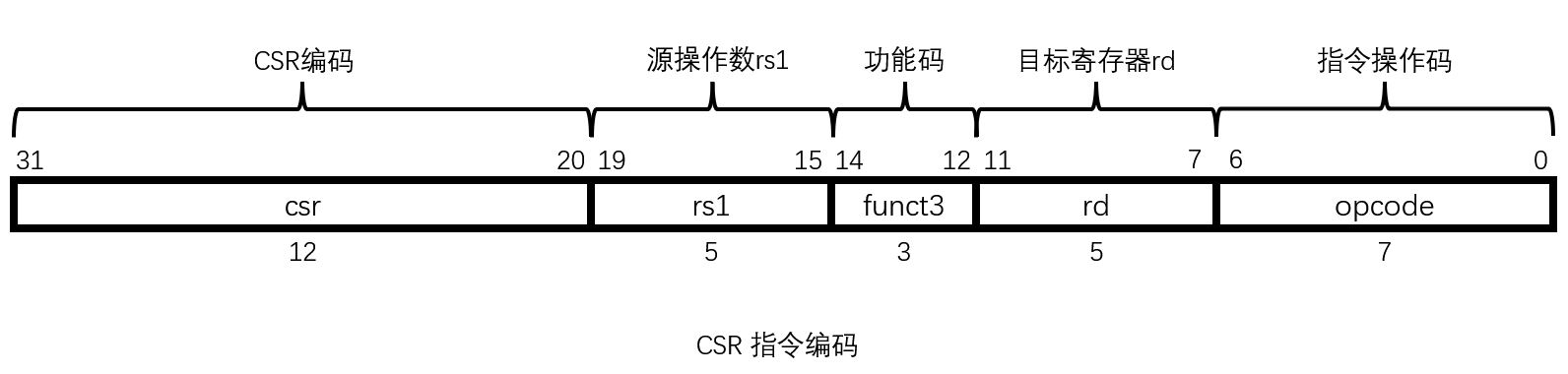
带着问题源码
- Netty 的 NioEventLoop 是如何实现的?它为什么能够保证 Channel 的操作是线程安全的?
- Netty 如何解决 JDK epoll 空轮询 Bug?
- NioEventLoop 是如何实现无锁化的?
一、作用与设计原理
Netty的NioEventLoop并不是一个存粹的I/O线程,除了负责I/O的读写外(用于处理 Channel 生命周期内的所有I/O事件,如accept、connect、read、write等I/O事件),还负责处理系统任务和延迟任务(定时任务);

主要就是做3个事:轮询 I/O 事件,处理 I/O 事件,处理异步任务队列

1.1 系统任务&延迟任务
NioEventLoop 内部有两个非常重要的异步任务队列,分别为普通任务队列和定时任务队列。
// 普通任务队列
private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue;默认使用的是 Mpsc Queue(多生产者单消费者队列)
static <T> Queue<T> newMpscQueue() {return USE_MPSC_CHUNKED_ARRAY_QUEUE ? new MpscUnboundedArrayQueue<T>(MPSC_CHUNK_SIZE): new MpscUnboundedAtomicArrayQueue<T>(MPSC_CHUNK_SIZE);}多个外部线程可能会并发操作同一个Channel,用来保证线程的安全性// 统计任务等收尾动作
private final Queue<Runnable> tailTasks// 延迟队列
PriorityQueue<ScheduledFutureTask<?>> scheduledTaskQueue;scheduledTaskQueue = new DefaultPriorityQueue<ScheduledFutureTask<?>>(SCHEDULED_FUTURE_TASK_COMPARATOR,11);1.1.1 系统任务
通过execute(Runnable task)方法实现,目的:当I/O线程和用户线程同时操作网络资源时,为了防止并发操作导致的锁竞争,将用户线程封装成task放入到普通队列中,由I/O线程负责执行
public void execute(Runnable task) {if (task == null) {throw new NullPointerException("task");}// 判断thread == this.thread;是否为当前EventExecutor内部线程,可能为其他线程调用该方法boolean inEventLoop = inEventLoop();// 加入到普通队列addTask(task);if (!inEventLoop) {// #AbstractChannel#write 可以写入非内部线程的任务startThread();if (isShutdown()) {boolean reject = false;try {if (removeTask(task)) {reject = true;}} catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {}if (reject) {reject();}}}if (!addTaskWakesUp && wakesUpForTask(task)) {wakeup(inEventLoop);}
}protected void addTask(Runnable task) {if (task == null) {throw new NullPointerException("task");}if (!offerTask(task)) {reject(task);}
}final boolean offerTask(Runnable task) {if (isShutdown()) {reject();}return taskQueue.offer(task);
}1.1.2延迟任务
ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) 对应的方法实现,具体实现后续专讲
二 、线程执行源码( 4.1.42.Final源码)
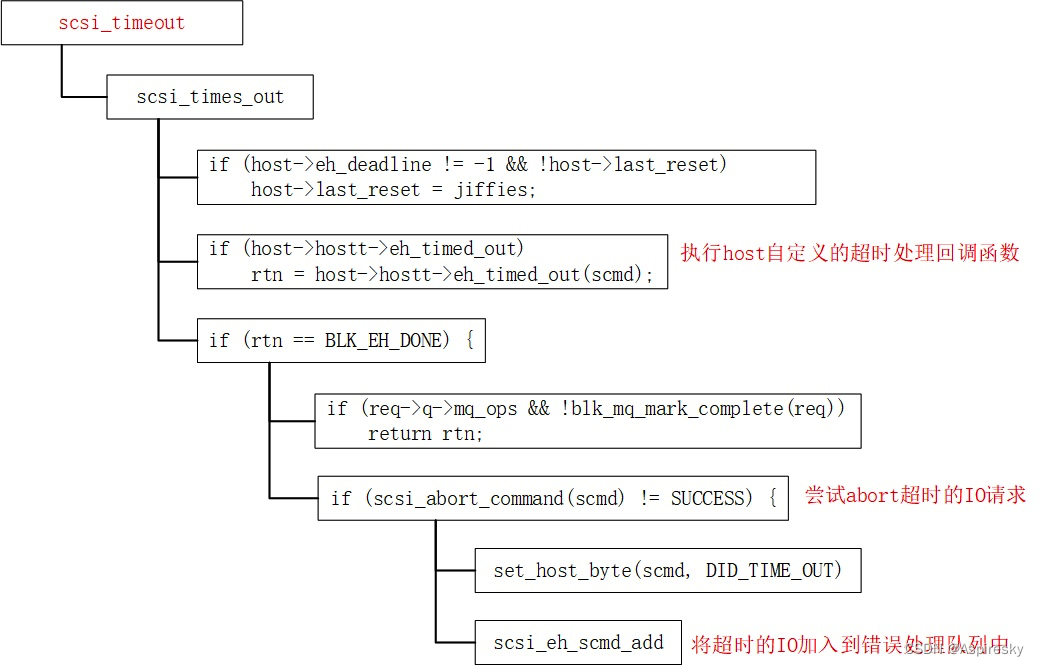
protected void run() {for (;;) {try {try {// 如果存在就绪I/O事件那么会返回对应就绪Channel的数量>=0进入default条件switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) {case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:continue;case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:case SelectStrategy.SELECT:// 无任务,则进行轮询I/O事件select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false)); // 轮询 I/O 事件if (wakenUp.get()) {selector.wakeup();}default:}} catch (IOException e) {// 重新构建SelectorrebuildSelector0();handleLoopException(e);continue;}cancelledKeys = 0;needsToSelectAgain = false;final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;if (ioRatio == 100) {try {processSelectedKeys(); // 处理 I/O 事件} finally {runAllTasks(); // 处理异步任务队列}} else {final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();try {processSelectedKeys(); // 处理 I/O 事件} finally {final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio); // 处理完 I/O 事件,再处理异步任务队列}}} catch (Throwable t) {handleLoopException(t);}try {if (isShuttingDown()) {closeAll();if (confirmShutdown()) {return;}}} catch (Throwable t) {handleLoopException(t);}}
}2.1 轮询 I/O 事件
selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())//实际调用
public int calculateStrategy(IntSupplier selectSupplier, boolean hasTasks) throws Exception {return hasTasks ? selectSupplier.get() : SelectStrategy.SELECT;
}// NioEventLoop#selectNowSupplier
private final IntSupplier selectNowSupplier = new IntSupplier() {@Overridepublic int get() throws Exception {// 若存在任务,则调用Selector选择器中的提供的非阻塞方法,// 执行后会立刻返回如果当前已经有就绪的Channel,会返回对应就绪Channel的数量否则返回0.return selectNow();}
}
// NioEventLoop#selectNow
int selectNow() throws IOException {try {return selector.selectNow();} finally {if (wakenUp.get()) {selector.wakeup();}}
}// 异步任务队列taskQueue和用于统计信息任务用的尾部队列tailTask是否有异步任务
protected boolean hasTasks() {return super.hasTasks() || !tailTasks.isEmpty();
}
可以得出在 I/O 事件循环的过程中 Netty 选择使用策略的具体判断步骤:
1、如果存在系统任务,则会执行selector.selectNow();并走到 default 分支后直接跳出,然后执行 I/O 事件处理 processSelectedKeys 和任务队列处理 runAllTasks 的逻辑。优先保证 CPU 能够及时处理系统任务。
2、如果不存在系统任务即任务队列为空,返回的是 SELECT 策略, 就会调用 select(boolean oldWakenUp) 方法
2.2 select(boolean oldWakenUp)
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp) throws IOException {Selector selector = this.selector;try {//计数器置0int selectCnt = 0;long currentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();//根据注册的定时任务,获取本次select的阻塞时间long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + this.delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);while(true) {//每次循环迭代都重新计算一次select的可阻塞时间long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;//如果可阻塞时间为0,表示已经有定时任务快要超时//此时如果是第一次循环(selectCnt=0),则调用一次selector.selectNow,然后退出循环返回//selectorNow方法的调用主要是为了尽可能检测出准备好的网络事件进行处理if (timeoutMillis <= 0L) {if (selectCnt == 0) { selector.selectNow();selectCnt = 1;}break;}//如果没有定时任务超时,但是有以前注册的任务(这里不限定是定时任务),//且成功设置wakenUp为true,则调用selectNow并返回if (this.hasTasks() && this.wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {selector.selectNow();selectCnt = 1;break;}//调用select方法,阻塞时间为上面算出的最近一个将要超时的定时任务时间int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);//计数器加1++selectCnt;if (selectedKeys != 0 || oldWakenUp || this.wakenUp.get() || this.hasTasks() || this.hasScheduledTasks()) {//进入这个分支,表示正常场景//selectedKeys != 0: selectedKeys个数不为0, 有io事件发生//oldWakenUp:表示进来时,已经有其他地方对selector进行了唤醒操作//wakenUp.get():也表示selector被唤醒//hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks():表示有任务或定时任务要执行//发生以上几种情况任一种则直接返回break;}//如果线程被中断,计数器置零,直接返回if (Thread.interrupted()) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely because Thread.currentThread().interrupt() was called. Use NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully() to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");}selectCnt = 1;break;}//这里判断select返回是否是因为计算的超时时间已过,//这种情况下也属于正常返回,计数器置1,进入下次循环long time = System.nanoTime();if (time - TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos) {//进入这个分支,表示超时,属于正常的场景//说明发生过一次阻塞式轮询, 并且超时selectCnt = 1;} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD > 0 && selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD) {//进入这个分支,表示没有超时,同时 selectedKeys==0//属于异常场景//表示启用了select bug修复机制,//即配置的io.netty.selectorAutoRebuildThreshold//参数大于3,且上面select方法提前返回次数已经大于//配置的阈值,则会触发selector重建//进行selector重建//重建完之后,尝试调用非阻塞版本select一次,并直接返回selector = this.selectRebuildSelector(selectCnt);selectCnt = 1;break;}currentTimeNanos = time;}//这种是对于关闭select bug修复机制的程序的处理,//简单记录日志,便于排查问题if (selectCnt > 3 && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.", selectCnt - 1, selector);}} catch (CancelledKeyException var13) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?", selector, var13);}}}第一步:检测若有定时任务要超时,则优先处理异步任务
