第五章 深度学习
三、OpenCV
5. 图像梯度处理
5.1 模糊处理
# 图像模糊处理示例
import cv2
import numpy as np## 中值滤波
im = cv2.imread("../data/lena.jpg", 0)
cv2.imshow("orig", im)# 调用medianBlur中值模糊
# 第二个参数为滤波模板的尺寸大小,必须是大于1的奇数,如3、5、7
im_median_blur = cv2.medianBlur(im, 5)
cv2.imshow('median_blur', im_median_blur)# 均值滤波
# 第二个参数为滤波模板的尺寸大小
im_mean_blur = cv2.blur(im, (3, 3))
cv2.imshow("mean_blur", im_mean_blur)# 高斯滤波
# 第三个参数为高斯核在X方向的标准差
im_gaussian_blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(im, (5, 5), 3)
cv2.imshow("gaussian_blur", im_gaussian_blur)# 使用高斯算子和filter2D自定义滤波操作
gaussan_blur = np.array([[1, 4, 7, 4, 1],[4, 16, 26, 16, 4],[7, 26, 41, 26, 7],[4, 16, 26, 16, 4],[1, 4, 7, 4, 1]], np.float32) / 273
# 使用filter2D, 第二个参数为目标图像的所需深度, -1表示和原图像相同
im_gaussian_blur2 = cv2.filter2D(im, -1, gaussan_blur)
cv2.imshow("gaussian_blur2", im_gaussian_blur2)cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行结果:

5.2 图像锐化处理
# 图像锐化示例
import cv2
import numpy as npim = cv2.imread("../data/lena.jpg", 0)
cv2.imshow("orig", im)# 锐化算子1
sharpen_1 = np.array([[-1, -1, -1],[-1, 9, -1],[-1, -1, -1]])
# 使用filter2D进行滤波操作
im_sharpen1 = cv2.filter2D(im, -1, sharpen_1)
cv2.imshow("sharpen_1", im_sharpen1)# 锐化算子2
sharpen_2 = np.array([[0, -1, 0],[-1, 8, -1],[0, 1, 0]]) / 4.0
# 使用filter2D进行滤波操作
im_sharpen2 = cv2.filter2D(im, -1, sharpen_2)
cv2.imshow("sharpen_2", im_sharpen2)cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行结果:

5.3 边沿检测
# 边沿检测示例
import cv2 as cvim = cv.imread('../data/lily.png', 0)
cv.imshow('Original', im)# # 水平方向滤波
# hsobel = cv.Sobel(im, cv.CV_64F, 1, 0, ksize=5)
# cv.imshow('H-Sobel', hsobel)
# # 垂直方向滤波
# vsobel = cv.Sobel(im, cv.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize=5)
# cv.imshow('V-Sobel', vsobel)
# 两个方向滤波
# cv2.CV_64F: 输出图像深度,本来应该设置为-1,但如果设成-1,可能会发生计算错误
# 所以通常先设置为精度更高的CV_64F
sobel = cv.Sobel(im, cv.CV_64F, 1, 1, ksize=5)
cv.imshow('Sobel', sobel)# Laplacian滤波:对细节反映更明显
laplacian = cv.Laplacian(im, cv.CV_64F)
cv.imshow('Laplacian', laplacian)# Canny边沿提取
canny = cv.Canny(im,50, # 滞后阈值240) # 模糊度
cv.imshow('Canny', canny)cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()
执行结果:

