关于脑区的划分方法及一些模板说明
- 前言
- 脑区划分方法的种类
- 一些标准的脑区划分模板
- 参考文献
前言
原创文章,未经同意请勿转载
Status: Completed
Author: xioabai_Ry
Time to Note: March 23, 2022
这里主要记录之前自己调研的有关脑区的划分方法及一些标准的脑区划分模板,其中,这里的模板主要是针对MRI的。其中脑影像/信号数据的划分方法没有在笔者的考虑范围内。
下面主要分为 【脑区划分方法的种类】 和常见的 【一些标准脑区划分模板】 的说明。
脑区划分方法的种类
- 根据《The Human Brainnetome Atlas and its Applications in Understanding of Brain Functions and Disorders》的参考文献 【文章链接、视频链接】
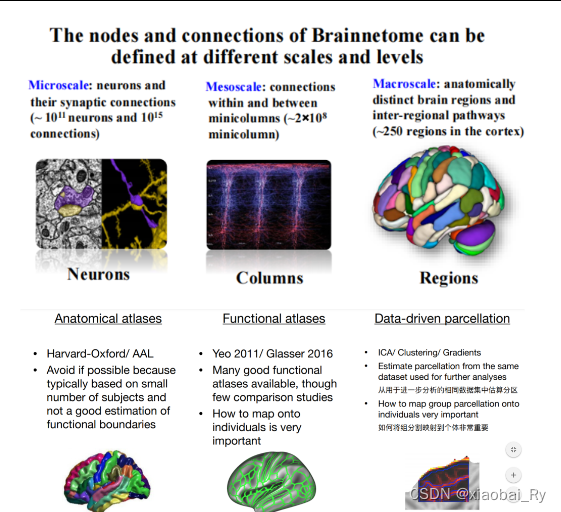
脑网络组(brainnetome)是由两个基本要素构成:
- 一是网络的节点(node)
- 二是节点跟节点的连接(connection)。
而脑网络组至少可以从三个不同的尺度进行定义和研究:
- 节点为神经元(neuron)的微观尺度
- 节点为神经元群的介观尺度(mesoscale)
- 节点为脑区的宏观尺度
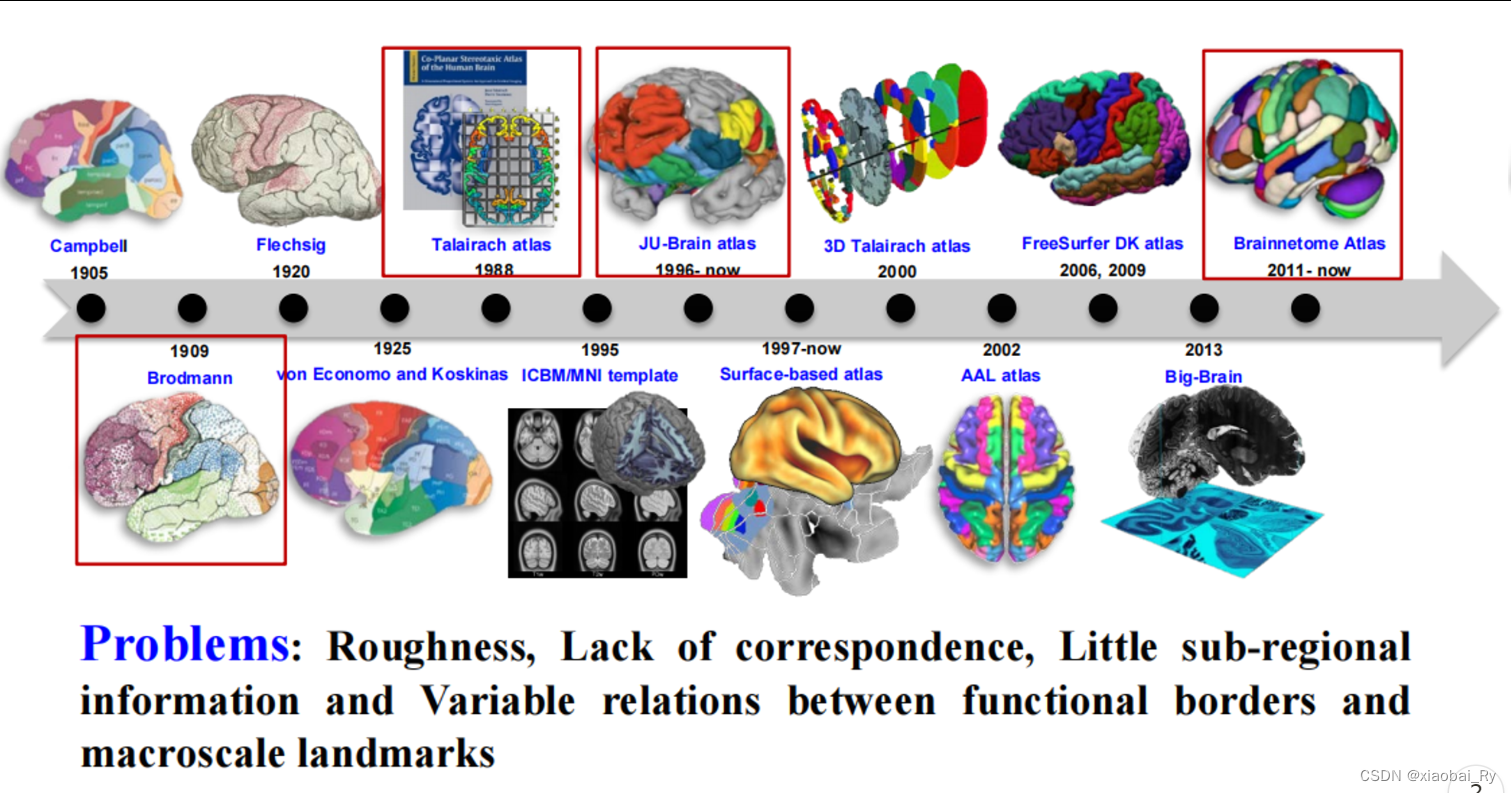
上图是蒋田仔老师团队整理的脑图谱发展历程(2019年)。脑图谱绘制,某种意义上就是图像处理。它是在寻找具有不同特性的脑区之间的边界,某种意义上就是一种图像分割。
最早的图谱叫Brodmann图谱。目前而言,该图谱是脑认知及脑疾病研究中使用得比较多的图谱。Brodmann图谱主要是基于细胞构筑进行绘制的脑图谱。Brodmann把皮层分成了52个不同的区域。现在看来,这个分区是非常粗糙的,而且有好多边界其实是错的。
📌 根据FSL的教程,脑区的划分方法(脑图谱中节点的定义)主要分为三种:
(1)解剖学上的脑图谱(结构模板,Anatomical atlases)
尽可能避免,因为通常基于少量被试,对功能边界不能良好的估计
(2)功能性划分的脑图谱(功能模板,Functional atlases)
虽然很少有⽐较研究,但可以使⽤许多功能良好的模板
(3)数据驱动下的脑图谱(数据驱动分区,Data-driven parcellation)
一些标准的脑区划分模板
-
在BrainNet Viewer工具箱中
In BrainNet Viewer, we provided several brain surface templates and example files (which were made from various brain parcellation methods) including (1) Colin brain, smoothed Colin brain, Colin brain with cerebellum, ICBM152 brain (MNI/Talaraich), smoothed ICBM152 brain (MNI/Talaraich), hemispheres of ICBM152, hemispheres of smoothed ICBM152 brain surface and a cerebellum surface in the folder ‘.