g o l a n g golang golang的 s t r i n g string string类型是不可修改的,对于拼接字符串来说,本质上还是创建一个新的对象将数据放进去。主要有以下几种拼接方式
拼接方式介绍
1.使用 s t r i n g string string自带的运算符 + + +
ans = ans + s
2. 使用格式化输出 f m t . S p r i n t f fmt.Sprintf fmt.Sprintf
ans = fmt.Sprintf("%s%s", ans, s)
3. 使用 s t r i n g s strings strings的 j o i n join join函数
一般适用于将字符串数组转化为特定间隔符的字符串的情况
ans=strings.join(strs,",")
4. 使用 s t r i n g s . B u i l d e r strings.Builder strings.Builder
builder := strings.Builder{}
builder.WriteString(s)
return builder.String()
5. 使用 b y t e s . B u f f e r bytes.Buffer bytes.Buffer
buffer := new(bytes.Buffer)
buffer.WriteString(s)
return buffer.String()
6. 使用 [ ] b y t e []byte []byte,并且提前设置容量
ans := make([]byte, 0, len(s)*n)
ans = append(ans, s...)
性能对比
先写一个随机生成长度为 n n n的字符串的函数
func getRandomString(n int) string {var tmp = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"ans := make([]uint8, 0, n)for i := 0; i < n; i++ {ans = append(ans, tmp[rand.Intn(len(tmp))])}return string(ans)
}
接下来分别写出上述拼接方式的实现,假设每次都拼接n次字符串s后返回。
1.使用 s t r i n g string string自带的运算符 + + +
循环 n n n次,每次都令答案字符串 a n s + ans+ ans+源字符串 s s s
func plusOperatorJoin(n int, s string) string {var ans stringfor i := 0; i < n; i++ {ans = ans + s}return ans
}
2. 使用格式化输出 f m t . S p r i n t f fmt.Sprintf fmt.Sprintf
循环 n n n次,使用 f m t . S p r i n t f fmt.Sprintf fmt.Sprintf达到拼接的目的
func sprintfJoin(n int, s string) string {var ans stringfor i := 0; i < n; i++ {ans = fmt.Sprintf("%s%s", ans, s)}return ans
}
3. 使用 s t r i n g s strings strings的 j o i n join join函数
拼接同一个字符串的话不适合用 j o i n join join函数,所以跳过这种方式
4. 使用 s t r i n g s . B u i l d e r strings.Builder strings.Builder
初始化 s t r i n g s . B u i l d e r strings.Builder strings.Builder,循环 n n n次,每次调用 W r i t e S t r i n g WriteString WriteString方法
func stringBuilderJoin(n int, s string) string {builder := strings.Builder{}for i := 0; i < n; i++ {builder.WriteString(s)}return builder.String()
}
5. 使用 b y t e s . B u f f e r bytes.Buffer bytes.Buffer
初始化 b y t e s . B u f f e r bytes.Buffer bytes.Buffer,循环 n n n次,每次调用 W r i t e S t r i n g WriteString WriteString方法
func bytesBufferJoin(n int, s string) string {buffer := new(bytes.Buffer)for i := 0; i < n; i++ {buffer.WriteString(s)}return buffer.String()
}
6. 使用 [ ] b y t e []byte []byte,并且提前设置容量
定义 a n s ans ans为 b y t e byte byte数组,并提前设置容量为 l e n ( s ) ∗ n len(s)*n len(s)∗n
func bytesJoin(n int, s string) string {ans := make([]byte, 0, len(s)*n)for i := 0; i < n; i++ {ans = append(ans, s...)}return string(ans)
}
测试代码
先随机生成一个长度为10的字符串,然后拼接10000次。
package high_stringsimport "testing"func benchmark(b *testing.B, f func(int, string) string) {var str = getRandomString(10)for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {f(10000, str)}
}func BenchmarkPlusOperatorJoin(b *testing.B) {benchmark(b, plusOperatorJoin)
