1、数值算法
(1)运算后产生结果accumulate()
#include "algostuff.hpp"using namespace std;int main() {vector<int> coll;INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 1, 9);PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);cout << "sum: " << accumulate(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), 0) << endl;cout << "sum: " << accumulate(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), -100) << endl;cout << "product: " << accumulate(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), 1, multiplies<int>()) << endl;cout << "product: " << accumulate(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), 0, multiplies<int>()) << endl;return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
sum: 45
sum: -55
product: 362880 这里是累称的结果
product: 0(2)计算两数列的内积inner_product()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;int main() {list<int> coll;INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 1, 6);PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);// 0 + 1*1 + 2*2 + 3*3+4*4 + 5*5+6*6cout << "innser product: " << inner_product(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),coll.cbegin(),0) << endl;// 0 + 1*6 + 2*5 + 3 * 4 + 4*3+5*2+6*1cout << "inner_product: " << inner_product(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),coll.crbegin(),0) << endl; // 1 * 1+1 * 2+2 * 3+3 * 4+4 * 5+5 * 6+6cout << "product of sums: " << inner_product(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), // first rangecoll.cbegin(), // second range1, // initial valuemultiplies<int>(), // outer operationplus<int>()) // inner operation<< endl;return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6
innser product: 91
inner_product: 56
product of sums: 46080(3)相对数列和绝对数列之间的转换partial_sum()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;int main() {vector<int> coll;INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 1, 6);PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);partial_sum(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));cout << endl;partial_sum(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "),multiplies<int>());cout << endl;return 0;
}
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 3 6 10 15 21
1 2 6 24 120 720(4)将绝对值转换成相对值adjacent_difference()
#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;int main() {deque<int> coll;INSERT_ELEMENTS(coll, 1, 6);PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll);adjacent_difference(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "));cout << endl;adjacent_difference(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "),plus<int>());cout << endl;adjacent_difference(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(), ostream_iterator<int>(cout, " "),multiplies<int>());cout << endl;return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 1 1 1 1 1
1 3 5 7 9 11
1 2 6 12 20 30#include "algostuff.hpp"
using namespace std;int main() {vector<int> coll = {17, -3, 22, 13, 13, -9};PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll, "coll: ");adjacent_difference(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),coll.begin());PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll, "relative: ");partial_sum(coll.cbegin(), coll.cend(),coll.begin());PRINT_ELEMENTS(coll, "absolute: ");return 0;
}
输出:
coll: 17 -3 22 13 13 -9
relative: 17 -20 25 -9 0 -22
absolute: 17 -3 22 13 13 -92、stack堆栈
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;int main()
{stack<int> st;// push three elements into the stackst.push(1);st.push(2);st.push(3);// pop and print two elements from the stackcout << st.top() << ' ';st.pop();cout << st.top() << ' ';st.pop();// modify top elementst.top() = 77;// push two new elementsst.push(4);st.push(5);// pop one element without processing itst.pop();// pop and print remaining elementswhile (!st.empty()) {cout << st.top() << ' ';st.pop();}cout << endl;
}
输出:
3 2 4 77 自定义stack 类
#ifndef STACK_HPP
#define STACK_HPP#include <deque>
#include <exception>template <typename T>
class Stack {
protected:std::deque<T> c;
public:class ReadEmptyStack : public std::exception {public:virtual const char* what() const throw() {return "read empty stack";}};typename std::deque<T>::size_type size() const {return c.size();}bool empty() const {return c.empty();}void push(const T& elem) {c.push_back(elem);}T pop() {if (c.empty()) {throw ReadEmptyStack();}T elem(c.back());c.pop_back();return elem;}T& top() {if (c.empty()) {throw ReadEmptyStack();}return c.back();}};#endif#include <iostream>