//该任务指定的延迟时间差值时间-(当前时间-delayedTask创建的时间) protected long delayNanos(long currentTimeNanos) {//当前纳秒减去启动纳秒,相当于一个自增的时间差值currentTimeNanos -= initialNanoTime();ScheduledFutureTask<?> scheduledTask = peekScheduledTask();if (scheduledTask == null) {return SCHEDULE_PURGE_INTERVAL;}// 得出最终触发还有多久return scheduledTask.delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);}// 根据当前参数传入的时间返回参数时间距离deadline触发还有多久public long delayNanos(long currentTimeNanos) {return deadlineToDelayNanos(currentTimeNanos, deadlineNanos);}static long deadlineToDelayNanos(long currentTimeNanos, long deadlineNanos) {return deadlineNanos == 0L ? 0L : Math.max(0L, deadlineNanos - currentTimeNanos);}
首先deadlineNanos为差值时间具体值如下:
private long deadlineNanos;deadlineNanos(getCurrentTimeNanos(), unit.toNanos(initialDelay))deadlineNanos为延迟任务创建时间-系统创建时间+delaystatic long deadlineNanos(long nanoTime, long delay) {long deadlineNanos = nanoTime + delay;// Guard against overflowreturn deadlineNanos < 0 ? Long.MAX_VALUE : deadlineNanos;}delayNanos计算结果为差值时间,还有多久延迟任务就要触发,如1s后;
selectDeadLineNanos 为当前时间+差值时间
timeoutMillis 为(任务多久后触发+0.5ms)/1000000L, 如果截止时间小于0.5ms,则timeoutMillis 为0,直接调非阻塞的selectNow()方法;若大于则进行阻塞,旧版本以毫秒为判断点。
有定时任务情况,select会在定时任务到期时返回。(存在定时任务到期很久的情况,这里补充知识:其他线程如果因为调用了selector.select()或者selector.select(long)这两个方法而阻塞,调用了selector.wakeup()之后,就会立即返回结果,并且返回的值!=0,所以在异步任务新增的时候,都会进行wakeup())
如果没有定时任务,delayNanos(currentTimeNanos)返回的值TimeUnit.SECONDS.toNanos(1),即1秒; select会在检查到任何NIO事件或executor任务时返回
第二步:若有异步任务,则优先执行任务
this.hasTasks() && this.wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)第三步:执行selcor(long)
解决Epollbug:
1、周期统计:事件轮询时间小于超时时间,并且在该时间周期内连续发生超过 SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD(默认512)次空轮询,说明可能触发了epoll空轮询 Bug
2、重建Selector
private Selector selectRebuildSelector(int selectCnt) throws IOException {logger.warn("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row; rebuilding Selector {}.", selectCnt, this.selector);//进行selector重建this.rebuildSelector();Selector selector = this.selector;//重建完之后,尝试调用非阻塞版本select一次,并直接返回selector.selectNow();return selector;}2.3 处理 I/O 事件
调用 processSelectedKeys() 方法处理 I/O 事件,Netty 通过 ioRatio参数控制I/O事件处理和任务处理的时间比例,默认为 ioRatio = 50。如果 ioRatio = 100表示每次都处理完 I/O 事件后,会执行所有的 task。如果 ioRatio < 100,也会优先处理完 I/O 事件,再处理异步任务队列。所以不论如何 processSelectedKeys() 都是先执行的,接下来跟进下 processSelectedKeys() 的源码:
private void processSelectedKeys() {if (selectedKeys != null) {processSelectedKeysOptimized();} else {processSelectedKeysPlain(selector.selectedKeys());}}
处理 I/O 事件时有两种选择,一种是处理 Netty 优化过的 selectedKeys,另外一种是正常的处理逻辑。根据是否设置了 selectedKeys 来判断使用哪种策略,这两种策略使用的 selectedKeys 集
合是不一样的。Netty 优化过的 selectedKeys 是 SelectedSelectionKeySet 类型,而正常逻辑使用的是 JDK HashSet 类型。
