一、前言
不同于之前的term。terms等结构化查询,全文搜索首先对查询词进行分析,然后根据查询词的分词结果构建查询。这里所说的全文指的是文本类型数据(text类型),默认的数据形式是人类的自然语言,如对话内容、图书名称、商品介绍和酒店名称等。结构化搜索关注的是数据是否匹配,全文搜索关注的是匹配程度;结构化搜索一般用于精确匹配,而全文搜索用于部分匹配。本章将详细介绍使用最多的全文搜索。
二、match查询
match查询是全文搜索的主要代表。对于最基本的match搜索来说,只要分词中的一个或者多个在文档中存在即可。例如搜索“京盛酒店”,查询词先被分词器切分为“京”“盛”“酒”“店”,因此,只要文档中包含这4个字中的任何一个字,都会被搜索到。
您可能会有疑问,为什么“京盛酒店被切分为4个字而不是“京盛”“酒店”两个词呢?这是因为在默认情况下,match查询使用的是标准分词器。该分词器比较适用于英文,如果是中文则按照字进行切分,因此默认的分词器不适合做中文搜索,在后面的章节中将介绍如何安装和使用中文分词器。
以下DSL示例为按照标题搜索“京盛酒店”:
POST /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match": { //匹配title字段为"金都酒店"的文档"title": "京盛酒店"}}
}
或者按照如下形式搜索:
POST /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match": {"title": {"query": "京盛酒店"}}}
}
搜索结果如下:
{..."hits" : {"total" : {"value" : 3,"relation" : "eq"},"max_score" : 1.3428942,"hits" : [{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "002","_score" : 1.3428942,"_source" : {"title" : "京盛酒店","city" : "北京","price" : "337.00","create_time" : "2020-07-29 13:00:00","amenities" : "充电停车场/可升降停车场","full_room" : false,"location" : {"lat" : 39.911543,"lon" : 116.403},"praise" : 60}},{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "30","_score" : 1.2387041,"_source" : {"title" : "京盛酒小店","city" : "上海","price" : "300.00","create_time" : "2022-01-29 22:52:00","amenities" : "露天游泳池,普通/充电停车场","full_room" : false,"praise" : 2000}},{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "27","_score" : 0.5495611,"_source" : {"title" : "盛况精选酒店","city" : "南昌","price" : "900.00","create_time" : "2022-07-29 22:50:00","amenities" : "露天游泳池,普通/充电停车场","full_room" : false,"location" : {"lat" : 56.918229,"lon" : 126.422011},"praise" : 200}}]}
