前言
如果GridLayoutManager使用item的布局都是wrap_cotent 那么会在布局更改时会出现一些出人意料的情况。(本文完全不具备可读性和说教性,仅为博主方便查找问题)
布局item:
<!--layout_item.xml-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.vb.rerdemo.MyConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:layout_marginTop="10dp"android:background="#f0f"><com.google.android.material.card.MaterialCardViewandroid:layout_width="match_parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:cardCornerRadius="10dp"app:cardBackgroundColor="#908000"android:layout_height="240dp"><TextViewandroid:id="@+id/tv"android:layout_gravity="center"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:text="hello world"android:layout_height="wrap_content"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /></com.google.android.material.card.MaterialCardView>
</com.vb.rerdemo.MyConstraintLayout>

//LastGapDecoration.kt
//给最后一行的item添加一个高度
class LastGapDecoration : ItemDecoration() {override fun getItemOffsets(outRect: Rect,view: View,parent: RecyclerView,state: RecyclerView.State) {super.getItemOffsets(outRect, view, parent, state)super.getItemOffsets(outRect, view, parent, state)val itemPosition = parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view)val gridLayoutManager = parent.layoutManager as? GridLayoutManager ?: returnval spanCount = gridLayoutManager.spanCountval itemCount = gridLayoutManager.itemCountif (spanCount <= 0) {return}val lastRowItemCount = itemCount % spanCountval lastRow =isLastRow(itemPosition, itemCount, spanCount, lastRowItemCount)Log.d("fmy","lastRow ${lastRow} itemPosition ${itemPosition} lastRowItemCount ${lastRowItemCount} itemCount ${itemCount} viewid ${view.hashCode()}")if (lastRow) {outRect.bottom = ScreenUtil.dp2px(40f,App.myapp)} else {outRect.bottom = 0}}private fun isLastRow(itemPosition: Int,itemCount: Int,spanCount: Int,lastRowItemCount: Int): Boolean {// 如果最后一行的数量不足一整行,则直接判断位置if (lastRowItemCount != 0 && itemPosition >= itemCount - lastRowItemCount) {return true}// 如果最后一行的数量足够一整行,则需要计算val rowIndex = itemPosition / spanCountval totalRow = ceil(itemCount.toDouble() / spanCount).toInt()return rowIndex == totalRow - 1}
}
当我们填充6个布局后的效果:
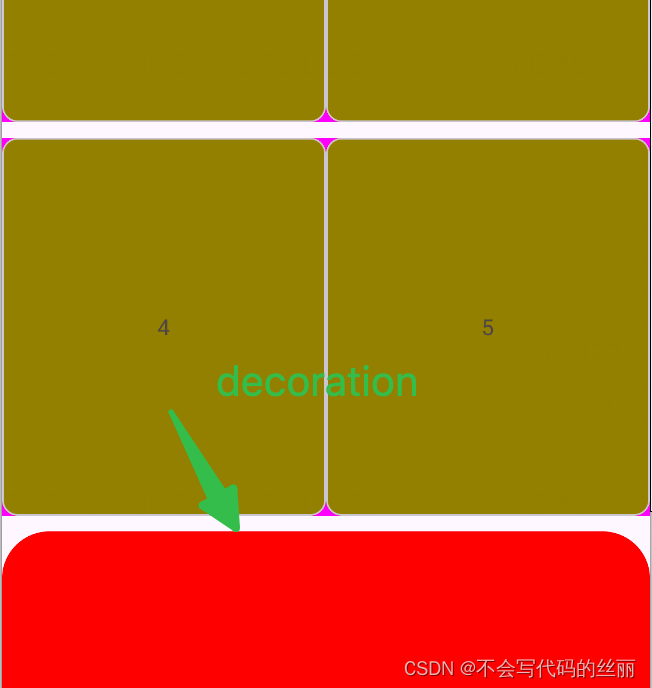
红色区域和4和5之间的间距通过LastGapDecoration完成。
此时我们移除3后:
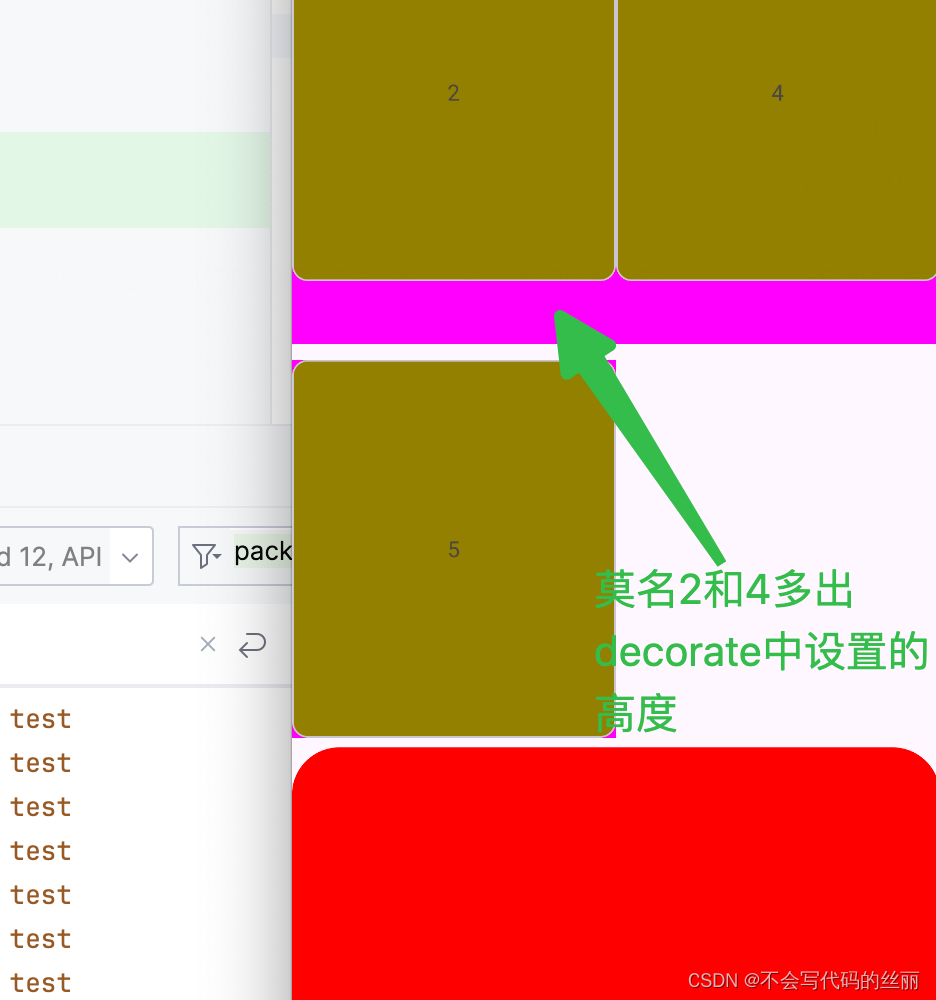
根本原因在于GridLayoutManager#layoutChunk函数中
