启动 hive 命令行:
hiveDML 数据操作
1、数据导入
1.1、向表中装载数据(load)
语法:
hive> load data [local] inpath '数据的path' [overwrite] into table student [partition (partcol1=val1,…)];
(1)load data:表示加载数据
(2)local:表示从本地加载数据到hive表;否则从HDFS加载数据到hive表
(3)inpath:表示加载数据的路径
(4)overwrite:表示覆盖表中已有数据,否则表示追加
(5)into table:表示加载到哪张表
(6)student:表示具体的表
(7)partition:表示上传到指定分区
创建一张表student:
create table student(id string,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';注意:如果不切换数据库,默认使用的是 default 数据库,并且保存路径是hdfs:///user/hive/warehouse/student/ ;如果使用了 db_hive1 ,则保存路径为:hdfs:///user/hive/warehouse/db_hive1/student/
1、加载本地文件到hive。
load data local inpath '/opt/module/hive-3.1.2/datas/student.txt' into table default.student;HDFS 下出现了我们的文件。
2、加载hdfs文件到hive。
load data inpath ‘/user/careate/student.txt’ into table student;3、覆盖式导入:
load data local inpath '/opt/module/hive-3.1.2/datas/student.txt' overwrite into table default.student;1.2、 通过查询语句向表中插入数据(Insert)
1)创建一张表
create table student1(id int, name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t’;2)基本模式插入数据
insert into table student1 values(1011,‘ldx’),(1012,‘ysy’);3)根据查询结果插入数据
insert into table student1select id, name from student where id < 1006;insert into 不会删除原表中的数据,只是追加到后面。
