一、动态 sql 是什么?
1、动态 SQL 是 MyBatis 的强大特性之一。在 JDBC 或其它类似的框架中,开发人员通常需要手动拼接 SQL 语句。根据不同的条件拼接 SQL 语句是一件极其痛苦的工作。
例如,拼接时要确保添加了必要的空格,还要注意去掉列表最后一个列名的逗号。而动态 SQL 恰好解决了这一问题,可以根据场景动态的构建查询。
2.动态SQL:code that is executed dynamically。
它一般是根据用户输入或外部条件动态组合的SQL语句块。
动态SQL能灵活的发挥SQL强大的功能、方便的解决一些其它方法难以解决的问题。 然而动态SQL有时候在执行性能 (效率)上面不如静态SQL,而且使用不恰当,往往会在安全方面存在隐患 (SQL 注入式攻击)。
二、Mybatis 动态 sql 是做什么的?
Mybatis 动态 sql 可以让我们在 Xml 映射文件内,以标签的形式编写动态 sql,完成逻辑判断和动态拼接 sql 的功能。
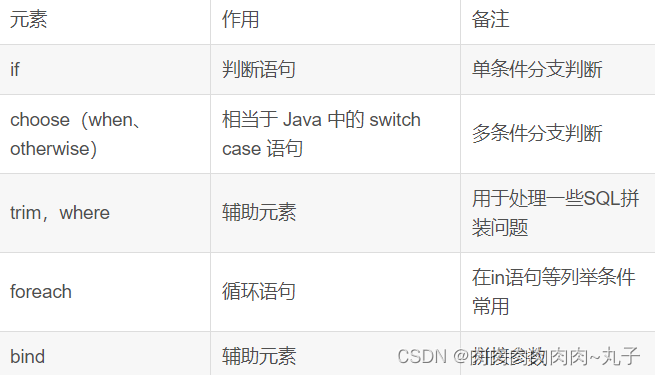
三、Mybatis 的 9 种 动 态 sql 标 签有哪些?
四、动态 sql 的执行原理?
使用 OGNL 从 sql 参数对象中计算表达式的值,根据表达式的值动态拼接 sql,以此来完成动态 sql 的功能。
五、MyBatis标签详解
1、if标签
MyBatis if 类似于 Java 中的 if 语句,是 MyBatis 中最常用的判断语句。
使用 if 标签可以节省许多拼接 SQL 的工作,把精力集中在 XML 的维护上。
1)不使用动态sql
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex"resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User"><!-- 这里和普通的sql 查询语句差不多,对于只有一个参数,后面的 #{id}表示占位符,里面 不一定要写id,写啥都可以,但是不要空着,如果有多个参数则必须写pojo类里面的属性 -->select * from user where username=#{username} and sex=#{sex}
</select>if 语句使用方法简单,常常与 test 属性联合使用。语法如下:
<if test="判断条件"> SQL语句</if>2)使用动态sql
上面的查询语句,我们可以发现,如果 #{username} 为空,那么查询结果也是空,应该使用 if 来判断,可多个 if 语句同时使用。
以下语句表示为可以按照网站名称(name)或者网址(url)进行模糊查询。如果您不输入名称或网址,则返回所有的网站记录。但是,如果你传递了任意一个参数,它就会返回与给定参数相匹配的记录。
<select id="selectAllWebsite" resultMap="myResult"> select id,name,url from website where 1=1 <if test="name != null"> AND name like #{name} </if> <if test="url!= null"> AND url like #{url} </if></select>2、where+if标签
where、if同时使用可以进行查询、模糊查询
注意:`<if>`失败后, `<where>` 关键字只会去掉库表字段赋值前面的and,不会去掉语句后面的and关键字
`<where>` 只会去掉`<if>` 语句中的最开始的and关键字。所以下面的形式是不可取的:
<select id="findQuery" resultType="Student"><include refid="selectvp"/><where><if test="sacc != null">sacc like concat('%' #{sacc} '%')</if><if test="sname != null">AND sname like concat('%' #{sname} '%')</if><if test="sex != null">AND sex=#{sex}</if><if test="phone != null">AND phone=#{phone}</if></where></select>这个“where”标签会知道如果它包含的标签中有返回值的话,它就插入一个‘where’。此外,如果标签返回的内容是以AND 或OR 开头的,则它会剔除掉。
3、set标签
set可以用来修改:
<update id="upd">update student<set><if test="sname != null">sname=#{sname},</if><if test="spwd != null">spwd=#{spwd},</if><if test="sex != null">sex=#{sex},</if><if test="phone != null">phone=#{phone}</if>sid=#{sid}</set>where sid=#{sid}</update>4、choose(when,otherwise) 语句
有时候,我们不想用到所有的查询条件,只想选择其中的一个,查询条件有一个满足即可
使用 choose 标签可以解决此类问题,类似于 Java 的 switch 语句
<select id="selectUserByChoose" resultType="com.ys.po.User" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">select * from user<where><choose><when test="id !='' and id != null">id=#{id}</when><when test="username !='' and username != null">and username=#{username}</when><otherwise>and sex=#{sex}</otherwise></choose></where></select>也就是说,这里我们有三个条件【id,username,sex】只能选择一个作为查询条件
如果 id 不为空,那么查询语句为:
select * from user where id=?如果 id 为空,那么看username 是否为空,如果不为空,那么语句为:
select * from user where username=?;如果 username 为空,那么查询语句为:
select * from user where sex=?5、trim标签
trim标记是一个格式化的标记,可以完成set或者是where标记的功能
① 用 trim 改写上面第二点的 if+where 语句
