在搜索应用中,传统的 Keyword Search 一直是主要的搜索方法,它适合精确匹配查询的场景,能够提供低延迟和良好的结果可解释性,但是 Keyword Search 并没有考虑上下文信息,可能产生不相关的结果。最近几年,基于向量检索技术的搜索增强技术 Semantic Search 越来越流行,通过使用机器学习模型将数据对象(文本、图像、音视频等)转化成向量,向量距离代表对象间的相似性,如果使用的模型和问题领域相关性高,则往往能更好地理解上下文和搜索意图,进而提高搜索结果的相关性,反之,如果模型和问题领域相关性不高,则效果会大打折扣。
Keyword Search 和 Semantic Search 都存在明显的优劣势,那么是否可以通过组合它们的优点来整体提高搜索的相关性?答案是,简单的算术组合并不能收到预期的效果,主要原因有两个:
-
首先是不同类型查询的评分并不在同一个可比较的维度,因此不能直接进行简单的算术计算。
-
其次是在分布式检索系统中,评分通常在分片级别,需要对所有分片的评分进行全局归一化处理。
综上,我们需要寻找一种理想的查询类型来解决这些问题,它能单独执行每个查询子句,同时收集分片级别的查询结果,最后对所有查询的评分进行归一化合并后返回最终的结果,这就是混合搜索(Hybrid Search) 方案。
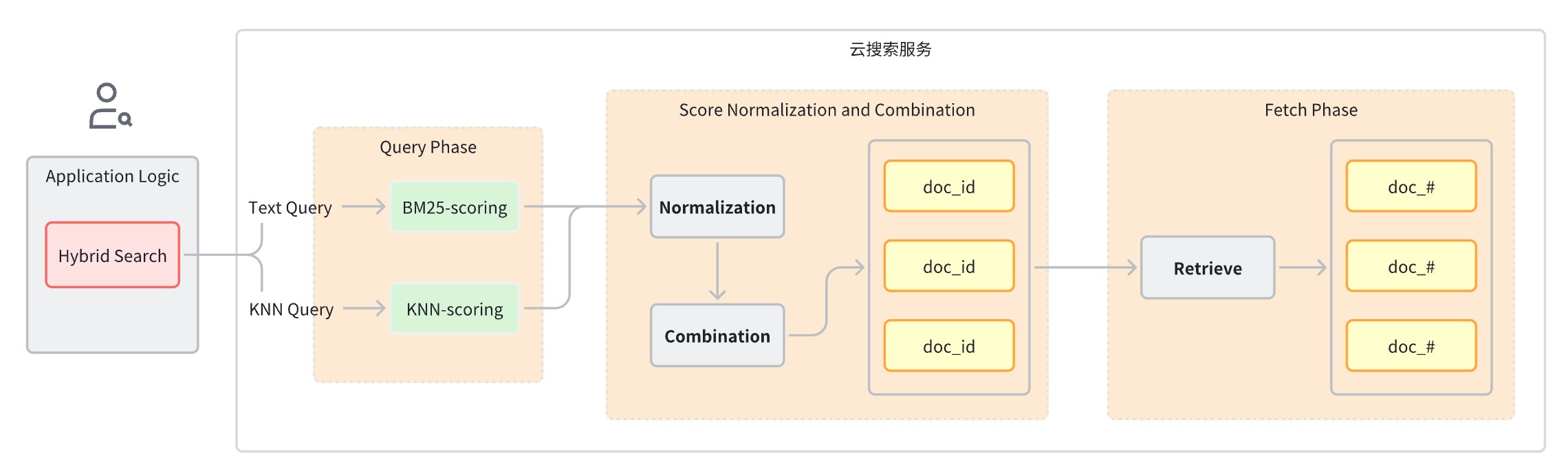
通常一次混合搜索查询可以分为以下几步:
-
查询阶段:使用混合查询子句进行 Keyword Search 和 Semantic Search。
-
评分归一化和合并阶段,该阶段在查询阶段之后。
-
由于每种查询类型都会提供不同范围的评分,该阶段对每一个查询子句的评分结果执行归一化操作,支持的归一化方法有 min_max、l2、rrf。
-
对归一化后的评分进行组合,组合方法有 arithmetic_mean、geometric_mean、harmonic_mean。
