一.什么是WebSocket
【1】WebSocket是一种协议,设计用于提供低延迟,全双工和长期运行的连接。
全双工:通信的两个参与方可以同时发送和接收数据,不需要等待对方的响应或传输完成。
【2】比较
传统通信(http协议):电子邮件,网页游览,存在延迟,需要用户主动请求来更新数据。
实时通信(websocket协议):即时消息传递,音视频通话,在线会议和实时数据传输等,可以实现即时的数据传输和交流,不需要用户主动请求或刷新来获取更新数据。

【3】WebSocket之前的世界(基于http):
(1)轮询:客户端定期向服务器发送请求
缺点--会产生大量的请求和响应,导致不必要的网络开销和延迟。
(2)长轮询:在客户端发出请求后,保持连接打开,等待新数据相应后再关闭连接。
缺点--虽然消灭了了无效轮询,但是还是需要频繁的建立和关闭连接。
(3)Comet:保持长连接,在返回请求后继续保持连接打开,并允许服务器通过流式传输,frame等推送技术来主动向客户端推送数据。
缺点--虽然模拟了事实通信,但还是基于http模型,使用推送技巧来实现的。
【4】那么怎么建立websocket连接呢?
需要通过HTTP发送一次常规的Get请求,并在请求头中带上Upgrade,告诉服务器,我想从HTTP升级成WebSocket,连接就建立成功了,之后客户端就可以像服务器发送信息。
二.入门案例
1.先搭建配置和程序的基本结构
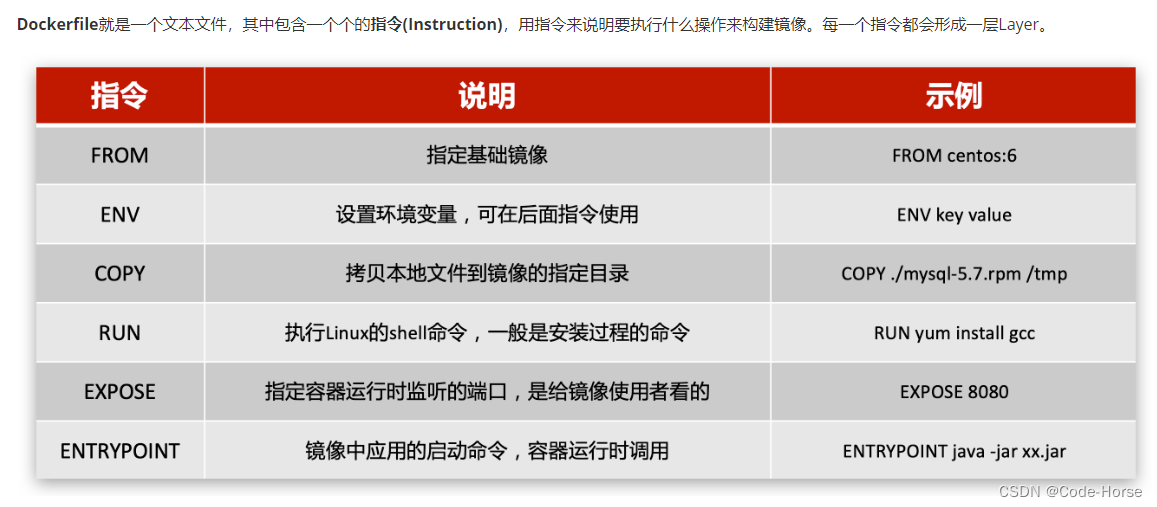
【1】导入依赖(websocket和fastjson)
springboot集成websocket,因为springboot项目都继承父项目,所以不用写依赖
<dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>
在websocket中不能直接像controller那样直接将对象return,所以需要fastjson之类的工具将对象转化为json字符串再返回给前端。
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba</groupId><artifactId>fastjson</artifactId><version>1.2.62</version>
</dependency>【2】开启springboot对websocket的支持
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig {@Bean//注入ServerEndpointExporter,自动注册使用@ServerEndpoint注解的public ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter(){return new ServerEndpointExporter();}