}
从结果中可以看到,匹配度最高的文档是002,该酒店的名称和查询词相同,得分为1.3428942;次之的文档是30,因为该酒店名称中包含“京”“盛”“酒”“店”。但是想比前一个文档多了一个“小”字,所以部分匹配。再次之的文档是27,它只有“盛”“酒”“店”三个字和查询词部分匹配,因此排在最后。
假设用户搜索名称中同时包含“京”和“盛”的酒店,显然之前最后一个文档27就不是用户想要命中的文档。那么在ES中,match搜索可以设置operator参数,该参数决定文档按照分词后的词集合进行“与”还是“或”匹配。在默认情况下,该参数的值为“或”关系,即operator的值为or,这也解释了搜索结果中包含部分匹配的文档。如果希望各个词之间的匹配结果是“与”关系,则可以设置operator参数的值为and。
下面的请求示例设置查询词之间的匹配结果为“与”关系:
POST /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match": {"title": {"query": "京盛酒店","operator": "and"}}}
}
搜索结果如下:
{..."hits" : {"total" : {"value" : 2,"relation" : "eq"},"max_score" : 1.3428942,"hits" : [{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "002","_score" : 1.3428942,"_source" : {"title" : "京盛酒店","city" : "北京","price" : "337.00","create_time" : "2020-07-29 13:00:00","amenities" : "充电停车场/可升降停车场","full_room" : false,"location" : {"lat" : 39.911543,"lon" : 116.403},"praise" : 60}},{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "30","_score" : 1.2387041,"_source" : {"title" : "京盛酒小店","city" : "上海","price" : "300.00","create_time" : "2022-01-29 22:52:00","amenities" : "露天游泳池,普通/充电停车场","full_room" : false,"praise" : 2000}}]}
}
有时搜索多个关键字,关键词和文档在某一个比例上匹配即可,如果使用“与”操作过于严苛,如果使用“或”操作又过于宽松。这时可以采用minimum_should_match参数,该参数叫作最小匹配参数,其值为一个数值,意义为可以匹配上的词的个数.在一般情况下将其设置为一个百分数,因为在真实场景中并不能精确控制具体的匹配数量。以下示例设置最小匹配为80%的文档:
POST /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match": {"title": {"query": "京盛酒店","operator": "or","minimum_should_match": "80%" //设置最小匹配度为80%}}}