-
-
根据组合后的评分对文档重新排序并返回给用户。
实现思路
从前面原理介绍,我们可以看到要实现一个混合检索应用,至少需要用到这些基础技术设施
-
全文检索引擎
-
向量检索引擎
-
用于向量 Embedding 的机器学习模型
-
将文本、音频、视频等数据转化成向量的数据管道
-
融合排序
火山引擎云搜索构建在开源的 Elasticsearch 和 OpenSearch 项目上,从第一天上线就支持了完善成熟的文本检索和向量检索能力,同时针对混合搜索场景也进行了一系列的功能迭代和演进,提供了开箱即用的混合搜索解决方案。本文将以图像搜索应用为例,介绍如何借助火山引擎云搜索服务的解决方案快速开发一个混合搜索应用。
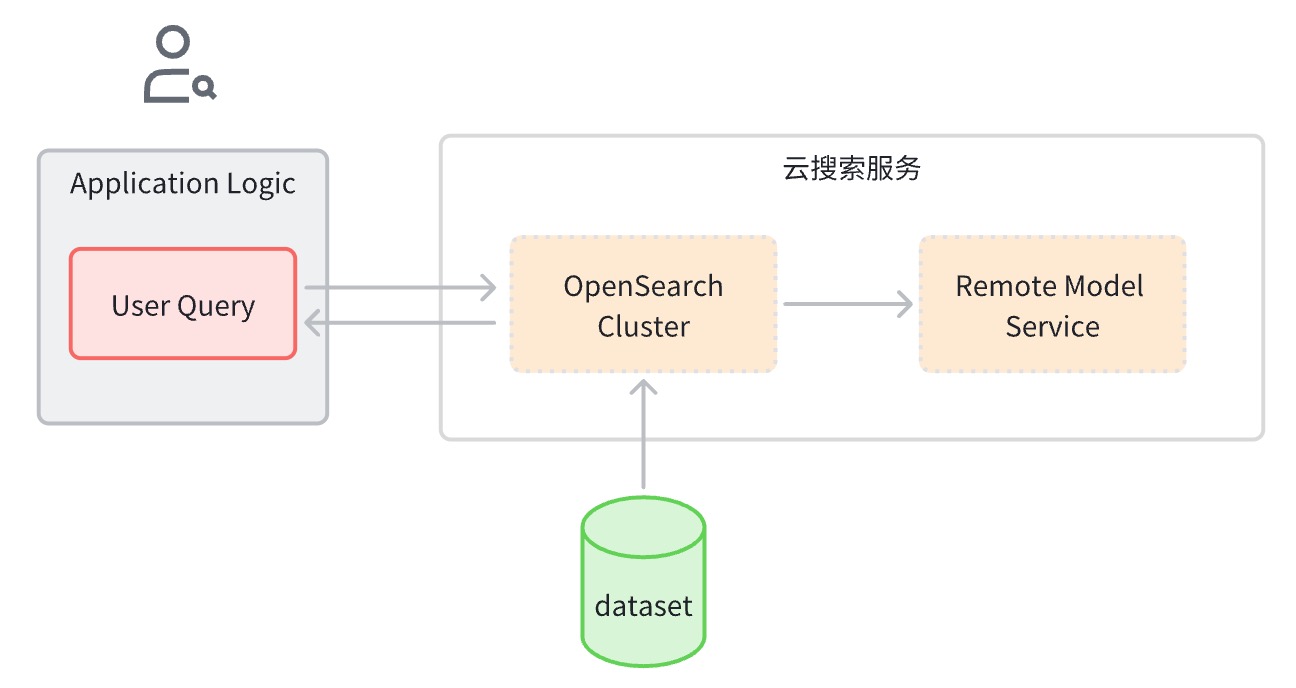
其端到端流程概括如下:
-
配置创建相关对象
-
Ingestion Pipeline:支持自动调用模型把图片转换向量并存到索引中
-
Search Pipeline:支持把文本查询语句自动转换成向量以便进行相似度计算
-
k-NN索引:存放向量的索引
-
-
将图像数据集数据写入 OpenSearch 实例,OpenSearch 会自动调用机器学习模型将文本转为 Embedding 向量。
-
Client 端发起混合搜索查询时,OpenSearch 调用机器学习模型将传入的查询转为 Embedding 向量。
-
OpenSearch 执行混合搜索请求处理,组合 Keyword Seach 和 Semantic Seach 的评分,返回搜索结果。
方案实战
环境准备
1.登录火山引擎云搜索服务(https://console.volcengine.com/es),创建实例集群,版本选择 OpenSearch 2.9.0。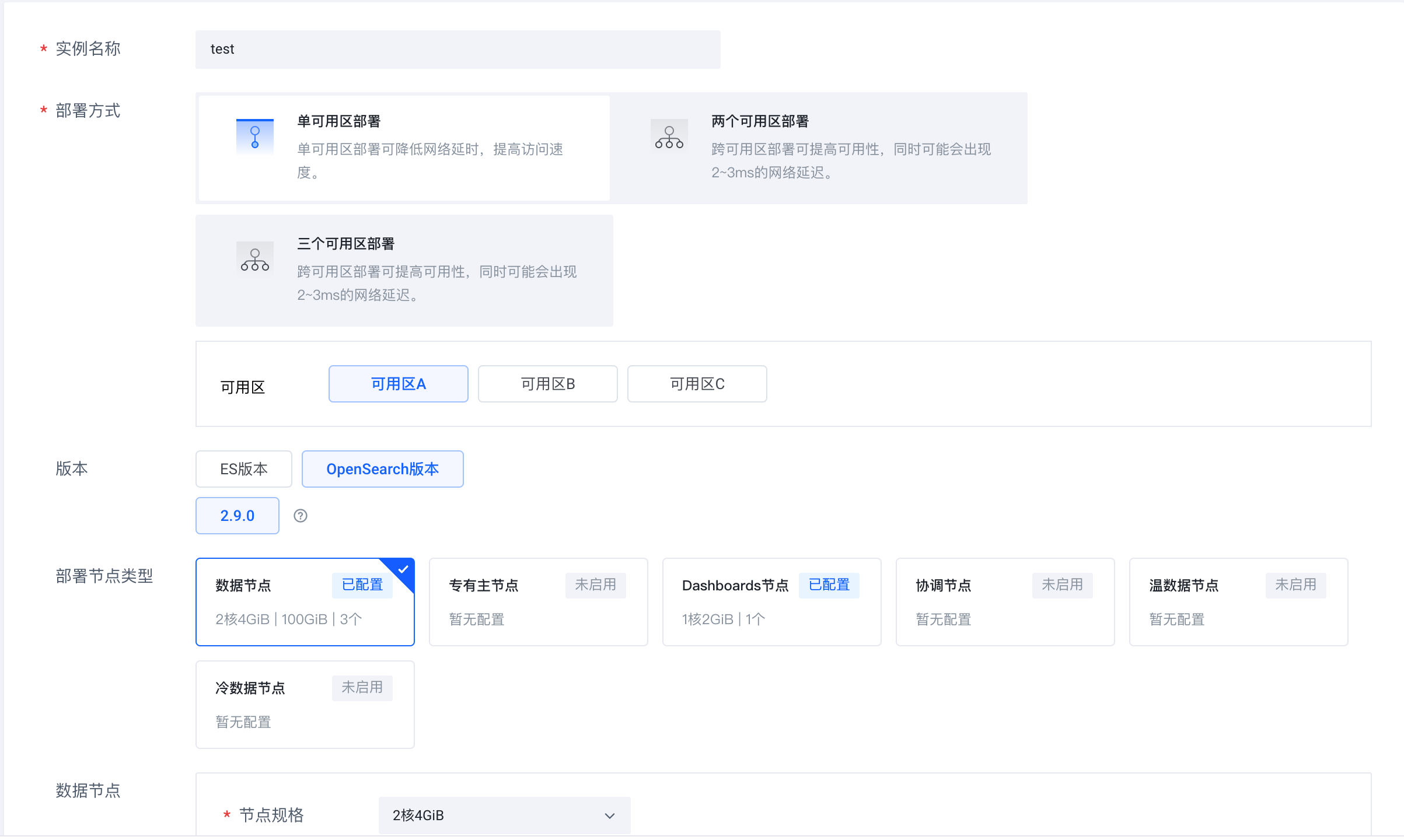
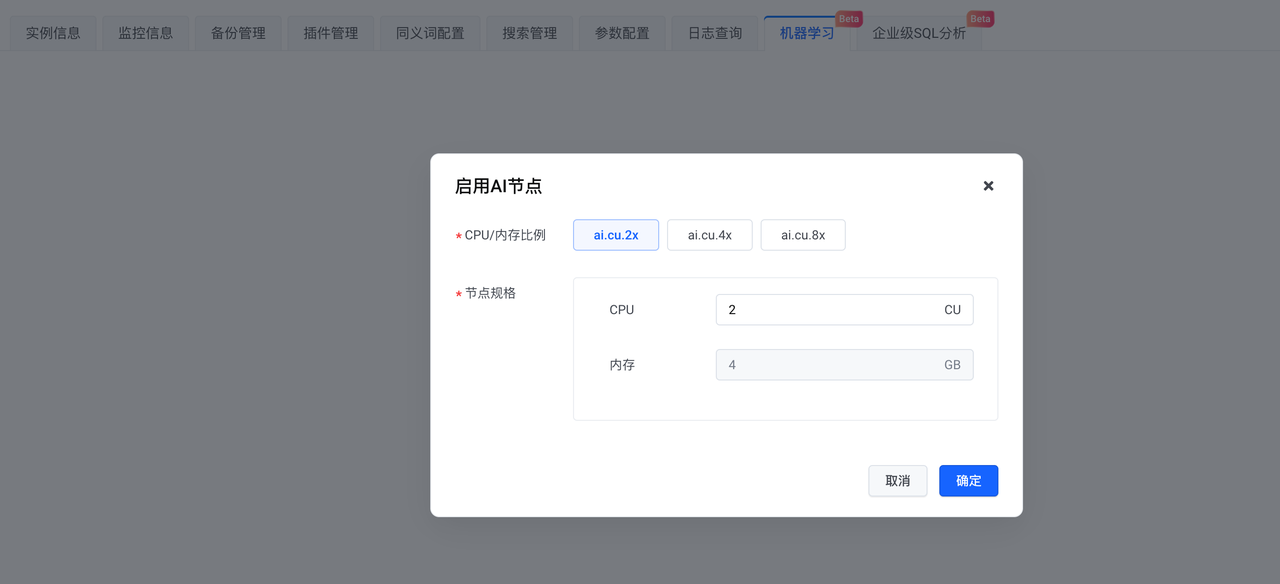
