文章目录
- 前言
- 一、@Autowired&@Value:
- 1.1 @Autowired:
- 1.2 @Value:
- 二、依赖注入:
- 2.1 注入点获取:
- 2.2 通过 populateBean 入口依赖注入
- 2.2.1 populateBean :主要通过 postProcessProperties 方法进行依赖注入
- 2.2.2 postProcessProperties 方法对@Autowired@Value 填充
- 三、扩展点
- 3.1 @Primary
- 3.2 @Qualifier
- 总结:
前言
在bean完成实例化后之后,还需要对其属性值进行填充。本文介绍@Autowired&@Value 依赖注入
一、@Autowired&@Value:
1.1 @Autowired:
@Autowired是Spring框架提供的一种依赖注入(Dependency Injection)的注解。它可以用于标注在字段、setter方法、构造函数或方法参数上,用于自动装配依赖对象。
@Autowired注解的作用可以总结如下:
(1). 自动装配依赖对象:当使用@Autowired注解标注在一个字段、setter方法、构造函数或方法参数上时,它告诉Spring容器需要自动装配一个对应的依赖对象。
(2). 解决依赖对象冲突:当有多个符合类型的依赖对象可用时,@Autowired注解会尝试根据类型来自动装配对应的依赖对象。如果出现依赖对象冲突,可以使用@Qualifier注解配合@Autowired注解来指定具体要注入的依赖对象。
(3). 支持按照类型匹配和名称匹配:当没有使用@Qualifier注解时,@Autowired注解会首先按照字段类型、方法参数类型或构造函数参数类型进行匹配,如果找到多个符合条件的依赖对象,会再根据字段名、方法名或构造函数参数名称进行匹配。
(4). 方便的依赖注入:使用@Autowired注解可以省去动配置依赖对象的步骤,Spring容器会自动帮助我们解析并装配所需的依赖对象。
需要注意的是,@Autowired解通常与Spring容器中的ApplicationContext一起使用。容器可以根据注解信息自动解析依赖关系,并将对应的依赖对象自动注入到被注解标注的字段、setter方法、构造函数或方法参数中。
1.2 @Value:
@Value是Spring框架提供的一种属性注入的注解。它可以用于标注在字段、setter方法、构造函数或方法参数上,用于注入属性值。
@Value注解的作用可以总结如下:
(1). 注入属性值:当使用@Value注解标注在一个字段、setter方法、构造函数或方法参数上时,它告诉Spring容器需要注入一个指定的属性值。
(2). 从配置文件中读取属性:@Value注解可以用于读取配置文件中的属性值。可以通过${}占位符来引用配置文件中的属性值,并将其注入到被注解标注的字段、setter方法、构造函数或方法参数中。
(3). 注入SpEL表达式值:@Value注解可以用于注入SpEL(Spring Expression Language)表达式值。可以在#{}内使用SpEL表达式,并将计算结果注入到被注解标注的字段、setter方法、构造函数或方法参数中。
(4). 简化配置:使用@Value注解可以省去手动配置属性值的过程,Spring容器会根据注解信息自动将属性值注入到对应的位置。
需要注意的是,@Value注解通常与Spring容器中的ApplicationContext一起使用。容器可以根据注解信息自动解析属性值,并将其注入到注解标注的字段、setter方法、构造函数或方法参数中。另外,@Value注解也支持注入外部化配置属性值,需要配置对应的PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer来解析配置文件中的属性值。
二、依赖注入:
2.1 注入点获取:
通过AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的 postProcessMergedBeanDefinition 处理 @Autowired@Value的注入点,在封装后放入到集合中;
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
// 获取到@Autowired 和@Value 注解的属性和方法的注入点
// 放入到 map 缓存中 private final Map<String, InjectionMetadata> injectionMetadataCache = new ConcurrentHashMap(256);InjectionMetadata metadata = this.findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, (PropertyValues)null);metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
findAutowiringMetadata 注入点获取:
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {String cacheKey = StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName();InjectionMetadata metadata = (InjectionMetadata)this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {synchronized(this.injectionMetadataCache) {metadata = (InjectionMetadata)this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {if (metadata != null) {metadata.clear(pvs);}// 获取@Autowired 和@Value 注解的属性,然后包装成类记录属性注入点metadata = this.buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);}}}return metadata;
}
buildAutowiringMetadata 注入点获取:
注解判断:寻找注入点 加了@Autowired 和@Value 注解的属性和方法
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {// 如果这个类是基本类 以java. 开头 直接进行返回if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;} else {List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList();Class<?> targetClass = clazz;do {List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> fieldElements = new ArrayList();// 属性的遍历ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, (field) -> {// 获取到注解MergedAnnotation<?> ann = this.findAutowiredAnnotation(field);if (ann != null) {if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {// 注解 的属性是static 直接返回 遍历下一个filed; static 修饰的 是属于类的if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {this.logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);}return;}// required 属性获取boolean required = this.determineRequiredStatus(ann);fieldElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));}});List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> methodElements = new ArrayList();// 方法的遍历 ,遍历处理@Autowired 和@Value 注解的方法ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, (method) -> {// 如果是桥接方法,则找到被桥接的方法Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);if (BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {MergedAnnotation<?