1.背景
因为验证证书的需要,需要把证书文件和公钥给到客户,考虑到多个文件交互的不便性,所以决定将2个文件合并成一个文件交互给客户。刚开始采用字符串拼接2个文件内容,但是由于是加密文件,采用字符串形式合并后,拆分后文件不可用,最后采用基于二进制流拆分和合并文件,效果不错!
2.代码工程
实验目的
对文件进行二进制流合并和拆分
合并代码
ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(publicCertsContent.length).array() 的作用是将 publicCertsContent(公钥证书内容)的长度转换为 4 个字节的整数,并写入到字节缓冲区中。具体作用如下:
ByteBuffer.allocate(4): 创建一个大小为 4 字节的ByteBuffer,因为 Java 中的整数(int)是 4 个字节。putInt(publicCertsContent.length): 将publicCertsContent的字节数组长度(即证书文件的字节长度)存入ByteBuffer。这样就把证书内容的长度存储为一个 4 字节的整数。array(): 将ByteBuffer转换为字节数组。这个数组包含了公钥证书内容长度的 4 字节表示形式。
这个表达式的作用是将 publicCertsContent 数组的长度转换为二进制的 4 字节表示形式,并写入输出流(outputStream)中。这样在以后读取合并文件时,代码可以知道该读取多少字节属于 publicCertsContent。 有小伙伴这里可能有疑问,4字节够存多大数字呢? 4 个字节(即 32 位)在计算机中用于存储整数,能表示的整数范围如下:
- 有符号整数(
int类型):- 范围是:-2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647
- 其中 1 位用于符号(正负),31 位用于数值。
- 无符号整数(
unsigned int,Java 中没有直接支持,但可以通过转换处理):- 范围是:0 到 4,294,967,295
通常 Java 中的 int 类型是有符号的,因此 4 个字节可以存储的整数范围为 -2^31 到 2^31 - 1,即 -2,147,483,648 到 2,147,483,647。所以只要不超过这个限制都能存下来
package com.et;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;public class FileMerger {public static void main(String[] args) {String privateKeys = "D:/IdeaProjects/Java-demo/file/src/main/resources/privateKeys.keystore";String publicCerts = "D:/IdeaProjects/Java-demo/file/src/main/resources/publicCerts.keystore";merger(privateKeys,publicCerts);}public static String merger(String privateKeys, String publicCerts) {String directoryPath = FileUtils.extractDirectoryPath(privateKeys);String mergedFile =directoryPath+"merge.keystore";try {byte[] privateKeysContent = FileUtils.readBinaryFile(privateKeys);byte[] publicCertsContent = FileUtils.readBinaryFile(publicCerts);// create outputStreamByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();// write keystore length(4 byte)outputStream.write(ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(privateKeysContent.length).array());// write keystore contentoutputStream.write(privateKeysContent);// witer license content(4 byte int )outputStream.write(ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(publicCertsContent.length).array());// write license contentoutputStream.write(publicCertsContent);// write merge content to fileFileUtils.writeBinaryFile(mergedFile, outputStream.toByteArray());System.out.println("merge success " + mergedFile);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return mergedFile;}}拆分代码
拆分逻辑就很简单了,先读取4字节,获取文件大小,然后依次获取文件内容就可以了 buffer.getInt() 可以正确读取文件中的大小信息。具体来说,它会从 ByteBuffer 中读取 4 个字节,并将这些字节解释为一个整数。 如果你按照之前的代码将文件内容合并时,将文件大小以 4 字节整数形式写入到文件中,那么你可以使用 buffer.getInt() 来读取这个大小。例如,假设你在合并文件时使用了如下方式写入大小:
outputStream.write(ByteBuffer.allocate(4).putInt(content.length).array());
在读取合并文件时,你可以这样做:
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(fileContent); // 假设 fileContent 是读取的字节数组
int size = buffer.getInt(); // 读取前 4 个字节,获取文件大小这里的 buffer.getInt() 会正确读取到前 4 个字节,并将其转换为整数,这样你就得到了文件内容的大小。 请确保在读取文件时,字节顺序(字节序)与写入时一致,默认情况下是大端序(Big Endian)。如果你的应用需要小端序(Little Endian),你可以使用 buffer.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN) 来设置字节序。
package com.et;import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;public class FileSplitter {public static void main(String[] args) {String mergedFile = "D:/IdeaProjects/Java-demo/file/src/main/resources/merge.keystore";split(mergedFile);}private static void debugContent(byte[] content, String fileName) {System.out.printf("File: %s%n", fileName);System.out.printf("Length: %d%n", content.length);System.out.print("Content: ");for (byte b : content) {System.out.printf("%02X ", b);}System.out.println();}static String[] split(String mergedFile) {String directoryPath = FileUtils.extractDirectoryPath(mergedFile);String privateKeysFile = directoryPath + ".privateKeys.keystore";String publicCertsFile = directoryPath + ".publicCerts.keystore";String[] filePaths = new String[]{privateKeysFile, publicCertsFile};try {// read merge contentbyte[] mergedContent = FileUtils.readBinaryFile(mergedFile);// use ByteBuffer parseByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(mergedContent);// read privateKeys content