2.待实例创建完毕,启用 AI 节点。
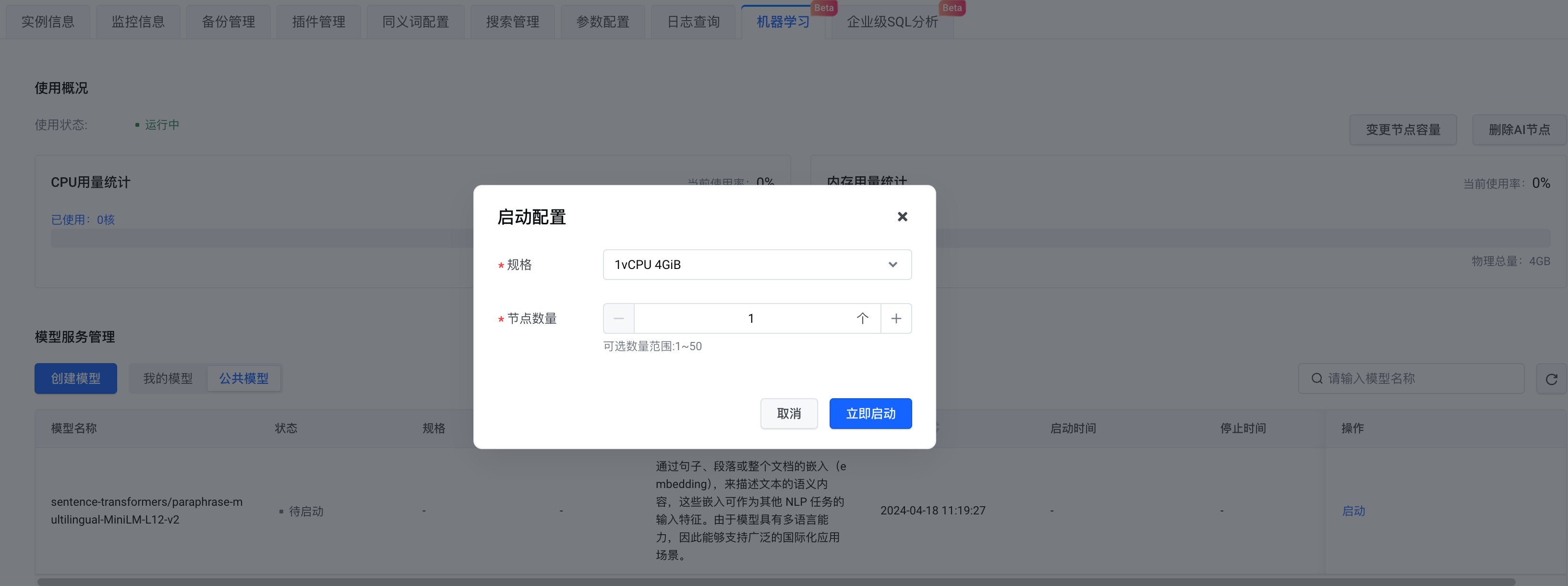
3.在模型选择上,可以创建自己的模型,也可以选择公共模型。这里我们选择公共模型,完成配置后,点击立即启动。
至此,准备好了 OpenSearch 实例和混合搜索所依赖的机器学习服务。
数据集准备
使用 Amazon Berkeley Objects Dataset(https://registry.opendata.aws/amazon-berkeley-objects/)作为数据集,数据集无需本地下载,直接通过代码逻辑上传到 OpenSearch,详见下面代码内容。
操作步骤
安装 Python 依赖
pip install -U elasticsearch7==7.10.1
pip install -U pandas
pip install -U jupyter
pip install -U requests
pip install -U s3fs
pip install -U alive_progress
pip install -U pillow
pip install -U ipython连接到 OpenSearch
# Prepare opensearch info
from elasticsearch7 import Elasticsearch as CloudSearch
from ssl import create_default_context
# opensearch info
opensearch_domain = '{{ OPENSEARCH_DOMAIN }}'
opensearch_port = '9200'
opensearch_user = 'admin'
opensearch_pwd = '{{ OPENSEARCH_PWD }}'