}
func BenchmarkSprintfJoin(b *testing.B) {benchmark(b, sprintfJoin)
}
func BenchmarkStringBuilderJoin(b *testing.B) {benchmark(b, stringBuilderJoin)
}
func BenchmarkBytesBufferJoin(b *testing.B) {benchmark(b, bytesBufferJoin)
}
func BenchmarkBytesJoin(b *testing.B) {benchmark(b, bytesJoin)
}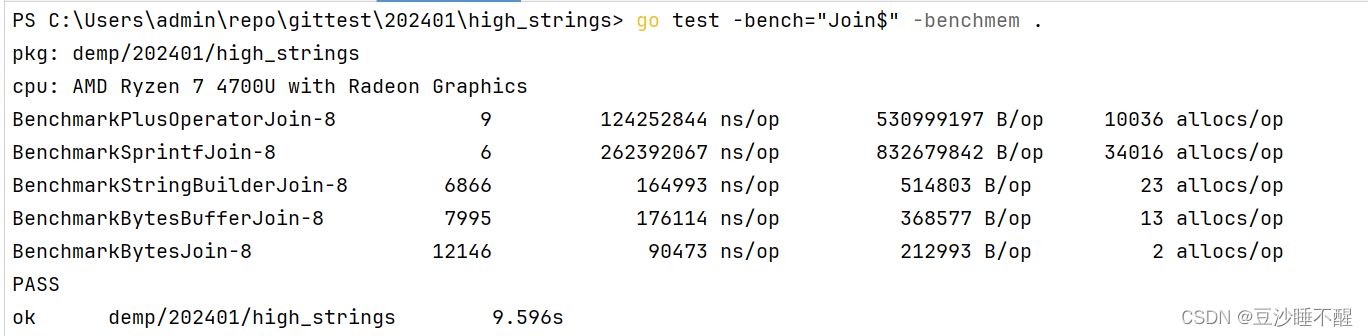
测试结果:
使用 [ ] b y t e []byte []byte > s t r i n g s . B u i l d e r strings.Builder strings.Builder >= b y t e s . B u f f e r bytes.Buffer bytes.Buffer > f m t . S p r i n t f fmt.Sprintf fmt.Sprintf > + + +运算符
源码分析
1.使用 s t r i n g string string自带的运算符 + + +
代码在runtime\string.go里
// concatstrings implements a Go string concatenation x+y+z+...
// The operands are passed in the slice a.
// If buf != nil, the compiler has determined that the result does not
// escape the calling function, so the string data can be stored in buf
// if small enough.
func concatstrings(buf *tmpBuf, a []string) string {idx := 0l := 0count := 0for i, x := range a {n := len(x)if n == 0 {continue}if l+n < l {throw("string concatenation too long")}l += ncount++idx = i}if count == 0 {return ""}// If there is just one string and either it is not on the stack// or our result does not escape the calling frame (buf != nil),// then we can return that string directly.if count == 1 && (buf != nil || !stringDataOnStack(a[idx])) {return a[idx]}s, b := rawstringtmp(buf, l)for _, x := range a {copy(b, x)b = b[len(x):]}return s
}- 首先计算拼接后的字符串长度
- 如果只有一个字符串并且不在栈上就直接返回
- 如果 b u f buf buf不为空并且 b u f buf buf可以放下这些字符串,就把拼接后的字符串放在 b u f buf buf里,否则在堆上重新申请一块内存
func rawstringtmp(buf *tmpBuf, l int) (s string, b []byte) {if buf != nil && l <= len(buf) {b = buf[:l]s = slicebytetostringtmp(&b[0], len(b))} else {s, b = rawstring(l)}return
}
// rawstring allocates storage for a new string. The returned
// string and byte slice both refer to the same storage.
// The storage is not zeroed. Callers should use
// b to set the string contents and then drop b.
func rawstring(size int) (s string, b []byte) {p := mallocgc(uintptr(size), nil, false)return unsafe.String((*byte)(p), size), unsafe.Slice((*byte)(p), size)
}- 然后遍历数组,将字符串 c o p y copy copy过去
2. 使用 s t r i n g s . B u i l d e r strings.Builder strings.Builder
介绍: s t r i n g s . B u i l d e r strings.Builder strings.Builder用于使用 W r i t e Write Write方法高效地生成字符串,它最大限度地减少了内存复制
拼接过程: b u i l d e r builder builder里有一个 b y t e byte byte类型的切片,每次调用 W r i t e S t r i n g WriteString WriteString的时候,是直接往该切片里追加字符串。因为切片底层的扩容机制是以倍数申请的,所以对比1而言,2的内存消耗要更少。
**结果返回:**在返回字符串的 S t r i n g String String方法里,是将 b u f buf buf数组转化为字符串直接返回的。
扩容机制: 想要缓冲区容量增加 n n n个字节,扩容后容量变为 2 ∗ l e n + n 2*len+n 2∗len+n
// A Builder is used to efficiently build a string using Write methods.
// It minimizes memory copying. The zero value is ready to use.