insert overwrite table student1select id, name from student where id < 1006;使用 insert overwrite 的话,原表中的数据被删除,被student 表中的数据覆盖。
1.3、查询语句中创建表并加载数据(As Select)
create table student3
as select id,name from student;Hive 不论是创建表还是查询数据(除了select * 都会产生 mapreduce 任务),所以执行时间不会很快。
1.4、创建时指定 location 来加载数据路径
这种方法就是我们上一篇讲的建表语句中,通过 location 关键字来指定表的数据源(其实也变相指定了我们表的存储路径),我们建表时指定了数据源路径下文件的解析方法(比如以 '\t' 为分割符号)。
create table if not exists student(id int,name string
)
row format delimitedfields terminated by '\t'
location 'hdfs:///user/hive/warehouse/student';该表一建立,我们在 hdfs 下的 /user/hive/warehouse/student/ 目录下放到文件就变成了表内容的源文件,解析方法就是以 '\t' 为分隔符。
1.5、Import 数据到指定 Hive表
import table student from '\user\hive\warehouse\export\student';数据导出
2.1、 Insert 导出
1)将查询结果导出到本地
-- 导出student表到linux本地目录
insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/hive-3.1.2/datas'
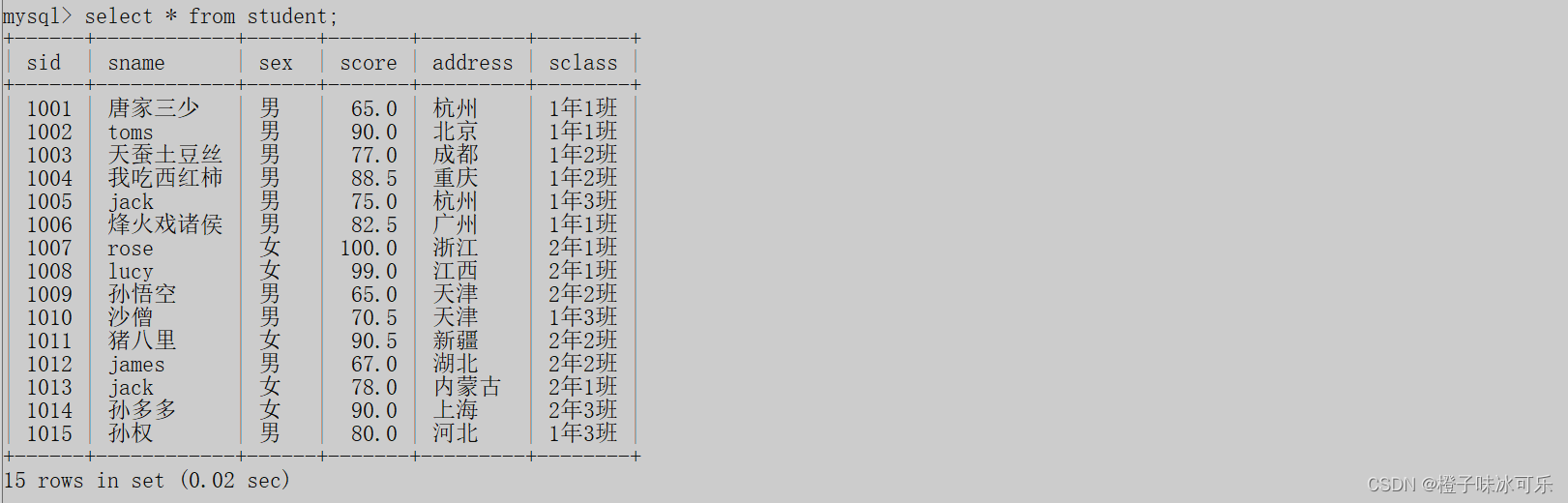
select * from student;
-- 导出结果
-- 1001lyh
-- 1002mht
-- 1003lj
-- 1004my2)将查询结果格式化后导出到本地
-- 格式化后导出到linux本地目录
insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/hive-3.1.2/datas/export/student'
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