}
这样的话就需要满足最后命中的文档字数占查询条件中“京盛酒店”的80%(向下取整),例如这里4*80%,其实查询结果只需要有条件中任意三个字符即可。
在Java客户端上可以使用QueryBuilders.matchQuery()方法构建match请求,分别给该方法传入字段名称和查询值即可进行match查询。以下代码展示了match请求的使用逻辑:
service层:
public List<Hotel> matchQuery(HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) throws IOException {//新建搜索请求String indexName = getNotNullIndexName(hotelDocRequest);SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName);SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();//查询title且查询值之间关系是or,并且最小匹配参数为80%MatchQueryBuilder matchQueryBuilder = new MatchQueryBuilder("title", hotelDocRequest.getTitle()).operator(Operator.OR).minimumShouldMatch("80%");searchSourceBuilder.query(matchQueryBuilder);searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);return getQueryResult(searchRequest);}
controller层:
@PostMapping("/query/match")public FoundationResponse<List<Hotel>> matchQuery(@RequestBody HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) {try {List<Hotel> hotelList = esQueryService.matchQuery(hotelDocRequest);if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(hotelList)) {return FoundationResponse.success(hotelList);} else {return FoundationResponse.error(100,"no data");}} catch (IOException e) {log.warn("搜索发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());} catch (Exception e) {log.error("服务发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());}}
postman调用截图:
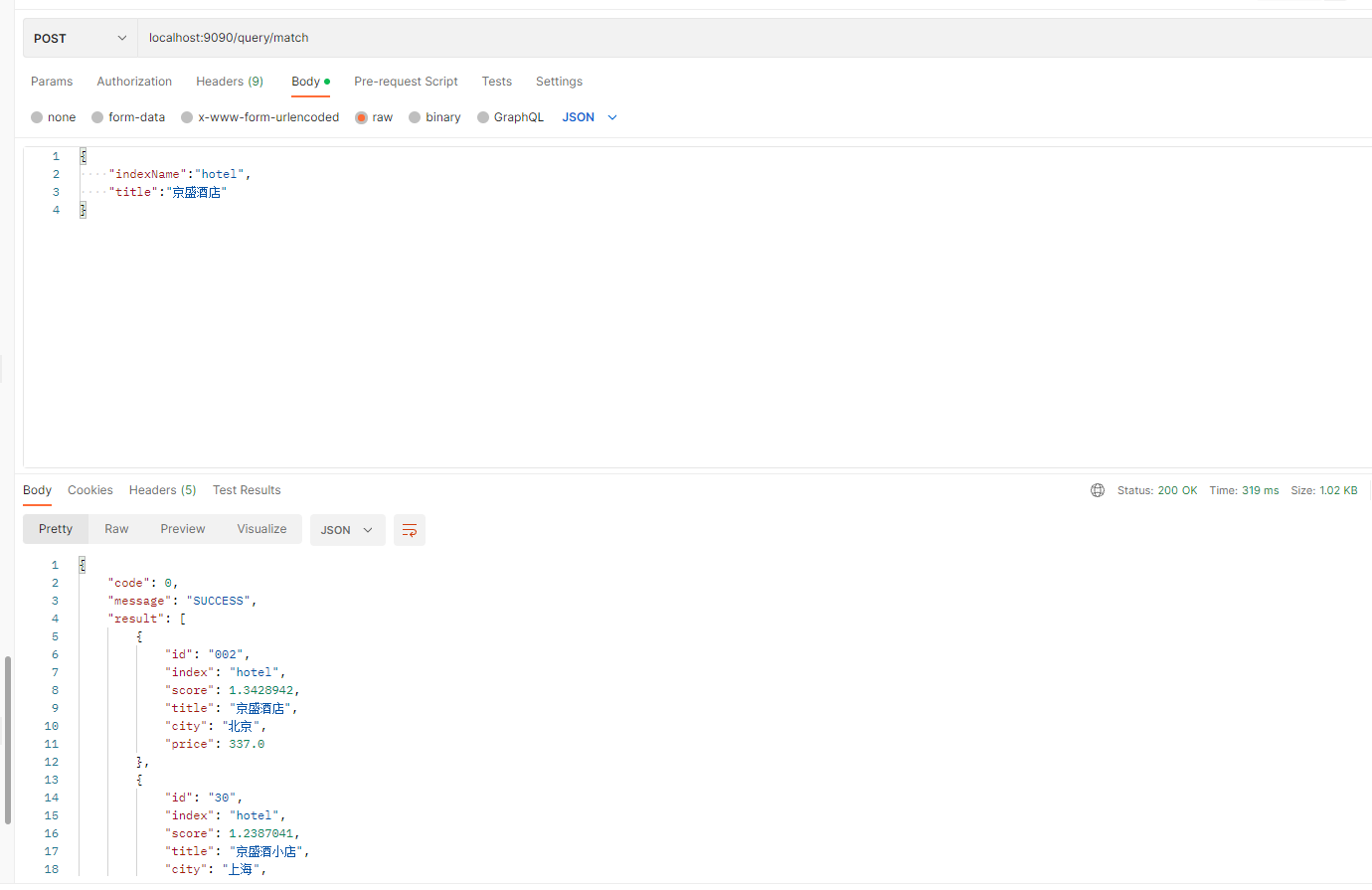
三、multi_match查询
有时用户需要在多个字段中查询关键词,除了使用布尔查询封装多个match查询之外,可替代的方案是使用multi_match。可以在multi_match的query子句中组织数据匹配规则,并在fields子句中指定需要搜索的字段列表。
