目录
- 0 专栏介绍
- 1 维诺图规划原理
- 2 ROS C++实现(栅格图搜索)
- 3 Python实现(路图搜索)
- 4 Matlab实现(路图搜索)
0 专栏介绍
🔥附C++/Python/Matlab全套代码🔥课程设计、毕业设计、创新竞赛必备!详细介绍全局规划(图搜索、采样法、智能算法等);局部规划(DWA、APF等);曲线优化(贝塞尔曲线、B样条曲线等)。
🚀详情:图解自动驾驶中的运动规划(Motion Planning),附几十种规划算法
1 维诺图规划原理
在地图结构 | 图解维诺图Voronoi原理(附C++/Python/Matlab仿真)中,我们介绍了维诺图的概念。维诺图(Voronoi Diagram),也称为泰森多边形(Thiessen Polygon),是一种用于将空间分割为一组区域的图形化方法,其中每个区域都由一个特定点(种子点)控制,使得每个点到其控制的种子点最近。
在路径规划领域,维诺图作为一种栅格图分解方法用于自主导航任务。与计算几何的概念类似,令离散点集为障碍栅格,则定义规划空间中离最近的两个障碍物具有相同距离的点集为广义维诺图(Generalized Voronoi Diagram, GVD)。GVD通过对空间划分有效减少了路径搜索维度,且沿着GVD边缘移动可确保在穿越障碍物时具有最大的安全间隙

建立维诺图后,搜索对象从全域栅格节点减少为维诺节点,搜索效率提高。基于维诺图的路径规划虽然不满足路径最优,但可以最大程度保证运动安全。总体来说,基于维诺图的路径规划分为两部分:
- 根据栅格地图建立维诺图
- 在维诺图上运用最短路算法
这里提供两种常见的算法流程:栅格图搜索与路图搜索,其中维诺图的构造算法详见地图结构 | 图解维诺图Voronoi原理(附C++/Python/Matlab仿真),本文不再赘述


接下来对这两种算法进行实现
2 ROS C++实现(栅格图搜索)
核心算法如下所示
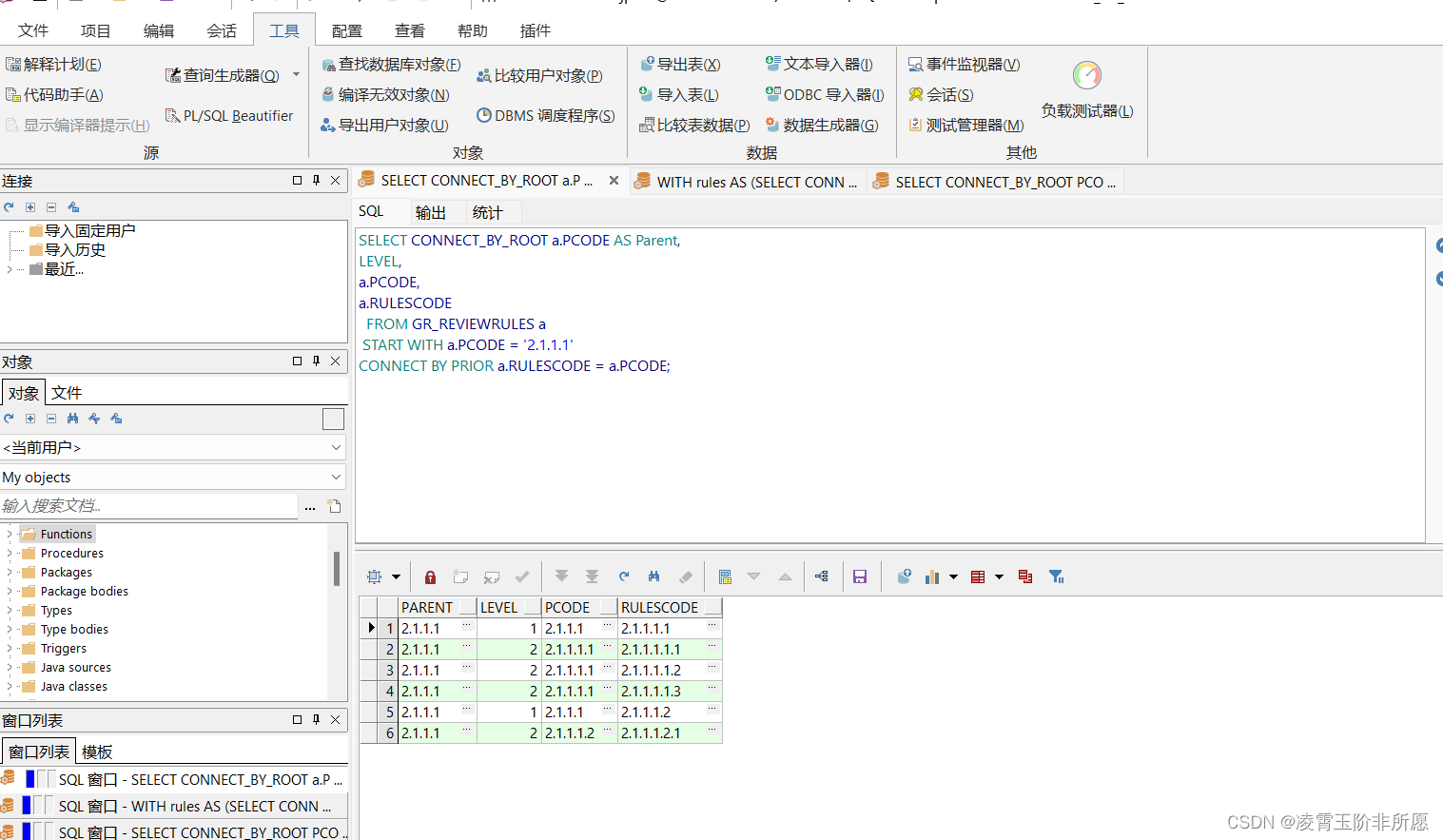
bool VoronoiPlanner::plan(VoronoiData** voronoi_diagram, const Node& start, const Node& goal, std::vector<Node>& path)
{voronoi_diagram_ = voronoi_diagram;// clear vectorpath.clear();// start/goal to Voronoi Diagram, shortest path in Voronoi Diagramstd::vector<Node> path_s, path_g, path_v;// start/goal point in Voronoi DiagramNode v_start, v_goal;if (!searchPathWithVoronoi(start, goal, path_s, &v_start))return false;if (!searchPathWithVoronoi(goal, start, path_g, &v_goal))return false;std::reverse(path_g.begin(), path_g.end());if (!searchPathWithVoronoi(v_start, v_goal, path_v))return false;path_g.insert(path_g.end(), path_v.begin(), path_v.end());path_g.insert(path_g.end(), path_s.begin(), path_s.end());path = path_g;return true;
