文章目录
- 读写文件
- 概述
- example
- csv
- 读文件
- 读取每个字段
- 读取机器学习数据库iris
- constexpr函数
- GMP大整数
- codeblock环境配置
- 数据类型
- 函数类
- Eigen
- minCoeff 和maxCoeff
- Array类
读写文件
概述
- fstream
typedef basic_fstream<char, char_traits<char>> fstream;
此类型是类模板 basic_fstream 的同义词,专用于具有默认字符特征的 char 类型的元素。
- ifstream
定义要用于从文件中按顺序读取单字节字符数据的流。
using namespace std;ifstream infile("hello.txt");if (!infile.bad())
{cout << infile.rdbuf();infile.close();
}
- ofstream
专用于 char 模板参数的类型 basic_ofstream。
typedef basic_ofstream<char, char_traits<char>> ofstream;
- openmode
如何与流进行交互。
class ios_base {
public:typedef implementation-defined-bitmask-type openmode;static const openmode in;static const openmode out;static const openmode ate;static const openmode app;static const openmode trunc;static const openmode binary;// ...
};
example
- 例1
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>using namespace std;int main(){//writeofstream fileOut;fileOut.open("hello.txt");fileOut<<"hello,world!"<<endl;fileOut<<"hello,hello";fileOut.close();//readifstream fileIn;char helloTxt[80];fileIn.open("hello.txt");fileIn>>helloTxt;cout<<helloTxt<<endl;fileIn>>helloTxt;cout<<helloTxt<<endl;fileIn.close();}hello,world!
hello,helloProcess returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.134 s
Press any key to continue.
- 例2
// basic_fstream_class.cpp
// compile with: /EHsc#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>using namespace std;int main(int argc, char **argv)
{fstream fs("hello.txt", ios::in | ios::out | ios::trunc);if (!fs.bad()){// Writefs << "hello,world" << endl;fs << "hello!" << endl;fs.close();// readfs.open("hello.txt", ios::in);cout << fs.rdbuf();fs.close();}
}
- 例3
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>using namespace std;int main(){//writeofstream fileOut;fileOut.open("hello.txt");fileOut<<"hello,world!"<<endl;fileOut<<"hello,hello";fileOut.close();//readifstream fileIn;char helloTxt[80];fileIn.open("hello.txt");while (fileIn>>helloTxt){cout<<helloTxt<<endl;}fileIn.close();}- 例4
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>using namespace std;int main(){//writeofstream fileOut;fileOut.open("hello.txt");fileOut<<"hello,world!"<<endl;fileOut<<"hello,hello";fileOut.close();//readifstream fileIn;char helloTxt[80];fileIn.open("hello1.txt");if (!fileIn.is_open()){cout<<"打开失败!"<<endl;return 0;}while (fileIn>>helloTxt){cout<<helloTxt<<endl;}fileIn.close();}- 例5
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>using namespace std;int main(){//writeofstream fileOut;fileOut.open("hello.txt");fileOut<<"hello,world!"<<endl;fileOut<<"hello,hello";fileOut.close();//readifstream fileIn;char helloChar;fileIn.open("hello.txt");if (!fileIn.is_open()){cout<<"打开失败!"<<endl;return 0;}int i=0;while (fileIn.get(helloChar)){cout<<helloChar;if (helloChar!='\n') i++;}cout<<endl<<"文件的字符数:"<<i<<endl;fileIn.close();}hello,world!
