目录
- 专栏列表
- 1. `os` 模块
- 2. `sys` 模块
- 3. `re` 模块
- 4. `json` 模块
- 5. `datetime` 模块
- 6. `math` 模块
- 7. `random` 模块
- 8. `collections` 模块
- 9. `itertools` 模块
- 10. `threading` 模块
- 11. `加密` 模块
- 总结
专栏列表
- Python教程(十):面向对象编程(OOP)
- Python教程(十一):单元测试与异常捕获
- Python教程(十二):面向对象高级编程详解
- Python教程(十三):常用内置模块详解

正文开始,如果觉得文章对您有帮助,请帮我三连+订阅,谢谢💖💖💖
1. os 模块
os模块提供了丰富的方法来与操作系统进行交互,包括文件和目录操作、环境变量访问等。
示例代码:
import os# 获取当前工作目录
current_directory = os.getcwd()
print(f"当前工作目录: {current_directory}")# 改变当前工作目录
os.chdir('../class-demo')
print(f"改变后的工作目录: {os.getcwd()}")# 列出目录中的文件和文件夹
entries = os.listdir('.')
print(f"目录中的条目: {entries}")# 检查路径是否存在
path_exists = os.path.exists('../class-demo/')
print(f"路径存在: {path_exists}")# 获取文件的大小
file_size = os.path.getsize('../class-demo/demo01.py')
print(f"文件大小: {file_size} 字节")

2. sys 模块
sys模块用于访问与Python解释器相关的变量和函数,如命令行参数、最大递归深度等。
示例代码:
import sys# 打印命令行参数
print(f"命令行参数: {sys.argv}")# 获取Python解释器的路径
print(f"Python解释器路径: {sys.executable}")# 设置并获取最大递归深度
sys.setrecursionlimit(1000)
print(f"最大递归深度: {sys.getrecursionlimit()}")

3. re 模块
re模块提供了正则表达式的功能,用于字符串的搜索、替换、匹配等。
示例代码:
import retext = 'Hello world!'res = re.match(r"(\w|\s)+", text)
print(res)
if res:print('成功匹配')
else:print('未匹配到')# 搜索数字
match = re.search(r'\d+', '这里有123个苹果')
print(f"搜索到的数字: {match.group()}")# 替换字符串中的单词
replaced = re.sub(r'苹果', '橙子', '我买了3个苹果')
print(f"替换后的字符串: {replaced}")# 匹配邮箱地址
emails = re.findall(r'[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}', '请联系example@example.com或test@example.net')
print(f"找到的邮箱地址: {emails}")

4. json 模块
json模块用于处理JSON数据,包括将Python对象编码成JSON字符串,以及将JSON字符串解码成Python对象。
示例代码:
import json# JSON 编码
data = {'name': '子羽', 'age': 30, 'city': '成都'}
json_string = json.dumps(data)
print(f"JSON 编码: {json_string}")# JSON 解码
decoded_data = json.loads(json_string)
print(f"JSON 解码: {decoded_data}")

5. datetime 模块
datetime模块提供了日期和时间的操作,可以创建日期和时间对象,进行日期时间的计算和格式化。
示例代码:
from datetime import datetime, timedelta, timezone# 获取当前日期和时间
now = datetime.now()
print(f"当前日期和时间: {now}")
dt = now.timestamp() # 把datetime转换为timestamp , timestamp是一个浮点数,整数位表示秒。
print(dt)print(f'当地时区:{datetime.fromtimestamp(dt)}') # 要把timestamp转换为datetime
print(f'utc时区:{datetime.fromtimestamp(dt, timezone.utc)}') # 要把timestamp转换为datetime# 增加日期
#timedelta(days=2, hours=12) # 2 天 12 小时
one_day = timedelta(days=1)
tomorrow = now + one_day
print(f"明天的日期: {tomorrow}")# 格式化日期
formatted_date = now.strftime('%Y年%m月%d日 %H时%M分%S秒')
print(f"格式化的日期: {formatted_date}")