}【3】定义EndPoint类实现(一个websocket的链接对应一个Endpoint类)
/*** @ServerEndpoint 注解的作用** @ServerEndpoint 注解是一个类层次的注解,它的功能主要是将目前的类定义成一个websocket服务器端,* 注解的值将被用于监听用户连接的终端访问URL地址,客户端可以通过这个URL来连接到WebSocket服务器端*/@Slf4j
@Component
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{name}")
public class WebSocket {/*** 与某个客户端的连接对话,需要通过它来给客户端发送消息*/private Session session;/*** 标识当前连接客户端的用户名*/private String name;/*** 用于存储每一个客户端对象对应的WebSocket对象,因为它是属于类的,所以要用static*/private static ConcurrentHashMap<String,WebSocket> webSocketSet = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();//下面有三个生命周期//生命周期一:连接建立成功调用的方法//注意:这个方法的参数列表中只能使用@PathParam结束路径参数,而且必须使用至少一个@PathParam接收路径参数@OnOpenpublic void OnOpen(Session session, @PathParam(value = "name") String name){log.info("----------------------------------");this.session = session;this.name = name;// name是用来表示唯一客户端,如果需要指定发送,需要指定发送通过name来区分webSocketSet.put(name,this);log.info("[WebSocket] 连接成功,当前连接人数为:={}",webSocketSet.size());log.info("----------------------------------");log.info("");GroupSending(name+" 来了");}//生命周期二:连接建立关闭调用的方法@OnClosepublic void