目录
1.遍历算法
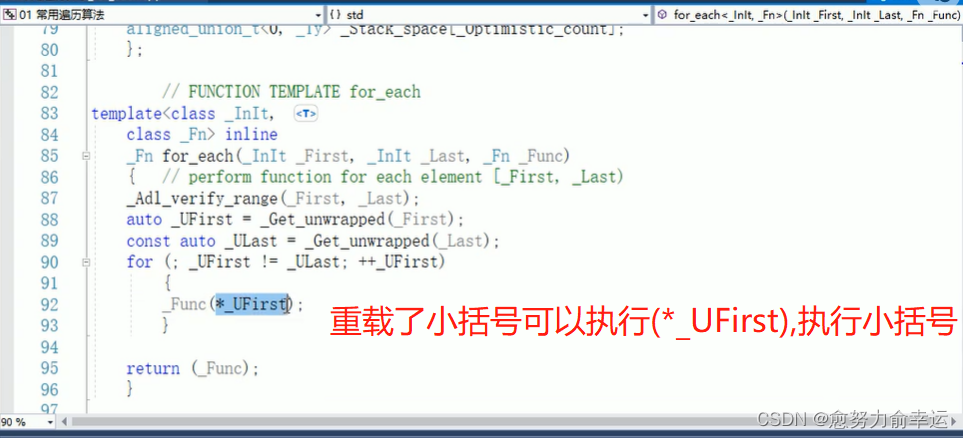
1.1for_earch
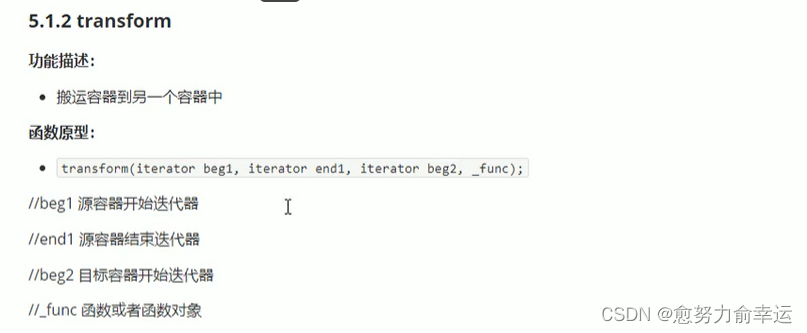
1.2transform
2.常用查找算法
2.1find,返回值是迭代器
2.1.1查找内置数据类型
2.1.2查找自定义数据类型
2.2fin_if 按条件查找元素
2.2.1查找内置的数据类型
2.2.2查找内置数据类型
2.3查找相邻元素adjeacent_find
2.4查找指定元素是否存在binarary_search
2.5统计元素的个数count
2.5.1统计内置数据类型
2.5.2统计自定义数据类型
2.6按条件统计元素个数
2.6.1统计内置数据类型
2.6.2统计自定义的数据类型
3.常用排序算法
3.1sort
1.遍历算法

1.1for_earch

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用遍历算法 for_each//利用普通函数实现
void print01(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}//仿函数(函数对象)本身是个类。不是一个函数
class print02
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print01);//第三个位置,普通函数是把函数名放过来cout << endl;for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print02());//第三个位置需要传入函数对象//类名加小括号,创建出匿名对象
}
int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}
1.2transform
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用遍历算法 transform//仿函数(函数对象)本身是个类。不是一个函数
class Transform
{
public://搬运过程中把每个元素取出来在返回回去,由于操作的是int型,所以返回intint operator()(int val){return val+100;//+100在搬到容器中}
};
class Myprint
{
public:void operator()(int val){cout << val << " ";}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}vector<int>vTarget;//目标容器vTarget.resize(v.size());//目标容器 需要提前开辟空间,不然报错transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(), Transform());//最后一个位置函数对象for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), Myprint());//最后一个位置函数对象cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.常用查找算法

2.1find,返回值是迭代器

2.1.1查找内置数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
//常用查找算法
//find//查找 内置数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//查找 容器中 是否有 5 这个元素vector<int>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 50);if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到!" << endl;}else{cout << "找到:" << *it << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.1.2查找自定义数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
//常用查找算法
//findclass Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}//重载== 让底层find知道如何对比person数据类型bool operator ==(const Person& p)//const防止修改p{if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
//查找 自定义数据类型
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);//放到容器中v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);Person p("bbb", 20);//查找是否有和p一样的vector<Person>::iterator it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), p);if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到元素:姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;}}
int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}2.2fin_if 按条件查找元素

2.2.1查找内置的数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
//常用查找算法
//find_if//1.查找内置数据类型
class GreaterFive
{
public://谓词返回boolbool operator()(int val)//find_if的底层也是取出每个元素并解引用,放到重载小括号里去操纵{return val > 5;//大于5 的时候就返回真}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//返回一个迭代器vector<int>::iterator it=find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());//第三个位置是匿名函数对象if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到大于5的元素" << endl;}else{cout << "找到大于5的数字为:" << *it << endl;}
}//2.查找自定义数据类型int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.2.2查找内置数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
//常用查找算法
//find_if//2.查找自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
class Great20
{
public:bool operator()(Person &p)//每个数据类型都是Perosn的数据类型用引用的方式传进来{return p.m_Age > 20;}
};
bool G2(Person& p)
{return p.m_Age > 20;
}
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;//创建数据Person p1("aaa", 10);Person p2("bbb", 20);Person p3("ccc", 30);Person p4("ddd", 40);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);//找年龄大于20的人vector<Person>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Great20());if (it == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到姓名:" << (*it).m_Name << "年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;}vector<Person>::iterator it1 = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Great20());if (it1 == v.end()){cout << "没有找到" << endl;}else{cout << "找到姓名:" << (*it1).m_Name << "年龄:" << it1->m_Age << endl;}
}
int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}2.3查找相邻元素adjeacent_find

