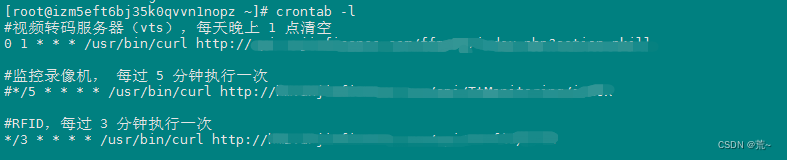
实例一:
1.在/application/command创建要配置的PHP类文件,需要继承Command类,并重写configure和execute两个方法,例如:
<?php
namespace app\command;
use think\console\Command;
use think\console\Input;
use think\console\Output;
use think\Db;
class Test extends Command
{// 配置定时器的信息protected function configure(){$this->setName('test')->setDescription('Command Test');}protected function execute(Input $input, Output $output){// 输出到日志文件$output->writeln("TestCommand:");// 定时器需要执行的内容// .....$output->writeln("end....");}
}2.修改application/command.php内容,加入上述的定时器内容
<?php
return ['application\command\Test', // 加入需要cmd运行的PHP文件
];3.添加shell执行文件
在项目根目录下创建shell脚本,例如crond.sh
#!/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/local/php/bin:/opt/someApp/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin # 将php路径加入都临时变量中
cd /home/wwwroot/域名/ # 进入项目的根目录下,保证可以运行php think的命令
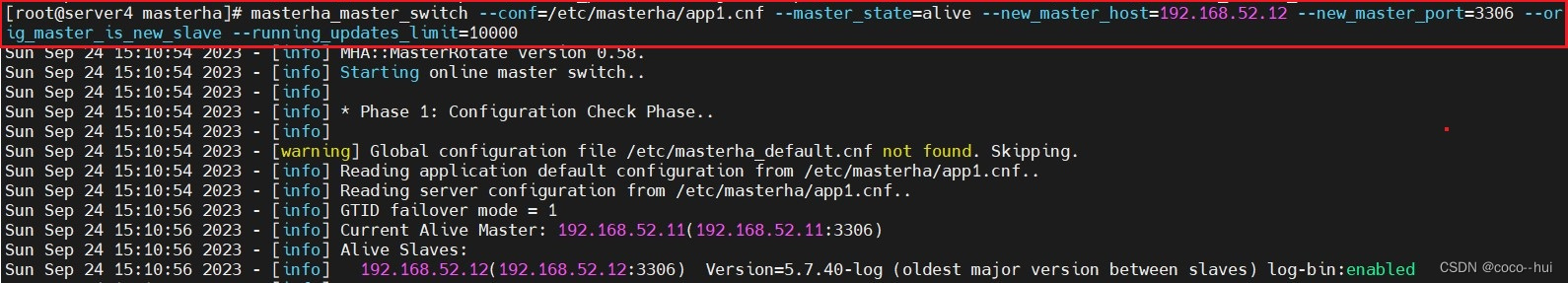
php think test # 执行在Test.php设定的名称注意:test 可执行命令是ThinkPHP自带的,可以通过 连接服务器,到/home/wwwroot/域名/ 目录下,输入 php think查询可以被执行的命令,如下:
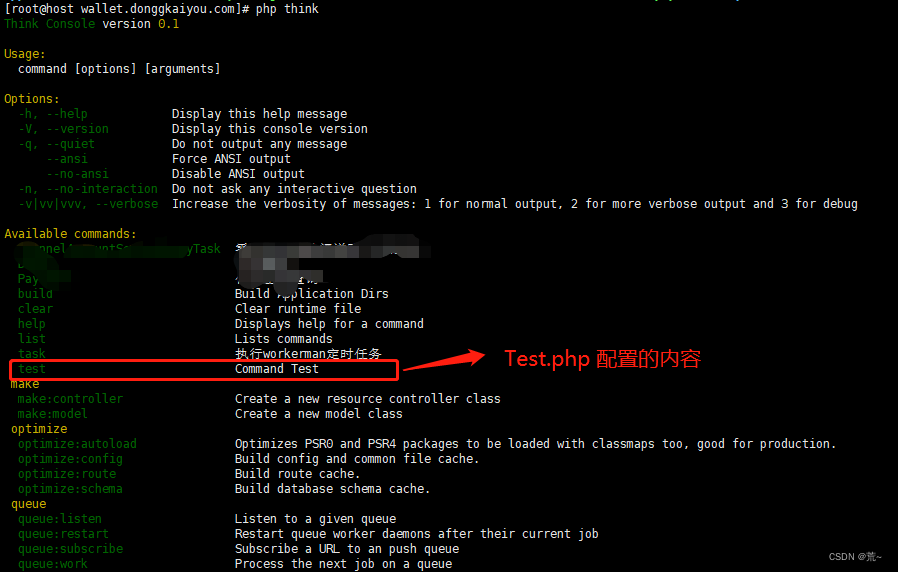
4.使用crontab设置定时器
有两种方式,效果是一样的:
1.连接到服务器,输入 crontab -e,写入:
0 0 * * * /home/wwwroot/域名/crond.sh
注意:1).0 0 * * * 是crontab的定时表达式,表示每天的0点0分执行该文件,具体详情可以访问《crontab定时写法》进行学习。
2).可以使用crontab -l 的命令查看已登录的账户有几个定时器。
3).可以到 /var/log/cron 文件查看日志文件,便于追踪错误。
2.连接到服务器,输入 vim /etc/crontab, 初始化内容为:
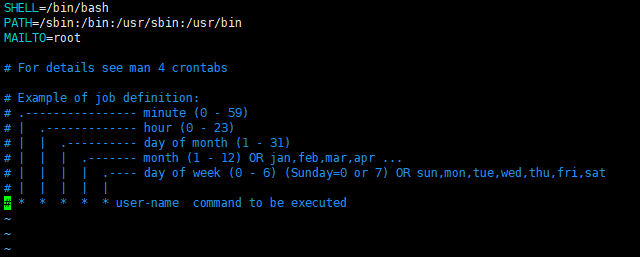
在该文件写入
0 0 * * * root /home/wwwroot/域名/crond.sh
最终的查看的结果是:
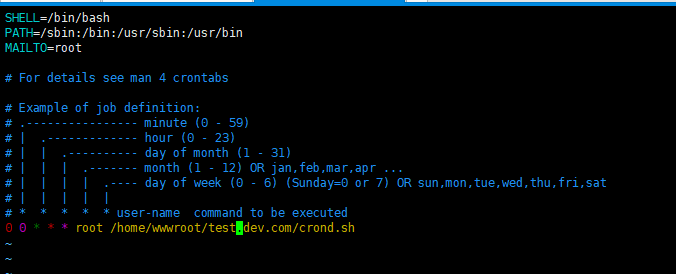
最后保存该文件
5.重启crond服务
service crond restart
如果 该命令无法重启,请使用systemctl restart crond 进行重启。
发现还有一个方法,需要修改本文的前三步,后面均一致。
1).新增Controller类,并编写相对应的方法,例如:
<?phpnamespace app\demo\controller;use think\Controller;
use think\Log;class Test extends Controller