6. 轮廓处理
边缘检测虽然能够检测出边缘,但边缘是不连续的,检测到的边缘并不是一个整体。图像轮廓是指将边缘连接起来形成的一个整体,用于后续的计算。
OpenCV提供了查找图像轮廓的函数cv2.findContours(),该函数能够查找图像内的轮廓信息,而函数cv2.drawContours() 能够将轮廓绘制出来。图像轮廓是图像中非常重要的一个特征信息,通过对图像轮廓的操作,我们能够获取目标图像的大小、位置、方向等信息。一个轮廓对应着一系列的点,这些点以某种方式表示图像中的一条曲线。
6.1 查找并绘制轮廓
查找轮廓函数:cv2.findContours
-
语法格式:contours,hierarchy=cv2.findContours(image,mode,method)
-
返回值
- contours:返回的轮廓。该返回值返回的是一组轮廓信息,每个轮廓都是由若干个点所构成的(每个轮廓为一个list表示)。例如,contours[i]是第i个轮廓(下标从0开始),contours[i][j]是第i个轮廓内的第j个点
- hierarchy:图像的拓扑信息(反映轮廓层次)。图像内的轮廓可能位于不同的位置。比如,一个轮廓在另一个轮廓的内部。在这种情况下,我们将外部的轮廓称为父轮廓,内部的轮廓称为子轮廓。按照上述关系分类,一幅图像中所有轮廓之间就建立了父子关系。每个轮廓contours[i]对应4个元素来说明当前轮廓的层次关系。其形式为:[Next,Previous,First_Child,Parent],分别表示后一个轮廓的索引编号、前一个轮廓的索引编号、第1个子轮廓的索引编号、父轮廓的索引编号
-
参数
- image:原始图像。灰度图像会被自动处理为二值图像。在实际操作时,可以根据需要,预先使用阈值处理等函数将待查找轮廓的图像处理为二值图像。
- mode:轮廓检索模式,有以下取值和含义:
取值 含义 cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL 只检测外轮廓 cv2.RETR_LIST 对检测到的轮廓不建立等级关系 cv2.RETR_CCOMP 检索所有轮廓并将它们组织成两级层次结构,上面的一层为外边界,下面的一层为内孔的边界 cv2.RETR_TREE 建立一个等级树结构的轮廓 - method:轮廓的近似方法,主要有如下取值:
取值 含义 cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE 存储所有的轮廓点,相邻两个点的像素位置差不超过1,即max(abs(x1-x2),abs(y2-y1))=1 cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE 压缩水平方向、垂直方向、对角线方向的元素,只保留该方向的终点坐标 cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_L1 使用teh-Chinl chain近似算法的一种风格 cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_TC89_KCOS 使用teh-Chinl chain近似算法的一种风格 -
注意事项
- 待处理的源图像必须是灰度二值图
- 都是从黑色背景中查找白色对象。因此,对象必须是白色的,背景必须是黑色的
- 在OpenCV 4.x中,函数cv2.findContours()仅有两个返回值
-
绘制轮廓:drawContours函数
- 语法格式:image=cv2.drawContours(image, contours,contourIdx, color)
- 参数
- image:待绘制轮廓的图像
- contours:需要绘制的轮廓,该参数的类型与函数 cv2.findContours()的输出 contours 相同,都是list类型
- contourIdx:需要绘制的边缘索引,告诉函数cv2.drawContours()要绘制某一条轮廓还是全部轮廓。如果该参数是一个整数或者为零,则表示绘制对应索引号的轮廓;如果该值为负数(通常为“-1”),则表示绘制全部轮廓。
- color:绘制的颜色,用BGR格式表示
# 查找图像轮廓
import cv2
import numpy as npim = cv2.imread("../data/3.png")
cv2.imshow("orig", im)gray = cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 图像二值化处理,将大于阈值的设置为最大值,其它设置为0
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)# 查找图像边沿:cv2.findContours
img, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, # 二值化处理后的图像cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, # 只检测外轮廓cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) # 存储所有的轮廓点
# 打印所有轮廓值
arr_cnt = np.array(contours)
print(arr_cnt[0].shape)
print(arr_cnt[1].shape)
print(arr_cnt[2].shape)
print(arr_cnt[3].shape)
# print(arr_cnt[0])# 绘制边沿
im_cnt = cv2.drawContours(im, # 绘制图像contours, # 轮廓点列表-1, # 绘制全部轮廓(0, 0, 255), # 轮廓颜色:红色2) # 轮廓粗细
cv2.imshow("im_cnt", im_cnt)cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行结果:

6.2 绘制矩形包围框
函数cv2.boundingRect()能够绘制轮廓的矩形边界。该函数的语法格式为:
retval = cv2.boundingRect(array) # 格式一
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(array) # 格式二
"""
参数:array:是灰度图像或轮廓
返回值:retval:表示返回的矩形边界的左上角顶点的坐标值及矩形边界的宽度和高度x, y, w, h: 矩形边界左上角顶点的x坐标、y坐标、宽度、高度
"""
代码:
# 绘制图像矩形轮廓
import cv2
import numpy as npim = cv2.imread("../data/cloud.png", 0)
cv2.imshow("orig", im)# 提取图像轮廓
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(im, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
img, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_LIST, # 不建立等级关系cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE) # 存储所有的轮廓点
print("contours[0].shape:", contours[0].shape)# 返回轮廓定点及边长
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contours[0]) # 计算矩形包围框的x,y,w,h
print("x:", x, "y:", y, "w:", w, "h:", h)# 绘制矩形包围框
brcnt = np.array([[[x, y]], [[x + w, y]], [[x + w, y + h]], [[x, y + h]]])
cv2.drawContours(im, # 绘制图像[brcnt], # 轮廓点列表-1, # 绘制全部轮廓(255, 255, 255), # 轮廓颜色:白色2) # 轮廓粗细cv2.imshow("result", im) # 显示绘制后的图像cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行结果:

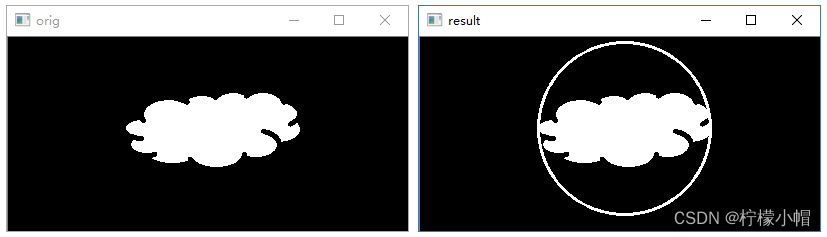
6.3 绘制圆形包围圈
函数 cv2.minEnclosingCircle() 通过迭代算法构造一个对象的面积最小包围圆形。该函数的语法格式为:
center,radius=cv2.minEnclosingCircle(points)
"""
参数:points: 轮廓数组
返回值:center: 最小包围圆形的中心radius: 最小包围圆形的半径
"""
代码:
# 绘制最小圆形
import cv2
import numpy as npim = cv2.imread("../data/cloud.png", 0)
cv2.imshow("orig", im)# 提取图像轮廓
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(im, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
img, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)(x, y), radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(contours[0])
center = (int(x), int(y))
radius = int(radius)
cv2.circle(im, center, radius, (255, 255, 255), 2) # 绘制圆cv2.imshow("result", im) # 显示绘制后的图像cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行结果:
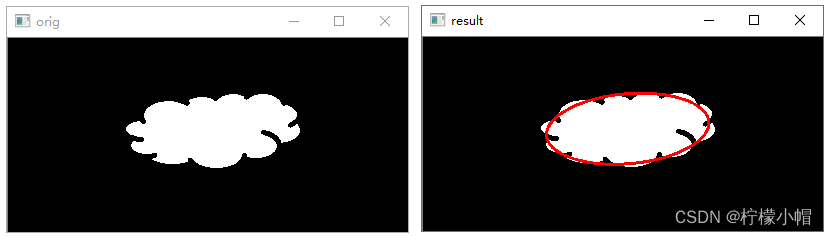
6.4 绘制最佳拟合椭圆
函数cv2.fitEllipse() 可以用来构造最优拟合椭圆。该函数的语法格式是:
retval=cv2.fitEllipse(points)
"""
参数:points: 轮廓
返回值:retval: 为RotatedRect类型的值,包含外接矩形的质心、宽、高、旋转角度等参数信息,这些信息正好与椭圆的中心点、轴长度、旋转角度等信息吻合
"""
代码:
# 绘制最优拟合椭圆
import cv2
import numpy as npim = cv2.imread("../data/cloud.png")
gray = cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow("orig", gray)# 提取图像轮廓
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
img, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(contours[0]) # 拟合最优椭圆
print("ellipse:", ellipse)
cv2.ellipse(im, ellipse, (0, 0, 255), 2) # 绘制椭圆cv2.imshow("result", im) # 显示绘制后的图像cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行结果:
6.5 逼近多边形
函数cv2.approxPolyDP() 用来构造指定精度的逼近多边形曲线。该函数的语法格式为:
approxCurve = cv2.approxPolyDP(curve,epsilon,closed)
"""
参数:curve: 轮廓epsilon: 精度,原始轮廓的边界点与逼近多边形边界之间的最大距离closed: 布尔类型,该值为True时,逼近多边形是封闭的;否则,逼近多边形是不封闭的
返回值:approxCurve: 逼近多边形的点集
"""
代码:
# 构建多边形,逼近轮廓
import cv2
import numpy as npim = cv2.imread("../data/cloud.png")
cv2.imshow("im", im)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)# 提取图像轮廓
ret, binary = cv2.threshold(gray, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
img, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(binary,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 精度一
adp = im.copy()
epsilon = 0.005 * cv2.arcLength(contours[0], True) # 精度,根据周长计算
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[0], epsilon, True) # 构造多边形
adp = cv2.drawContours(adp, [approx], 0, (0, 0, 255), 2) # 绘制多边形
cv2.imshow("result_0.005", adp)
# 精度二
adp2 = im.copy()
epsilon = 0.01 * cv2.arcLength(contours[0], True) # 精度,根据周长计算
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(contours[0], epsilon, True) # 构造多边形
adp = cv2.drawContours(adp2, [approx], 0, (0, 0, 255), 2) # 绘制多边形
cv2.imshow("result_0.01", adp2)cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
执行结果:

7. 视频基本处理
7.1 读取摄像头
import numpy as np
import cv2cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 实例化VideoCapture对象, 0表示第一个摄像头
while cap.isOpened():ret, frame = cap.read() # 捕获帧cv2.imshow("frame", frame)c = cv2.waitKey(1) # 等待1毫秒,等待用户输入if c == 27: # ESC键breakcap.release() # 释放摄像头
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
7.2 播放视频文件
import numpy as np
import cv2cap = cv2.VideoCapture("D:\\tmp\\min_nong.mp4") # 打开视频文件
while cap.isOpened():ret, frame = cap.read() # 读取帧cv2.imshow("frame", frame) # 显示c = cv2.waitKey(25)if c == 27: # ESC键breakcap.release() # 释放视频设备
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
7.3 捕获并保存视频
import numpy as np
import cv2""" 编解码4字标记值说明
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('I','4','2','0')表示未压缩的YUV颜色编码格式,色度子采样为4:2:0。该编码格式具有较好的兼容性,但产生的文件较大,文件扩展名为.avi。
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('P','I','M','I')表示 MPEG-1编码类型,生成的文件的扩展名为.avi。
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('X','V','I','D')表示MPEG-4编码类型。如果希望得到的视频大小为平均值,可以选用这个参数组合。该组合生成的文件的扩展名为.avi。
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('T','H','E','O')表示Ogg Vorbis编码类型,文件的扩展名为.ogv。
cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc('F','L','V','I')表示Flash视频,生成的文件的扩展名为.flv。
"""
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc("I", "4", "2", "0") # 编解码4字标记值
out = cv2.VideoWriter("output.avi", # 文件名fourcc, # 编解码类型20, # fps(帧速度)(640, 480)) # 视频分辨率while cap.isOpened():ret, frame = cap.read() # 读取帧if ret == True:out.write(frame) # 写入帧cv2.imshow("frame", frame)if cv2.waitKey(1) == 27: # ESC键breakelse:breakcap.release()
out.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
8. 综合案例
8.1 利用OpenCV实现图像校正
【任务描述】
我们对图像中的目标进行分析和检测时,目标往往具有一定的倾斜角度,自然条件下拍摄的图像,完全平正是很少的。因此,需要将倾斜的目标“扶正”的过程就就叫做图像矫正。该案例中使用的原始图像如下:

【代码】
# 图像校正示例
import cv2
import numpy as np
import mathim = cv2.imread("../data/paper.jpg")
gray = cv2.cvtColor(im, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('im', im)# 模糊
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
# 膨胀
dilate = cv2.dilate(blurred, (3, 3))
# 检测边沿
edged = cv2.Canny(dilate, # 原始图像30, 120) # 滞后阈值、模糊度
# cv2.imshow("edged", edged)# 轮廓检测
img, cnts, hie = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(),cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, # 只检测外轮廓cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) # 只保留该方向的终点坐标
docCnt = None# 绘制轮廓
im_cnt = cv2.drawContours(im, # 绘制图像cnts, # 轮廓点列表-1, # 绘制全部轮廓(0, 0, 255), # 轮廓颜色:红色2) # 轮廓粗细
cv2.imshow("im_cnt", im_cnt)# 计算轮廓面积,并排序
if len(cnts) > 0:cnts = sorted(cnts, # 数据key=cv2.contourArea, # 排序依据,根据contourArea函数结果排序reverse=True)for c in cnts:peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True) # 计算轮廓周长approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True) # 轮廓多边形拟合# 轮廓为4个点表示找到纸张if len(approx) == 4:docCnt = approxbreakprint(docCnt)# 用圆圈标记处角点
points = []
for peak in docCnt:peak = peak[0]# 绘制圆cv2.circle(im, # 绘制图像tuple(peak), 10, # 圆心、半径(0, 0, 255), 2) # 颜色、粗细points.append(peak) # 添加到列表
print(points)
cv2.imshow("im_point", im)# 校正
src = np.float32([points[0], points[1], points[2], points[3]]) # 原来逆时针方向四个点
dst = np.float32([[0, 0], [0, 488], [337, 488], [337, 0]]) # 对应变换后逆时针方向四个点
m = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst) # 生成透视变换矩阵
result = cv2.warpPerspective(gray.copy(), m, (337, 488)) # 透视变换""" 根据勾股定理计算宽度、高度,再做透视变换
h = int(math.sqrt((points[1][0] - points[0][0])**2 + (points[1][1] - points[0][1])**2)) # 宽度
w = int(math.sqrt((points[2][0] - points[1][0])**2 + (points[2][1] - points[1][1])**2)) # 高度
print("w:", w, " h:", h)
dst = np.float32([[0, 0], [0, h], [w, h], [w, 0]])
m = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst) # 生成透视变换矩阵
result = cv2.warpPerspective(gray.copy(), m, (w, h)) # 透视变换
"""cv2.imshow("result", result) # 显示透视变换结果cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
【执行结果】

