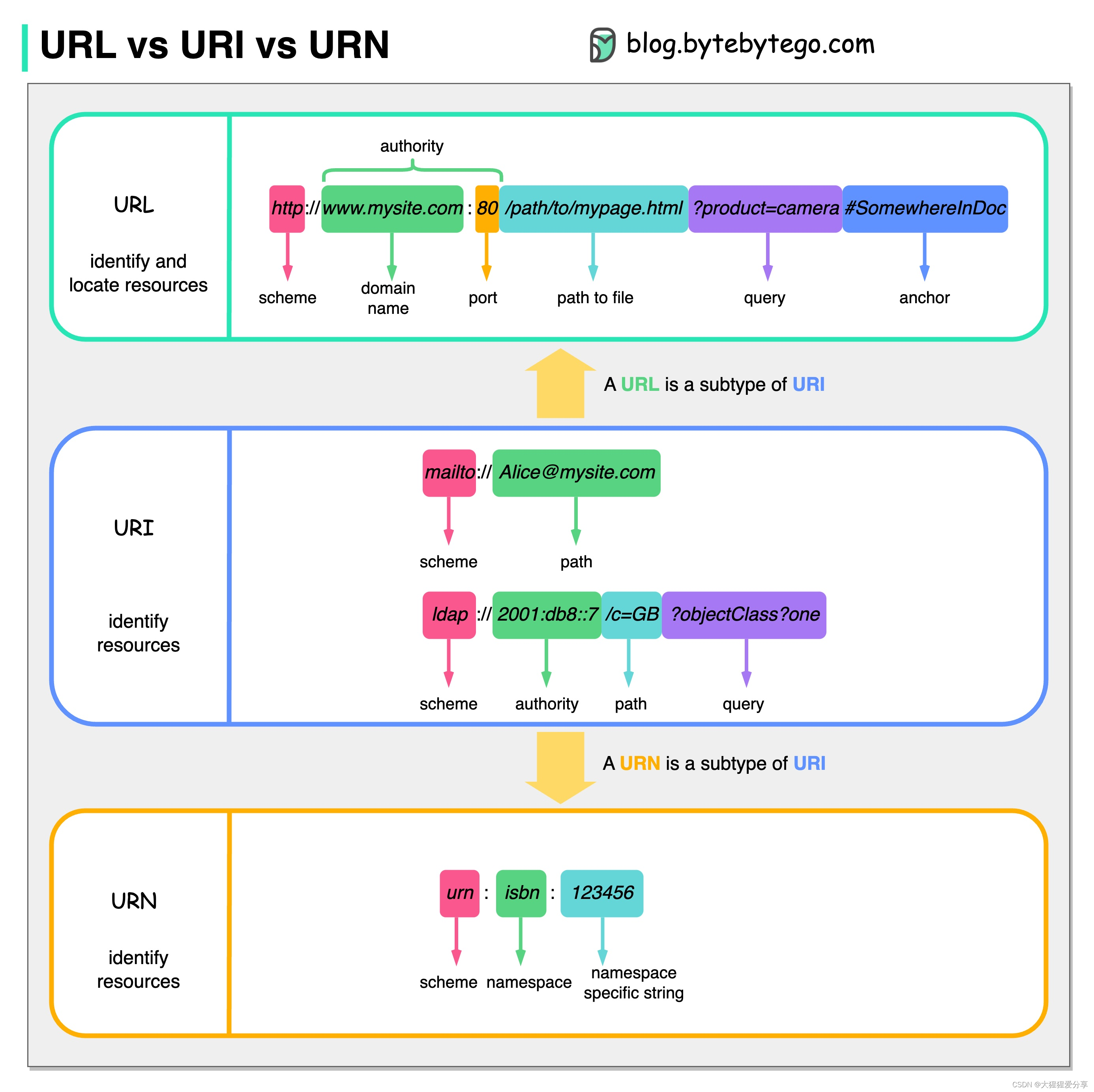
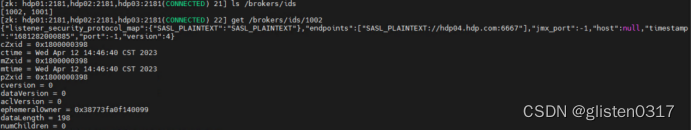
A.jagged Swaps(思维)
题意:
给出一个包含 n n n个数字的序列,每次可以选择一个同时大于左右两边相邻的数字,将这个数字与它右边的数字交换,问能否在经过若干次操作后使序列变为升序。
分析:
由于交换只能向后进行,且第一个元素无法向后交换(不存在左边的数字),而其他大的数字均可以通过交换到达自己的位置,因此只需要考虑开始时序列的第一个数字是否为1,如果是1,就是"YES",否则,就是"NO"。
hint:包含 n n n个数字的序列恰好包含 1 ∼ n 1 \sim n 1∼n中每一个数字。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;int a[15];void solve() {int n;cin >> n;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cin >> a[i];}if (a[1] != 1) {cout << "NO" << endl;} else {cout << "YES" << endl;}
}int main() {int Case;cin >> Case;while (Case--) {solve();}return 0;
}B.AB Flipping(思维)
题意:
给出一个长度为 n n n且仅包含"AB"两种字符的字符串,每次可以选择一个下标 i i i,当字符串中第 i i i个字符为'A',且第 i + 1 i + 1 i+1个字符为'B',那么可以让第 i i i个字符和第 i + 1 i + 1 i+1个字符交换。
要求每个下标 i i i均只能选择一次,问最多可以进行多少次交换。
分析:
当出现连续的'B'前面有一个'A'时,这段连续区间上的'B'均可以向前交换一次,交换次数为这段连续的'B'的长度,而经过一次交换之后,由于每个下标只能被选择一次,那么仅有第一个'B'还能向前交换,可以认为这段连续的'B'交换完成后就只剩下开头这一个'B'了。使用变量维护还能向前交换的'B'的个数,从后往前遍历模拟即可。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;string s;void solve() {int n;cin >> n >> s;int cnt = 0, ans = 0;for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {if (s[i] == 'B') {cnt++;} else {ans += cnt;cnt = min(cnt, 1);//如果当前没有遇到过B,就让cnt保持在0}}cout << ans << endl;
}int main() {solve();return 0;
}
C.Matching Arrays(贪心)
题意:
给出两个包含 n n n个数字的数组 a a a和 b b b,这两个数组的美丽值为满足 a i > b i a_i > b_i ai>bi的下标 i i i的个数。
题目会给出一个数字 x x x,问能否对 b b b重新排列,使得这两个数组的美丽值等于 x x x。
分析:
虽然题目要求只能对 b b b重排,但为了便于处理,两个数组都需要排序,同时为了记录数组 a a a原本的数字位置,需使用结构体存储数据。
贪心:将 a a a中最大的 x x x个元素与 b b b中最小的 x x x个元素按大小次序进行比较,如果这部分元素无法构成 x x x的美丽值,由于 a a a中剩余元素更小, b b b中剩余元素更大,那么无论怎么交换元素,都无法使美丽值增加,此时本题无解。
检查:比较完 a a a中最大的 x x x个元素与 b b b中最小的 x x x个元素后,还需要考虑剩余的元素是否还会产生美丽值,同样采用按大小次序依次比较,如果产生美丽值那么同样表示本题无解。
输出:如果可以构造,那么需要根据记录的 a a a中每个数字排序前的位置将对应的 b b b数组元素输出。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;struct Node{int val, id;bool operator < (const Node &o) const {return val < o.val;}