public class GridLayoutManager extends LinearLayoutManager {View[] mSet;//layoutChunk 每次调用只拿取当前行view进行对比计算//比如GridLayoutManager一行两个那么每次会拿取每行的对应view进行计算void layoutChunk(RecyclerView.Recycler recycler, RecyclerView.State state,LayoutState layoutState, LayoutChunkResult result) {int count = 0;while (count < mSpanCount && layoutState.hasMore(state) && remainingSpan > 0) {//略... 经过一些的计算mSet放入本次要进行摆放的view//count 一般为GridLayoutManager的spanCount数量mSet[count] = view;count++;}//maxSize是指在本次layoutChunk中所有view里面最大的高度数据。(包含view自身和ItemDecorations得到的)int maxSize = 0;// we should assign spans before item decor offsets are calculatedfor (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {//计算ItemDecorationscalculateItemDecorationsForChild(view, mDecorInsets);//调用measure计算view宽高 核心!!!//核心代码点:注意这里调用子view的measure参数为layoutparameter高度//我们把这里称为操作AmeasureChild(view, otherDirSpecMode, false);//核心代码点:这里这里会得到这个view的宽高和ItemDecorations填充的高度和final int size = mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedMeasurement(view);//核心代码点: 记录最大数值if (size > maxSize) {maxSize = size;}}//我们把这里称为操作B//取出当前行中的所有view。保证行高度一致for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {final View view = mSet[i];if (mOrientationHelper.getDecoratedMeasurement(view) != maxSize) {final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();final Rect decorInsets = lp.mDecorInsets;final int verticalInsets = decorInsets.top + decorInsets.bottom+ lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;final int horizontalInsets = decorInsets.left + decorInsets.right+ lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;final int totalSpaceInOther = getSpaceForSpanRange(lp.mSpanIndex, lp.mSpanSize);final int wSpec;final int hSpec;if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {wSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(totalSpaceInOther, View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY,horizontalInsets, lp.width, false);//核心代码点: 这里会强制当前行所有view的高度与最高的view保持一致。 hSpec = View.MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(maxSize - verticalInsets,View.MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);} else {//略}//执行测量measureChildWithDecorationsAndMargin(view, wSpec, hSpec, true);}} }
}
上面的代码可以总结为:
- 取出当前的所有view
- 对所有view执行一次高度测量,并记录当前最高的view数据
- 在此执行一次测量,保证当前行的所有view高度一致
我们重点再看一眼measureChild函数
private void measureChild(View view, int otherDirParentSpecMode, boolean alreadyMeasured) {final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();final Rect decorInsets = lp.mDecorInsets;final int verticalInsets = decorInsets.top + decorInsets.bottom+ lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;final int horizontalInsets = decorInsets.left + decorInsets.right+ lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;final int availableSpaceInOther = getSpaceForSpanRange(lp.mSpanIndex, lp.mSpanSize);final int wSpec;final int