下面的示例在title和amenities两个字段中同时搜索“假日”关键词:
POST /hotel/_search
{"query": {"multi_match": {"query": "假日","fields": ["amenities","title"]}}
}
搜索结果如下:
{"took" : 14,"timed_out" : false,"_shards" : {"total" : 1,"successful" : 1,"skipped" : 0,"failed" : 0},"hits" : {"total" : {"value" : 4,"relation" : "eq"},"max_score" : 4.2939954,"hits" : [{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "28","_score" : 4.2939954,"_source" : {"title" : "京盛假日酒店","city" : "上海","price" : "600.00","create_time" : "2021-04-29 22:52:00","amenities" : "露天游泳池,普通/充电停车场","full_room" : false,"praise" : 200}},{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "003","_score" : 1.9696801,"_source" : {"title" : "文雅文化酒店","city" : "天津","price" : "260.00","create_time" : "2021-02-27 22:00:00","amenities" : "提供假日party,免费早餐,浴池,充电停车场","full_room" : true,"location" : {"lat" : 39.186555,"lon" : 117.162767},"praise" : 30}},{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "29","_score" : 1.9163029,"_source" : {"title" : "京盛欣欣酒店","city" : "上海","price" : "700.00","create_time" : "2022-01-29 22:52:00","amenities" : "提供假日party,露天游泳池,普通/充电停车场","full_room" : false,"praise" : 200}},{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "004","_score" : 1.6876338,"_source" : {"title" : "京盛集团酒店","city" : "上海","price" : "800.00","create_time" : "2021-05-29 21:35:00","amenities" : "浴池(假日需预订),室内游泳池,普通停车场/充电停车场","full_room" : true,"location" : {"lat" : 36.940243,"lon" : 120.394},"praise" : 100}}]}
}
根据结果可以看到,命中的文档要么在title中包含“假日”关键词,要么在amenities字段中包含“假日”关键词。