{public function test(){Log::error('start test crond demo.....');Log::error('end test crond demo.....');}}访问test方法的路由:demo/test/test
2).添加shell执行文件
在项目根目录下创建shell脚本,例如crond.sh
#!/bin/sh
PATH=/usr/local/php/bin:/opt/someApp/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
# 1.执行 php 命令不需要到thinkphp项目的目录下 2.index.php为入口文件 3.第三个参数为需要执行方法的路由
php /home/wwwroot/域名/index.php demo/test/test
后面的步骤从本文第4步开始,就可以完成定时功能。
个人意见:第二种方法符合API引用的思维,觉得比较容易被接受,第一种有点引用插件的感觉,对于刚接触项目的用户友好一点,可以知道项目的定时器;因此个人觉得这两种都可以,看个人习惯。
实例二:可后台自定义定时任务
PHP函数:https://blog.csdn.net/meimeieee/article/details/79556191
Linux crontab:https://www.cnblogs.com/longjshz/p/5779215.html
第一种:PHP函数
这个可根据业务需求在项目后台做成配置页面,运营人员也可配置。
<?php//开始任务public function startCrond($id) {Db::name('crond')->where(['id' => $id])->setField('run', 1);$this->execCrond($id);}//终止任务public function abortCrond($id) {Db::name('crond')->where(['id' => $id])->setField('run', 0);}//执行任务public function execCrond($id) {ignore_user_abort(); //关掉浏览器,PHP脚本也可以继续执行.set_time_limit(0); // 通过set_time_limit(0)可以让程序无限制的执行下去do {$crond_info = Db::name('crond')->where(['id' => $id])->find();if (!$crond_info['run']) {die('process abort'); //终止任务}if (1 == $crond_info['type']) {//每过多少秒执行一次file_get_contents($crond_info['command']);Db::name('crond')->where(['id' => $crond_info['id']])->setInc('exec_count'); //自增累计执行次数sleep($crond_info['interval']); // 间隔} elseif (2 == $crond_info['type']) {//每天只执行一次$newDate = date("H:i"); //获取当前时分,比对if ($crond_info['interval'] == $newDate) {file_get_contents($crond_info['command']);Db::name('crond')->where(['id' => $crond_info['id']])->setInc('exec_count'); //自增累计执行次数sleep(3600 * 24); // 间隔} else {sleep(60); // 间隔}}} while (true);}//任务1public function testCrond1() {Db::name('test')->insert(['crond_id' => '1', 