lengthint privateKeysLength = buffer.getInt();// read privateKeys contentbyte[] privateKeysContent = new byte[privateKeysLength];buffer.get(privateKeysContent);// read publicCerts content lengthint publicCertsLength = buffer.getInt();// read publicCerts contentbyte[] publicCertsContent = new byte[publicCertsLength];buffer.get(publicCertsContent);// write privateKeys and publicCerts content to fileFileUtils.writeBinaryFile(privateKeysFile, privateKeysContent);FileUtils.writeBinaryFile(publicCertsFile, publicCertsContent);System.out.println("merge file split " + privateKeysFile + " and " + publicCertsFile);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return filePaths;}private static byte[] extractContent(byte[] mergedContent, byte[] beginMarker, byte[] endMarker) {int beginIndex = indexOf(mergedContent, beginMarker);int endIndex = indexOf(mergedContent, endMarker, beginIndex);if (beginIndex != -1 && endIndex != -1) {// Move past the start markerbeginIndex += beginMarker.length;// Adjust endIndex to exclude the end markerint adjustedEndIndex = endIndex;// Extract contentreturn Arrays.copyOfRange(mergedContent, beginIndex, adjustedEndIndex);} else {return new byte[0]; // Return empty array if markers are not found}}private static byte[] removeEmptyLines(byte[] content) {// Convert byte array to list of linesList<byte[]> lines = splitIntoLines(content);// Filter out empty lineslines = lines.stream().filter(line -> line.length > 0).collect(Collectors.toList());// Reassemble contentreturn mergeLines(lines);}private static List<byte[]> splitIntoLines(byte[] content) {List<byte[]> lines = new ArrayList<>();int start = 0;for (int i = 0; i < content.length; i++) {if (content[i] == '\n') { // Line breaklines.add(Arrays.copyOfRange(content, start, i));start = i + 1;}}if (start < content.length) {lines.add(Arrays.copyOfRange(content, start, content.length));}return lines;}private static byte[] mergeLines(List<byte[]> lines) {ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();for (byte[] line : lines) {try {outputStream.write(line);outputStream.write('\n'); // Re-add line break} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}return outputStream.toByteArray();}private static int indexOf(byte[] array, byte[] target) {return indexOf(array, target, 0);}private static int indexOf(byte[] array, byte[] target, int start) {for (int i = start; i <= array.length - target.length; i++) {if (Arrays.equals(Arrays.copyOfRange(array, i, i + target.length), target)) {return i;}}return -1; // Return -1 if target not found}}工具类
package com.et;import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;public class FileUtils {static byte[] readBinaryFile(String filePath) throws IOException {File file = new File(filePath);try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file)) {byte[] fileBytes = new byte[(int) file.length()];fis.read(fileBytes);return fileBytes;}}public static String extractDirectoryPath(String filePath) {File file = new File(filePath);return file.getParent()+File.separator; // 获取文件所在的目录}static void writeBinaryFile(String filePath, byte[] content) throws IOException {try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(filePath)) {fos.write(content);}}
}以上只是一些关键代码,所有代码请参见下面代码仓库
代码仓库
- https://github.com/Harries/Java-demo(file)
3.测试
测试类
package com.et;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("Hello world!");String privateKeys = "D:/IdeaProjects/Java-demo/file/src/main/resources/privateKeys.keystore";String publicCerts = "D:/IdeaProjects/Java-demo/file/src/main/resources/publicCerts.keystore";FileMerger.merger(privateKeys,publicCerts);String mergedFile = "D:/IdeaProjects/Java-demo/file/src/main/resources/merge.keystore";FileSplitter.split(mergedFile);}
}运行main方法,日志显示如下
merge success D:\IdeaProjects\Java-demo\file\src\main\resources\merge.keystore
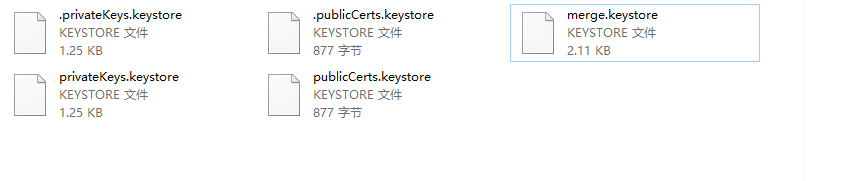
merge file split D:\IdeaProjects\Java-demo\file\src\main\resources\.privateKeys.keystore and D:\IdeaProjects\Java-demo\file\src\main\resources\.publicCerts.keystore拆分后文件于原文件大小一模一样
4.引用
- java使用ByteBuffer记录文件大小并进行多文件合并和拆分 | Harries Blog™