hello,hello
文件的字符数:23Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.248 s
Press any key to continue.更多内容在微软文档
csv
读文件
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>using namespace std;int main(){//readifstream fileIn;char helloChar;fileIn.open("e:/ml_data/iris/iris.data");if (!fileIn.is_open()){cout<<"打开失败!"<<endl;return 0;}int i=0;while (fileIn.get(helloChar)){cout<<helloChar;if (helloChar!='\n') i++;}cout<<endl<<"文件的字符数:"<<i<<endl;fileIn.close();}
读取每个字段
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>using namespace std;
vector<string> split(const string &text, char separator);
int main(){//readifstream fileIn;char helloStr[100];vector<string> sampleDatas;fileIn.open("e:/ml_data/iris/iris.data");if (!fileIn.is_open()){cout<<"打开失败!"<<endl;return 0;}while (fileIn>>helloStr){sampleDatas=split(helloStr,',');for (const string &data: sampleDatas) {cout << data<<" " ;}cout<<endl;}fileIn.close();}vector<string> split(const string &text, char separator) {vector<string> tokens;stringstream ss(text);string item;while (getline(ss, item, separator)) {if (!item.empty()) {tokens.push_back(item);}}return tokens;
}读取机器学习数据库iris
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <regex>using namespace std;
struct IrisDa{float *irisX;int dataSize;int d;~IrisDa(){delete[] irisX;}
};vector<string> split(const string &text, char separator);
string removeSpaces(const string& input);
void rbLearn(const IrisDa *irisDa);int main(){ifstream fileIn;char helloStr[100];//read csvfileIn.open("e:/ml_data/iris/iris_sample.data");if (!fileIn.is_open()){cout<<"打开失败!"<<endl;return 0;}regex strRx(R"((\d+)(\.)