> ann = this.findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {this.logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);}return;}if (method.getParameterCount() == 0 && this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {this.logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " + method);}boolean required = this.determineRequiredStatus(ann);PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);methodElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));}}});elements.addAll(0, this.sortMethodElements(methodElements, targetClass));elements.addAll(0, fieldElements);targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();// 子类遍历完毕,然后遍历父类} while(targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);// 封装对象并返回return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);}
}
2.2 通过 populateBean 入口依赖注入
2.2.1 populateBean :主要通过 postProcessProperties 方法进行依赖注入
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {if (bw == null) {if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");}} else {if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {Iterator var4 = this.getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware.iterator();while(var4.hasNext()) {InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor)var4.next();// 先执行bean 的实例化之后方法if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {return;}}}PropertyValues pvs = mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null;int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();if (resolvedAutowireMode == 1 || resolvedAutowireMode == 2) {MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues((PropertyValues)pvs);if (resolvedAutowireMode == 1) {this.autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);}if (resolvedAutowireMode == 2) {this.autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);}pvs = newPvs;}boolean hasInstAwareBpps = this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();boolean needsDepCheck = mbd.getDependencyCheck() != 0;PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;if (hasInstAwareBpps) {if (pvs == null) {pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();}PropertyValues pvsToUse;for(Iterator var9 = this.getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware.iterator(); var9.hasNext(); pvs = pvsToUse) {InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor)var9.next();// @Autowired@Value, @Resource 注解的进行属性注入pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties((PropertyValues)pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);if (pvsToUse == null) {if (filteredPds == null) {filteredPds = this.filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);}pvsToUse = bp.postProcessPropertyValues((PropertyValues)pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);if (pvsToUse == null) {return;}}}}if (needsDepCheck) {if (filteredPds == null) {filteredPds = this.filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);}this.checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, (PropertyValues)pvs);}if (pvs != null) {// 如果在BeanDefinition 中定义了 bean 的value 进行value 值的填充this.applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, (PropertyValues)pvs);}}
}2.2.2 postProcessProperties 方法对@Autowired@Value 填充
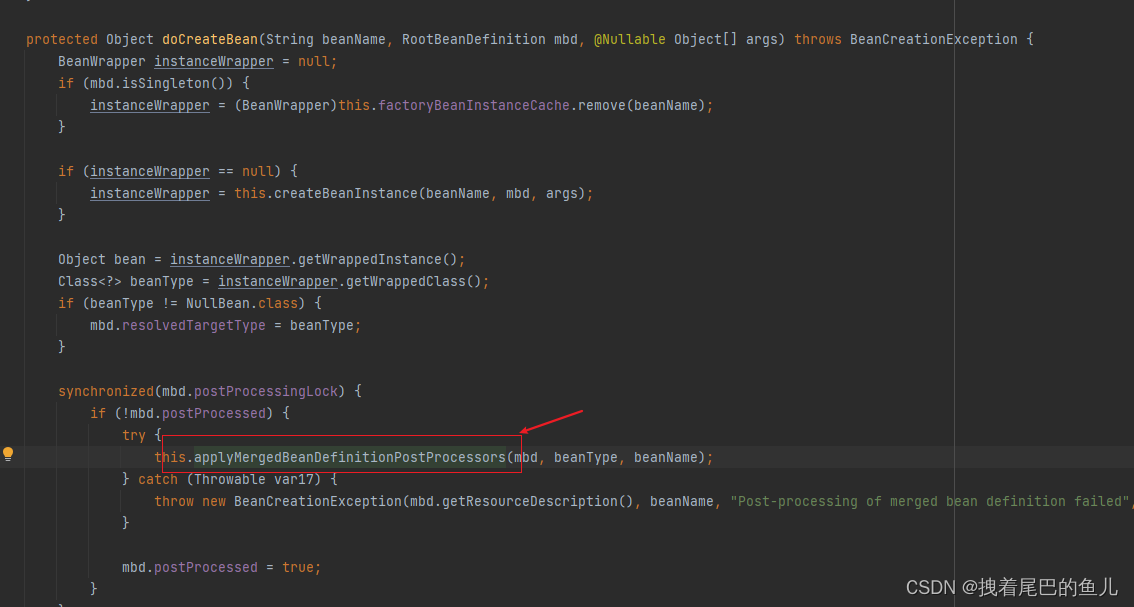
populateBean 方法中 postProcessProperties 进行依赖注入:通过AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 下postProcessProperties进行属性值的填充:
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {// 获取缓存的注入点InjectionMetadata metadata = this.findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);try {// 给注入点 ,设置值metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);return pvs;} catch (BeanCreationException var6) {throw var6;} catch (Throwable var7) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", var7);}
}
inject 遍历进行赋值:
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate = checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements;if (!((Collection)elementsToIterate).isEmpty()) {Iterator var6 = ((Collection)elementsToIterate).iterator();while(var6.hasNext()) {InjectedElement element = (InjectedElement)var6.next();// 属性或者方法进行赋值element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);}}}