}
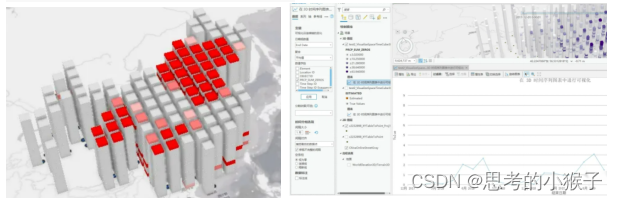
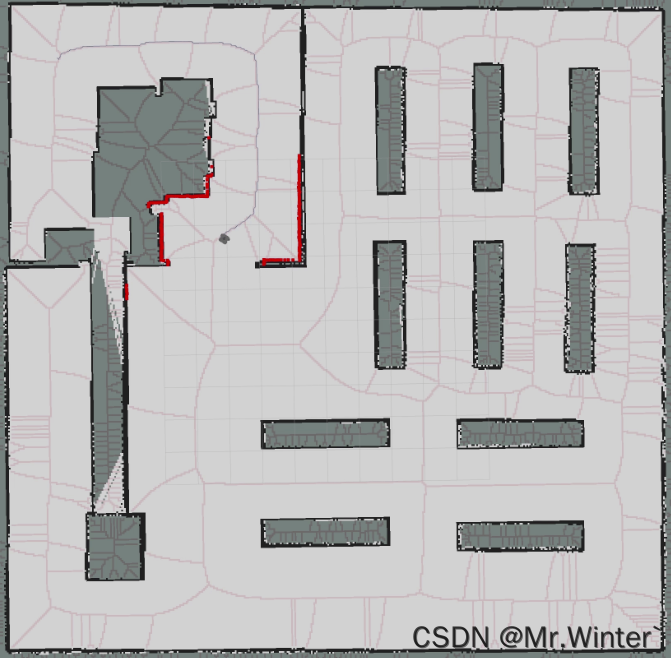
效果如下
3 Python实现(路图搜索)
核心代码如下:
def plan(self):# sampling voronoi diagramvor = Voronoi(np.array(list(self.env.obstacles)))vx_list = [ix for [ix, _] in vor.vertices] + [self.start.x, self.goal.x]vy_list = [iy for [_, iy] in vor.vertices] + [self.start.y, self.goal.y]sample_num = len(vx_list)expand = [Node((vx_list[i], vy_list[i])) for i in range(sample_num)]# generate road map for voronoi nodesroad_map = {}node_tree = cKDTree(np.vstack((vx_list, vy_list)).T)for node in expand:edges = []_, index_list = node_tree.query([node.x, node.y], k=sample_num)for i in range(1, len(index_list)):node_n = expand[index_list[i]]if not self.isCollision(node, node_n):edges.append(node_n)if len(edges) >= self.n_knn:breakroad_map[node] = edges# calculate shortest path using graph search algorithmcost, path = self.getShortestPath(road_map)return cost, path, expand
效果如下:
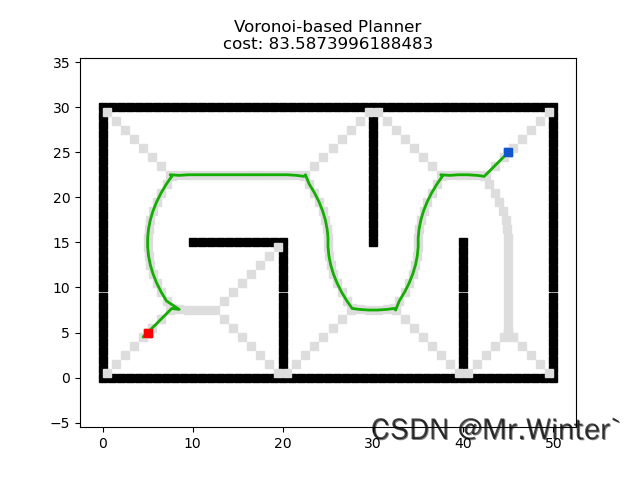
4 Matlab实现(路图搜索)
function [path, goal_reached, cost, EXPAND] = voronoi_plan(map, start, goal)% Maximum expansion distance one stepmax_dist = 3;% map size[y_range, x_range] = size(map);% resolutionresolution = 0.1;% number of edges from one sampled pointn_knn = 5;% construct Voronoi diagram[ox, oy] = find(map == 