欢迎来到Cefler的博客😁
🕌博客主页:那个传说中的man的主页
🏠个人专栏:题目解析
🌎推荐文章:题目大解析2

目录
- 👉🏻List概念
- 👉🏻List constructor
- 👉🏻Iterators
- 👉🏻Capacity
- 👉🏻Element access
- 👉🏻Modifiers
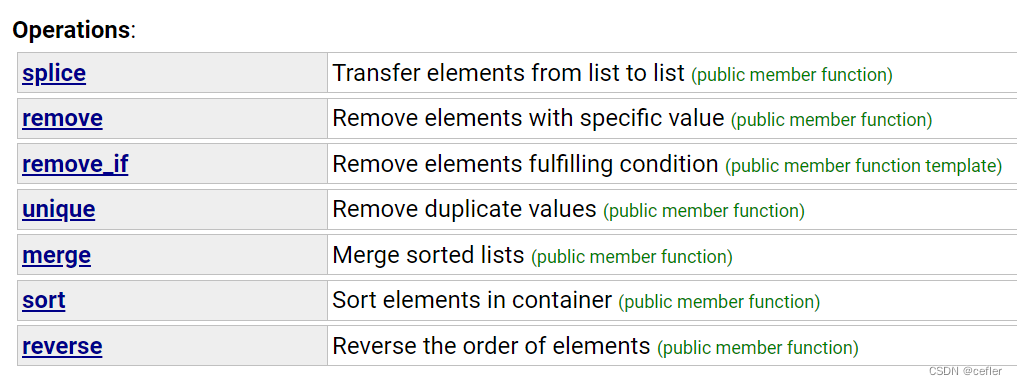
- 👉🏻Operations
- sort
- merge
- unique
- remove
- splice
- 👉🏻list的模拟实现
- list_node(链表结点)
- 封装迭代器
- insert
- erase
- push_back
- 头插/删,尾插/删
- empty_init函数
- 无参构造函数
- swap函数、clear函数、拷贝构造函数、析构函数
- 迭代器的begin和end() 【非const】
- 🌛插入自定义类型,编译器优化书写格式->
👉🏻List概念
C++中的list是一种双向链表数据结构。它可以存储任意类型的元素,并且可以在常数时间内在任意位置插入或删除元素。list提供了许多操作,如在开头或结尾插入/删除元素,访问元素,以及在列表中搜索元素。与向量(vector)相比,list的插入和删除操作更高效,但是访问元素的效率较低。
👉🏻List constructor
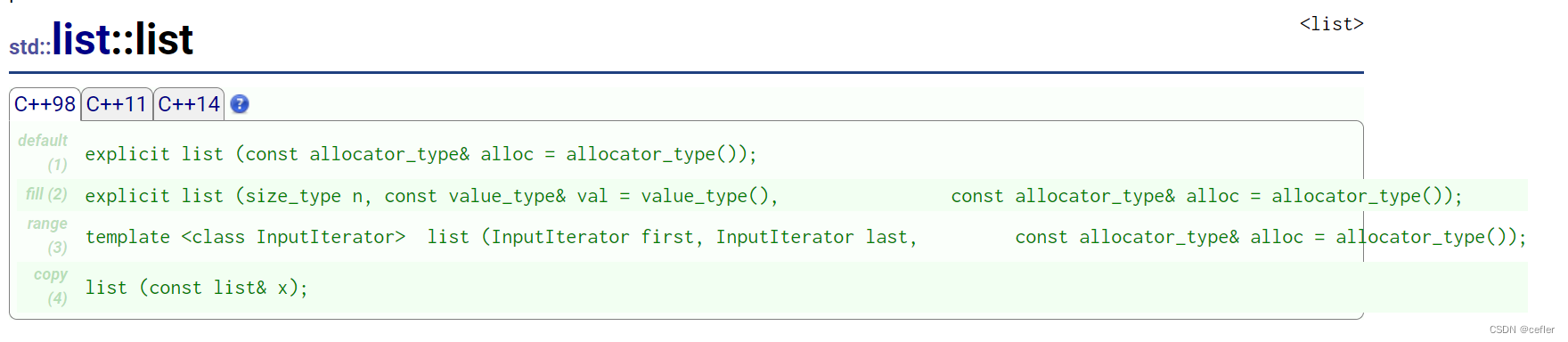
和vector差不多,list的构造函数中,有:
- 无参默认构造
- n个val值构造
- 模板函数,迭代器区间初始化构造
- 拷贝构造
List官方文档
👉🏻Iterators

👉🏻Capacity

👉🏻Element access

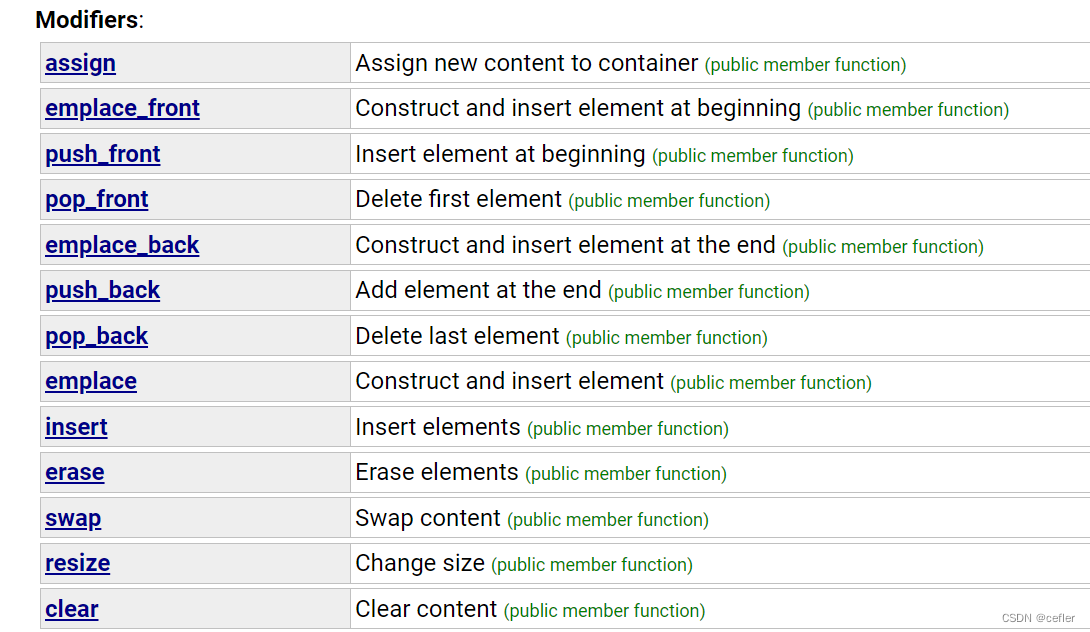
👉🏻Modifiers
👉🏻Operations
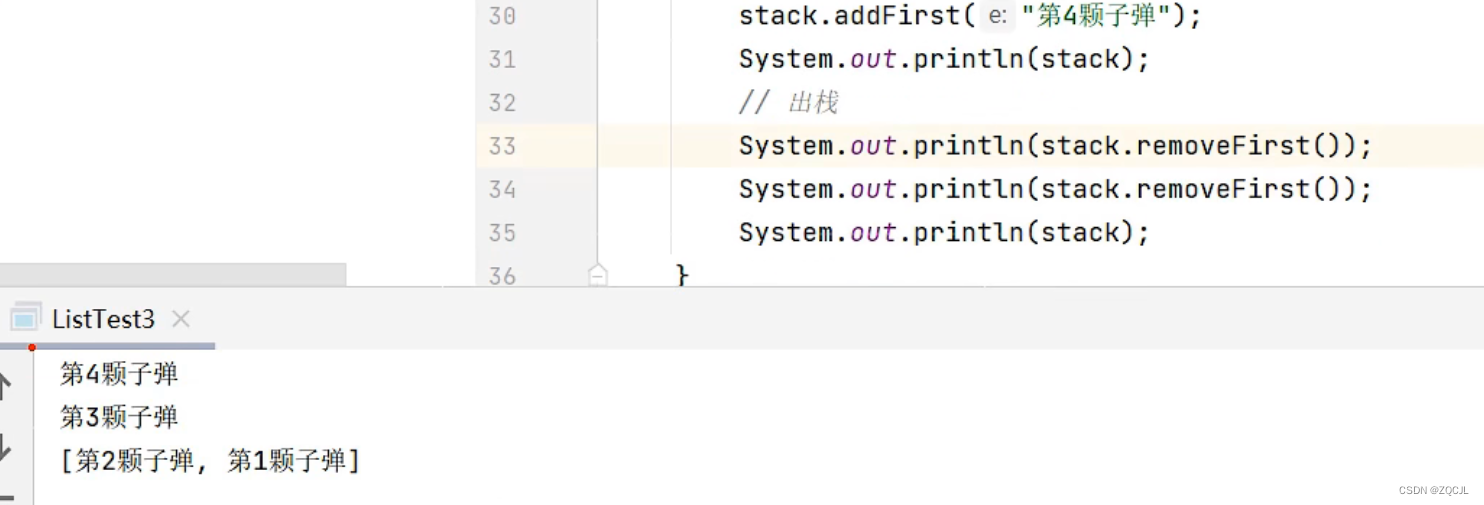
sort
可能有人会问,std中不是有提供一个全局的sort函数,为什么list内部还要再支持一个sort接口?
我们看下原因

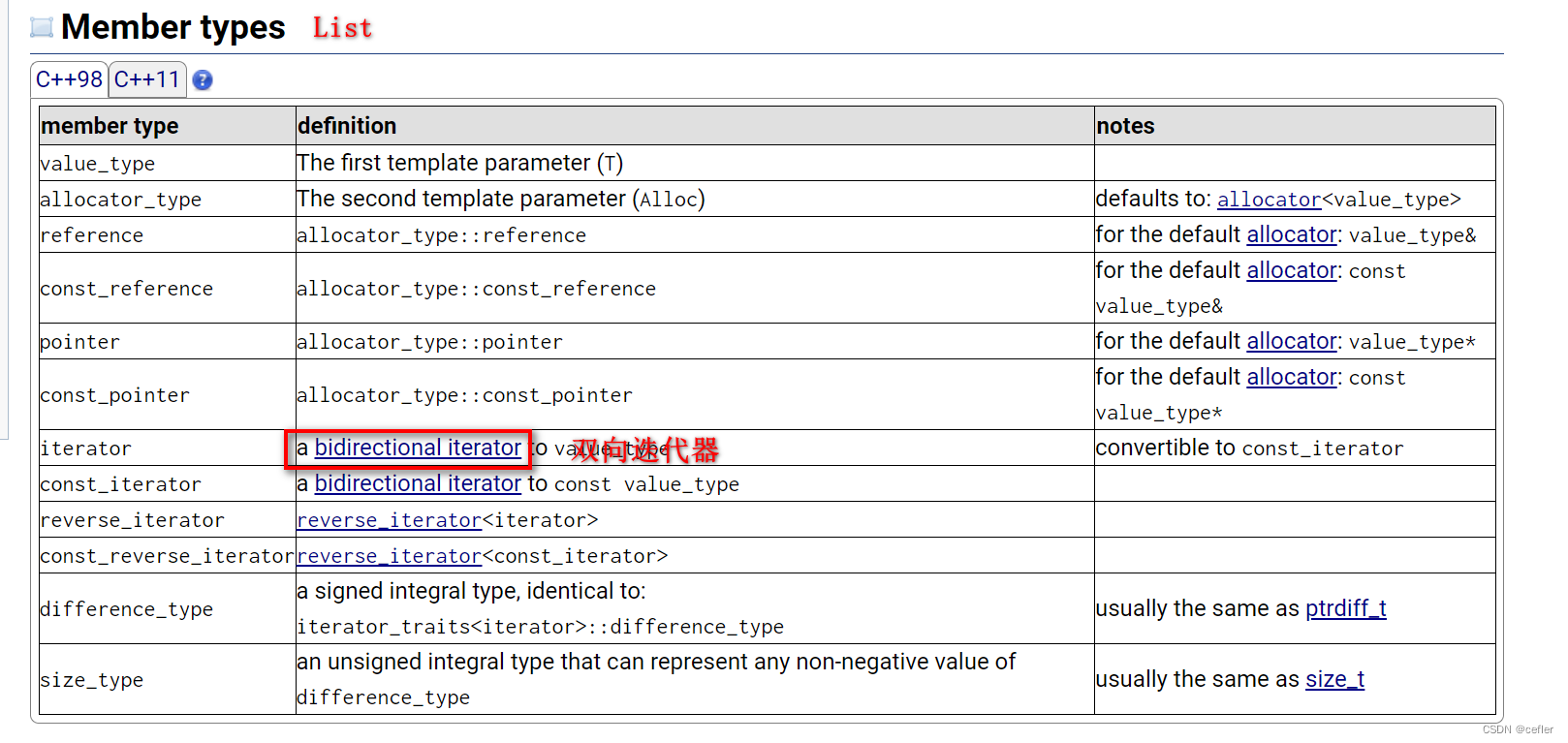
噢,原来是因为list的迭代器是双向迭代器,而std的sort只接收随机迭代器类型,因为双向迭代器不支持+/-功能,所以list用不了std的sort,只能自己造轮子了。

list的sort默认情况下是升序,list的排序有:
- 升序:< less
- 降序:> greater