<select id="selectUserByUsernameAndSex" resultType="user" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">select * from user<!-- <where><if test="username != null">username=#{username}</if><if test="username != null">and sex=#{sex}</if></where> --><trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and | or"><if test="username != null">and username=#{username}</if><if test="sex != null">and sex=#{sex}</if></trim></select>prefix:前缀
prefixoverride:去掉第一个and或者是or
② 用 trim 改写上面第三点的 if+set 语句
<!-- 根据 id 更新 user 表的数据 --><update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.ys.po.User">update user u<!-- <set><if test="username != null and username != ''">u.username = #{username},</if><if test="sex != null and sex != ''">u.sex = #{sex}</if></set> --><trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=","><if test="username != null and username != ''">u.username = #{username},</if><if test="sex != null and sex != ''">u.sex = #{sex},</if></trim>where id=#{id}</update>suffix:后缀
suffixoverride:去掉最后一个逗号(也可以是其他的标记,就像是上面前缀中的and一样)
③ trim+if同时使用可以添加
<insert id="add">insert into student<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=","><if test="sname != null">sname,</if><if test="spwd != null">spwd,</if><if test="sex != null">sex,</if><if test="phone != null">phone,</if></trim>
<trim prefix="values (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=","><if test="sname != null">#{sname},</if><if test="spwd != null">#{spwd},</if><if test="sex != null">#{sex},</if><if test="phone != null">#{phone}</if></trim>
</insert>6、foreach标签
foreach是用来对集合的遍历,这个和Java中的功能很类似。通常处理SQL中的in语句。
foreach 元素的功能非常强大,它允许你指定一个集合,声明可以在元素体内使用的集合项(item)和索引(index)变量。
它也允许你指定开头与结尾的字符串以及集合项迭代之间的分隔符。这个元素也不会错误地添加多余的分隔符
你可以将任何可迭代对象(如 List、Set 等)、Map 对象或者数组对象作为集合参数传递给 foreach。
当使用可迭代对象或者数组时,index 是当前迭代的序号,item 的值是本次迭代获取到的元素;当使用 Map 对象(或者 Map.Entry 对象的集合)时,index 是键,item 是值。
//批量查询
<select id="findAll" resultType="Student" parameterType="Integer"><include refid="selectvp"/> WHERE sid in<foreach item="ids" collection="array" open="(" separator="," close=")">#{ids}</foreach>
</select>
//批量删除
<delete id="del" parameterType="Integer">delete from student where sid in<foreach item="ids" collection="array" open="(" separator="," close=")">#{ids}</foreach>
</delete>7、sql语句
在实际开发中会遇到许多相同的SQL,比如根据某个条件筛选,这个筛选很多地方都能用到,我们可以将其抽取出来成为一个公用的部分,这样修改也方便,一旦出现了错误,只需要改这一处便能处处生效了,此时就用到了<sql>这个标签了。
当多种类型的查询语句的查询字段或者查询条件相同时,可以将其定义为常量,方便调用。为求 <select> 结构清晰也可将 sql 语句分解。
<sql id="selectvp">select * from student
</sql>8、include标签
这个标签和<sql>是天仙配,是共生的,include用于引用sql标签定义的常量。比如引用上面sql标签定义的常量。
refid这个属性就是指定<sql>标签中的id值(唯一标识)
<select id="findbyid" resultType="student"><include refid="selectvp"/>WHERE 1=1<if test="sid != null">AND sid like #{sid}</if>
</select>-
9、bind标签
mybatis的动态SQL都是用OGNL表达式进行解析的,如果需要创建OGNL表达式以外的变量,可以用bind标签。
<select id="selectBlogsLike" resultType="Blog">
<bind name="pattern" value="'%' + _parameter.getTitle() + '%'" />
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE title LIKE #{pattern}
</select>