(\d+))");smatch match;while (fileIn>>helloStr){//construct x(n) and d(n)IrisDa *irisDa=new IrisDa;vector<string> sampleDatas=split(helloStr,',');int dataCount=sampleDatas.size();float *irisX= new float[dataCount];//x(n)irisX[0]=1.0;int irisD;//d(n)int i=1;for (const string &data: sampleDatas) {string irisData=removeSpaces(data);bool found = regex_match(irisData, match, strRx);if (found) {irisX[i]=stof(irisData);i++;}else{if (irisData=="Iris-setosa"){irisD=1;}else{irisD=-1;}}}irisDa->irisX=irisX;irisDa->d=irisD;irisDa->dataSize=dataCount;rbLearn(irisDa);}fileIn.close();
}void rbLearn(const IrisDa *irisDa){cout<<"正在处理数据..."<<endl;for (int i=0;i<irisDa->dataSize;i++) {cout<<irisDa->irisX[i]<<" ";}cout<<endl;
}vector<string> split(const string &text, char separator) {vector<string> tokens;stringstream ss(text);string item;while (getline(ss, item, separator)) {if (!item.empty()) {tokens.push_back(item);}}return tokens;
}string removeSpaces(const string& input) {string result = input;result.erase(std::remove(result.begin(), result.end(), ' '), result.end());return result;
}constexpr函数
函数可能在编译时求值,则声明它为constexpr,以提高效率。需要使用constexpr告诉编译器允许编译时计算。
constexpr int min(int x, int y) { return x < y ? x : y; }
void test(int v)
{int m1 = min(-1, 2); // 可能在编译期计算constexpr int m2 = min(-1, 2); // 编译时计算int m3 = min(-1, v); // 运行时计算constexpr int m4 = min(-1, v); // 错误,不能在编译期计算
}
int dcount = 0;
constexpr int double(int v)
{++dcount; // constexpr 函数无副作用,因为这一行错误return v + v;
}
constexpr函数被隐式地指定为内联函数,此外,constexpr允许递归。
#include <iostream>
constexpr int fac(int n)
{return n > 0 ? n * fac( n - 1 ) : 1;
}
inline int myadd(int x,int y){return x+y;};
int main()
{int n;std::cout<<"请输入阶乘参数:";std::cin>>n;std::cout<<std::endl<<fac(n)<<std::endl;std::cout<<myadd(12,55)<<std::endl;return 0;
}
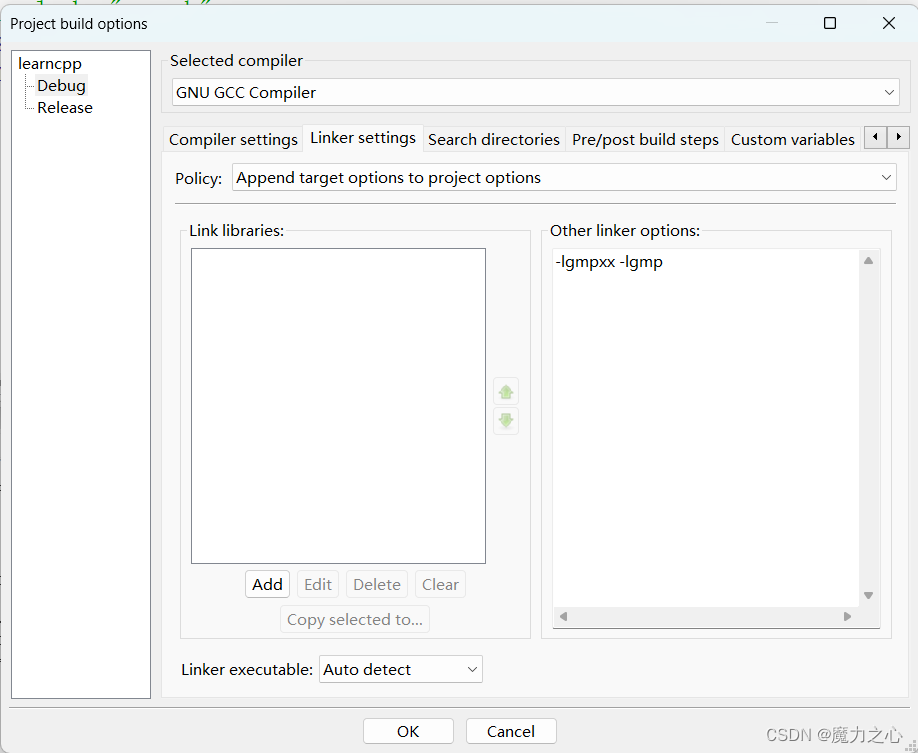
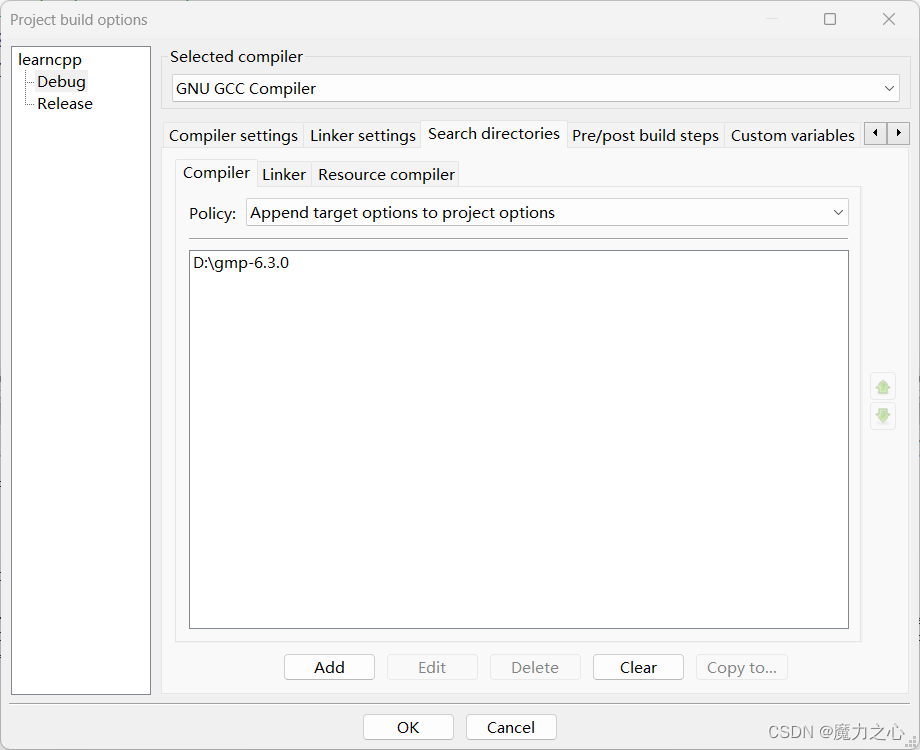
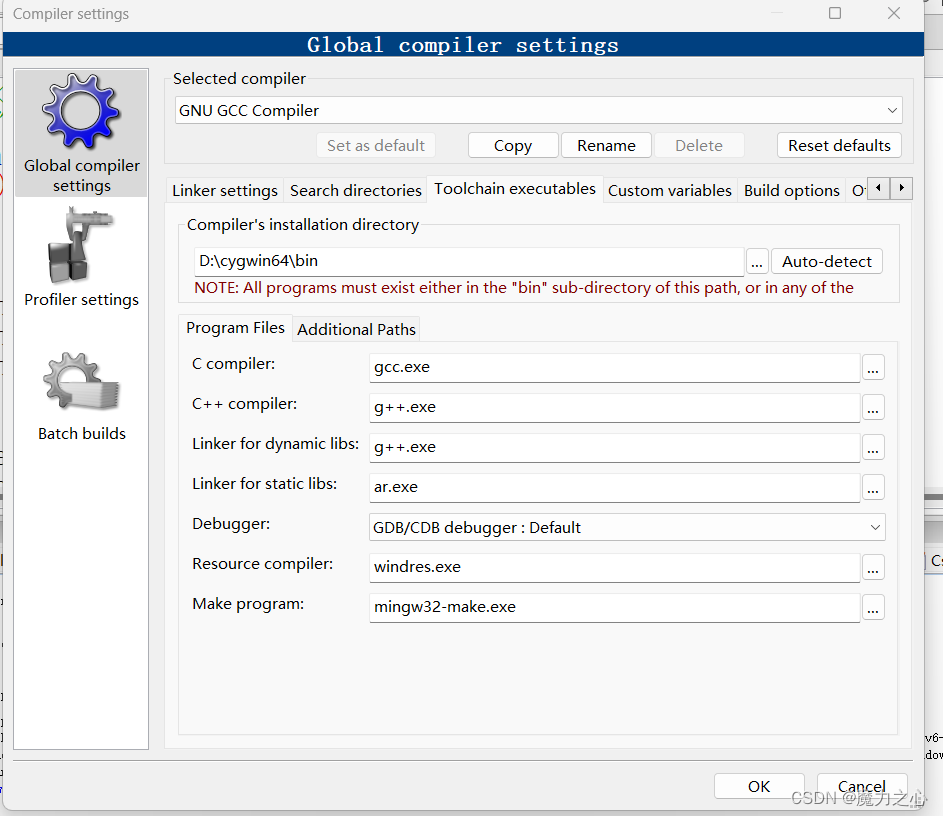
GMP大整数
codeblock环境配置

数据类型
- 整型
mpz_t sum;struct foo { mpz_t x, y; };mpz_t vec[20];
- 有理数
mpq_t quotient;
也是高倍精度分数。
- 浮点数
mpf_t fp;
浮点函数接受并返回C类型mp_exp_t中的指数。目前,这通常是很长的,但在某些系统上,这是效率的一个指标。
- 指针