2);[vx, vy] = voronoi(oy, ox);start(:, [1 2]) = start(:, [2 1]);goal(:, [1 2]) = goal(:, [2 1]);% Voronoi diagram filterindex_x = intersect(find(vx(1, :) > 0 & vx(1, :) < x_range), ...find(vx(2, :) > 0 & vx(2, :) < x_range));index_y = intersect(find(vy(1, :) > 0 & vy(1, :) < y_range), ...find(vy(2, :) > 0 & vy(2, :) < y_range));index = intersect(index_x, index_y);vx = vx(:, index); vy = vy(:, index);vd_vertex = [];EXPAND = [];for i = 1:length(index)node1 = [vx(1, i), vy(1, i)];node2 = [vx(2, i), vy(2, i)]; if ~all(node1 == node2) && ~is_collision(node1, node2, map, -1, resolution)EXPAND = [EXPAND, [vx(:, i); vy(:, i)]];vd_vertex = [vd_vertex; [vx(:, i), vy(:, i)]];endendvd_vertex = [unique(vd_vertex, 'rows'); start; goal];% generate road map for voronoi nodesroad_map = containers.Map();num_vd = size(vd_vertex, 1);for i = 1:num_vdknn_nodes = vd_vertex(knnsearch(vd_vertex, vd_vertex(i, :), 'K', num_vd), :);edges = [];for j = 1:num_vdif ~is_collision(vd_vertex(i, :), knn_nodes(j, :), map, max_dist, resolution)edges = [edges; knn_nodes(j, :)];endif size(edges, 1) == n_knnbreak;endend% hash-map: from grid index to edgesroad_map(string(vd_vertex(i, 1) + x_range * vd_vertex(i, 2))) = edges;end[path, goal_reached, cost] = get_shortest_path(road_map, start, goal, map, max_dist, resolution);if goal_reachedpath(:, [1 2]) = path(:, [2 1]);elsepath = [];cost = 0;end
end
效果如下:

完整工程代码请联系下方博主名片获取
🔥 更多精彩专栏:
- 《ROS从入门到精通》
- 《Pytorch深度学习实战》
- 《机器学习强基计划》
- 《运动规划实战精讲》
- …