}a[200005], b[200005];int ans[200005];void solve() {int n, x;cin >> n >> x;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cin >> a[i].val;a[i].id = i;}sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cin >> b[i].val;b[i].id = i;}sort(b + 1, b + 1 + n);for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++) {if (a[i + n - x].val <= b[i].val) {//a中最大的x个与b中最小的x个对位比较cout << "NO" << endl;return;}ans[a[i + n - x].id] = b[i].val;//将当前b中元素放入对应的a中元素原本所在下标对应的位置上}for (int i = 1; i <= n - x; i++) {if (a[i].val > b[i + x].val) {//剩余的n-x个元素对位比较cout << "NO" << endl;return;}ans[a[i].id] = b[i + x].val;}cout << "YES" << endl;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cout << ans[i] << ' ';}cout << endl;
}int main() {int Case;cin >> Case;while (Case--) {solve();}return 0;
}
D.Ones and Twos(思维,数据结构)
题意:
给出一个仅包含 1 , 2 1,2 1,2的数组。
有 q q q个询问,询问分以下两种情况:
-
"1 s",询问数组中能否找出一个子段和为 s s s -
"2 i v",将数组中第 i i i个数字修改为 v v v
分析:
通过分析样例,可以发现以下规律:如果子段的左右端点数字均为1,那么可以组成任意值在 1 ∼ 1 \sim 1∼(子段数字之和)以内的数字。
根据以上规律,想要组成尽可能多的数字,那么选择的一定是最左和最右的两个 1 1 1中间的子段(包含端点)。
然后需要根据以下情况进行分类讨论:
-
数组中存在 1 1 1,这两个 1 1 1之间的子段总和为 s u m sum sum
-
x ≤ s u m x \le sum x≤sum,则可以组成
-
x > s u m x \gt sum x>sum,分成以下两种情况:
-
x x x与 s u m sum sum奇偶性相同,为了尽可能使总和最大,一定会选择将选择的子段向左右扩散,且此时左右元素一定均为2,只要整个数组的数字总和可以达到 x x x,那么就能组成 x x x。
-
奇偶性不同时,可以删去子段一侧的 1 1 1,再加上另一侧的 2 2 2,看组成的子段数字总和能否到达 x x x。
-
-
-
数组中不存在 1 1 1,那么能组成的只有偶数,且能组成的偶数 x x x的值要在数组中数字总和的范围内。
hint:可以通过 s e t set set对所有 1 1 1所在的位置(下标)进行维护,通过 ∗ ( b e g i n ( ) ) *(begin()) ∗(begin())和 ∗ ( − − e n d ( ) ) *(--end()) ∗(−−end())(end()函数返回的是最后一个元素的下一个迭代器,需要通过前自减得到最后一个元素的迭代器)来获得集合中最小和最大的元素。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;
int n, q, a[100005], cnt;set<int> S;bool check(int x) {if (S.empty()) {//数组中没有1if (x % 2 == 1) return false;if (n * 2 < x) return false;return true;}int first = *S.begin(), last = *(--S.end());//获得最前和最后的1所在的下标int sum = (last - first + 1) * 2 - S.size();//将区间内所有的数视为2,计算出总和,减去1的数量,就是该子段的数字总和if (sum >= x) return true;//被1包围的子段已经能组成x了if (x % 2 == sum % 2) {int add = n - (last - first + 1);//计算出未被加上的2的数量if (sum + add * 2 >= x) return true;} else {int add = max(n - last, first - 1);//计算左右两边最多有多少个2if (sum - 1 + add * 2 >= x) return true;}return false;