OnClose(){webSocketSet.remove(this.name);log.info("[WebSocket] 退出成功,当前连接人数为:={}",webSocketSet.size());GroupSending(name+" 走了");}//生命周期三:连接建立关闭调用的方法收到客户端消息后调用的方法@OnMessagepublic void OnMessage(String message_str){//只要某个客户端给服务端发送消息,就给它发送666AppointSending(this.name,"666");}//生命周期四:发生错误后调用的方法@OnErrorpublic void onError(Session session, Throwable error){log.info("发生错误");error.printStackTrace();}/*** 群发* @param message*/public void GroupSending(String message){for (String name : webSocketSet.keySet()){try {webSocketSet.get(name).session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}/*** 指定发送* @param name* @param message*/public void AppointSending(String name,String message){try {webSocketSet.get(name).session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}
}简单说就是每有一个客户端连接这个websocket,就会给生成一个websocket对象,并调用OnOpen方法打印日志和存储用户信息。然后连接保持,中间如果这个连接出错,调用OnError方法,如果客户端给服务端发送信息,就调用OnMessage,直到连接关闭,才调用OnClose方法。
然后服务端给客户端发送消息是通过你定义的EndPoint类的session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message)方法,如果你要返回json对象要用fastjson之类进行转换成json格式的字符串。
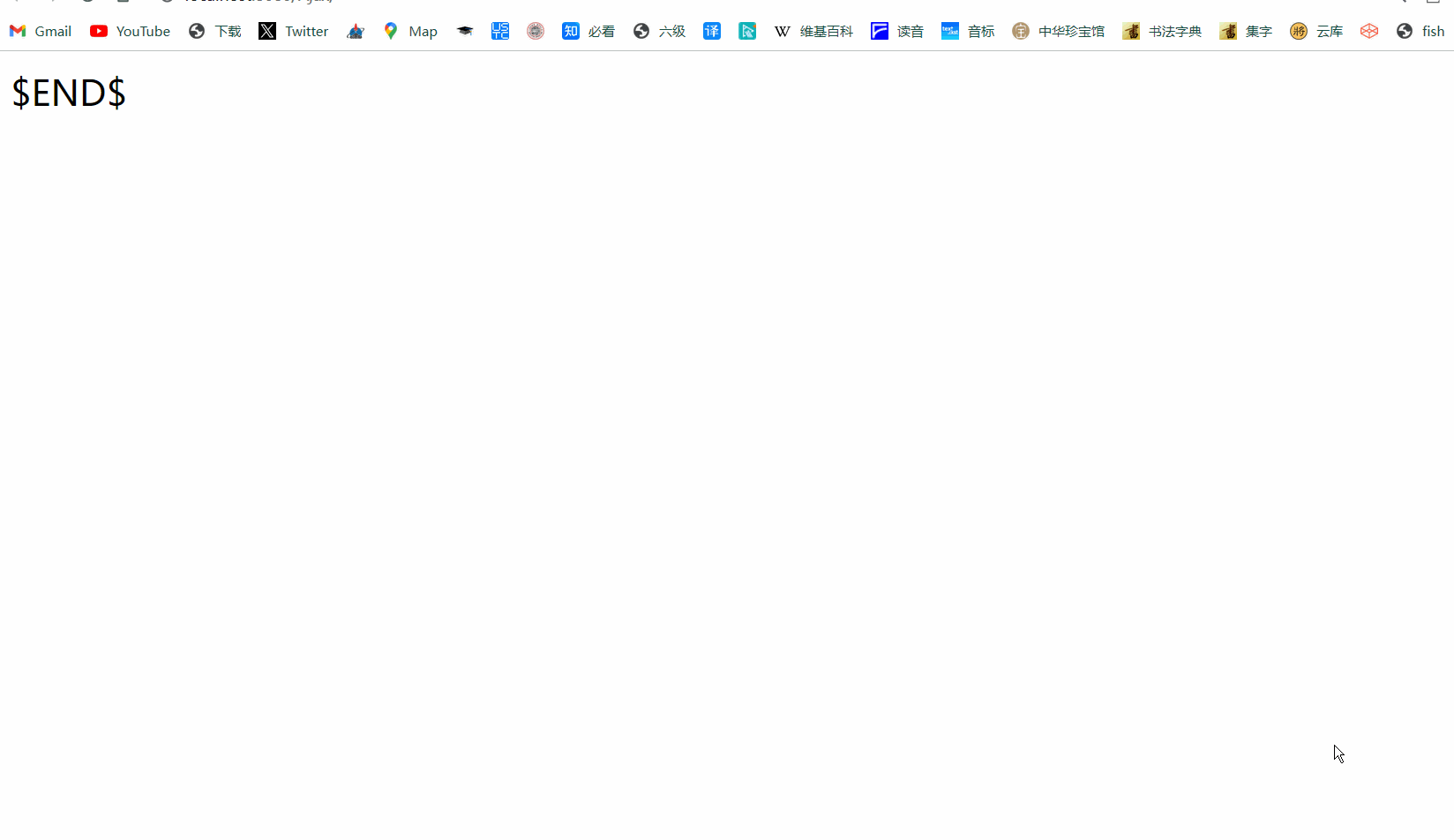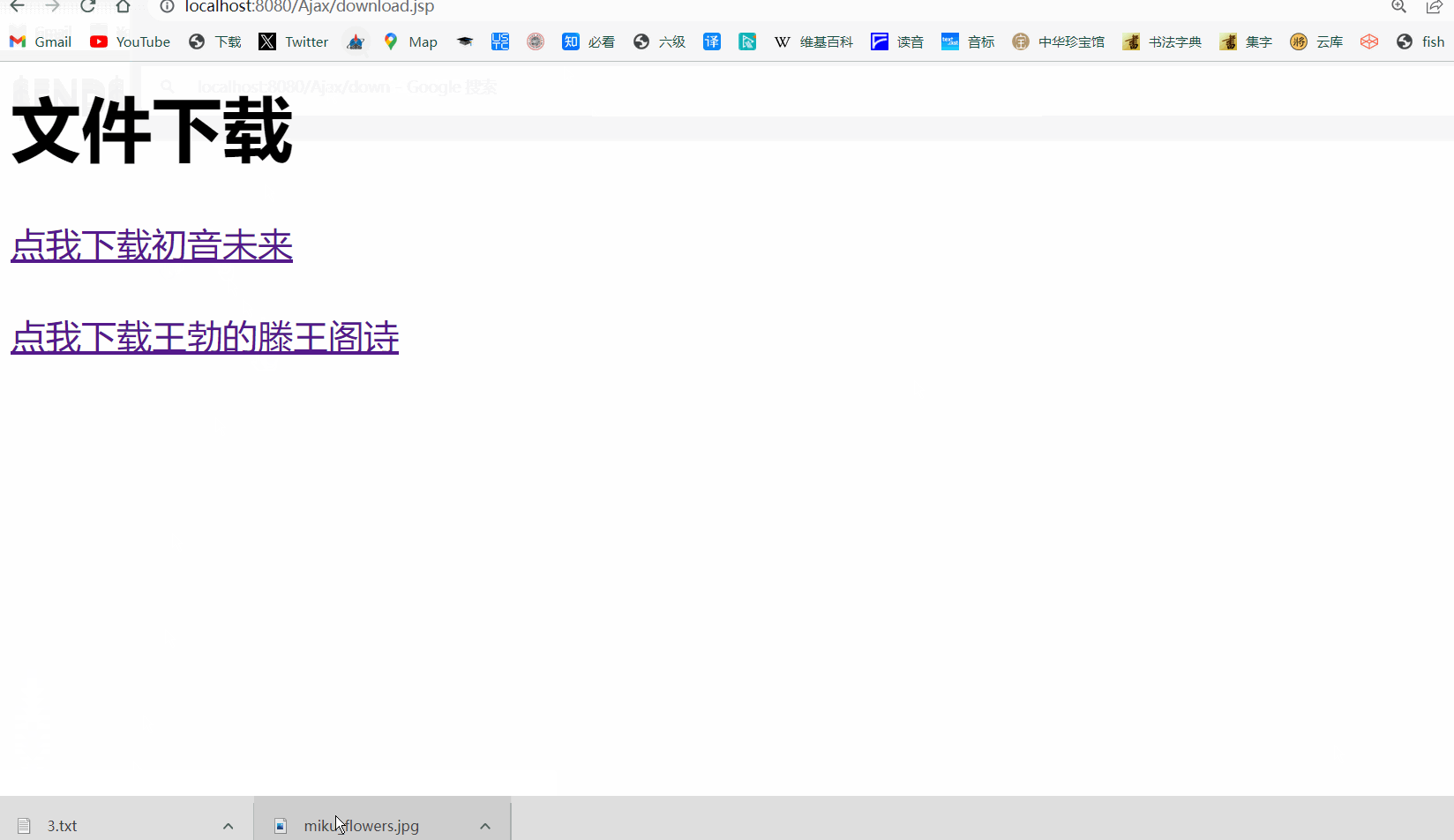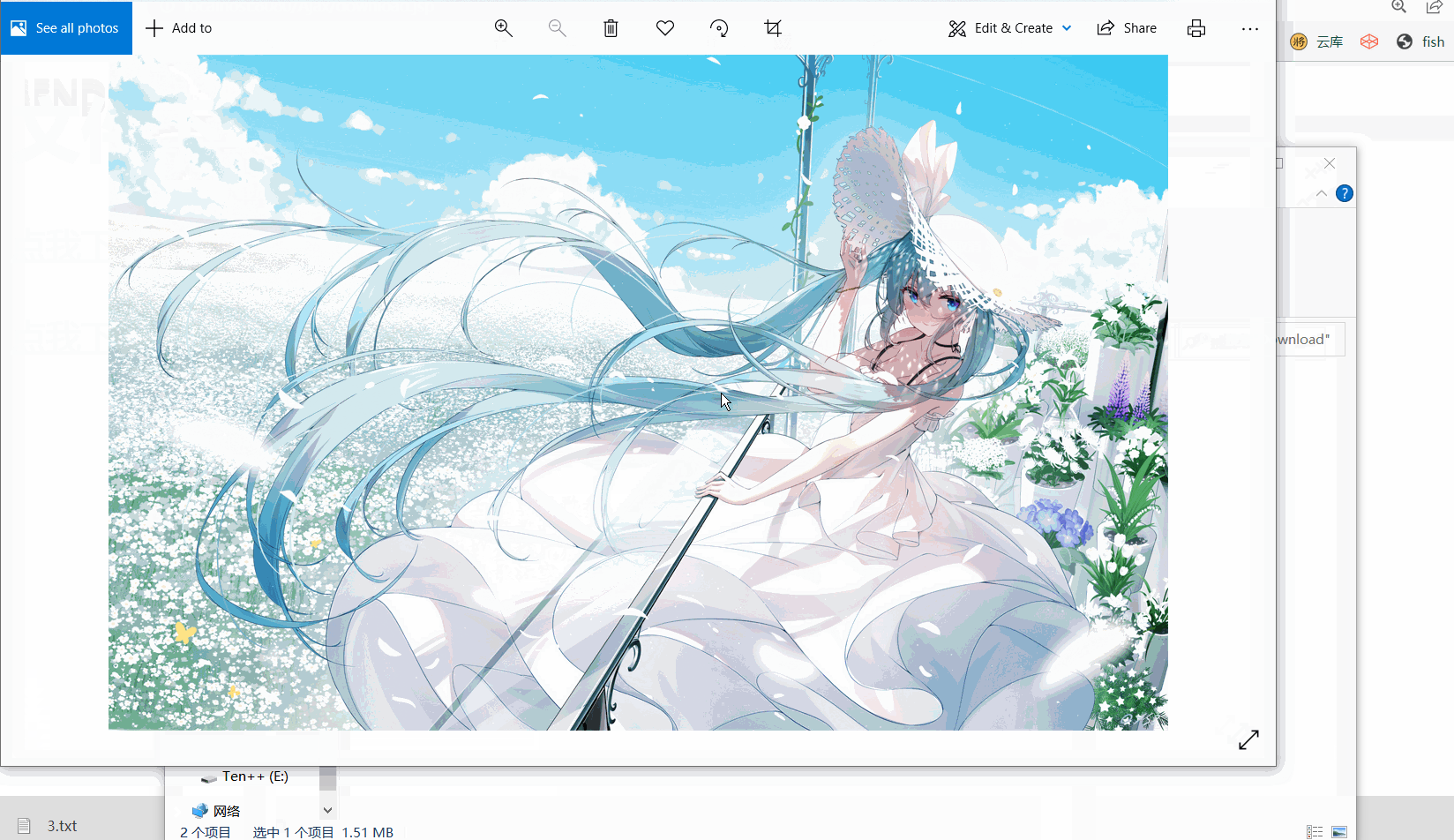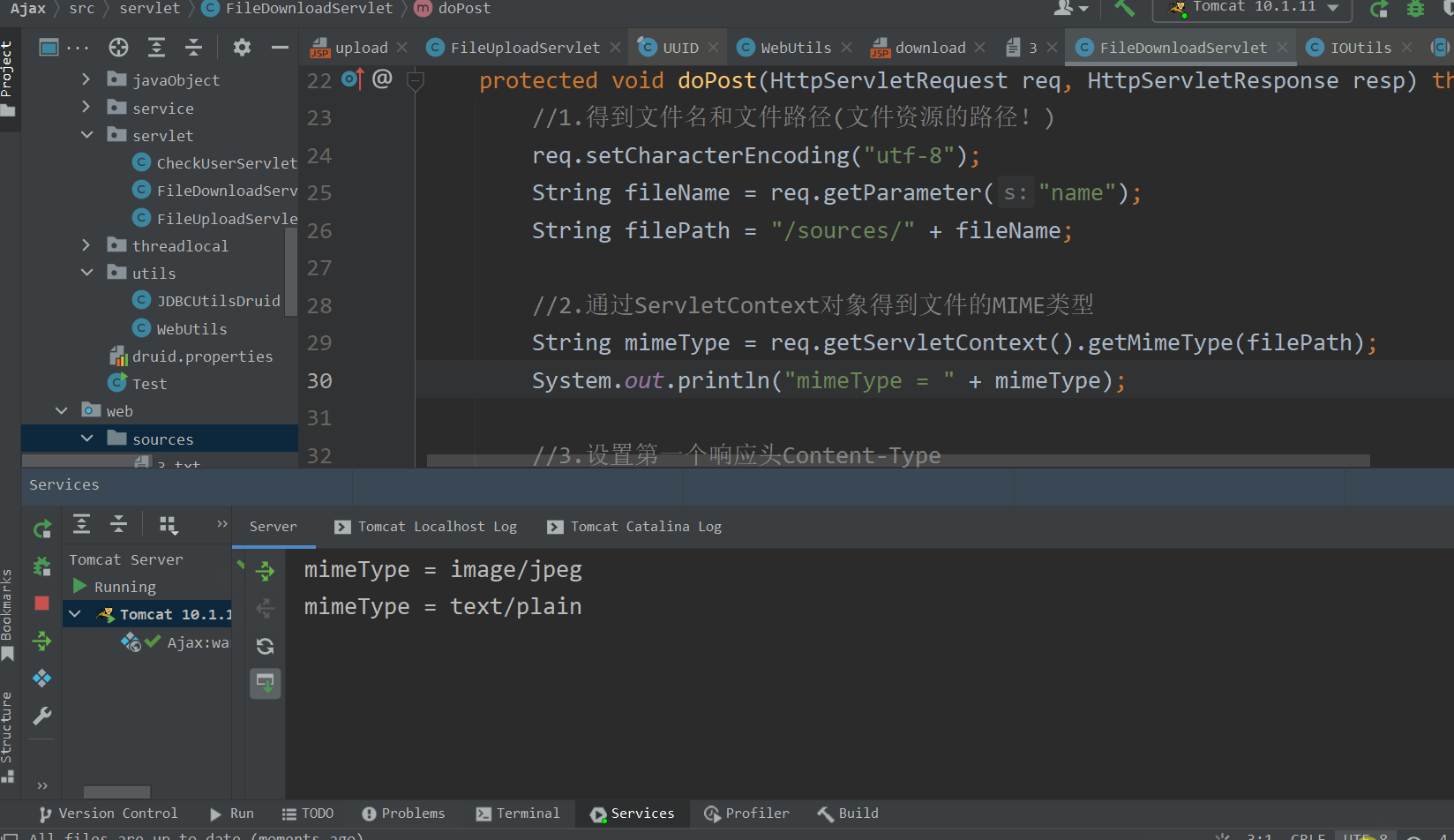