list<int> l;for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++){l.push_back(i);}//我们想要个降序greater<int> gt;// list<int> l;for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++){l.push_back(i);}//我们想要个降序greater<int> gt;//l.sort(greater<int> ());匿名对象也可以l.sort(gt);
list的sort底层是实现是用归并排序
std的sort底层实现是快速排序,要比list的排序快,所以有时候,如果数据量比较少一般直接用list的排序,
但如果数据量大的话,我们可以先将list里面的数据拷贝到vector上,然后借助vector用std的排序进行快排,排序完之后,用assign的迭代器区间再拷贝回list中,这样就可以偷梁换柱了。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <algorithm> //使用sort排序记得包含头文件
using namespace std;
void Test1()
{list<int> l;for (int i = 10; i >=0; i--){l.push_back(i);}vector<int> v(l.begin(), l.end());//拷贝进vectorsort(v.begin(), v.end());l.assign(v.begin(), v.end());//再拷贝回去list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){cout << *it << " ";it++;}
}
merge
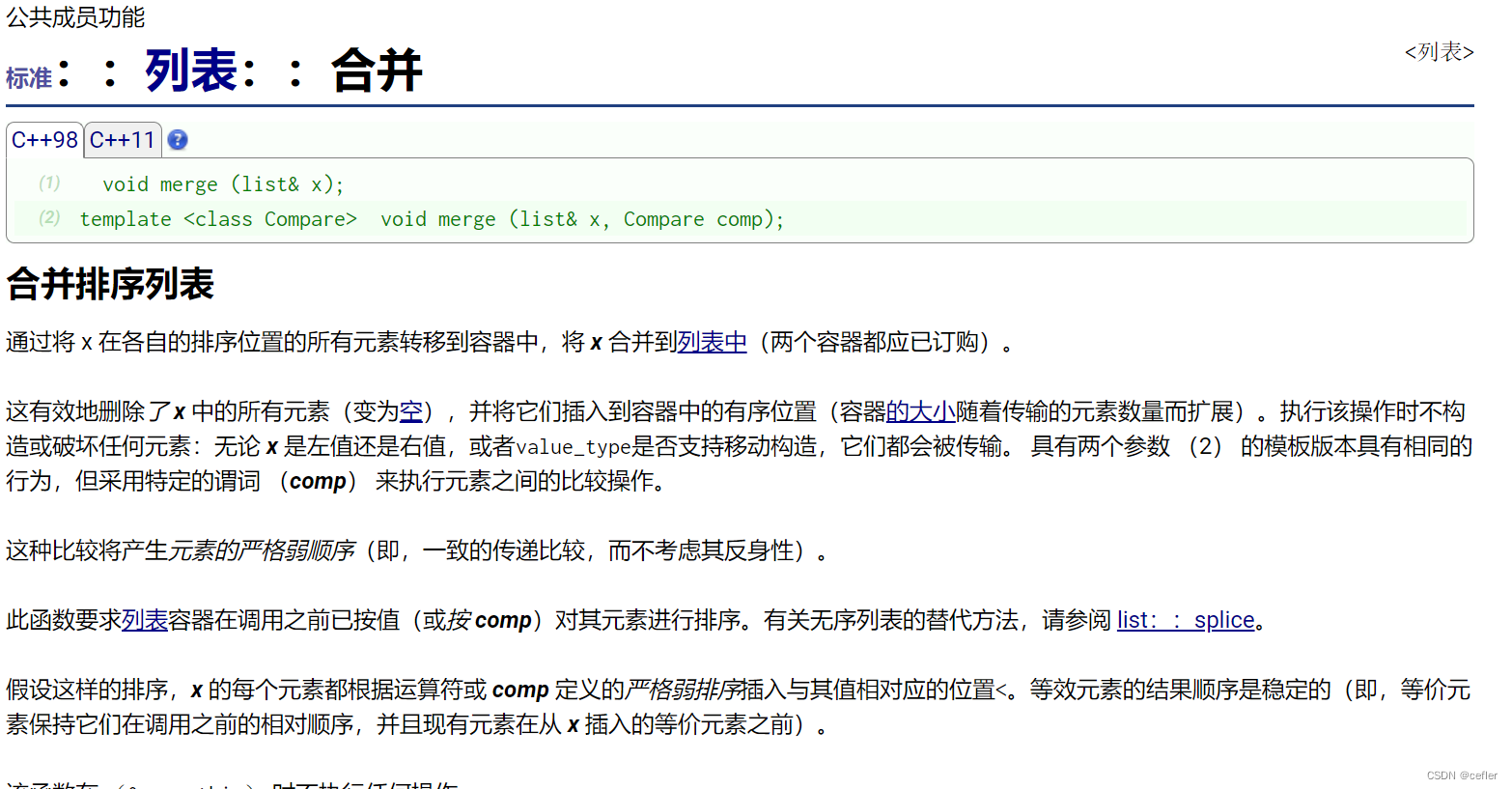
合并两个链表,但是前提是这两个链表是有序的。
// list::merge
#include <iostream>
#include <list>// compare only integral part:
bool mycomparison (double first, double second)
{ return ( int(first)<int(second) ); }int main ()
{std::list<double> first, second;first.push_back (3.1);first.push_back (2.2);first.push_back (2.9);second.push_back (3.7);second.push_back (7.1);second.push_back (1.4);first.sort();second.sort();first.merge(second);// (second is now empty)second.push_back (2.1);first.merge(second,mycomparison);std::cout << "first contains:";for (std::list<double>::iterator it=first.begin(); it!=first.end(); ++it)std::cout << ' ' << *it;std::cout << '\n';return 0;
