1. IO概述
1.1 什么是IO
生活中,你肯定经历过这样的场景。当你编辑一个文本文件,忘记了ctrl+s ,可能文件就白白编辑了。当你电脑上插入一个U盘,可以把一个视频,拷贝到你的电脑硬盘里。那么数据都是在哪些设备上的呢?键盘、内存、硬盘、外接设备等等。
我们把这种数据的传输,可以看做是一种数据的流动,按照流动的方向,以内存为基准,分为输入input 和输出output ,即流向内存是输入流,流出内存的输出流。
Java中I/O操作主要是指使用java.io包下的内容,进行输入、输出操作。输入也叫做读取数据,输出也叫做作写出数据。
1.2 IO的分类
根据数据的流向分为:输入流和输出流。
- 输入流 :把数据从
其他设备上读取到内存中的流。 - 输出流 :把数据从
内存中写出到其他设备上的流。
格局数据的类型分为:字节流和字符流。
- 字节流 :以字节为单位,读写数据的流。
- 字符流 :以字符为单位,读写数据的流。
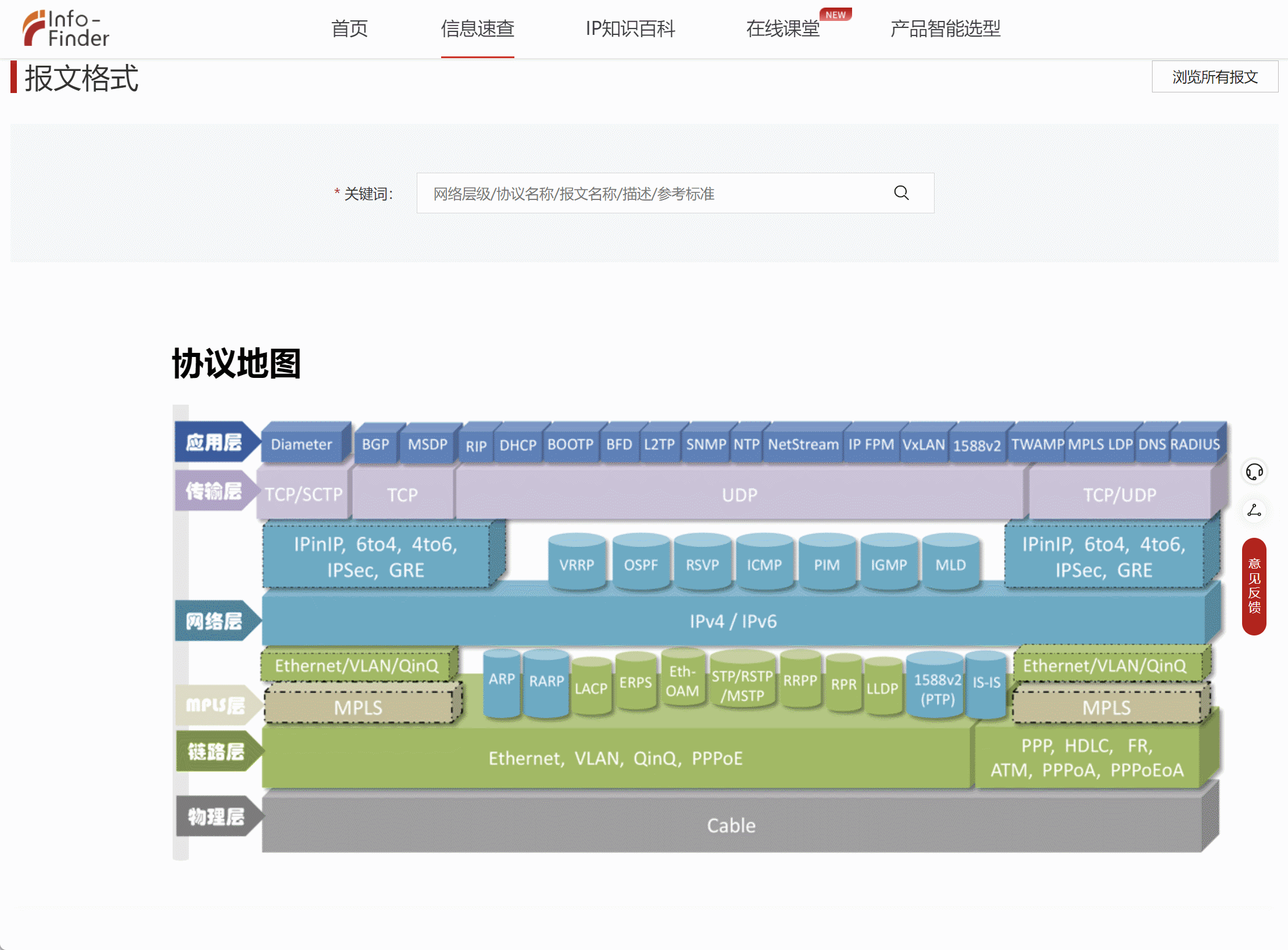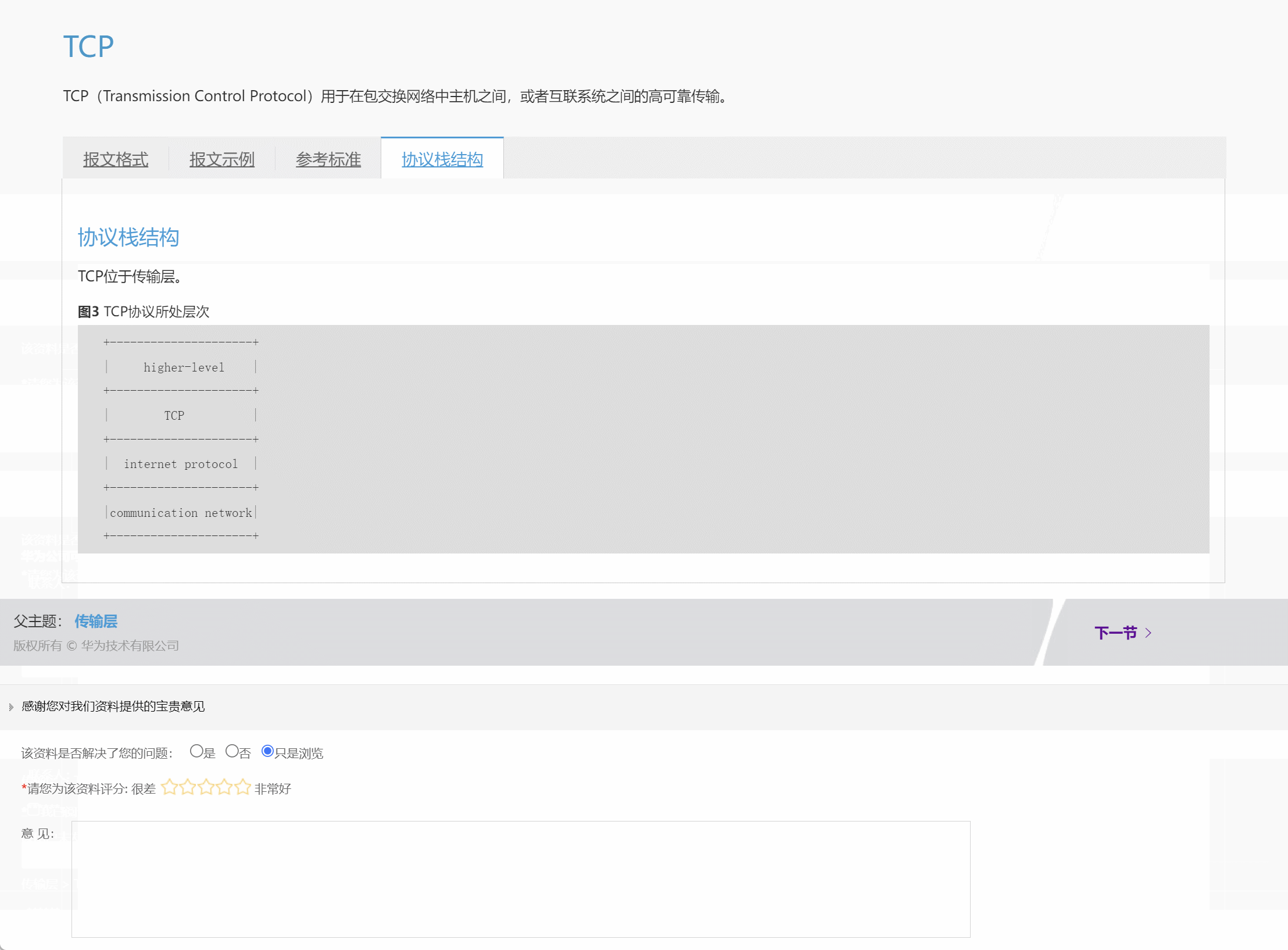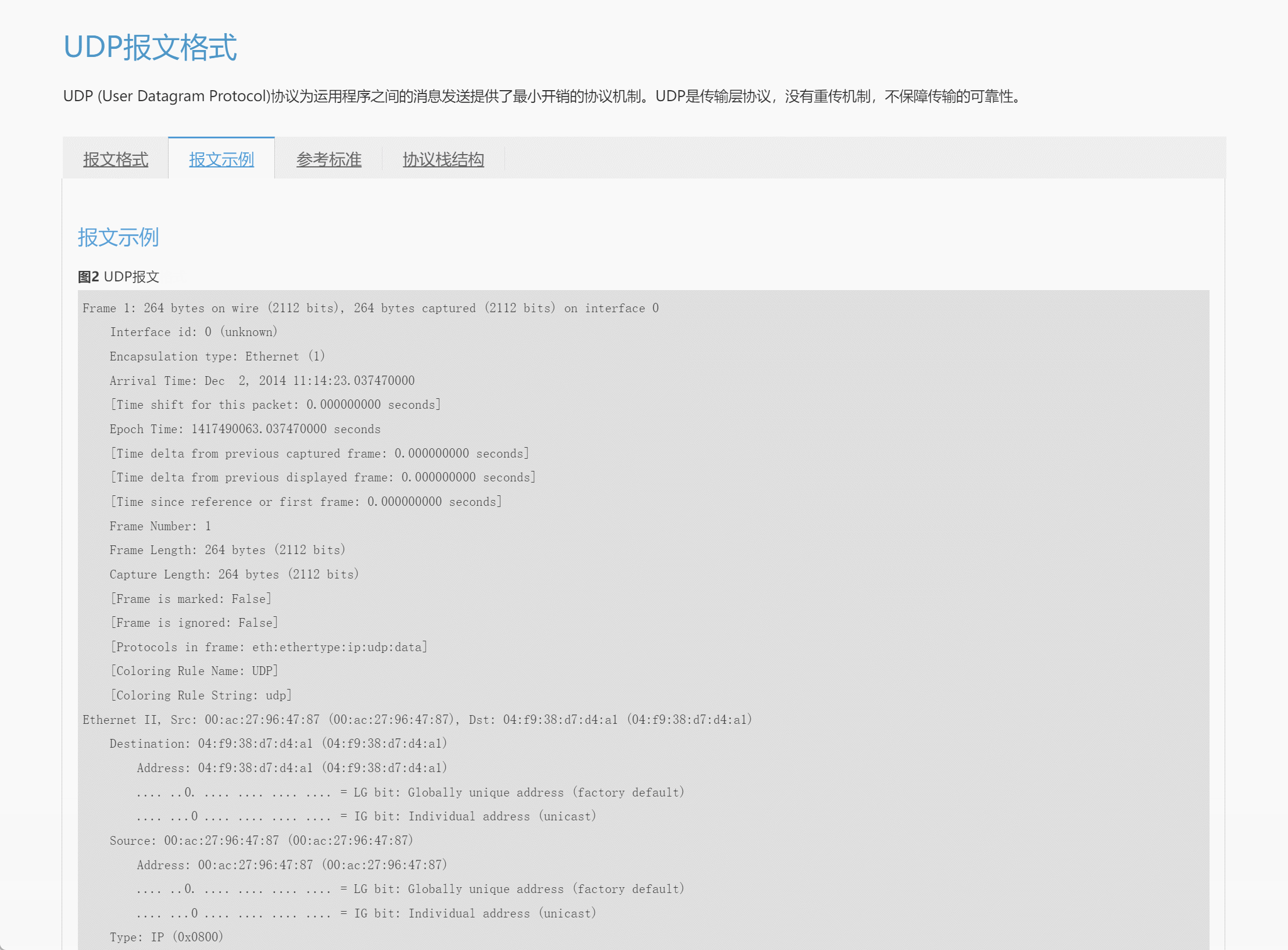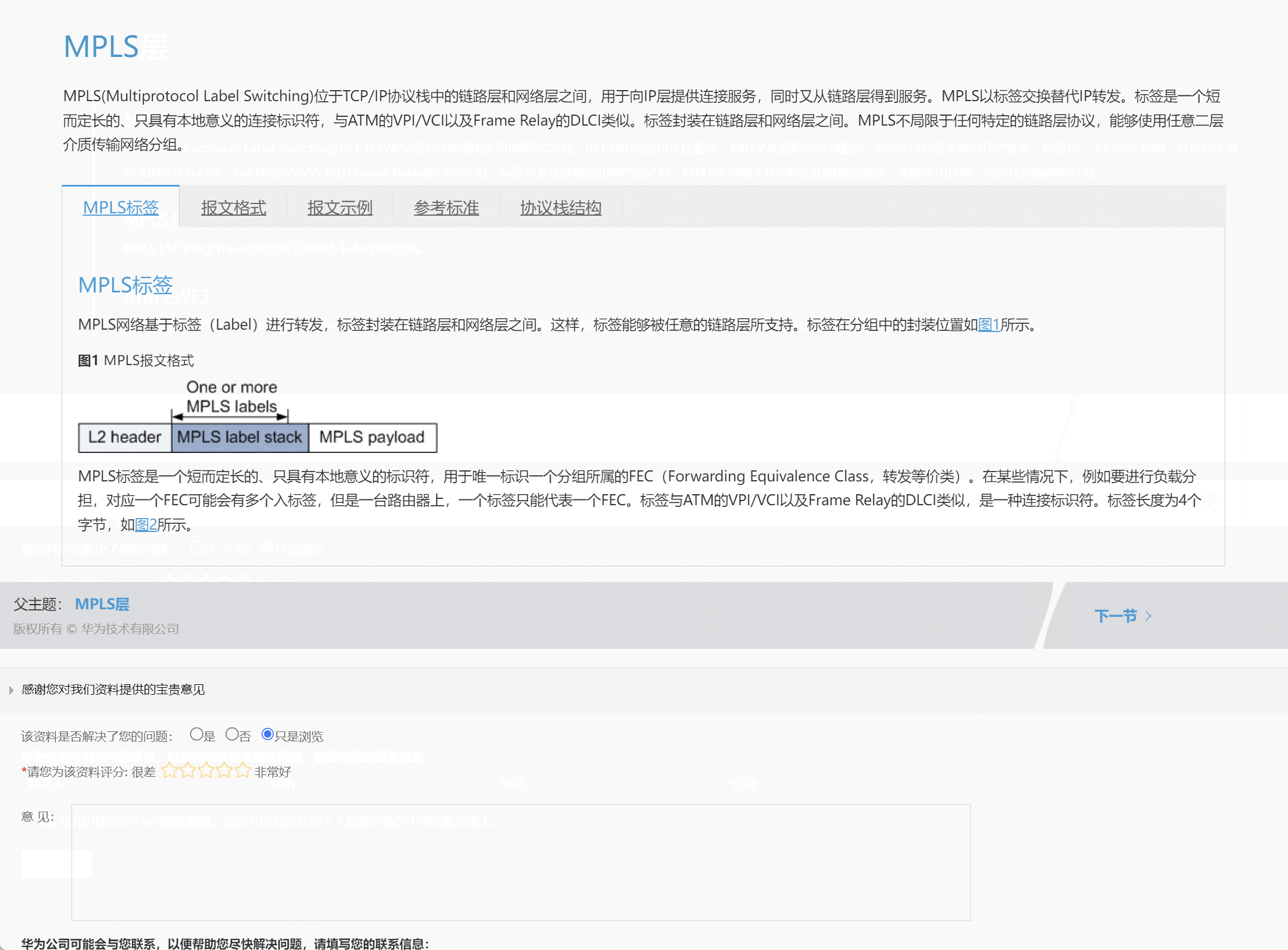
1.3 IO的流向说明图解

1.4 顶级父类们
| 输入流 | 输出流 | |
|---|---|---|
| 字节流 | 字节输入流 InputStream | 字节输出流 OutputStream |
| 字符流 | 字符输入流 Reader | 字符输出流 Writer |
2. 字节流
