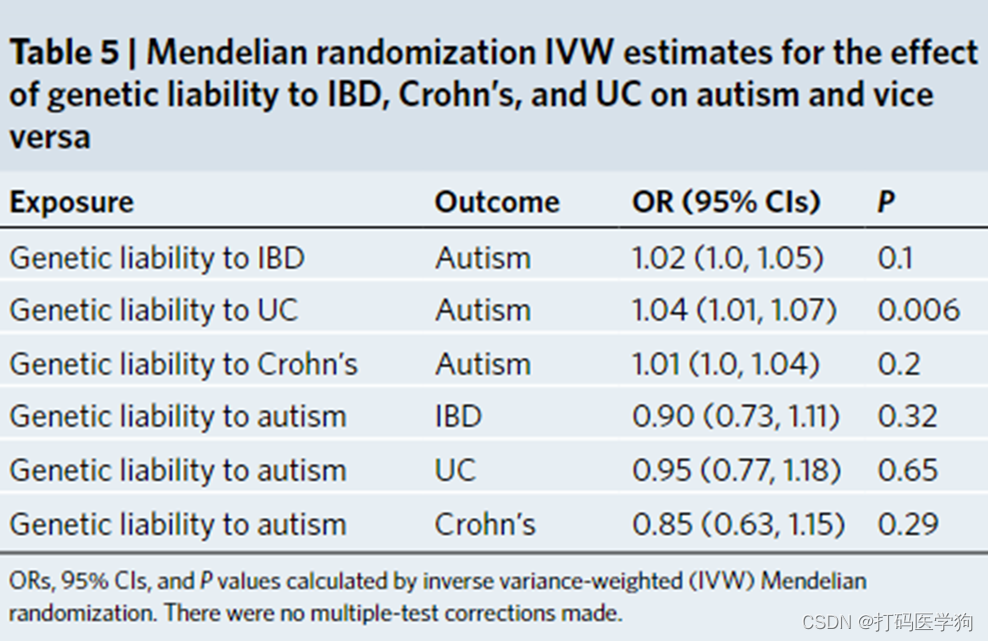
上表就是孟德尔随机化的结果,其实是双向MR,可以发现仅UC是Autism的因(p=0.006<0.05)
这里做双向MR我是万万想不到的,一开始我觉得没必要做子代自闭症对亲代IBD的因果推断,后来想到可能是因为海子得了自闭症影响父母情绪、生活、甚至健康,导致父母IBD
4. 结论
Four complementary approaches to investigate the associations between parental diagnoses and genetic liability to IBD and autism in children.
1. On conducting a nationwide register-based cohort study in Sweden we found evidence of associations between parental diagnoses of IBD and autism in children. Importantly, the maternal effect sizes were larger than the paternal sizes.
2. PRS analyses in the ALSPAC birth cohort suggested associations between maternal genetic liability to IBD and autism traits in children.
3. Two-sample MR studies provided evidence of a potential causal effect of genetic liability to IBD on autism risk.
4. There was no evidence to suggest a genetic correlation between autism and IBD, as indicated by LDSC analyses.
In conclusion, triangulating evidence from a nationwide register-based cohort study, genetic correlation, PRS analyses, and MR, we found evidence suggesting associations between parental, particularly maternal, diagnoses of IBD, and autism in children.
也就是说作者证明了父母(特别是母亲)IBD 和子代自闭症之间存在因果关联
更多内容请看原文
另外这篇文章还有对应的研究简报,链接:
Uncovering links between parental inflammatory bowel disease and autism in children | Nature Medicine
Expert opinion
“This study combines four strategies to elucidate the connection between autism and gastrointestinal symptoms. The reported association between parental — mainly maternal — IBD and autism in the offspring is intriguing. Two aspects of this research stand out. First, the implication that maternal genetic factors, possibly involving the immune system, may influence fetal brain development in utero. Second, the elegant demonstration of the value of integrating independent strategies to address one question from different angles.” Jacob Vorstman, The Hospital for Sick Children, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
专家评论:“这项研究结合了四种策略来阐明自闭症和胃肠道症状之间的联系。父母ーー主要是母亲ーー IBD 与后代自闭症之间的关联性报道是耐人寻味的。本文的研究突出了两个方面。首先,可能涉及免疫系统的母体遗传因素可能影响胎儿在子宫内的大脑发育。其次,优雅地展示了整合独立战略从不同角度解决同一问题的价值。
Behind the paper
The idea of this project arose when C.D. (then in her final year as PhD student) and I were brainstorming potential projects for an academic fellow (Aws Sadik) joining our research group. We are interested in the role of inflammation in autism and have increasingly used a triangulation framework to strengthen causal inference using epidemiological data. Our multidisciplinary collaborators in Sweden, Denmark, Norway and the United Kingdom enthusiastically supported our plans and helped to design and conduct the project during the COVID-19 pandemic. The use of multiple methods was an excellent training opportunity for Dr. Sadik, who is beginning his career as a clinical academic psychiatrist, and for C.D., whose submitted PhD thesis features this work. I am proud that these skilled future research leaders began the next steps of their careers having contributed to answering an important research question with an article in Nature Medicine as lead co-authors. D.R.
作者说这篇文章灵感来自于一次头脑风暴。他们对炎症和自闭症感兴趣
所谓头脑风暴(Brain-storming)最早是精神病理学上的用语,指精神病患者的精神错乱状态而言的,现在转而为无限制的自由联想和讨论,其目的在于产生新观念或激发创新设想。【百度百科】
其实这种活动挺好的,但大多数会议或讨论是一些无实质意义的谋财害命。