Mpz_ptr用于指向mpz_t中的元素类型的指针
Mpz_srcptr for const指针指向mpz_t中的元素类型
Mpq_ptr用于指向mpq_t中的元素类型的指针
Mpq_srcptr for const指针指向mpq_t中的元素类型
Mpf_ptr用于指向mpf_t中元素类型的指针
Mpf_srcptr for const指针指向mpf_t中的元素类型
指向gmp_randstate_t中元素类型的指针
Gmp_randstate_srcptr for const指针指向gmp_randstate_t中的元素类型
函数类
用于有符号整数算术的函数,其名称以mpz_开头。关联类型为mpz_t。这门课大约有150个函数
用于有理数算术的函数,其名称以mpq_开头。关联类型为mpq_t。这门课大约有35个函数,但整数函数可以分别对分子和分母进行算术运算。
用于浮点运算的函数,其名称以mpf_开头。关联类型为mpf_t。这门课大约有70个函数。
对自然数进行操作的快速低级函数。这些由前面组中的函数使用,您也可以从时间要求非常严格的用户程序中直接调用它们。这些函数的名称以mpn_开头。关联类型为mp_limb_t数组。这个类中大约有60个(难以使用的)函数。
各种各样的功能。设置自定义分配的函数和生成随机数的函数。
Eigen
minCoeff 和maxCoeff
不带参数时,返回最小元素和最大元素,带参数时,返回元素所在坐标
#include <iostream>
#include "e:/eigen/Eigen/Dense"
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main(){Matrix2d m {{1,2},{3,4}};std::ptrdiff_t i, j;int minOfM = m.minCoeff(&i,&j);cout << "Here is the matrix m:\n" << m << endl;cout << "Its minimum coefficient (" << minOfM<< ") is at position (" << i << "," << j << ")\n\n";int maxOfM= m.maxCoeff(&i,&j);cout << "Its maximum coefficient (" << maxOfM<< ") is at position (" << i << "," << j << ")\n\n";RowVector4i v = RowVector4i::Random();int maxOfV = v.maxCoeff(&i);cout << "Here is the vector v: " << v << endl;cout << "Its maximum coefficient (" << maxOfV<< ") is at position " << i << endl;int minOfV = v.minCoeff(&j);cout << "Its minimum coefficient (" << minOfV<< ") is at position " << j << endl;}Here is the matrix m:
1 2
3 4
Its minimum coefficient (1) is at position (0,0)Its maximum coefficient (4) is at position (1,1)Here is the vector v: 730547559 -226810938 607950953 640895091
Its maximum coefficient (730547559) is at position 0
Its minimum coefficient (-226810938) is at position 1Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 0.305 s
Press any key to continue.Array类
Array类提供了通用数组,而Matrix类则用于线性代数。此外,Array类提供了一种简单的方法来执行系数操作,这种操作可能没有线性代数意义,比如向数组中的每个系数添加一个常数,或者对两个数组进行系数乘。