2.1 一切皆为字节
一切文件数据(文本、图片、视频等)在存储时,都是以二进制数字的形式保存,都一个一个的字节,那么传输时一样如此。所以,字节流可以传输任意文件数据。在操作流的时候,我们要时刻明确,无论使用什么样的流对象,底层传输的始终为二进制数据。
2.2 字节输出流【OutputStream】
java.io.OutputStream 抽象类是表示字节输出流的所有类的超类,将指定的字节信息写出到目的地。它定义了字节输出流的基本共性功能方法。
public void close():关闭此输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。public void flush():刷新此输出流并强制任何缓冲的输出字节被写出。public void write(byte[] b):将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流。public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len):从指定的字节数组写入 len字节,从偏移量 off开始输出到此输出流。public abstract void write(int b):将指定的字节输出流。
小贴士:
close方法,当完成流的操作时,必须调用此方法,释放系统资源。
2.3 FileOutputStream类
OutputStream有很多子类,我们从最简单的一个子类开始。
java.io.FileOutputStream 类是文件输出流,用于将数据写出到文件。
构造方法
public FileOutputStream(File file):创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。public FileOutputStream(String name): 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。
当你创建一个流对象时,必须传入一个文件路径。该路径下,如果没有这个文件,会创建该文件。如果有这个文件,会清空这个文件的数据。
- 构造举例,代码如下:
public class FileOutputStreamConstructor throws IOException {public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用File对象创建流对象File file = new File("a.txt");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("b.txt");}
}
写出字节数据
- 写出字节:
write(int b)方法,每次可以写出一个字节数据,代码使用演示:
public class FOSWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt"); // 写出数据fos.write(97); // 写出第1个字节fos.write(98); // 写出第2个字节fos.write(99); // 写出第3个字节// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
输出结果:
abc
小贴士:
- 虽然参数为int类型四个字节,但是只会保留一个字节的信息写出。
- 流操作完毕后,必须释放系统资源,调用close方法,千万记得。
- 写出字节数组:
write(byte[] b),每次可以写出数组中的数据,代码使用演示:
public class FOSWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt"); // 字符串转换为字节数组byte[] b = "黑马程序员".getBytes();// 写出字节数组数据fos.write(b);// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
输出结果:
黑马程序员
- 写出指定长度字节数组:
write(byte[] b, int off, int len),每次写出从off索引开始,len个字节,代码使用演示:
public class FOSWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt"); // 字符串转换为字节数组byte[] b = "abcde".getBytes();// 写出从索引2开始,2个字节。索引2是c,两个字节,也就是cd。fos.write(b,2,2);// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
输出结果:
cd
数据追加续写
经过以上的演示,每次程序运行,创建输出流对象,都会清空目标文件中的数据。如何保留目标文件中数据,还能继续添加新数据呢?