\Data\SurfTemplate’; and (2) node and edge files for Automated Anatomical Labeling (AAL, 90 regions) (Tzourio-Mazoyer et al., 2002), Brodmann areas (82 regions) (Brodmann, 1909), Desikan-Killiany Atlas (68 regions) (Desikan et al., 2006), Harvard-Oxford Atlas (HOA, 112 regions) (Smith et al., 2004), ROIs defined by Dosenbach et al.(160 ROIs) (Dosenbach et al., 2010), ROIs defined by Fair et al. (34 ROIs) (Fair et al., 2009), LONI Probabilistic Brain Atlas (40 regions) (Shattuck et al., 2008), ROIs defined by Power et al. (264 ROIs) (Power et al., 2011) and others (e.g., customized ROIs by users) in the folder ‘.\Data\ExampleFiles’. -
在FSL/Freesurfer工具箱中 ( https://osf.io/k89fh/wiki/Surface/ )
- Icosahedron
Here we have provided different resolutions of tesselation with 42, 162, 362, 642, 1002, and 1442 tessels per hemisphere. They are named accordingly (e.g. Icosahedron-42 vs. Icosahedron-162). - Brodmann area probabilistic atlas
The Brodmann area (BA) probabilistic atlas is created using a probabilistic cytoarchitectonic map (Fischel et al., Cerebral Cortex, 2008).
Power 2011
This thirteen network parcellation was defined using graph theory on resting-state fMRI data, using both parcel- (AAL atlas) and voxel-based methods.