// Do not copy a non-zero Builder.
type Builder struct {addr *Builder // of receiver, to detect copies by valuebuf []byte
}// String returns the accumulated string.
func (b *Builder) String() string {return unsafe.String(unsafe.SliceData(b.buf), len(b.buf))
}// grow copies the buffer to a new, larger buffer so that there are at least n
// bytes of capacity beyond len(b.buf).
func (b *Builder) grow(n int) {buf := make([]byte, len(b.buf), 2*cap(b.buf)+n)copy(buf, b.buf)b.buf = buf
}
// WriteString appends the contents of s to b's buffer.
// It returns the length of s and a nil error.
func (b *Builder) WriteString(s string) (int, error) {b.copyCheck()b.buf = append(b.buf, s...)return len(s), nil
}3. 使用 b y t e s . B u f f e r bytes.Buffer bytes.Buffer
介绍: b y t e s . B u f f e r bytes.Buffer bytes.Buffer跟 s t r i n g s . B u i l d e r strings.Builder strings.Builder的底层都是 b y t e byte byte数组,区别在于扩容机制和返回字符串的 S t r i n g String String方法。
结果返回: 因为 b y t e s . B u f f e r bytes.Buffer bytes.Buffer实际上是一个流式的字节缓冲区,可以向尾部写入数据,也可以读取头部的数据。所以在返回字符串的 S t r i n g String String方法里,只返回了缓冲区里未读的部分,所以需要重新申请内存来存放返回的结果。内存会比 s t r i n g s . B u i l d e r strings.Builder strings.Builder稍慢一些。
扩容机制: 想要缓冲区容量至少增加 n n n个字节, m m m是未读的长度, c c c是当前的容量。
优化点在于如果 n < = c / 2 − m n <= c/2-m n<=c/2−m,也就是当前容量的一半都大于等于现有的内容(未读的字节数)加上所需要增加的字节数,就复用当前的数组,把未读的内容拷贝到头部去。
We can slide things down instead of allocating a new slice. We only need m+n <= c to slide, but we instead let capacity get twice as large so we don’t spend all our time copying.
我们可以向下滑动,而不是分配一个新的切片。我们只需要m+n<=c来滑动,但我们让容量增加了一倍,这样我们就不会把所有的时间都花在复制上。
否则的话也是 2 ∗ l e n + n 2*len+n 2∗len+n的扩张
// A Buffer is a variable-sized buffer of bytes with Read and Write methods.
// The zero value for Buffer is an empty buffer ready to use.
type Buffer struct {buf []byte // contents are the bytes buf[off : len(buf)]off int // read at &buf[off], write at &buf[len(buf)]lastRead readOp // last read operation, so that Unread* can work correctly.
}
// String returns the contents of the unread portion of the buffer
// as a string. If the Buffer is a nil pointer, it returns "<nil>".
//
// To build strings more efficiently, see the strings.Builder type.
func (b *Buffer) String() string {if b == nil {// Special case, useful in debugging.return "<nil>"}return string(b.buf[b.off:])
}
// WriteString appends the contents of s to the buffer, growing the buffer as
// needed. The return value n is the length of s; err is always nil. If the
// buffer becomes too large, WriteString will panic with ErrTooLarge.
func (b *Buffer) WriteString(s string) (n int, err error) {b.lastRead = opInvalidm, ok := b.tryGrowByReslice(len(s))if !ok {m = b.grow(len(s))}return copy(b.buf[m:], s), nil
}// grow grows the buffer to guarantee space for n more bytes.
// It returns the index where bytes should be written.
// If the buffer can't grow it will panic with ErrTooLarge.
func (b *Buffer) grow(n int) int {m := b.Len()// If buffer is empty, reset to recover space.if m == 0 && b.off != 0 {b.Reset()}// Try to grow by means of a reslice.if i, ok := b.tryGrowByReslice(n); ok {return i}if b.buf == nil && n <= smallBufferSize {b.buf = make([]byte, n, smallBufferSize)return 0}c := cap(b.buf)if n <= c/2-m {// We can slide things down instead of allocating a new// slice. We only need m+n <= c to slide, but// we instead let capacity get twice as large so we// don't spend all our time copying.copy(b.buf, b.buf[b.off:])} else if c > maxInt-c-n {panic(ErrTooLarge)} else {// Add b.off to account for b.buf[:b.off] being sliced off the front.b.buf = growSlice(b.buf[b.off:], b.off+n)}// Restore b.off and len(b.buf).b.off = 0b.buf = b.buf[:m+n]return m
}
字符串拼接性能及原理
GoLang bytes.Buffer基础使用方法详解








![【C++入门到精通】function包装器 | bind() 函数 C++11 [ C++入门 ]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/2b8dd8add78842b5aadcc661e9255f47.png#pic_center)