public FileOutputStream(File file, boolean append): 创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件。public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append): 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件。
这两个构造方法,参数中都需要传入一个boolean类型的值,true 表示追加数据,false 表示清空原有数据。这样创建的输出流对象,就可以指定是否追加续写了,代码使用演示:
public class FOSWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt",true); // 字符串转换为字节数组byte[] b = "abcde".getBytes();// 写出从索引2开始,2个字节。索引2是c,两个字节,也就是cd。fos.write(b);// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
文件操作前:cd
文件操作后:cdabcde
写出换行
Windows系统里,换行符号是\r\n 。把
以指定是否追加续写了,代码使用演示:
public class FOSWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("fos.txt"); // 定义字节数组byte[] words = {97,98,99,100,101};// 遍历数组for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {// 写出一个字节fos.write(words[i]);// 写出一个换行, 换行符号转成数组写出fos.write("\r\n".getBytes());}// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}输出结果:
a
b
c
d
e
- 回车符
\r和换行符\n:
- 回车符:回到一行的开头(return)。
- 换行符:下一行(newline)。
- 系统中的换行:
- Windows系统里,每行结尾是
回车+换行,即\r\n;- Unix系统里,每行结尾只有
换行,即\n;- Mac系统里,每行结尾是
回车,即\r。从 Mac OS X开始与Linux统一。
2.4 字节输入流【InputStream】
java.io.InputStream 抽象类是表示字节输入流的所有类的超类,可以读取字节信息到内存中。它定义了字节输入流的基本共性功能方法。
public void close():关闭此输入流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。public abstract int read(): 从输入流读取数据的下一个字节。public int read(byte[] b): 从输入流中读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到字节数组 b中 。
小贴士:
close方法,当完成流的操作时,必须调用此方法,释放系统资源。
2.5 FileInputStream类
java.io.FileInputStream 类是文件输入流,从文件中读取字节。
构造方法
FileInputStream(File file): 通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream ,该文件由文件系统中的 File对象 file命名。FileInputStream(String name): 通过打开与实际文件的连接来创建一个 FileInputStream ,该文件由文件系统中的路径名 name命名。
当你创建一个流对象时,必须传入一个文件路径。该路径下,如果没有该文件,会抛出FileNotFoundException 。
- 构造举例,代码如下:
public class FileInputStreamConstructor throws IOException{public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用File对象创建流对象File file = new File("a.txt");FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream(file);// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileInputStream fos = new FileInputStream("b.txt");}
}
读取字节数据
- 读取字节:
read方法,每次可以读取一个字节的数据,提升为int类型,读取到文件末尾,返回-1,代码使用演示:
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt");// 读取数据,返回一个字节int read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);read = fis.read();System.out.println((char) read);// 读取到末尾,返回-1read = fis.read();System.out.println( read);// 关闭资源fis.close();}
}
输出结果:
a
b
c
d
e
-1
循环改进读取方式,代码使用演示:
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt");// 定义变量,保存数据int b ;// 循环读取while ((b = fis.read())!=-1) {System.out.println((char)b);}// 关闭资源fis.close();}
}
输出结果:
a
b
c
d
e
小贴士:
- 虽然读取了一个字节,但是会自动提升为int类型。
- 流操作完毕后,必须释放系统资源,调用close方法,千万记得。
- 使用字节数组读取:
read(byte[] b),每次读取b的长度个字节到数组中,返回读取到的有效字节个数,读取到末尾时,返回-1,代码使用演示:
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{// 使用文件名称创建流对象.FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt"); // 文件中为abcde// 定义变量,作为有效个数int len ;// 定义字节数组,作为装字节数据的容器 byte[] b = new byte[2];// 循环读取while (( len= fis.read(b))!=-1) {// 每次读取后,把数组变成字符串打印System.out.println(new String(b));}// 关闭资源fis.close();}
}输出结果:
ab
cd
ed
错误数据d,是由于最后一次读取时,只读取一个字节e,数组中,上次读取的数据没有被完全替换,所以要通过len ,获取有效的字节,代码使用演示:
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{// 使用文件名称创建流对象.FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("read.txt"); // 文件中为abcde// 定义变量,作为有效个数int len ;// 定义字节数组,作为装字节数据的容器 byte[] b = new byte[2];// 循环读取while (( len= fis.read(b))!=-1) {// 每次读取后,把数组的有效字节部分,变成字符串打印System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));// len 每次读取的有效字节个数}// 关闭资源fis.close();}
}输出结果:
ab
cd
e
小贴士:
使用数组读取,每次读取多个字节,减少了系统间的IO操作次数,从而提高了读写的效率,建议开发中使用。
2.6 字节流练习:图片复制
复制原理图解

案例实现
复制图片文件,代码使用演示:
public class Copy {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 1.创建流对象// 1.1 指定数据源FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\test.jpg");// 1.2 指定目的地FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("test_copy.jpg");// 2.读写数据// 2.1 定义数组byte[] b = new byte[1024];// 2.2 定义长度int len;// 2.3 循环读取while ((len = fis.read(b))!=-1) {// 2.4 写出数据fos.write(b, 0 , len);}// 3.关闭资源fos.close();fis.close();}
}
小贴士:
流的关闭原则:先开后关,后开先关。
3. 字符流
当使用字节流读取文本文件时,可能会有一个小问题。就是遇到中文字符时,可能不会显示完整的字符,那是因为一个中文字符可能占用多个字节存储。所以Java提供一些字符流类,以字符为单位读写数据,专门用于处理文本文件。
3.1 字符输入流【Reader】
java.io.Reader抽象类是表示用于读取字符流的所有类的超类,可以读取字符信息到内存中。它定义了字符输入流的基本共性功能方法。
public void close():关闭此流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源。public int read(): 从输入流读取一个字符。public int read(char[] cbuf): 从输入流中读取一些字符,并将它们存储到字符数组 cbuf中 。
3.2 FileReader类
java.io.FileReader 类是读取字符文件的便利类。构造时使用系统默认的字符编码和默认字节缓冲区。
小贴士:
字符编码:字节与字符的对应规则。Windows系统的中文编码默认是GBK编码表。
idea中UTF-8
字节缓冲区:一个字节数组,用来临时存储字节数据。
构造方法
FileReader(File file): 创建一个新的 FileReader ,给定要读取的File对象。FileReader(String fileName): 创建一个新的 FileReader ,给定要读取的文件的名称。
当你创建一个流对象时,必须传入一个文件路径。类似于FileInputStream 。
- 构造举例,代码如下:
public class FileReaderConstructor throws IOException{public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用File对象创建流对象File file = new File("a.txt");FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileReader fr = new FileReader("b.txt");}
}
读取字符数据
- 读取字符:
read方法,每次可以读取一个字符的数据,提升为int类型,读取到文件末尾,返回-1,循环读取,代码使用演示:
public class FRRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileReader fr = new FileReader("read.txt");// 定义变量,保存数据int b ;// 循环读取while ((b = fr.read())!=-1) {System.out.println((char)b);}// 关闭资源fr.close();}
}
输出结果:
黑
马
程
序
员
小贴士:虽然读取了一个字符,但是会自动提升为int类型。
- 使用字符数组读取:
read(char[] cbuf),每次读取b的长度个字符到数组中,返回读取到的有效字符个数,读取到末尾时,返回-1,代码使用演示:
public class FRRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileReader fr = new FileReader("read.txt");// 定义变量,保存有效字符个数int len ;// 定义字符数组,作为装字符数据的容器char[] cbuf = new char[2];// 循环读取while ((len = fr.read(cbuf))!=-1) {System.out.println(new String(cbuf));}// 关闭资源fr.close();}
}
输出结果:
黑马
程序
员序
获取有效的字符改进,代码使用演示:
public class FISRead {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileReader fr = new FileReader("read.txt");// 定义变量,保存有效字符个数int len ;// 定义字符数组,作为装字符数据的容器char[] cbuf = new char[2];// 循环读取while ((len = fr.read(cbuf))!=-1) {System.out.println(new String(cbuf,0,len));}// 关闭资源fr.close();}
}输出结果:
黑马
程序
员
3.3 字符输出流【Writer】
java.io.Writer 抽象类是表示用于写出字符流的所有类的超类,将指定的字符信息写出到目的地。它定义了字节输出流的基本共性功能方法。
void write(int c)写入单个字符。void write(char[] cbuf)写入字符数组。abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)写入字符数组的某一部分,off数组的开始索引,len写的字符个数。void write(String str)写入字符串。void write(String str, int off, int len)写入字符串的某一部分,off字符串的开始索引,len写的字符个数。void flush()刷新该流的缓冲。void close()关闭此流,但要先刷新它。
3.4 FileWriter类
java.io.FileWriter 类是写出字符到文件的便利类。构造时使用系统默认的字符编码和默认字节缓冲区。
构造方法
FileWriter(File file): 创建一个新的 FileWriter,给定要读取的File对象。FileWriter(String fileName): 创建一个新的 FileWriter,给定要读取的文件的名称。
当你创建一个流对象时,必须传入一个文件路径,类似于FileOutputStream。
- 构造举例,代码如下:
public class FileWriterConstructor {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用File对象创建流对象File file = new File("a.txt");FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("b.txt");}
}
基本写出数据
写出字符:write(int b) 方法,每次可以写出一个字符数据,代码使用演示:
public class FWWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt"); // 写出数据fw.write(97); // 写出第1个字符fw.write('b'); // 写出第2个字符fw.write('C'); // 写出第3个字符fw.write(30000); // 写出第4个字符,中文编码表中30000对应一个汉字。/*【注意】关闭资源时,与FileOutputStream不同。如果不关闭,数据只是保存到缓冲区,并未保存到文件。*/// fw.close();}
}
输出结果:
abC田
小贴士:
- 虽然参数为int类型四个字节,但是只会保留一个字符的信息写出。
- 未调用close方法,数据只是保存到了缓冲区,并未写出到文件中。
关闭和刷新
因为内置缓冲区的原因,如果不关闭输出流,无法写出字符到文件中。但是关闭的流对象,是无法继续写出数据的。如果我们既想写出数据,又想继续使用流,就需要flush 方法了。
flush:刷新缓冲区,流对象可以继续使用。close:先刷新缓冲区,然后通知系统释放资源。流对象不可以再被使用了。
代码使用演示:
public class FWWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");// 写出数据,通过flushfw.write('刷'); // 写出第1个字符fw.flush();fw.write('新'); // 继续写出第2个字符,写出成功fw.flush();// 写出数据,通过closefw.write('关'); // 写出第1个字符fw.close();fw.write('闭'); // 继续写出第2个字符,【报错】java.io.IOException: Stream closedfw.close();}
}
小贴士:即便是flush方法写出了数据,操作的最后还是要调用close方法,释放系统资源。
写出其他数据
- 写出字符数组 :
write(char[] cbuf)和write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len),每次可以写出字符数组中的数据,用法类似FileOutputStream,代码使用演示:
public class FWWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt"); // 字符串转换为字节数组char[] chars = "黑马程序员".toCharArray();// 写出字符数组fw.write(chars); // 黑马程序员// 写出从索引2开始,2个字节。索引2是'程',两个字节,也就是'程序'。fw.write(b,2,2); // 程序// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
- 写出字符串:
write(String str)和write(String str, int off, int len),每次可以写出字符串中的数据,更为方便,代码使用演示:
public class FWWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt"); // 字符串String msg = "黑马程序员";// 写出字符数组fw.write(msg); //黑马程序员// 写出从索引2开始,2个字节。索引2是'程',两个字节,也就是'程序'。fw.write(msg,2,2); // 程序// 关闭资源fos.close();}
}
- 续写和换行:操作类似于FileOutputStream。
public class FWWrite {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 使用文件名称创建流对象,可以续写数据FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt",true); // 写出字符串fw.write("黑马");// 写出换行fw.write("\r\n");// 写出字符串fw.write("程序员");// 关闭资源fw.close();}
}
输出结果:
黑马
程序员
小贴士:字符流,只能操作文本文件,不能操作图片,视频等非文本文件。
当我们单纯读或者写文本文件时 使用字符流 其他情况使用字节流
4. IO异常的处理
JDK7前处理
之前的入门练习,我们一直把异常抛出,而实际开发中并不能这样处理,建议使用try...catch...finally 代码块,处理异常部分,代码使用演示:
public class HandleException1 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 声明变量FileWriter fw = null;try {//创建流对象fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");// 写出数据fw.write("黑马程序员"); //黑马程序员} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if (fw != null) {fw.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
}
JDK7的处理(扩展知识点了解内容)
还可以使用JDK7优化后的try-with-resource 语句,该语句确保了每个资源在语句结束时关闭。所谓的资源(resource)是指在程序完成后,必须关闭的对象。
格式:
try (创建流对象语句,如果多个,使用';'隔开) {// 读写数据
} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();
}
代码使用演示:
public class HandleException2 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建流对象try ( FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt"); ) {// 写出数据fw.write("黑马程序员"); //黑马程序员} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
JDK9的改进(扩展知识点了解内容)
JDK9中try-with-resource 的改进,对于引入对象的方式,支持的更加简洁。被引入的对象,同样可以自动关闭,无需手动close,我们来了解一下格式。
改进前格式:
// 被final修饰的对象
final Resource resource1 = new Resource("resource1");
// 普通对象
Resource resource2 = new Resource("resource2");
// 引入方式:创建新的变量保存
try (Resource r1 = resource1;Resource r2 = resource2) {// 使用对象
}
改进后格式:
// 被final修饰的对象
final Resource resource1 = new Resource("resource1");