- Icosahedron
-
一个模板汇集的网站信息 (Cortical Atlas Parcellations (MNI-Space) – Lead-DBS)
注:
Craddock 200 and Craddock 400 parcellations that contain 200 and 392 ROIs
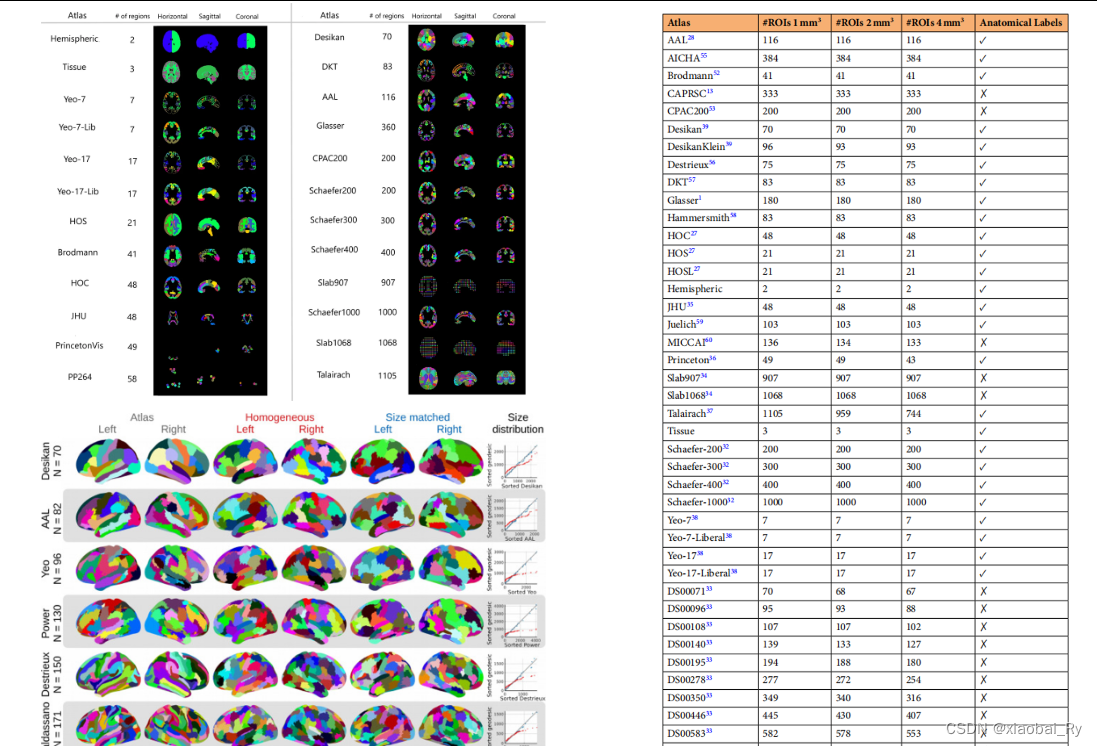
AAL90,其它还有AAL116,Brodmann82,Power264,Gordon333
这个网站包含一些比较新提出来的脑图模板
(1)在BrainNet Viewer工具箱中,AAL模板中只含有90个regions(有些工具箱子是116,为什么是呢?116 AAL ROIs, 90 of which were located in the cerebral cortex(大脑皮层), 8 in the subcortical gray matter(皮层下灰质), and 18 in the cerebellum(小脑). 实际中, AAL模板有多个版本,具体可见:AAL-AAL3变化数据记载,而AAL模板所对应的各脑区功能在其中可见(网上有易获取的资源)
(2) Yeo模板也一直在更新之中,也有多个ROIs的版本,具体可见:https://github.com/ThomasYeoLab/CBIG/tree/master/stable_projects/brain_parcellation/Schaefer2018_LocalGlobal
(3)Fair 2009 年 【34 ROIs】的论文作者中也有Power JD(第三作者),但Power JD在2011年以第一作者发表了 264 ROIs。
(4)在BrainNet Viewer中,HO模板采用2004年文章的设定【112 ROIs】,而在2006年的文章中为 138 ROIs,96 were located in the cerebral cortex, 15 covered subcortical gray matter, and 27 were located in the cerebellum.
参考文献
- FSL的官方教程
- 几种常见的功能性脑网络划分方式
- AAL模板
- BrainNet Viewer:人类大脑连接的网络可视化工具



![[计网01] 物理层 详细解析笔记,特性](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/93e31d78ef9a463098704c288688565f.png)