且之前在Match搜索讲到的operator,minimum_should_match等参数在multi_match搜索中同样适用。
在Java客户端上可以使用QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery()方法或者直接new MultiMatchQueryBuilder()构建multi_match请求
可以看到,我们构造MultiMatchQueryBuilder,除了查询值,字段它接收的是一个可变长String数组:
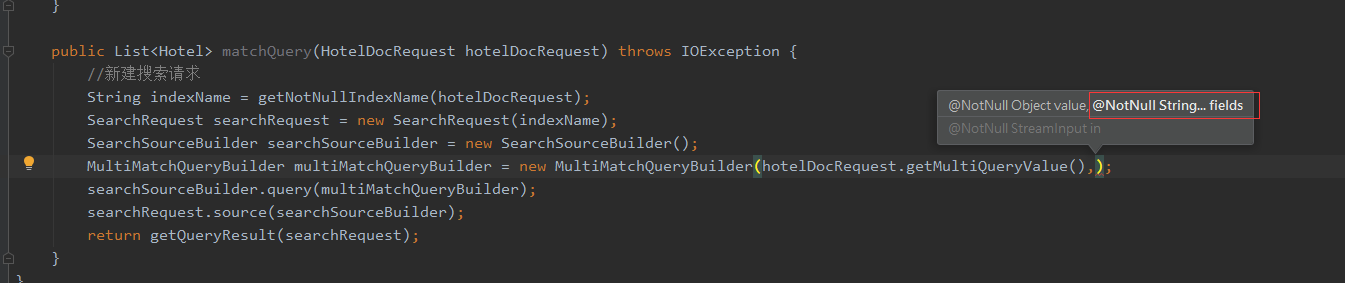
所以我们可以在传参hotelDocRequest加两个参数,一个是multiQueryValue代表要查询的值,另一个是multiQueryPropertyNames代表想要在哪些字段查询
分别给该方法传入查询值和多个字段名称即可进行multi_match查询。以下代码展示了multi_match请求的使用逻辑:
Service层
由于上面讲到构造MultiMatchQueryBuilder接收的是可变长String数组,所以我们要对传参的List通过list.stream().toArray(String[]::new);转化为String可变长数组(String…等价于String[])。
public List<Hotel> multiMatchQuery(HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) throws IOException {//新建搜索请求String indexName = getNotNullIndexName(hotelDocRequest);SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName);SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();MultiMatchQueryBuilder multiMatchQueryBuilder = new MultiMatchQueryBuilder(hotelDocRequest.getMultiQueryValue(), hotelDocRequest.getMultiQueryPropertyNames().toArray(new String[0]));searchSourceBuilder.query(multiMatchQueryBuilder);searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);return getQueryResult(searchRequest);}
controller层:
@PostMapping("/query/multiMatch")public FoundationResponse<List<Hotel>> multiMatchQuery(@RequestBody HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) {try {List<Hotel> hotelList = esQueryService.multiMatchQuery(hotelDocRequest);if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(hotelList)) {return FoundationResponse.success(hotelList);} else {return FoundationResponse.error(100,"no data");}} catch (IOException e) {log.warn("搜索发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());} catch (Exception e) {log.error("服务发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());}}
postman运行截图:
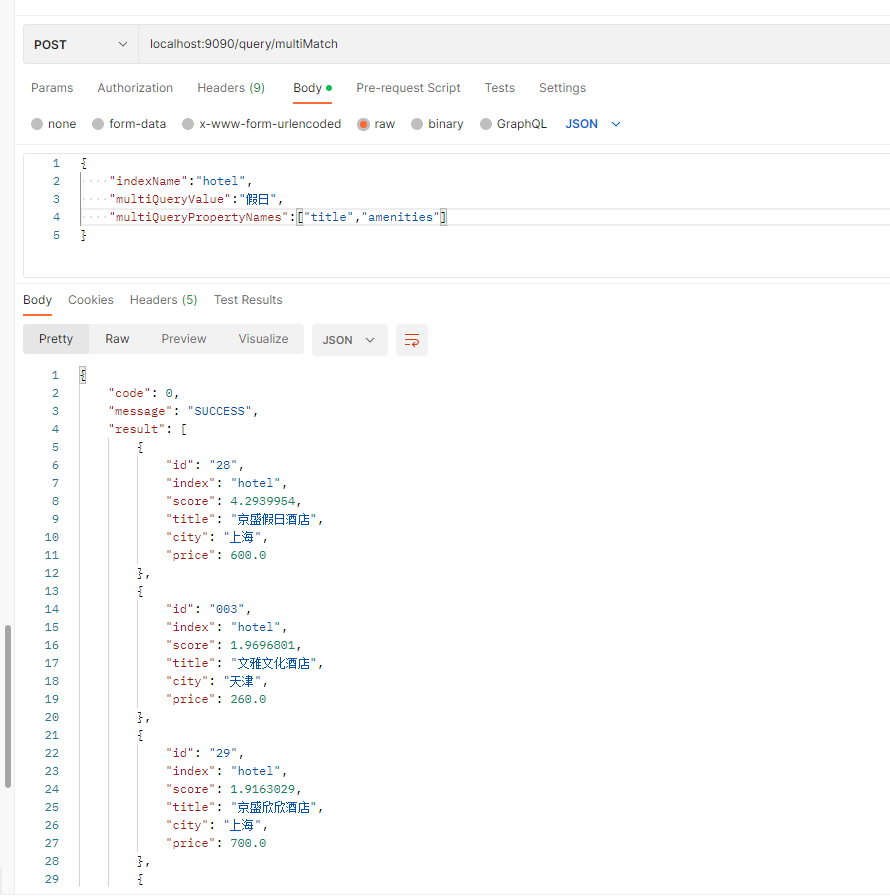
四、match_phrase查询
match_phrase用于匹配短语,与match查询不同的是,match_phrase用于搜索确切的短语或临近的词语。假设在酒店标题中搜索“京盛酒店”,希望酒店标题中的“京盛酒店”四字完全按照搜索词的顺序并且紧邻,此时就需要使用match_phrase查询:
POST /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match_phrase": {"title": {"query": "京盛酒店"}}}
}
结果如下:
{..."hits" : {"total" : {"value" : 1,"relation" : "eq"},"max_score" : 1.3428942,"hits" : [{"_index" : "hotel","_type" : "_doc","_id" : "002","_score" : 1.3428942,"_source" : {"title" : "京盛酒店","city" : "北京","price" : "337.00","create_time" : "2020-07-29 13:00:00","amenities" : "充电停车场/可升降停车场","full_room" : false,"location" : {"lat" : 39.911543,"lon" : 116.403},"praise" : 60}}]}
}
根据上述结果可知,使用match_phrase查询后,只有文档002命中,而类似之前的“京盛集团酒店”等类似文档没有被命中,这是为什么呢?
我们知道,在默认标准分词器的情况下,文档002的title字段被切分为“京”“盛”“酒”“店”,其中这些分词后的文档下标“京”代表0,盛”代表1,“酒”代表2,“店”代表3,而对于match_phrase查询,在不去设置下标移动步长的情况下这些分词文档想要移动到理想位置(查询词的位置,这里就是京盛酒店)的步数默认就是0,而可以发现,我们命中的文档002“京盛酒店”,这个文档下标其实就已经是理想位置了,不需要额外移动,相当于步长就是0,所以能够命中。而对于“京盛集团酒店”,分词后“盛”想要移动到“酒”这个下标,需要移动2次,所以步长是2,不符合默认的步长,所以无法命中。
那么如果需要“京盛集团酒店”也能够被命中,则可以设置match_phrase查询的slop参数,它用来调节匹配词之间的距离阈值,即上面说的步长,下面的DSL将slop设置为2
POST /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match_phrase": {"title": {"query": "京盛酒店","slop":2}}}
}
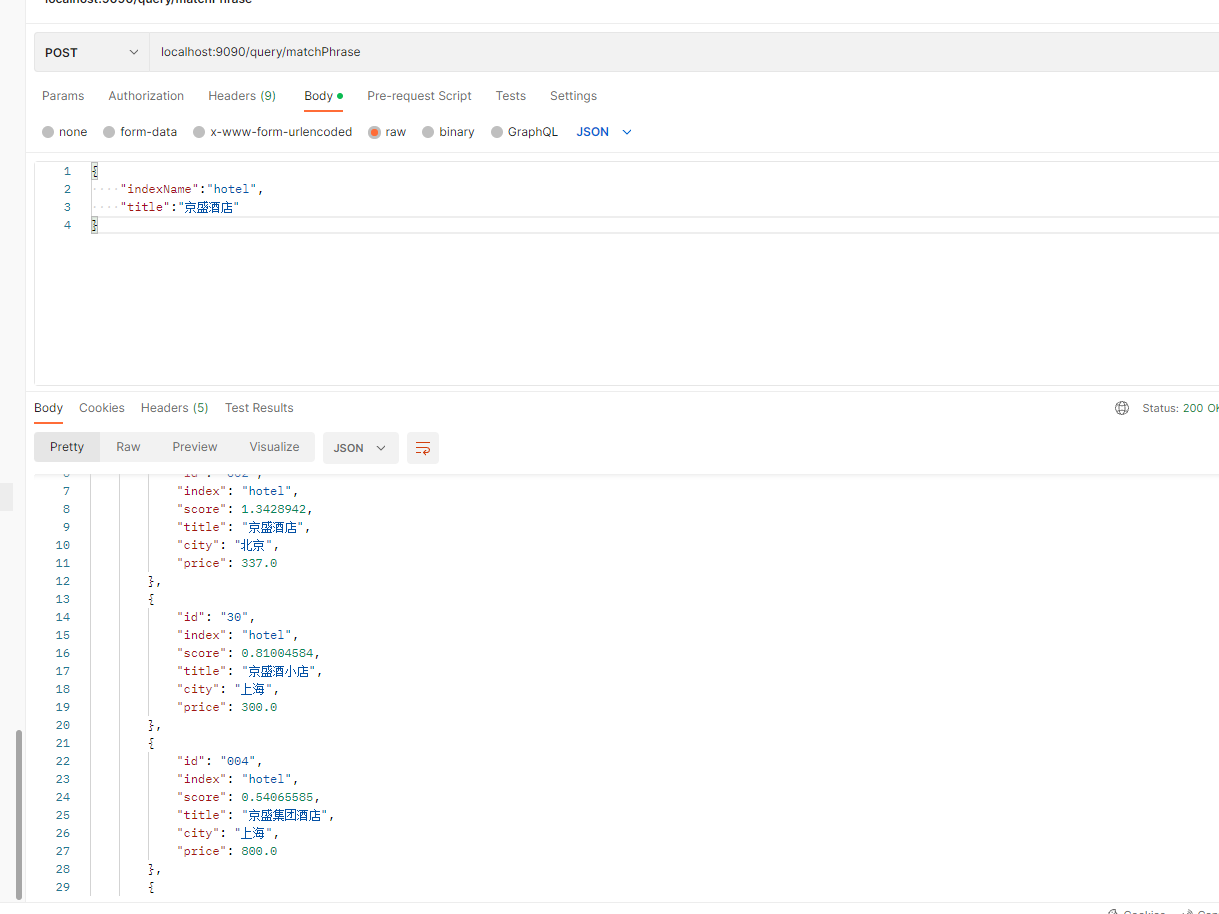
可以看到这样就能命中“京盛集团酒店”了