// 普通对象
Resource resource2 = new Resource("resource2");// 引入方式:直接引入
try (resource1; resource2) {// 使用对象
}
改进后,代码使用演示:
public class TryDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 创建流对象final FileReader fr = new FileReader("in.txt");FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("out.txt");// 引入到try中try (fr; fw) {// 定义变量int b;// 读取数据while ((b = fr.read())!=-1) {// 写出数据fw.write(b);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
5. 综合练习
练习1:拷贝文件夹
public class Test01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//拷贝一个文件夹,考虑子文件夹//1.创建对象表示数据源File src = new File("D:\\aaa\\src");//2.创建对象表示目的地File dest = new File("D:\\aaa\\dest");//3.调用方法开始拷贝copydir(src,dest);}/** 作用:拷贝文件夹* 参数一:数据源* 参数二:目的地** */private static void copydir(File src, File dest) throws IOException {dest.mkdirs();//递归//1.进入数据源File[] files = src.listFiles();//2.遍历数组for (File file : files) {if(file.isFile()){//3.判断文件,拷贝FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,file.getName()));byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len;while((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){fos.write(bytes,0,len);}fos.close();fis.close();}else {//4.判断文件夹,递归copydir(file, new File(dest,file.getName()));}}}
}练习2:文件加密
public class Test02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*为了保证文件的安全性,就需要对原始文件进行加密存储,再使用的时候再对其进行解密处理。加密原理:对原始文件中的每一个字节数据进行更改,然后将更改以后的数据存储到新的文件中。解密原理:读取加密之后的文件,按照加密的规则反向操作,变成原始文件。^ : 异或两边相同:false两边不同:true0:false1:true100:110010010: 10101100100^ 0001010__________1101110^ 0001010__________1100100*/}public static void encryptionAndReduction(File src, File dest) throws IOException {FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);int b;while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {fos.write(b ^ 2);}//4.释放资源fos.close();fis.close();}}练习3:数字排序
文本文件中有以下的数据:
2-1-9-4-7-8
将文件中的数据进行排序,变成以下的数据:
1-2-4-7-8-9
实现方式一:
public class Test03 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*文本文件中有以下的数据:2-1-9-4-7-8将文件中的数据进行排序,变成以下的数据:1-2-4-7-8-9*///1.读取数据FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\a.txt");StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();int ch;while((ch = fr.read()) != -1){sb.append((char)ch);}fr.close();System.out.println(sb);//2.排序String str = sb.toString();String[] arrStr = str.split("-");//2-1-9-4-7-8ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();for (String s : arrStr) {int i = Integer.parseInt(s);list.add(i);}Collections.sort(list);System.out.println(list);//3.写出FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\a.txt");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {if(i == list.size() - 1){fw.write(list.get(i) + "");}else{fw.write(list.get(i) + "-");}}fw.close();}
}
实现方式二:
public class Test04 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {/*文本文件中有以下的数据:2-1-9-4-7-8将文件中的数据进行排序,变成以下的数据:1-2-4-7-8-9细节1:文件中的数据不要换行细节2:bom头*///1.读取数据FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\a.txt");StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();int ch;while((ch = fr.read()) != -1){sb.append((char)ch);}fr.close();System.out.println(sb);//2.排序Integer[] arr = Arrays.stream(sb.toString().split("-")).map(Integer::parseInt).sorted().toArray(Integer[]::new);//3.写出FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\a.txt");String s = Arrays.toString(arr).replace(", ","-");String result = s.substring(1, s.length() - 1);fw.write(result);fw.close();}
}