# remote config for model server
model_remote_config = {"method": "POST","url": "{{ REMOTE_MODEL_URL }}","params": {},"headers": {"Content-Type": "application/json"},"advance_request_body": {"model": "sentence-transformers/paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2"}
}
# dimension for knn vector
knn_dimension = 384
# load cer and create ssl context
ssl_context = create_default_context(cafile='./ca.cer')
# create CloudSearch client
cloud_search_cli = CloudSearch([opensearch_domain, opensearch_port],ssl_context=ssl_context,scheme="https",http_auth=(opensearch_user, opensearch_pwd))
# index name
index_name = 'index-test'# pipeline id
pipeline_id = 'remote_text_embedding_test'
# search pipeline id
search_pipeline_id = 'rrf_search_pipeline_test'1.填入 OpenSearch 链接地址和用户名密码信息。model_remote_config 是远程机器学习模型连接配置,可在模型调用信息查看,将调用信息中的 remote_config 配置全部复制到 model_remote_config。
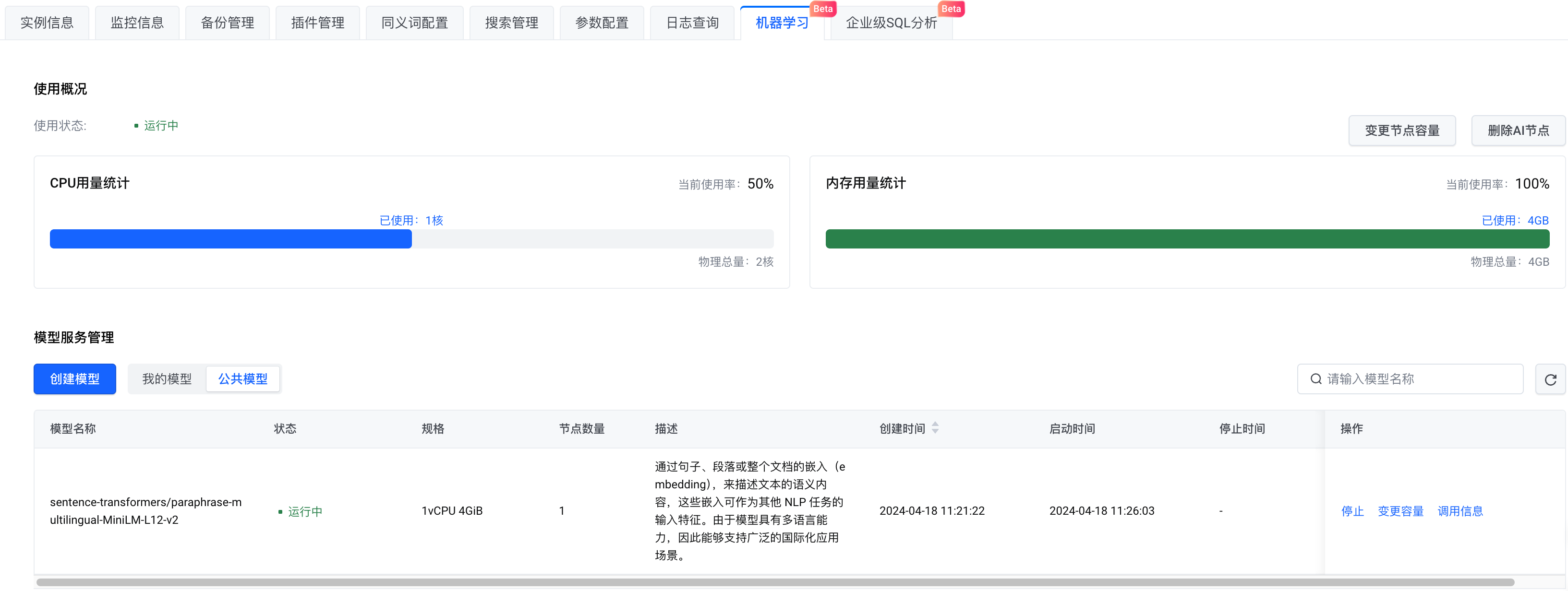
2.在实例信息->服务访问部分,下载证书到当前目录。
3.给定索引名称、Pipeline ID 和 Search Pipeline ID。
创建 Ingest Pipeline
创建 Ingest Pipeline,指定使用的机器学习模型,将指定字段转换为向量后嵌入回去。如下,将 caption 字段转为向量存储到 caption_embedding 中。
# Create ingest pipeline
pipeline_body = {"description": "text embedding pipeline for remote inference","processors": [{"remote_text_embedding": {"remote_config": model_remote_config,"field_map": {"caption": "caption_embedding"}}}]
}
# create request
resp = cloud_search_cli.ingest.put_pipeline(id=pipeline_id, body=pipeline_body)
print(resp)创建 Search Pipeline
创建查询需要使用的 Pipeline,配置好远程模型。
支持的归一化方法和加权求和方法:
-
归一化方法:
min_max,l2,rrf -
加权求和方法:
arithmetic_mean,geometric_mean,harmonic_mean
这里选择 rrf 归一化方法。
# Create search pipeline
import requests
search_pipeline_body = {"description": "post processor for hybrid search","request_processors": [{"remote_embedding": {"remote_config": model_remote_config}}],"phase_results_processors": [ # normalization and combination{"normalization-processor": {"normalization": {"technique": "rrf", # the normalization technique in the processor is set to rrf"parameters": {"rank_constant": 60 # param}},"combination": {"technique": "arithmetic_mean", # the combination technique is set to arithmetic mean"parameters": {"weights": [0.4,0.6]}}}}]
}
headers = {'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
# create request
resp = requests.put(url="https://" + opensearch_domain + ':' + opensearch_port + '/_search/pipeline/' + search_pipeline_id,auth=(opensearch_user, opensearch_pwd),json=search_pipeline_body,headers=headers,verify='./ca.cer')
print(resp.text)创建 k-NN 索引
-
将事先创建好的 Ingest Pipeline 配置到 index.default_pipeline 字段中;