}void solve() {S.clear();cin >> n >> q;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cin >> a[i];if (a[i] == 1) {S.insert(i);cnt++;}}while (q--) {int op;cin >> op;if (op == 1) {int x;cin >> x;if (check(x)) {cout << "YES" << endl;} else {cout << "NO" << endl;}} else {int i, v;cin >> i >> v;if (a[i] == 1) S.erase(i);a[i] = v;if (a[i] == 1) S.insert(i);}}
}int main() {int Case;cin >> Case;while (Case--) {solve();}return 0;
}
E. Permutation Sorting(数据结构)
题意:
给一个大小为 n n n的排列 a a a,如果满足 a i = i a_i=i ai=i,那么称下标 i i i是良好的,每一秒,将所有不好的下标 i i i取出来作为一个子序列,保证下标 i i i是升序的。
假设这个序列为 s 1 − s k s_1-s_k s1−sk,那么对 1 − k 1-k 1−k的每个 i i i,使得 s i % k + 1 = s i s_{i\%k+1}=s_i si%k+1=si。现在对于每一个下标 i i i,询问下标 i i i第一次变好的时间。
分析:
我们假设 i i i与 a i a_i ai之间存在一条边,并且将每组 [ i , a i ] [i,a_i] [i,ai]看作一个区间,那么对于每一个下标 i i i,它的答案为:区间长度 − 1 − -1- −1−在它之前的并且被它完全包含的区间。
我们可以用二维数点来维护有哪些区间被当前处理的区间包含,将左端点当作 x x x坐标,右端点当作 y y y坐标,类似于求二维前缀和。考虑到这里是环形数组,可以倍长简化操作。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>typedef long long LL;
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n;
int a[N];
int ans[N];
int id[N];
int tr[2 * N];
int vis[N];void add(int x, int k) {for (; x <= n; x += (x & -x))tr[x] += k;
}int ask(int x, int res = 0) {for (; x; x -= (x & -x))res += tr[x];return res;
}int qry(int l, int r) {if (l <= r)return ask(r) - ask(l - 1);elsereturn ask(n) - qry(r, l - 1);
}void Init() {for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)tr[i] = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)ans[i] = 0, vis[i] = 0;
}int main() {int t = 1;cin >> t;while (t--) {cin >> n;Init();for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cin >> a[i];id[a[i]] = i;}for (int i = 1; i <= 2 * n; i++) {int x = (i - 1) % n + 1;if (vis[x]) {ans[x] = qry(id[x] + 1, x) + 1;add(id[x], -1);vis[x] = 0;}if (a[x] != x) {add(x, 1);vis[a[x]] = 1;}}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {cout << ans[i] << " ";}cout << endl;}return 0;
}
以下学习交流QQ群,群号: 546235402,大家可以加群一起交流做题思路,分享做题技巧,欢迎大家的加入。