2.案例一:如果数据库对应的数据改变就向前端发送新的数据信息,解决长轮询的问题
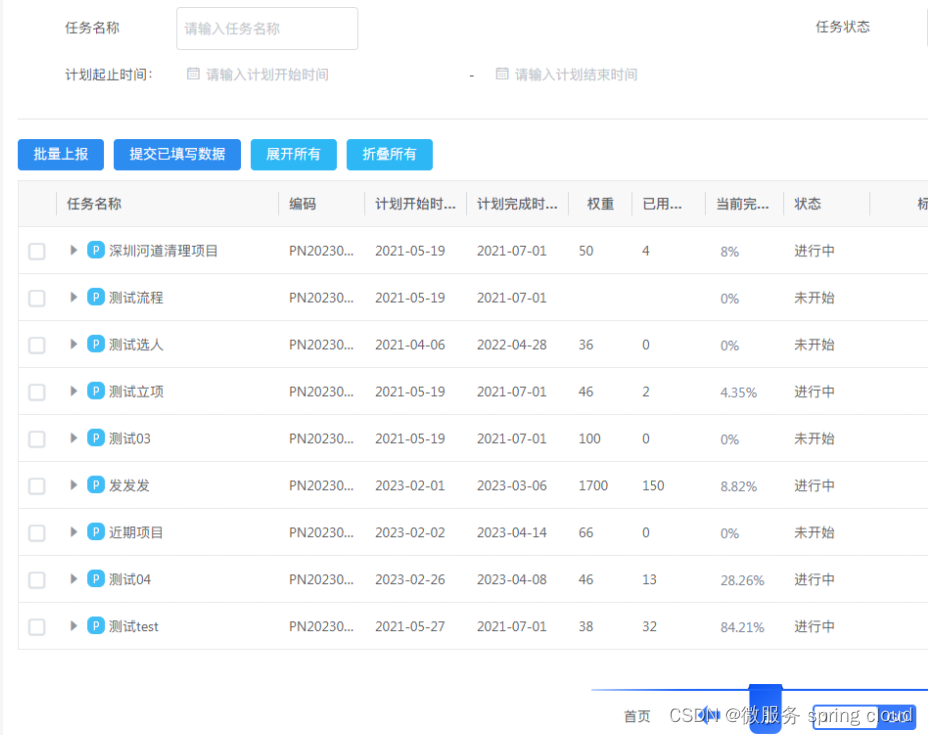
场景:签到页面显示对应的签到信息,要根据信息的改变,如课程的签到状态,需要签到什么课程等信息的改变来在客户端实时更新这些信息。使用webSocket代替轮询解决这个问题。
下面是ui界面:
【1】在configure中增加代码,主要是为了通过配置类进而使得websocket获取请求头中的token
参考文章
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class WebSocketConfig extends ServerEndpointConfig.Configurator {// 创建ServerEndpointExporter的Bean,用于自动注册WebSocket端点@Beanpublic ServerEndpointExporter serverEndpointExporter() {return new ServerEndpointExporter();}/*** 建立握手时,连接前的操作* 在这个方法中可以修改WebSocket握手时的配置信息,并将一些额外的属性添加到用户属性中*/@Overridepublic void modifyHandshake(ServerEndpointConfig sec, HandshakeRequest request, HandshakeResponse response) {// 获取用户属性final Map<String, Object> userProperties = sec.getUserProperties();// 获取HTTP请求头信息Map<String, List<String>> headers = request.getHeaders();// 通过"Authorization"键从请求头中获取对应的token,并存储在用户属性中List<String> header1 = headers.get("Authorization");userProperties.put("Authorization", header1.get(0));}/*** 初始化端点对象,也就是被@ServerEndpoint所标注的对象* 在这个方法中可以自定义实例化过程,比如通过Spring容器获取实例*/@Overridepublic <T> T getEndpointInstance(Class<T> clazz) throws InstantiationException {return super.getEndpointInstance(clazz);}/*** 