2.3.1 processSelectedKeysPlain
private void processSelectedKeysPlain(Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys) {// check if the set is empty and if so just return to not create garbage by// creating a new Iterator every time even if there is nothing to process.// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/597if (selectedKeys.isEmpty()) {return;}// 遍历所有就绪的SelectionKeyIterator<SelectionKey> i = selectedKeys.iterator();for (;;) {final SelectionKey k = i.next();// 如selectionKey = javaChannel().register(eventLoop().unwrappedSelector(), 0, this);进行挂载在attachment上final Object a = k.attachment();// 需要自行删除i.remove();// i/o事件if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);} else {// 异步任务时@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;processSelectedKey(k, task);}if (!i.hasNext()) {break;}if (needsToSelectAgain) {selectAgain();selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();// Create the iterator again to avoid ConcurrentModificationExceptionif (selectedKeys.isEmpty()) {break;} else {i = selectedKeys.iterator();}}}}2.3.1.1 processSelectedKey
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe();if (!k.isValid()) { // 检查 Key 是否合法final EventLoop eventLoop;try {eventLoop = ch.eventLoop();} catch (Throwable ignored) {return;}if (eventLoop != this || eventLoop == null) {return;}unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); // Key 不合法,直接关闭连接return;}try {int readyOps = k.readyOps();// 处理连接事件NioSocketChannelif ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {int ops = k.interestOps();// 移除对connect事件的监听,否则Selector会一直通知ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;k.interestOps(ops);// 触发channelActive处理connect事件unsafe.finishConnect();}// 处理可写事件if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {ch.unsafe().forceFlush();}// 处理可读事件或accept事件。服务端NioServerSocketChannel中的Read方法处理的是Accept事件,NioSocketChannel中的Read方法处理的是Read事件。if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {unsafe.read();}} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());}}2.3.1.2 needsToSelectAgain
protected void doDeregister() throws Exception {eventLoop().cancel(selectionKey());
}/**
* 将socketChannel从selector中移除 取消监听IO事件
* */
void cancel(SelectionKey key) {key.cancel();cancelledKeys ++;// 当取消的 Key 超过默认阈值 256,needsToSelectAgain 设置为 true,为了清除无效SelectionKeyif (cancelledKeys >= CLEANUP_INTERVAL) {cancelledKeys = 0;needsToSelectAgain = true;}}2.3.2 processSelectedKeysOptimized
private void processSelectedKeysOptimized() {for (int i = 0; i < selectedKeys.size; ++i) {final SelectionKey k = selectedKeys.keys[i];selectedKeys.keys[i] = null;final Object a = k.attachment();if (a instanceof AbstractNioChannel) {processSelectedKey(k, (AbstractNioChannel) a);} else {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")NioTask<SelectableChannel> task = (NioTask<SelectableChannel>) a;processSelectedKey(k, task);}if (needsToSelectAgain) {selectedKeys.reset(i + 1);selectAgain();i = -1;}}}final class SelectedSelectionKeySet extends AbstractSet<SelectionKey> {SelectionKey[] keys;int size;SelectedSelectionKeySet() {keys = new SelectionKey[1024];}@Overridepublic boolean add(SelectionKey o) {if (o == null) {return false;}keys[size++] = o;if (size == keys.length) {increaseCapacity();}return true;}..........}因为SelectedSelectionKeySet 内部使用的是 SelectionKey 数组,所以 processSelectedKeysOptimized 可以直接通过遍历数组取出 I/O 事件,相比 JDK HashSet 的遍历效率更高。相比于 HashSet,SelectionKey[] 不需要考虑哈希冲突的问题,所以可以实现 O(1) 时间复杂度的 add 操作。