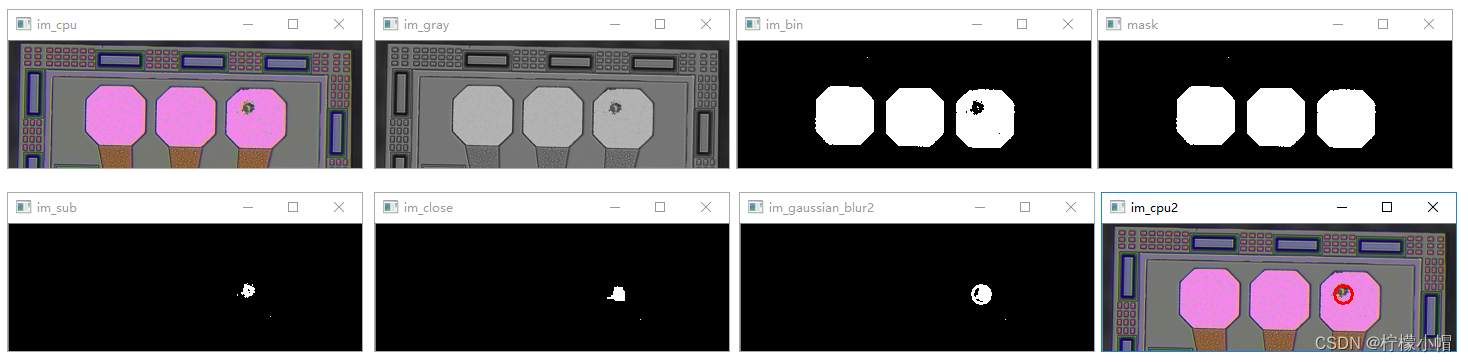
8.2 利用OpenCV检测芯片瑕疵
【任务描述】
利用图像技术,检测出芯片镀盘区域瑕疵。样本图像中,粉红色区域为镀盘区域,镀盘内部空洞为瑕疵区域,利用图像技术检测镀盘是否存在瑕疵,如果存在则将瑕疵区域标记出来。

【代码】
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math# 第一步:图像预处理
## 1. 转换成灰度图像,进行二值化处理
im_cpu = cv2.imread("../../data/CPU3.png")
im_gray = cv2.cvtColor(im_cpu, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # 转换成灰度图像# 提取出度盘轮廓
ret, im_bin = cv2.threshold(im_gray, 162, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 图像二值化
cv2.imshow("im_cpu", im_cpu)
cv2.imshow("im_gray", im_gray)
cv2.imshow("im_bin", im_bin)# 提取轮廓、绘制边沿
img, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(im_bin, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)# 绘制前景对象轮廓
mask = np.zeros(im_bin.shape, np.uint8)
mask = cv2.drawContours(mask, contours, -1, (255, 0, 0), -1) # 绘制实心轮廓
cv2.imshow("mask", mask)# 前景实心轮廓图和二值化图相减
im_sub = cv2.subtract(mask, im_bin)
cv2.imshow("im_sub", im_sub)# 图像闭运算,先膨胀后腐蚀,去除内部毛刺
k = np.ones((10, 10), np.uint8)
im_close = cv2.morphologyEx(im_sub, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, k, iterations=3)
cv2.imshow("im_close", im_close)# 提取、绘制轮廓、计算面积
img, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(im_close, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)(x, y), radius = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(contours[1])
center = (int(x), int(y))
radius = int(radius)
print("center:", center, " radius:", radius)
cv2.circle(im_close, center, radius, (255, 0, 0), 2) # 绘制圆
cv2.imshow("im_gaussian_blur2", im_close)# 在原始图片上绘制瑕疵
cv2.circle(im_cpu, center, radius, (0, 0, 255), 2) # 绘制圆
cv2.imshow("im_cpu2", im_cpu)#计算面积
area = math.pi * radius * radius
print("area:", area)
if area > 12:print("度盘表面有缺陷")cv2.waitKey()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
【执行结果】