}
输出:
first contains: 1.4 2.2 2.9 2.1 3.1 3.7 7.1
请注意,在第二次合并中,函数 mycompare(仅比较整数部分)没有考虑 2.1 低于 2.2 或 2.9,因此它入到它们之后,在 3.1 之前
unique
unique 函数的作用是将容器中相邻的重复元素保留一个,并删除其余的重复元素。具体而言,它会遍历容器中的元素,将相邻的重复元素中的后一个元素删除。
以下是 std::list 的 unique 函数的用法示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <list>int main() {std::list<int> myList = {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5};myList.unique();for (const auto& element : myList) {std::cout << element << " ";}return 0;
}
输出结果为:1 2 3 4 5。
注意,unique 函数只能去除相邻的重复元素,如果容器中存在非相邻的重复元素,它们不会被去除。如果需要去除所有重复元素,可以先使用 std::sort 函数对容器进行排序,然后再使用 unique 函数
remove
remove 函数用于删除容器中指定的元素。
remove 函数的工作原理是遍历容器,找到所有与指定值相等的元素,并将它们从容器中删除。
remove 函数的语法如下:
void remove(const T& value);
splice
splice 是 std::list 类提供的一个成员函数,用于将另一个 std::list 的元素插入到当前 std::list 中的指定位置。
splice 函数的语法如下:👇🏻
void splice (iterator position, list& x);
void splice (iterator position, list& x, iterator i);
void splice (iterator position, list& x, iterator first, iterator last);
- 第一个版本将 x 中的所有元素插入到当前 list 的 position 之前。
- 第二个版本将 x 中第i个元素开始之后的元素插入到当前 list 的 position 之前。
- 第三个版本将 x 中的 [first, last) 范围内的元素插入到当前 list 的 position 之前。