#include <exception>
#include "Stack.hpp"using namespace std;
int main() {try {Stack<int> st;st.push(1);st.push(2);st.push(3);cout << st.pop() << " ";cout << st.pop() << " ";st.top() = 77;st.push(4);st.push(5);st.pop();cout << st.pop() << " ";cout << st.pop() << endl;cout << st.pop() << endl;} catch (const exception& e) {cerr << "EXCEPTION: " << e.what() << endl;}return 0;
}
输出:
3 2 4 77
EXCEPTION: read empty stack3、queue队列
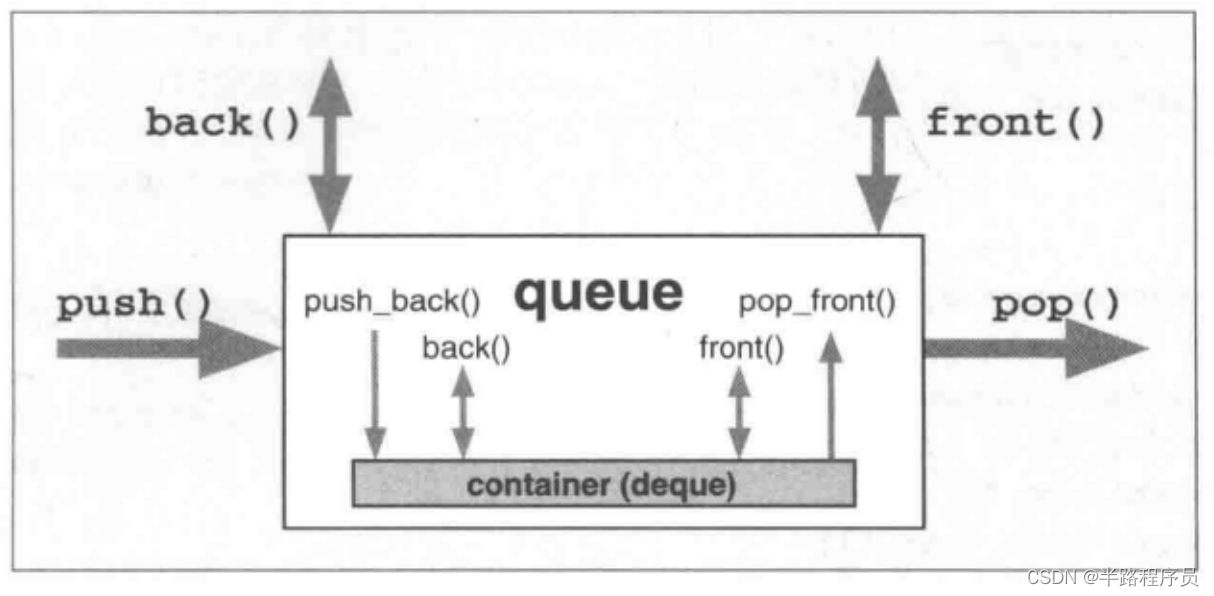
自定义queue
#ifndef QUEUE_HPP
#define QUEUE_HPP#include <deque>
#include <exception>template <typename T>
class Queue {
protected:std::deque<T> c;
public:class ReadEmptyQueue : public std::exception {public:virtual const char* what() const throw() {return "read empty queue";}};typename std::deque<T>::size_type size() const {return c.size();}bool empty() const {return c.empty();}void push(const T& elem) {c.push_back(elem);}T pop() {if (c.empty()) {throw ReadEmptyQueue();}T elem(c.front());c.pop_front();return elem;}T& fron() {if (c.empty()) {throw ReadEmptyQueue();}return c.front();}
};#endif#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <exception>
#include "Queue.hpp" // use special queue class
using namespace std;int main()
{try { Queue<string> q;// insert three elements into the queueq.push("These ");q.push("are ");q.push("more than ");// pop two elements from the queue and print their valuecout << q.pop();cout << q.pop();// push two new elementsq.push("four ");q.push("words!");// skip one elementq.pop();// pop two elements from the queue and print their valuecout << q.pop();cout << q.pop() << endl;// print number of remaining elementscout << "number of elements in the queue: " << q.size()<< endl;// read and print one elementcout << q.pop() << endl;}catch (const exception& e) {cerr << "EXCEPTION: " << e.what() << endl;}
}
输出:
These are four words!
number of elements in the queue: 0
EXCEPTION: read empty queue4、priority queue 带优先级的队列
namespace std {template <typename T, typename Container = vector<T>,typename Compare = less<typename Container::value_typy>>class priority_queue {protected:Compare comp;Container c;public:explicit priority_queue(const Compare& cmp = Compare(),const Container& cont = Container()):comp(cmp),c(cont) {make_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);}void push(const value_type& x) {c.push_back(x);push_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);}void pop() {pop_heap(c.begin(), c.end(), comp);c.pop_back();}bool empty() const {return c.empty();}size_type size() const {return c.size();}const value_type& top() const {return c.front();}...};
}priority_queue()内部使用的heap相关算法。
5、bitset
#include <bitset>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{// enumeration type for the bits// - each bit represents a colorenum Color { red, yellow, green, blue, white, black, //...,numColors };// create bitset for all bits/colorsbitset<numColors> usedColors;// set bits for two colorsusedColors.set(red);usedColors.set(blue);// print some bitset datacout << "bitfield of used colors: " << usedColors << endl;cout << "number of used colors: " << usedColors.count() << endl;cout << "bitfield of unused colors: " << ~usedColors << endl;// if any color is usedif (usedColors.any()) {// loop over all colorsfor (int c = 0; c < numColors; ++c) {// if the actual color is usedif (usedColors[(Color)c]) {//...}}}
}#include <bitset>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <limits>
using namespace std;int main()
{// print some numbers in binary representationcout << "267 as binary short: "<< bitset<numeric_limits<unsigned short>::digits>(267)<< endl;cout << "267 as binary long: "<< bitset<numeric_limits<unsigned long>::digits>(267)<< endl;cout << "10,000,000 with 24 bits: "<< bitset<24>(1e7) << endl;// write binary representation into stringstring s = bitset<42>(12345678).to_string();cout << "12,345,678 with 42 bits: " << s << endl;// transform binary representation into integral numbercout << "\"1000101011\" as number: "<< bitset<100>("1000101011").to_ullong() << endl;
}
输出:
267 as binary short: 0000000100001011
267 as binary long: 00000000000000000000000100001011
10,000,000 with 24 bits: 100110001001011010000000
12,345,678 with 42 bits: 000000000000000000101111000110000101001110
"1000101011" as number: 555




![[Verilog] Verilog 基本格式和语法](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2310f282f3e14ab9823d51eba1b8cab8.png)