那么 SelectedSelectionKeySet生成摘录核心源码片段如下:
private SelectorTuple openSelector() {final SelectedSelectionKeySet selectedKeySet = new SelectedSelectionKeySet();Object maybeException = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {@Overridepublic Object run() {try {Field selectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("selectedKeys");Field publicSelectedKeysField = selectorImplClass.getDeclaredField("publicSelectedKeys");if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 9 && PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe()) {long selectedKeysFieldOffset = PlatformDependent.objectFieldOffset(selectedKeysField);long publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset =PlatformDependent.objectFieldOffset(publicSelectedKeysField);if (selectedKeysFieldOffset != -1 && publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset != -1) { // 存储为数组PlatformDependent.putObject(unwrappedSelector, selectedKeysFieldOffset, selectedKeySet);// 存储为数组PlatformDependent.putObject(unwrappedSelector, publicSelectedKeysFieldOffset, selectedKeySet);return null;}}。。。。。} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {return e;} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {return e;}}}); // 省略其他代码
}2.4 异步任务
处理异步任务队列 runAllTasks
2.4.1 runAllTasks
protected boolean runAllTasks() {assert inEventLoop();boolean fetchedAll;boolean ranAtLeastOne = false;do {fetchedAll = fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue();if (runAllTasksFrom(taskQueue)) {ranAtLeastOne = true;}} while (!fetchedAll); // keep on processing until we fetched all scheduled tasks.if (ranAtLeastOne) {lastExecutionTime = getCurrentTimeNanos();}afterRunningAllTasks();return ranAtLeastOne;}2.4.1 runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos)
protected boolean runAllTasks(long timeoutNanos) {// 合并定时任务到普通任务队列fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue(); // 从普通任务队列中取出任务并处理Runnable task = pollTask();if (task == null) {afterRunningAllTasks();return false;}// 计算任务处理的超时时间final long deadline = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime() + timeoutNanos;long runTasks = 0;long lastExecutionTime;for (;;) {safeExecute(task); // 执行任务runTasks ++;// 每执行 64 个任务检查一下是否超时if ((runTasks & 0x3F) == 0) {lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();if (lastExecutionTime >= deadline) {break;}}task = pollTask(); // 继续取出下一个任务if (task == null) {lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime();break;}}// 收尾工作afterRunningAllTasks();this.lastExecutionTime = lastExecutionTime;return true;}真正处理任务的 safeExecute() 就是直接调用的 Runnable 的 run() 方法。因为异步任务处理是有超时时间的,所以 Netty 采取了定时检测的策略,每执行 64 个任务的时候就会检查一下是否超时,对性能的折中考虑,如果异步队列中有大量的短时间任务,每一次执行完都检测一次超时性能会有所降低。