注意,splice 操作会改变被插入的 list,并且被插入的元素会从原来的 list 中移除。
以下是一个示例代码,演示了如何使用 splice 函数:👇🏻
#include <iostream>
#include <list>int main() {std::list<int> list1 = {1, 2, 3};std::list<int> list2 = {4, 5, 6};auto it = list1.begin();std::advance(it, 2); // 将迭代器移动到第三个元素的位置list1.splice(it, list2); // 将 list2 中的所有元素插入到 list1 的第三个元素之前// 输出 list1 的元素for (const auto& num : list1) {std::cout << num << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;// 输出 list2 的元素for (const auto& num : list2) {std::cout << num << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}
输出结果为:
1 2 4 5 6 3
👉🏻list的模拟实现
list_node(链表结点)
template <class T>//模板结构体,为了存储可能不同的数据类型struct list_node //这边用strcut主要是想开放所有的成员变量,所以不用class{T _data;list_node<T>* _next;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node(const T& val = T()):_data(val), _next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr){}};
封装迭代器
template <class T>struct __list_iterator//封装一个迭代器,实现迭代器的++/--等等功能,解引用//迭代器牛逼之处//封装屏蔽底层差异和实现细节//提供统一的访问修改方式{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef __list_iterator<T> self;Node* _node;__list_iterator(Node* node)//传参进来:_node(node){}self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}self operator++(int)//后置++{self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}self operator--(int)//后置--{self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->() //指针访问结构体{return &(_node->_data);}bool operator!