6. math 模块
math模块包含了许多数学函数,如三角函数、指数、对数、幂运算等。
示例代码:
import math# 计算平方根
sqrt = math.sqrt(16)
print(f"平方根: {sqrt}")# 幂
print(math.pow(3,3))# 计算正弦值
sin_value = math.sin(math.pi / 2)
print(f"正弦值: {sin_value}")# 计算对数
log_value = math.log(10)
print(f"对数值: {log_value}")

7. random 模块
random模块用于生成随机数,进行随机选择、设置随机数生成器的种子等。
示例代码:
import random# 随机选择一个元素
item = random.choice(['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'])
print(f"随机选择的水果: {item}")print(f'{random.random() }') # 返回从区间[0.0, 1.0)随机抽取的浮点数# 随机打乱列表
list_to_shuffle = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
random.shuffle(list_to_shuffle)
print(f"打乱后的列表: {list_to_shuffle}")# 设置随机数生成器的种子 , 设置随机种子后,是每次运行 文件的输出结果都一样
print(f'{random.seed(0)}')
print(f'{random.random() * 1000}')
print(f'{random.random() * 1000}')

8. collections 模块
collections模块提供了额外的容器类型,如namedtuple、deque、Counter、OrderedDict等。
示例代码:
from collections import namedtuple, deque, Counter# 使用 namedtuple 创建一个命名元组
Point = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])
point = Point(1, 2)
print(f"命名元组: {point}")# 使用 deque 实现队列
queue = deque()
queue.append('right')
queue.appendleft('left')print(f"队列: {queue}")# 使用 Counter 进行计数
words = ['apple', 'orange', 'apple', 'pear', 'orange', 'banana']
word_counts = Counter(words)
print(f"单词计数: {word_counts}")

9. itertools 模块
itertools模块提供了构建迭代器的工具,用于创建复杂的迭代操作。
示例代码:
from itertools import product, permutations, combinations# 笛卡尔积
cartesian_product = list(product([1, 2], ['a', 'b']))
print(f"笛卡尔积: {cartesian_product}")# 排列
word_permutations = list(permutations('ABC'))
print(f"排列: {word_permutations}")# 组合
letter_combinations = list(combinations('ABCD', 2))
print(f"组合: {letter_combinations}")

10. threading 模块
threading模块用于实现多线程,允许并发执行。
示例代码:
from threading import Thread# 定义线程要执行的函数
def print_numbers():for i in range(5):print(f"线程打印: {i}")# 创建线程
thread = Thread(target=print_numbers)
thread.start() # 启动线程# 等待线程完成
#thread.join()
print("主线程继续执行")

11. 加密 模块
Python的
hashlib提供了常见的哈希算法,如MD5,SHA1等等。
HMAC(Hash-based Message Authentication Code)算法是一种基于哈希函数的消息认证码算法 , 相当于md5(message + salt)
示例代码:
import hashlib
import hmac
md5 = hashlib.md5()
md5.update('我的密码 123456?'.encode('utf-8'))
print('md5加密结果:',md5.hexdigest())sha = hashlib.sha1()
sha.update('789456'.encode('utf-8'))
print('sha加密结果:',sha.hexdigest())# hmacmsg = b'Hello, world!'
# message = b'Hello, world!'
key = b'123'
res = hmac.new(key, msg, hashlib.md5)
print('hmac加密结果:',res.hexdigest())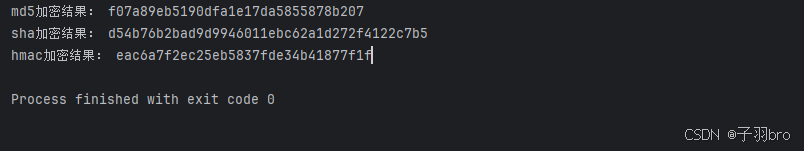
总结
这些示例提供了每个模块的多种用法。由于Python的动态特性,这些模块可以用于更复杂的场景和应用。在实际开发中,你可以根据需要选择适合的模块和方法。