-
同时,配置 properties,将 caption_embedding 设置为 knn_vector,这里使用 faiss 中的 hnsw。
# Create k-NN index
# create index and set settings, mappings, and properties as needed.
index_body = {"settings": {"index.knn": True,"number_of_shards": 1,"number_of_replicas": 0,"default_pipeline": pipeline_id # ingest pipeline},"mappings": {"properties": {"image_url": {"type": "text"},"caption_embedding": {"type": "knn_vector","dimension": knn_dimension,"method": {"engine": "faiss","space_type": "l2","name": "hnsw","parameters": {}}},"caption": {"type": "text"}}}
}
# create index
resp = cloud_search_cli.indices.create(index=index_name, body=index_body)
print(resp)加载数据集
读取数据集到内存中,并过滤出部分需要使用的数据。
# Prepare dataset
import pandas as pd
import string
appended_data = []
for character in string.digits[0:] + string.ascii_lowercase:if character == '1':breaktry:meta = pd.read_json("s3://amazon-berkeley-objects/listings/metadata/listings_" + character + ".json.gz",lines=True)except FileNotFoundError:continueappended_data.append(meta)
appended_data_frame = pd.concat(appended_data)
appended_data_frame.shape
meta = appended_data_frame
def func_(x):us_texts = [item["value"] for item in x if item["language_tag"] == "en_US"]return us_texts[0] if us_texts else None
meta = meta.assign(item_name_in_en_us=meta.item_name.apply(func_))
meta = meta[~meta.item_name_in_en_us.isna()][["item_id", "item_name_in_en_us", "main_image_id"]]
print(f"#products with US English title: {len(meta)}")
meta.head()
image_meta = pd.read_csv("s3://amazon-berkeley-objects/images/metadata/images.csv.gz")
dataset = meta.merge(image_meta, left_on="main_image_id", right_on="image_id")
dataset.head()上传数据集