=(const self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const self& s){return _node == s._node;}};
insert
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* newnode = new Node(x);//先开辟新空间Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;//insert后pos仍指向原空间,迭代器没失效++_size;return iterator(newnode);}
erase
iterator erase(iterator pos){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;//上一个结点Node* next = cur->_prev;//下一个结点prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete cur;//delete之后,cur即pos指向的空间已经不是原空间了,迭代器妥妥失效了!//所以需要返回删除位置的下一位置--_size;return iterator(next);}
push_back
void push_back(const T& x){//先建新空间Node* tail = _head->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);tail->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = tail;newnode->_next = _head;_head->_prev = newnode;}
insert进行尾插:
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}
头插/删,尾插/删
void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}void pop_back(){erase(--end());}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}
empty_init函数
void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}
无参构造函数
void empty_init(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}list(){empty_init();}
swap函数、clear函数、拷贝构造函数、析构函数
void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(this->_head, lt._head);std::swap(this->_size, lt._size);}void clear(){_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}/* void clear() //全部清除版本{iterator it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}*/
list( list<T>& lt)//拷贝构造{empty_init();for (auto e : lt){push_back(e);}}~list(){//clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}
迭代器的begin和end() 【非const】
typedef __list_iterator<T> iterator;iterator begin() //返回值会将_head->_next的值拷入进行构造{//return (iterator)_head;这边无需强转return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}
🌛插入自定义类型,编译器优化书写格式->
struct AA{AA(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0):_a1(a1), _a2(a2){}int _a1;int _a2;};void test_list3(){list<AA> lt;lt.push_back(AA(1, 1));lt.push_back(AA(2, 2));lt.push_back(AA(3, 3));list<AA>::iterator it = lt.begin();while (it != lt.end()){//cout << (*it)._a1<<" "<<(*it)._a2 << endl;cout << it->_a1 << " " << it->_a2 << endl;cout << it.operator->()->_a1 << " " << it.operator->()->_a1 << endl;++it;}cout << endl;/* int* p = new int;*p = 1;AA* ptr = new AA;ptr->_a1 = 1;*/}