'date' => date('YmdHis')]);}//任务2public function testCrond2() {Db::name('test')->insert(['crond_id' => '2', 'date' => date('YmdHis')]);}//任务3public function testCrond3() {Db::name('test')->insert(['crond_id' => '3', 'date' => date('YmdHis')]);}CREATE TABLE `bs_crond` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`type` tinyint(2) NOT NULL DEFAULT '1' COMMENT '1、以秒为周期,2、以天为周期',`interval` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT 'type=1:间隔秒数,type=2:每天的执行时间时分 示例12:10',`command` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '任务',`path` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,`exec_count` int(11) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '累计执行统计',`run` varchar(10) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '是否开始 1、正常执行,0、终止',PRIMARY KEY (`id`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=191 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=COMPACT COMMENT='周期任务';CREATE TABLE `test` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`crond_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,`date` datetime DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
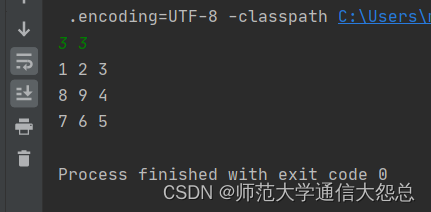
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=352 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='测试表';执行结果:
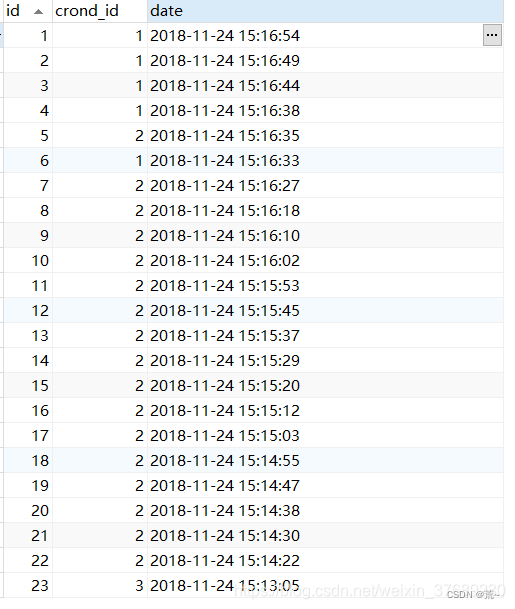
crontab的基本格式:
f1 f2 f3 f4 f5 command
分 时 日 月 周 命令
第一列f1代表分钟1~59:当f1为*表示每分钟都要执行;为*/n表示每n分钟执行一次;为a-b表示从第a分钟到第b分钟这段时间要执行;为a,b,c,...表示第a,b,c分钟要执行
第二列f2代表小时0~23(0表示凌晨):当f2为*表示每小时都要执行;为*/n表示每n小数执行一次;为a-b表示从第a小时到第b小时这段时间要执行;为a,b,c,...表示第a,b,c小时要执行
第三列f3代表日1~31:含义如上所示,以此类推
第四列f4代表月1~12:含义如上所示,以此类推
第五列f5代表星期0~6(0表示星期天):含义如上所示,以此类推
第六列command代表要运行的命令
命令参数:
crontab -l 在标准输出上显示当前的crontab
crontab -r 删除当前的crontab文件
crontab -e 编辑当前的crontab文件