hSpec;if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {wSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(availableSpaceInOther, otherDirParentSpecMode,horizontalInsets, lp.width, false);//mOrientationHelper.getTotalSpace()可以先忽略//verticalInsets 就是decorate中的高度和一些margin等数值//lp.height如果是wrapcontent那么一返回高度为0的MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED//lp.height如果不是wrapcontent那么一返回高度为父亲高度减去verticalInsets的MeasureSpec.EXACTLY//lp.height如果是一个明确数值那么一返回高度为设置的高度的MeasureSpec.EXACTLY//总结getChildMeasureSpec传入布局参数高度和decorate高度hSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(mOrientationHelper.getTotalSpace(), getHeightMode(),verticalInsets, lp.height, true);} else {//略}//透传给子view测量measureChildWithDecorationsAndMargin(view, wSpec, hSpec, alreadyMeasured);}
measureChildWithDecorationsAndMargin函数会根据必要性确定是否要执行子view的测量操作。
private void measureChildWithDecorationsAndMargin(View child, int widthSpec, int heightSpec,boolean alreadyMeasured) {RecyclerView.LayoutParams lp = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();final boolean measure;if (alreadyMeasured) {measure = shouldReMeasureChild(child, widthSpec, heightSpec, lp);} else {measure = shouldMeasureChild(child, widthSpec, heightSpec, lp);}//根据情况是否执行if (measure) {child.measure(widthSpec, heightSpec);}}boolean shouldReMeasureChild(View child, int widthSpec, int heightSpec, LayoutParams lp) {return !mMeasurementCacheEnabled|| !isMeasurementUpToDate(child.getMeasuredWidth(), widthSpec, lp.width)|| !isMeasurementUpToDate(child.getMeasuredHeight(), heightSpec, lp.height);}boolean shouldMeasureChild(View child, int widthSpec, int heightSpec, LayoutParams lp) {return child.isLayoutRequested()|| !mMeasurementCacheEnabled|| !isMeasurementUpToDate(child.getWidth(), widthSpec, lp.width)|| !isMeasurementUpToDate(child.getHeight(), heightSpec, lp.height);}
shouldReMeasureChild可以总结为:
- 如果没有开启缓存那么一定执行测绘
- 如果开启了缓存那么判断之前是否执行过相同参数测量
在了解上面的信息我们可以总结一下流程发现问题:
我们假设假设wrapcotent计算的高度为50
decorate插入的高度为10
插入0时:0执行操作A,不执行操作B
插入1时:
- 0和1同时执行操作A,不执行操作B。0由于之前测绘过不会触发onmeasure。 1触发onmeasure
插入2时:
- 0和1同时执行操作A,不执行操作B , 0和1不会触发onmeasure。 2执行操作A并触发onmeasure
插入3时:
- 0和1同时执行操作A,不执行操作B , 0和1不会触发onmeasure。 3和2执行操作A ,2不会触发onmeasure,3触发onmeasure。
移除1时:
- 0 和 1 同时执行操作A (0 和1不会触发onmeasure)操作B不会执行(虽然1被移除 但是由于预布局存在还需要进行一次比较)
- 2 和 3 同时执行操作A (2 和3不会触发onmeasure). 由于2移动第一行不会有decorate高度,因此2执行操作B并触发onmeasure。2 高度为60(移除后2和3虽然不在一行但需要执行预布局)
- 0和2进行同时执行操作A (0 和2不会触发onmeasure),同时0会被执行操作B把高度填充到60. (虽然2没有decorate的高度 但是上一次预布局引起了2高度错误)
- 3 同时执行操作A (不会触发onmeasure) 不会触发操作B
解决方案:
val manager = GridLayoutManager(this, 2)
manager.isMeasurementCacheEnabled = false