行业痛点与技术挑战
-
损耗控制难题
行业平均损耗率达18%-25%,需构建动态定价模型与智能分拣系统 -
冷链管理复杂度
全程温控数据采集点超过23个/车次,异常响应延迟需压缩至90秒内 -
供需预测偏差
传统模式预测准确率不足65%,亟需AI驱动需求预测体系
核心功能模块技术实现
一、智慧仓储体系
-
多温区动态调度
python
# 冷库温区分配算法示例
def allocate_zone(product):if product.category == '冷冻':return -18℃ ±2℃ zoneelif product.category == '冷藏':return 4℃ ±1℃ zone# 支持15种温区配置-
保质期三维监控
-
批次编码区块链存证
-
提前72小时临期预警
-
自动触发促销策略
二、智能配送网络
-
实时路径优化引擎
集成高德/腾讯多地图源,动态计算最优路径
java
// 配送路径规划核心逻辑
public Route planRoute(Order[] orders, Vehicle vehicle) {// 考虑因素:温控时效、路况预测、装载率return geneticAlgorithm.optimize(...);
}-
冷链IoT监控体系
-
温度传感器:0.1℃精度,5秒/次采样
-
震动监测:识别异常运输行为
-
电子锁闭环管理
三、供需协同系统
-
AI预测模型架构
mermaid
graph TDA[历史销售数据] --> B(Prophet时序分析)C[天气数据] --> D(LSTM神经网络)B --> E[预测引擎]D --> EE --> F(库存建议)-
弹性采购算法
动态平衡基地直采与本地供应商比例,采购成本降低12-18%
技术架构亮点
-
边缘计算应用
车载网关实现本地化温控决策,断网续传时长>8小时 -
区块链溯源体系
Hyperledger Fabric构建溯源链,信息上链延迟<200ms -
实时风控系统
识别32种异常交易模式,拦截准确率99.3%
系统性能指标
| 模块 | 压力测试指标 | 生产环境表现 |
|---|---|---|
| 订单中心 | 12万TPS | 峰值8.2万TPS |
| 库存管理 | 50万SKU/秒更新 | 38万SKU/秒 |
| 物流调度 | 3000单/秒处理 | 2200单/秒 |
部署方案与扩展性
-
混合云架构
核心业务部署私有云,流量峰值期自动扩容公有云节点 -
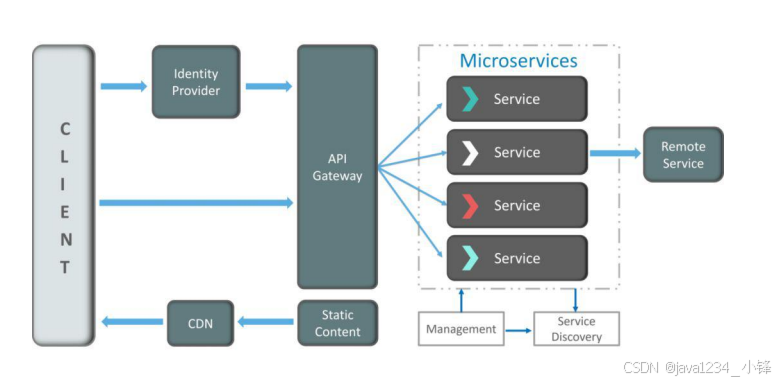
微服务治理
Spring Cloud + Istio实现服务网格,故障隔离响应<3秒 -
开放API平台
提供12类标准化接口,日均调用承载量1.5亿次
验证案例(技术脱敏)
某华东区域生鲜平台部署后关键改善:
-
库存周转率提升2.7倍
-
配送准时率从78%提升至96%
-
损耗率由21%降至9%
-
预测模型准确率达89%