尾部队列作用:例如任务循环的耗时、占用物理内存的大小等等,都可以向尾部队列添加一个收尾任务完成统计数据的实时更新
三、最新版4.1.96源码
protected void run() {int selectCnt = 0;for (;;) {try {int strategy;try {// 如果存在就绪I/O事件那么会返回对应就绪Channel的数量>=0进入default条件strategy = selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks());switch (strategy) {case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE:continue;case SelectStrategy.BUSY_WAIT:// fall-through to SELECT since the busy-wait is not supported with NIOcase SelectStrategy.SELECT:// 无任务,则进行轮询I/O事件long curDeadlineNanos = nextScheduledTaskDeadlineNanos();if (curDeadlineNanos == -1L) {// -1代表当前定时任务队列中没有定时任务curDeadlineNanos = NONE; // nothing on the calendar}nextWakeupNanos.set(curDeadlineNanos);try {if (!hasTasks()) {strategy = select(curDeadlineNanos);}} finally {// This update is just to help block unnecessary selector wakeups// so use of lazySet is ok (no race condition)nextWakeupNanos.lazySet(AWAKE);}// fall throughdefault:}} catch (IOException e) {// If we receive an IOException here its because the Selector is messed up. Let's rebuild// the selector and retry. https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/8566rebuildSelector0();selectCnt = 0;handleLoopException(e);continue;}selectCnt++;cancelledKeys = 0;needsToSelectAgain = false;final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio;boolean ranTasks;// IO占比为100,则进行IO事件if (ioRatio == 100) {try {// 异步任务执行,优先保证 CPU 能够及时处理异步任务if (strategy > 0) {processSelectedKeys();// 处理 I/O 事件}} finally {// Ensure we always run tasks.ranTasks = runAllTasks();}} else if (strategy > 0) {// 存在异步任务final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime();try {processSelectedKeys();} finally {// Ensure we always run tasks.final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime;// 异步任务执行,优先保证 CPU 能够及时处理异步任务ranTasks = runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio);}} else {ranTasks = runAllTasks(0); // This will run the minimum number of tasks}if (ranTasks || strategy > 0) {if (selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS && logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times in a row for Selector {}.",selectCnt - 1, selector);}selectCnt = 0;} else if (unexpectedSelectorWakeup(selectCnt)) { // Unexpected wakeup (unusual case)selectCnt = 0;}} catch (CancelledKeyException e) {// Harmless exception - log anywayif (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + " raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?",selector, e);}} catch (Error e) {throw e;} catch (Throwable t) {handleLoopException(t);} finally {// Always handle shutdown even if the loop processing threw an exception.try {if (isShuttingDown()) {closeAll();if (confirmShutdown()) {return;}}} catch (Error e) {throw e;} catch (Throwable t) {handleLoopException(t);}}}}private int select(long deadlineNanos) throws IOException {if (deadlineNanos == NONE) {return selector.select();}// Timeout will only be 0 if deadline is within 5 microsecslong timeoutMillis = deadlineToDelayNanos(deadlineNanos + 995000L) / 1000000L;return timeoutMillis <= 0 ? selector.selectNow() : selector.select(timeoutMillis);}