filed 属性的注入 AutowiredFieldElement
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {Field field = (Field)this.member;Object value;if (this.cached) {try {value = AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.resolveCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);} catch (BeansException var7) {this.cached = false;AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.logger.debug("Failed to resolve cached argument", var7);value = this.resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);}} else {// 获取valuevalue = this.resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);}if (value != null) {ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);// 反射设置valuefield.set(bean, value);}}
resolveFieldValue 获取value:
private Object resolveFieldValue(Field field, Object bean, @Nullable String beanName) {// 获取字段依赖描述 @Autowired 的 required 属性获取DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet(2);Assert.state(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");// bean 的类型转换器获取TypeConverter typeConverter = AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory.getTypeConverter();Object value;try {// 通过spring 容器获取beanvalue = AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);} catch (BeansException ar12) {throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException((String)null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), var12);}synchronized(this) {if (!this.cached) {if (value == null && !this.required) {this.cachedFieldValue = null;} else {Object cachedFieldValue = desc;AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);if (value != null && autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {String autowiredBeanName = (String)autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();if (AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) && AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(desc, autowiredBeanName);}}this.cachedFieldValue = cachedFieldValue;this.cached = true;}}return value;}
}
method 方法的注入 AutowiredMethodElement
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {if (!this.checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {// 没有在beandefintion 中为其设置 值,则进入Method method = (Method)this.member;Object[] arguments;if (this.cached) {try {arguments = this.resolveCachedArguments(beanName, this.cachedMethodArguments);} catch (BeansException var8) {this.cached = false;AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.logger.debug("Failed to resolve cached argument", var8);arguments = this.resolveMethodArguments(method, bean, beanName);}} else {// 获取多个参数的的beanarguments = this.resolveMethodArguments(method, bean, beanName);}if (arguments != null) {try {ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);// 反射执行method.invoke(bean, arguments);} catch (InvocationTargetException var7) {throw var7.getTargetException();}}}
}resolveMethodArguments 获取方法的参数值:
@Nullable
private Object[] resolveMethodArguments(Method method, Object bean, @Nullable String beanName) {// 这个方法有几个参数int argumentCount = method.getParameterCount();// 存放对应参数的结果beanObject[] arguments = new Object[argumentCount];DependencyDescriptor[] descriptors = new DependencyDescriptor[argumentCount];Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet(argumentCount * 2);Assert.state(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");TypeConverter typeConverter = AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory.getTypeConverter();// 遍历入参for(int ix = 0; ix < arguments.length; ++ix) {// 封装方法参数占位符MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, ix);// 方法参数依赖描述DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());descriptors[ix] = currDesc;try {// 向spring 容器获取beanObject arg = AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);if (arg == null && !this.required) {arguments = null;break;}arguments[ix] = arg;} catch (BeansException var17) {throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException((String)null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), var17);}}synchronized(this) {if (!this.cached) {if (arguments != null) {DependencyDescriptor[] cachedMethodArguments = (DependencyDescriptor[])Arrays.copyOf(descriptors, argumentCount);AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == argumentCount) {Iterator<String> it = autowiredBeanNames.iterator();Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();for(int i = 0; i < paramTypes.length; ++i) {String autowiredBeanName = (String)it.next();if (arguments[i] != null && AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) && AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.this.beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, paramTypes[i])) {cachedMethodArguments[i] = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(descriptors[i], autowiredBeanName);}}}this.cachedMethodArguments = cachedMethodArguments;this.cached = true;} else {this.cachedMethodArguments = null;}}return arguments;}
}
}
resolveDependency 最终都通过改方法获取bean:
@Nullable
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {// 初始化 方法参数/属性 名称的 发现其descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.getParameterNameDiscoverer());if (Optional.class == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {return this.createOptionalDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName);} else if (ObjectFactory.class != descriptor.getDependencyType() && ObjectProvider.class != descriptor.getDependencyType()) {if (javaxInjectProviderClass == descriptor.getDependencyType()) {return (new Jsr330Factory()).createDependencyProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);} else {// 如果有lazy 注解 则返回一个代理对象,没有lazy 注解则返回nullObject result = this.getAutowireCandidateResolver().getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(descriptor, requestingBeanName);if (result == null) {// 非lazy的依赖注入result = this.doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);}return result;}} else {return new DependencyObjectProvider(descriptor, requestingBeanName);}
}
getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary :
ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver 下的getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary 如过被@Lazy 注解标注,返回一个代理对象,等到改对象真正被使用的时候才去获取到真正的bean
@Nullable
public Object getLazyResolutionProxyIfNecessary(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName) {// 有lazy 注解 通过buildLazyResolutionProxy获取一个代理对象,没有返回null// 有lazy 注解 当真正使用的时候 在从spring 容器中获取到对应的bean 然后使用return this.isLazy(descriptor) ? this.buildLazyResolutionProxy(descriptor, beanName) : null;
}
isLazy 判断是否懒加载:
protected boolean isLazy(DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {Annotation[] var2 = descriptor.getAnnotations();int var3 = var2.length;for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {Annotation ann = var2[var4];Lazy lazy = (Lazy)AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(ann, Lazy.class);if (lazy != null && lazy.value()) {return true;}}MethodParameter methodParam = descriptor.getMethodParameter();if (methodParam != null) {Method method = methodParam.getMethod();if (method == null || Void.TYPE == method.getReturnType()) {Lazy lazy = (Lazy)AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(methodParam.getAnnotatedElement(), Lazy.class);if (lazy != null && lazy.value()) {return true;}}}return false;
}doResolveDependency 处理非懒加载的bean进行注入:
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);Object var23;try {Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);if (shortcut != null) {Object var20 = shortcut;return var20;}Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();// 获取@Value 注解的值Object value = this.getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);Object var11;if (value == null) {// 根据bean 的类型和名字获取bean// 如果使用 Map<String,UserSerivce> 或者List <UserService>则会 拿到UserService 类型的多个bean// 注意Map 的key 必须是String 因为key 为bean 的名称// List的泛型为Object 会拿到所有的bean ,如果是<T> 则拿不到bean// bean name 获取的筛选责任链:// 1 SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver检查BeanDefinition的autowireCandidate属性,为true表示通过筛选// 2 GenericTypeAwareAutowireCandidateResolver检查BeanDefinition的beanClass属性和当前注入点的type是否匹配,// 匹配则通过筛选// 3 QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolvel检查BeanDefinition的qualifier属性// 和当前注入点的qualifier属性是否匹配,匹配则通过筛选Object multipleBeans = this.resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);// 如果不是Map /List /Array 则multipleBeans 为null, 为普通的对象注入if (multipleBeans != null) {// 如果获取到了bean 则直接返回var23 = multipleBeans;return var23;}// 根据类型获取得到多个bean key 为bean 的名称,value 为bean对象或者bean 的classMap<String, Object> matchingBeans = this.findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {// 根据类型没有获取到bean 并且required 为true 则报错if (this.isRequired(descriptor)) {this.raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);}var11 = null;return var11;}Object instanceCandidate;Object result;String autowiredBeanName;if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {//根据类型获取到多个bean ,需要根据名称再次进行过滤autowiredBeanName = this.determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);if (autowiredBeanName == null) {// 如果按照名称没有找到,它的required 是true 则报错if (!this.isRequired(descriptor) && this.indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {result = null;return result;}result = descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);return result;}// 根据bean 的名称获取到beaninstanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);} else {Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = (Map.Entry)matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();autowiredBeanName = (String)entry.getKey();instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();}if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);}// 如果现在的bean 还只是class 则创建这个beanif (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);}result = instanceCandidate;if (instanceCandidate instanceof NullBean) {if (this.isRequired(descriptor)) {this.raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);}result = null;}if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());}Object var14 = result;return var14;}if (value instanceof String) {// value 占位符 @Value("${xxx.test}") 获取key 为xxx.test 的value值// 如果是@Value("#{userService}") # 的表达式 返回#{userService}"String strVal = this.resolveEmbeddedValue((String)value);BeanDefinition bd = beanName != null && this.containsBean(beanName) ? this.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null;// 表达式解析 向spring获取 userService 的beanvalue = this.evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);}TypeConverter converter = typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : this.getTypeConverter();try {// 如果类型转换器,则使用转换器 对value 进行转换var23 = converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());} catch (UnsupportedOperationException var18) {var11 = descriptor.getField() != null ? converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) : converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter());return var11;}} finally {ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);}return var23;
}
determineAutowireCandidate 多个相同类型的bean 进行名称的过滤:
@Nullable
protected String determineAutowireCandidate(Map<String, Object> candidates, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) {Class<?> requiredType = descriptor.getDependencyType();// 先看下这些bean 有没有被@Primary 注解标识,标注多个报错String primaryCandidate = this.determinePrimaryCandidate(candidates, requiredType);if (primaryCandidate != null) {return primaryCandidate;} else {// 获取优先级最高的bean 通过@Priority 类的注解 多个@Priority 值一样则报错String priorityCandidate = this.determineHighestPriorityCandidate(candidates, requiredType);if (priorityCandidate != null) {return priorityCandidate;} else {// 按照bean的名称 获取一个并返回Iterator var6 = candidates.entrySet().iterator();String candidateName;Object beanInstance;do {if (!var6.hasNext()) {return null;}Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = (Map.Entry)var6.next();candidateName = (String)entry.getKey();beanInstance = entry.getValue();} while((beanInstance == null || !this.resolvableDependencies.containsValue(beanInstance)) && !this.matchesBeanName(candidateName, descriptor.getDependencyName()));return candidateName;}}
}
三、扩展点
3.1 @Primary
@Primary 是 Spring 框架中的一个注解,用于指定在存在多个候选者时首选的 bean 实例。
当存在多个相同类型的 bean 实例需要被注入时,使用 @Primary 注解标注的 bean 实例将被视为首选的实例,优先被注入。
使用方法:
- 定义多个相同类型的 bean 实例,并在其中一个实例上添加
@Primary注解。
@Component
@Primary
public class PrimaryBean implements MyBean {// ...