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//adjacent_find
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(0);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(0);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(1);v.push_back(4);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(3);vector<int>::iterator it=adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());if (it == v.end()){cout << "未找到相邻重复元素" << endl;}else{cout << "找到相邻重复元素:" << *it << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.4查找指定元素是否存在binarary_search

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//binary_search 二分查找法,在无序的序列中不可以用
void test01()
{vector<int>v;for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){v.push_back(i);}//查找容器中是否有9//注意容器必须是有序的序列//如果无序结果未知bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 9);if (ret){cout << "找到了元素" << endl;}else{cout << "没找到" << endl;}
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.5统计元素的个数count

2.5.1统计内置数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//count//1.统计内置数据类型
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);int num=count(v.begin(), v.end(), 40);cout << "40的元素个数为:" <<num<< endl;int num1 = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 1);cout << "1的元素个数为:" << num1 << endl;//输出0
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.5.2统计自定义数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//count//2.统计自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}bool operator==(const Person& p)//底层要加const,{if (m_Age==p.m_Age){return true;}else{return false;}}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};
void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 30);Person p5("曹操", 40);//将人员插入到容器中v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);Person p("诸葛亮", 35);//统计与诸葛亮年龄相同的有几人int num = count(v.begin(), v.end(), p);cout << "和诸葛亮同岁数的人员个数为:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}2.6按条件统计元素个数

2.6.1统计内置数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//count_if//1.统计内置数据类型
class Greater20
{
public:bool operator()(int val){return val > 20;}
};
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);v.push_back(20);int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), Greater20());cout << "大于20的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}2.6.2统计自定义的数据类型
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用查找算法
//count_if//2.统计自定义的数据类型
class Person
{
public:Person(string name, int age){m_Name = name;this->m_Age = age;}string m_Name;int m_Age;
};class AgeGreater20
{
public:bool operator()(Person &p){return p.m_Age > 20;}
};void test02()
{vector<Person>v;Person p1("刘备", 35);Person p2("关羽", 35);Person p3("张飞", 35);Person p4("赵云", 40);Person p5("曹操", 20);v.push_back(p1);v.push_back(p2);v.push_back(p3);v.push_back(p4);v.push_back(p5);//统计 大于20岁人员个数int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), AgeGreater20());cout << "大于20的元素个数为:" << num << endl;
}int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}3.常用排序算法

3.1sort

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
//常用排序算法
//sort
void myPrint(int val)
{cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{vector<int>v;v.push_back(10);v.push_back(30);v.push_back(50);v.push_back(20);v.push_back(40);//利用sort进行升序,默认情况下升序sort(v.begin(), v.end());for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), myPrint);cout << endl;//改变为降序sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());//greater<int>()内建函数对象,需要包含functional头文件,编译器高的不包含functional头文件也不会出错for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;
}int main()
{test01();system("pause");return 0;
}bool compare(int a,int b)
{ return a < b; //升序排列,如果改为return a>b,则为降序
}
int a[20]={2,4,1,23,5,76,0,43,24,65},i;
for(i=0;i<20;i++) cout<< a[i]<< endl;
sort(a,a+20,compare);
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<stack>
#include<algorithm>
#include<bitset>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>struct Point
{int x;int y;//Point(int xx, int yy) :x(xx), y(yy) {};bool operator < (Point& p) {if (x != p.x) {return x < p.x;} else {return y < p.y;}}
};int main()
{vector<Point> p;p.push_back(Point{ 1,2 });p.push_back(Point{ 1,3 });Point p1;p1.x = 2;p1.y = 1;p.push_back(p1);sort(p.begin(), p.end());for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++) {cout << p[i].x << " " << p[i].y << endl;}/*输出:1 21 32 1*/system("pause");return 0;
}--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------struct Point
{int x;int y;
};
bool Cmp(Point& p1, Point& p2) {if (p1.x != p2.x) {return p1.x < p2.x;} else {return p1.y < p2.y;}
}int main()
{vector<Point> p;p.push_back(Point{ 1,2 });p.push_back(Point{ 1,3 });Point p1;p1.x = 2;p1.y = 1;p.push_back(p1);sort(p.begin(), p.end(),Cmp);for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++) {cout << p[i].x << " " << p[i].y << endl;}/*输出:1 21 32 1*/system("pause");return 0;
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------struct Point
{int x;int y;
};
class cmp
{
public:bool operator()(Point& p1, Point& p2)const {if (p1.x != p2.x) {return p1.x < p2.x;} else {return p1.y < p2.y;}}
};int main()
{vector<Point> p;p.push_back(Point{ 1,2 });p.push_back(Point{ 1,3 });Point p1;p1.x = 2;p1.y = 1;p.push_back(p1);sort(p.begin(), p.end(), cmp());for (int i = 0; i < p.size(); i++) {cout << p[i].x << " " << p[i].y << endl;}/*输出:1 21 32 1*/system("pause");return 0;
}



![NSS [HXPCTF 2021]includer‘s revenge](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9544c5640f40e7501e0c6fa997973ae8.png)