上传数据集到 Opensearch,针对每条数据,传入 image_url 和 caption。无需传入 caption_embedding,将通过远程机器学习模型自动生成。
# Upload dataset
import json
from alive_progress import alive_bar
cnt = 0
batch = 0
action = json.dumps({"index": {"_index": index_name}})
body_ = ''with alive_bar(len(dataset), force_tty=True) as bar:for index, row in (dataset.iterrows()):if row['path'] == '87/874f86c4.jpg':continuepayload = {}payload['image_url'] = "https://amazon-berkeley-objects.s3.amazonaws.com/images/small/" + row['path']payload['caption'] = row['item_name_in_en_us']body_ = body_ + action + "\n" + json.dumps(payload) + "\n"cnt = cnt + 1if cnt == 100:resp = cloud_search_cli.bulk(request_timeout=1000,index=index_name,body=body_)cnt = 0batch = batch + 1body_ = ''bar()
print("Total Bulk batches completed: " + str(batch))混合搜索查询
以查询 shoes 为例,查询中包含两个查询子句,一个是 match 查询,一个是 remote_neural 查询。查询时将事先创建好的 Search Pipeline 指定为查询参数,Search Pipeline 会将传入的文本转为向量,存储到 caption_embedding 字段,用于后续查询。
# Search with search pipeline
from urllib import request
from PIL import Image
import IPython.display as display
def search(text, size):resp = cloud_search_cli.search(index=index_name,body={"_source": ["image_url", "caption"],"query": {"hybrid": {"queries": [{"match": {"caption": {"query": text}}},{"remote_neural": {"caption_embedding": {"query_text": text,"k": size}}}]}}},params={"search_pipeline": search_pipeline_id},)return resp
k = 10
ret = search('shoes', k)
for item in ret['hits']['hits']:display.display(Image.open(request.urlopen(item['_source']['image_url'])))print(item['_source']['caption'])混合搜索演示
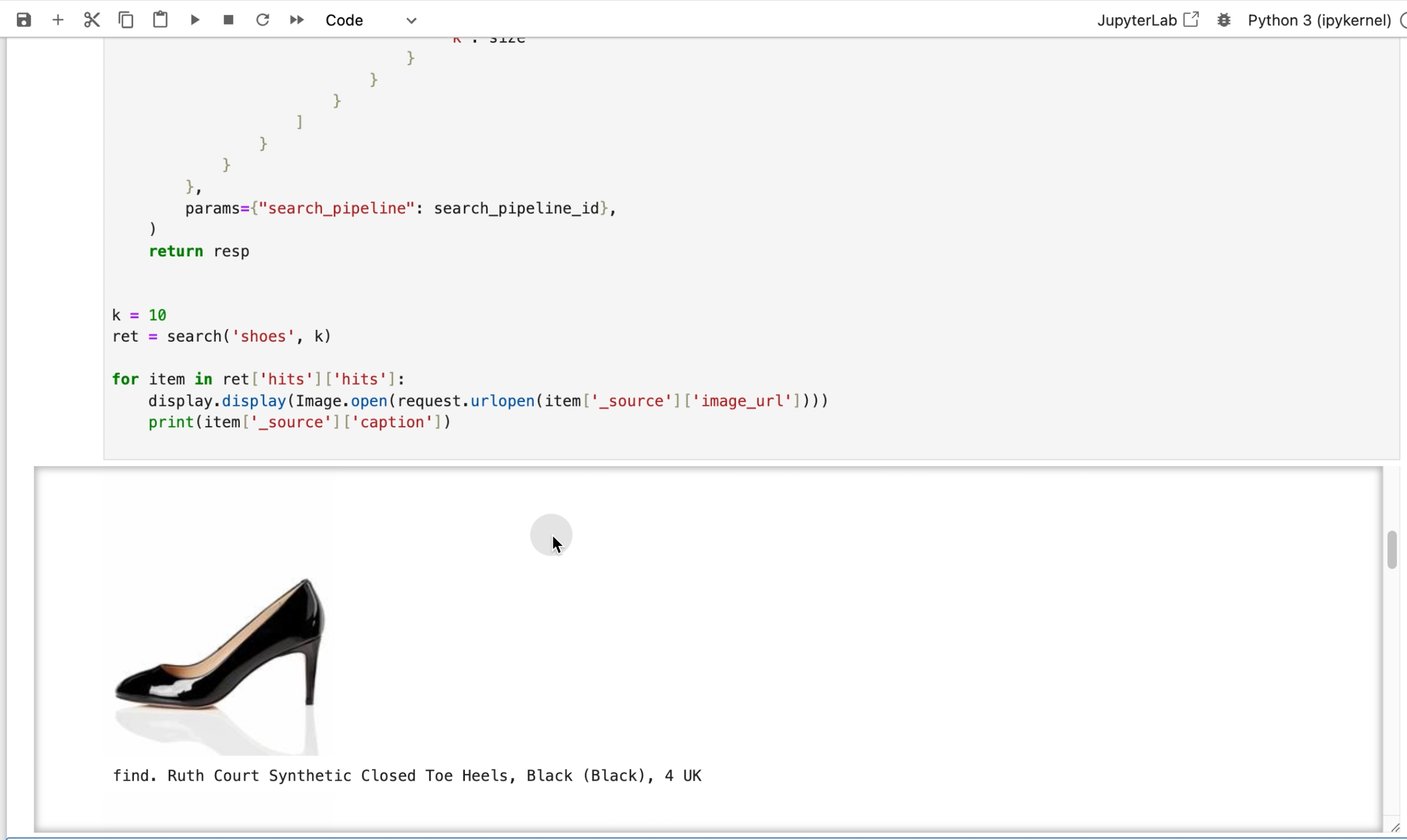
以上就是以图像搜索应用为例,介绍如何借助火山引擎云搜索服务的解决方案快速开发一个混合搜索应用的实战过程,欢迎大家登陆火山引擎控制台操作!