}@Component
public class AnotherBean implements MyBean {// ...
}
- 在需要注入的地方使用对应的类型进行注入。
@Component
public class MyComponent {@Autowiredprivate MyBean bean;// ...
}
在上面的示例中,PrimaryBean 类上使用了 @Primary 注解,意味着它是首选的 bean 实例。当需要注入 MyBean 类型的实例时,会优先选择注入 PrimaryBean 实例。这样就可以通过 @Primary 注解指定首选的 bean 实例,解决多个候选者的注入歧义。
3.2 @Qualifier
@Qualifier 是 Spring 框架中的一个注解,用于解决依赖注入时的歧义性问题。当存在多个类型一致的 bean 实例可供选择时,可以通过 @Qualifier 注解进行标识,以明确指定要注入的 bean 实例。
通常情况下,@Qualifier 注解与其他注解(如 @Autowired、@Resource)共同使用,用于指定具体要注入的 bean例。
使用方法:
- 定义多个相同类型的 bean 实例,并添加对应的
@Qualifier注解标识符,可以是类名首字母小写的形式。
@Component
@Qualifier("beanA")
public class BeanA implements MyBean {// ...
}@Component
@Qualifier("beanB")
public class BeanB implements MyBean {// ...
}
- 在需要注入的地方使用
@Qualifier注解指定要注入的具体 bean 实例。
@Component
public class MyComponent {@Autowired@Qualifier("beanA")private MyBean bean;// ...
}
在上面的示例中,通过 @Qualifier("beanA") 指定要注入的 bean 实例为标识符为 “beanA” 的 BeanA 类。这样就可以解决依赖注入时的歧义性问题,确保正确注入指定的 bean 实例。
总结:
在bean 实例化之后 通过populateBean 对属性和方法的入参进行依赖注入,首先扫描记录哪些属性和方法需要进行依赖注入,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 的 postProcessMergedBeanDefinition @Autowired 和@Value 注解的属性和方法的注入点;
然后遍历完成注入,通过AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 进行完成@Autowired 和@Value的依赖注入;
@Autowired 和@Value 依赖注入: AutowiredFieldElement 和AutowiredMethodElement 分别对属性和方法的入参进行依赖注入
DefaultListableBeanFactory.doResolveDependency 方法中首先对@Value 进行处理:
- 如果使用@Value(" x x x " ) 使用 {xxx}") 使用 xxx")使用 符号则解析到xxx 对应的value 值,然后判断是否有类型转换器,有的话则进行转换在赋值,没有直接赋值,如果类型错误则报错;
- 如果使用@Value(“#{xxx}”) 使用$ 符号则解析到xxx 对应的value 值,然后在容器中寻找对应xxx 的bean ,找到后进行赋值,找不到则报错;
@Value 处理之后,获取到该类型的所以bean,获取的过程:
- SimpleAutowireCandidateResolver检查BeanDefinition的autowireCandidate属性,为true表示通过筛选;可以通过在bean的@Autowired注解中设置required属性来控制,默认情况下,required属性的值为true,表示该bean是必需进行自动装配的。如果没有找到匹配的依赖项,则会抛出NoSuchBeanDefinitionException异常。要将required属性设置为false,表示该依赖项是可选的,如果找不到匹配的依赖项,Spring会将该字段设置为null,而不会抛出异常 ;
- GenericTypeAwareAutowireCandidateResolver检查BeanDefinition的beanClass和当前注入点的type是否匹配,匹配则通过筛选;
- QualifierAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver检查BeanDefinition的qualifier属性值和当前注入点的qualifier属性值是否匹配,匹配则通过筛选
- 把筛选之后的bean添加到一个Map中key为beanName,value为bean对象,如果Map中有多个Bean,继续进行筛选;
- 从多个Bean中获取被@Primary注解标注的Bean;
- 从多个Bean中获取优先级最高的Bean;
- 从多个Bean中获取注入点name对应的bean;
- 通过反射进行属性赋值或方法调用;