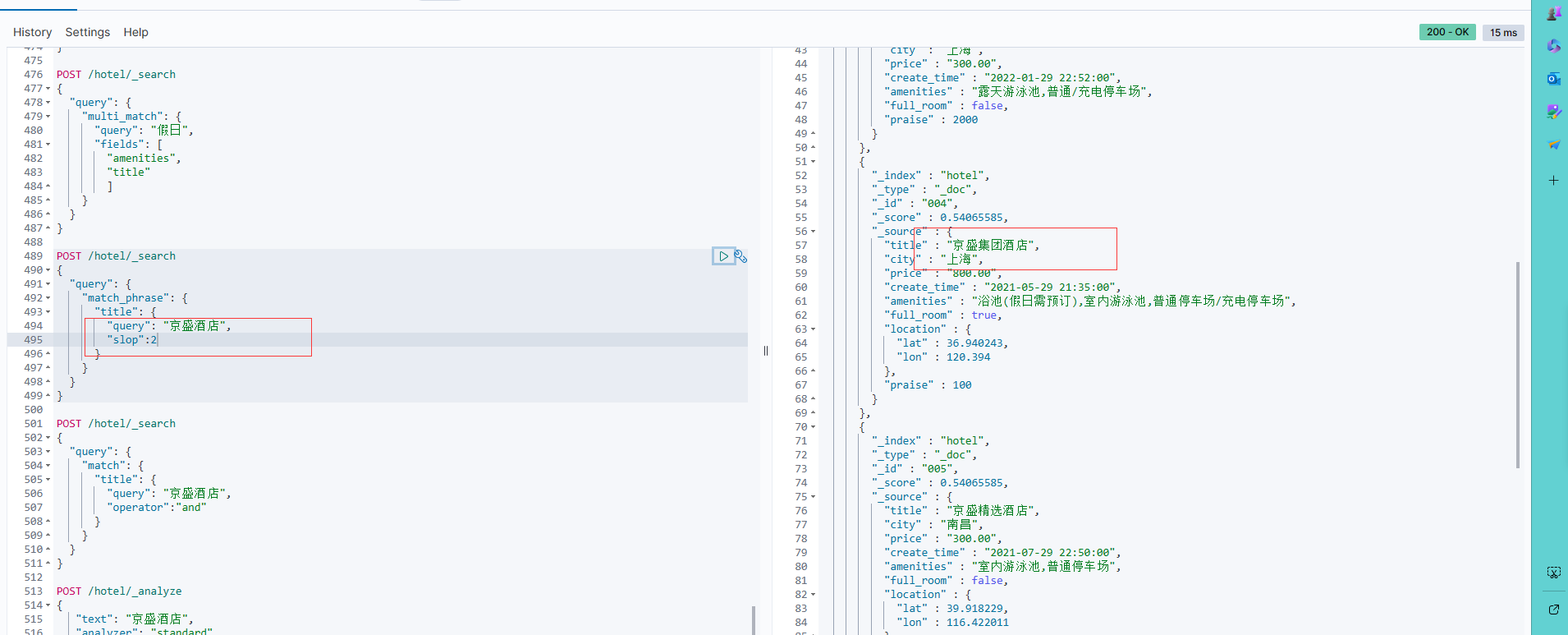
在Java客户端上可以使用QueryBuilders.matchPhraseQuery()方法构建match_phrase请求,分别给该方法传入查询字段和值即可运行multi_match查询。这一点和match搜索很像。以下代码展示了match_phrase请求的使用逻辑:
Service层:
public List<Hotel> matchPhraseQuery(HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) throws IOException {//新建搜索请求String indexName = getNotNullIndexName(hotelDocRequest);SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(indexName);SearchSourceBuilder searchSourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();//构造MatchPhraseQueryBuilder且设置步长为2MatchPhraseQueryBuilder matchPhraseQueryBuilder = new MatchPhraseQueryBuilder("title", hotelDocRequest.getTitle()).slop(2);searchSourceBuilder.query(matchPhraseQueryBuilder);searchRequest.source(searchSourceBuilder);return getQueryResult(searchRequest);}
Controller层:
@PostMapping("/query/matchPhrase")public FoundationResponse<List<Hotel>> matchPhraseQuery(@RequestBody HotelDocRequest hotelDocRequest) {try {List<Hotel> hotelList = esQueryService.matchPhraseQuery(hotelDocRequest);if (CollUtil.isNotEmpty(hotelList)) {return FoundationResponse.success(hotelList);} else {return FoundationResponse.error(100,"no data");}} catch (IOException e) {log.warn("搜索发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());} catch (Exception e) {log.error("服务发生异常,原因为:{}", e.getMessage());return FoundationResponse.error(100, e.getMessage());}}
Postman运行截图:








![java八股文面试[多线程]——sleep wait join yield](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/7e288643040b63449dde9aa59802b8d6.webp?x-oss-process=image/format,png)