获取指定会话的指定请求头的值** @param session WebSocket会话对象* @param headerName 请求头名称* @return 请求头的值*/public static String getHeader(Session session, String headerName) {// 从会话的用户属性中获取指定请求头的值final String header = (String) session.getUserProperties().get(headerName);// 如果请求头的值为空或空白,则记录错误日志,并关闭会话if (StrUtil.isBlank(header)) {log.error("获取header失败,不安全的链接,即将关闭");try {session.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}return header;}
}【2】编写ServerEndpoint
这里主要有三个技术点:
技术点一:注入mapper或service
这里注入如果按controller的方式直接注入无法注入成功,需要设置成静态变量然后写个方法赋值。
技术点二:获取请求头中的token,通过配置可以使用session.getUserProperties().get("")获取请求头
技术点三:建立线程,每隔一段时间检查数据库并更新客户端的数据
@Slf4j
@Component
@ServerEndpoint(value = "/websocket/studentNowAttendances/{userId}",configurator = WebSocketConfig.class)
public class CourseAttendanceEndPoint {//技术点一:注入mapper或service//这里注入如果按controller的方式直接注入无法注入成功,需要设置成静态变量然后写个方法赋值。private static StudentMapper studentMapper;@Autowiredpublic void setStudentMapper (StudentMapper studentMapper){CourseAttendanceEndPoint.studentMapper = studentMapper;}private static CourseAttendanceService courseAttendanceService;@Autowiredpublic void setCourseAttendanceService (CourseAttendanceService