select * from student;
-- 格式化导出结果
-- 1001 lyh
-- 1002 mht
-- 1003 lj
-- 1004 my导出结果:

3)将查询结果格式化后导出到 HDFS(少了 local 关键字)
-- 将查询结果格式化导出到 hdfs
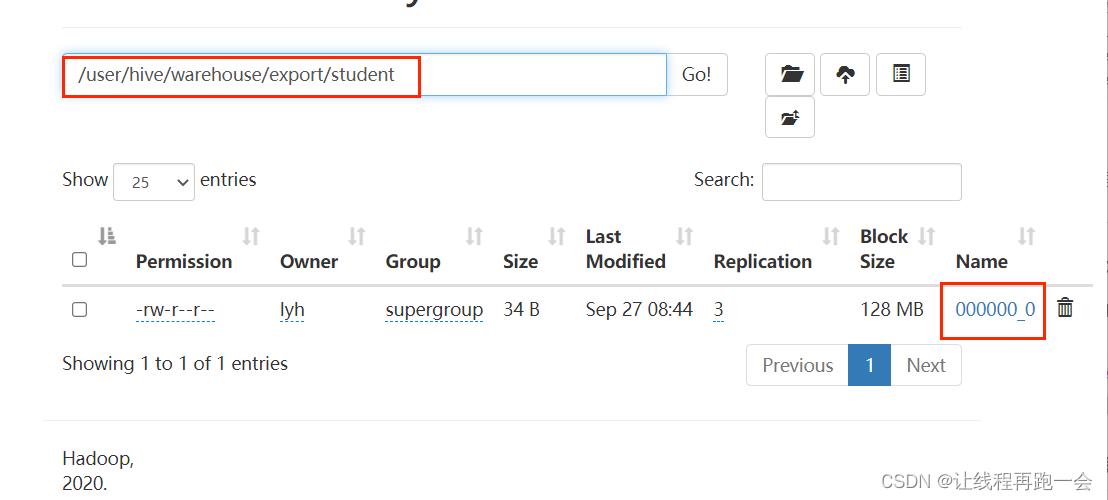
insert overwrite directory '/user/hive/warehouse/export/student'
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
select * from student1;注意:insert 导出,导出的目录不用自己提前创建,hive会帮我们自动创建。但是因为是 overwrite ,所以要小心导出的目录中原本存不存在数据,以免覆盖造成误删。
导出结果:
2.2、Hadoop 命令导出到本地
使用hadoop命令将我们Hive表的hdfs目录下的文件导出到本地(linux)。
hadoop fs -get /user/hive/warehouse/student/student.txt /opt/module/hive/datas/export/student.txt2.3、Hive Shell 命令导出
这里不需要进入 hive 命令行,因为我们使用了 hive -e
hive -e 'select * from default.stduent;' >> /opt/module/hive/datas/export/student1.txt导出结果:
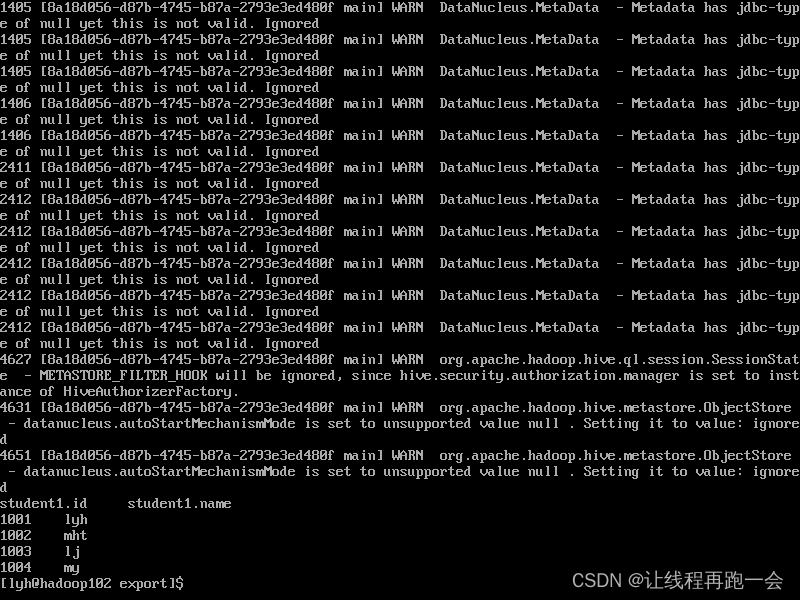 我们发现,导出的 studen2.txt 中,包含了大量的日志信息,必须通过配置日志等级才能省去它,个人感觉还是不用这种方法为好。
我们发现,导出的 studen2.txt 中,包含了大量的日志信息,必须通过配置日志等级才能省去它,个人感觉还是不用这种方法为好。
2.4、export 导出到 HDFS
-- export 导出到hdfs
export table student1 to
'/user/hive/warehouse/export/student1';导出的结果是一个 student1 目录,下面包含了两个
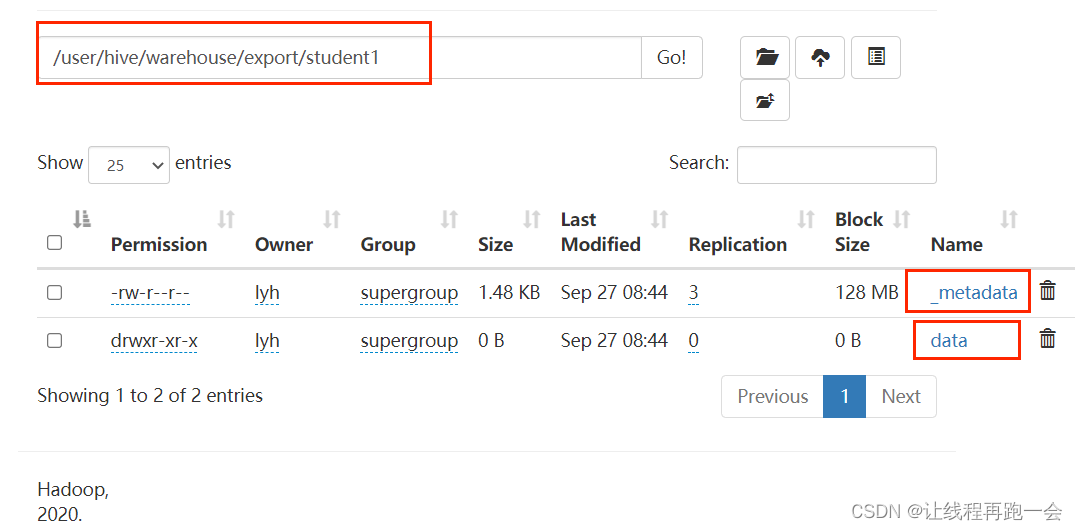
其中,_metadata 是元数据信息,而 data 是一个目录,下面存放着名为 000000_0 的文件,打开是我们该 Hive 表的内容。
1.5、Sqoop 导出
还没学 Sqoop ,以后再做更新。