courseAttendanceService){CourseAttendanceEndPoint.courseAttendanceService = courseAttendanceService;}private static RedisCache redisCache;@Autowiredprivate void setRedisCache (RedisCache redisCache){CourseAttendanceEndPoint.redisCache = redisCache;}/*** 与某个客户端的连接对话,需要通过它来给客户端发送消息*/private Session session;/*** 标识当前连接客户端的用userId*/private String studentId;/*** 用于存所有的连接服务的客户端,这个对象存储是安全的* 注意这里的key和value,设计的很巧妙,value刚好是本类对象 (用来存放每个客户端对应的MyWebSocket对象)*/private static ConcurrentHashMap<String, CourseAttendanceEndPoint> webSocketSet = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();//线程private ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;//存储该学生用户获取到的课程信息private StudentAttendanceNow lastCourseInfo = new StudentAttendanceNow();/*** 群发* @param message*/public void groupSending(String message){for (String name : webSocketSet.keySet()){try {webSocketSet.get(name).session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}/*** 指定发送* @param studentId* @param message*/public void appointSending(String studentId,String message){System.out.println(webSocketSet.get(studentId).session);try {webSocketSet.get(studentId).session.getBasicRemote().sendText(message);}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 连接建立成功调用的方法* session为与某个客户端的连接会话,需要通过它来给客户端发送数据*/@OnOpenpublic void OnOpen(Session session, EndpointConfig config,@PathParam("userId") String userId){log.info("----------------------------------");//技术点二:获取请求头中的token,通过配置可以使用session.getUserProperties().get("")获取请求头// 获取用户属性//获取HttpSession对象final String Authorization = (String) session.getUserProperties().get("Authorization");System.out.println(Authorization);Claims claims= JwtUtil.parseJwt(Authorization);userId=claims.getSubject();QueryWrapper<Student> studentQueryWrapper=new QueryWrapper<Student>();studentQueryWrapper.eq("userid",userId);Student student=studentMapper.selectOne(studentQueryWrapper);//为这个websocket的studentId和session变量赋值,因为后面还要用到studentId=student.getId().toString();// studentId是用来表示唯一客户端,如果需要指定发送,需要指定发送通过studentId来区分this.session=session;//这句话一定要写,不然后面就会报错session为空//将studentId及其对应的websocket实例保存在属于类的webSocketSet中,便于后续发送信息时候可以知道要发送给哪个实例webSocketSet.put(studentId,this);//打印websocket信息log.info("[WebSocket] 连接成功,当前连接人数为:={}",webSocketSet.size());log.info("----------------------------------");log.info("");//技术点三:建立线程,每隔一段时间检查数据库并更新客户端的数据//建立线程,每个一段时间检查客户端对应在websocket中的数据有没有改变,有改变将信息重新发给客户端scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::checkDatabaseAndUpdateClients, 0, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);}//每个一段时间检查客户端对应在websocket中的数据有没有改变,有改变将信息重新发给客户端private void checkDatabaseAndUpdateClients() {// 模拟查询最新的课程信息// 假设从数据库或其他数据源中查询得到最新的课程信息System.out.println("666");try{//获取当前的信息StudentAttendanceNow currentCourseInfo = courseAttendanceService.getStudentAttendanceNow(studentId);//与之前的信息进行比较,如果说当前数据与上次存储的数据相比发生了改变,那就替换掉原来的数据并把新的数据发送给客户端if(lastCourseInfo.equals(currentCourseInfo)==false){lastCourseInfo=currentCourseInfo;System.out.println(studentId);appointSending(studentId, JSON.toJSONString(currentCourseInfo));}}catch (Exception e){//防止没有查询到数据等异常System.out.println(e);}}/*** 连接关闭调用的方法*/@OnClosepublic void OnClose(){//退出时将用户从记录中删除,并在log中打印退出信息webSocketSet.remove(this.studentId);log.info("[WebSocket] 退出成功,当前连接人数为:={}",webSocketSet.size());// 关闭定时任务scheduler.shutdown();}/*** 收到客户端消息后调用的方法*/@OnMessagepublic void OnMessage(Session session,String message){}/*** 发生错误时调用* @param session* @param error*/@OnErrorpublic void onError(Session session, Throwable error){log.info("发生错误");error.printStackTrace();}}