文章目录
- 一、概念
- 二、OJ练习
- 2.1 区间选点
- 2.2 区间合并
- 2.3 区间
- 2.4 合并果子
- 2.5 排队接水
- 2.6 货仓选址
- 2.7 防晒
- 2.8 畜栏预定
- 2.9 雷达设备
- 2.10 国王游戏
- 2.11 耍杂技的牛
- 2.12 给树染色
- 2.13 任务
- 2.14 能量石
- 三、总结
一、概念
贪心是一种在每次决策时采取当前意义下最优策略的算法,因此,使用贪心法要求问题的整体最优性可以由局部最优性导出。贪心算法的正确性需要证明,常见的证明手段有:
- 微扰(邻项交换)
- 证明在任意局面下,任何对局部最优策略的微小改变都会造成整体结果变差。经常用于以“排序”为贪心策略的证明。
- 范围缩放
- 证明任何对局部最优策略作用范围的扩展都不会造成整体结果变差
- 决策包容性
- 证明在任意局面下,作出局部最优决策以后,在问题状态空间中的可达集合包含了作出其他任何决策后的可达集合。换言之,这个局部最优策略提供的可能性包含其他所有策略提供的可能性。
- 反证法
- 数学归纳法
贪心算法在算法体系中较为特殊,这里通过几道例题来体会贪心算法的应用。
二、OJ练习
2.1 区间选点
区间选点 - 45D - Codeforces
题目保证了有解,我们该如何选出可行解呢?
我们考虑把区间按照右端点升序排序,然后遍历所有区间,对于每个区间选取区间内没有被选取的最左端点
如何证明正确性?——反证法
假设按照上述策略出现某个区间无点可选,该区间为[l, r],说明有r - l + 1个右端点不小于l,不超过r的区间选择了[l, r]内的r - l + 1个点
它们选择[l, r]内的点说明它们在[0, l - 1]的部分都被选完了,否则按照靠左原则应该选取[0, l - 1]的点,那么[l, r]内就存在r - l + 2个区间的右端点,此时原问题无解,与题目条件矛盾,故策略正确。
对于区间问题通用操作是按照某端点排序,在处理区间问题没有头绪的时候可以试着排序来寻找突破口。
n = int(input())lines = []for _ in range(n):a, b = map(int, input().split())lines.append((a, b, _))
lines.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])st = set()
ans = [0] * n
for l, r, idx in lines:for i in range(l, r + 1):if not (i in st):st.add(i)ans[idx] = ibreakfor x in ans:print(x, end=' ')2.2 区间合并
P2082 区间覆盖(加强版) - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
即求区间合并后的长度
那么我们将区间按照左端点升序排序,然后顺序遍历区间
记录当前合并区间的左端点L,右端点R,对于遍历到的区间[l, r]
如果l > R,那么说明和前面的区间不相交,我们累加前面区间的长度后更新当前合并区间为[l, r]
否则,更新R = max(R, r)
证明很简单,就是假设存在两个可以合并的区间没有合并,然后反证推出矛盾即可,不再赘述。
n = int(input())
lines = [tuple(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(n)]
lines.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])res = 0
L, R = 0, -1
for x, y in lines:if x <= R:R = max(R, y)else:res += R - L + 1L, R = x, y
print(res + (R - L + 1))
2.3 区间
[P2434 SDOI2005] 区间 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
和上一道题做法一样,是在上一道题目的基础上加上了输出具体方案
我们只需开一个数组表示当前的不合并区间数组,如果当前区间和最后一个不相交就加入数组,否则就维护最后一个区间的最右端点
n = int(input())
lines = [tuple(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(n)]
lines.sort(key=lambda x: x[0])res = 0
ans = [lines[0]]
for x, y in lines:if x <= ans[-1][1]:ans[-1] = (ans[-1][0], max(ans[-1][1], y))else:ans.append((x, y))
for x, y in ans:print(x, y)
2.4 合并果子
148. 合并果子 - AcWing题库
很明显的贪心思路,每次区所有堆中最小的两堆合并即可
为什么是正确的呢?
我们合并的过程其实可以构造出一棵树,这棵树和Huffman树其实是等价的。
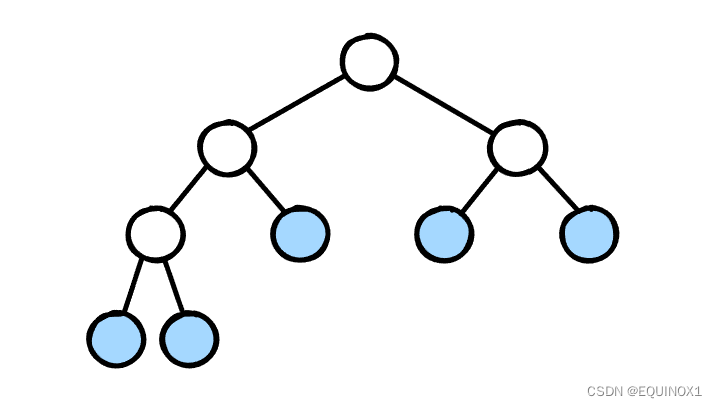
上图中蓝色代表初始的果子堆,每个结点都是由两个孩子合并而来
初始蓝色结点的贡献为深度 乘 结点权值
我们只需证明按照贪心策略得到的树中:蓝色结点的权值 * 深度之和最小即可
引理:权值最小的两个点的深度一定最深,且互为兄弟
证明:如果不是,两个点中至少有一个可以和最后一层的某个权值不小于自身的结点交换,那么两个结点可以交换到最后一层并且成为兄弟,那么 蓝色结点的权值 * 深度之和至少不会变大,甚至变小,故得证
那么最优解的值等价于 权值最小的两个点的值相加 加上 两个点合并后与剩余的n - 2个点构造出的最优树的值
同样的,我们如此迭代下去,可以构造出一棵最优解树,故得证。
import heapq
n = int(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
heapq.heapify(a)
res = 0
while len(a) > 1:x = heapq.heappop(a)y = heapq.heappop(a)res += x + yheapq.heappush(a, x + y)
print(res)
2.5 排队接水
P1223 排队接水 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
每个人接的越早,它的时间就会越多人忍受
所以我们让接的少的人优先接水即可
证明也很简单,同样反证,然后总可以按照贪心策略构造出不比最优解差甚至更优的解
n = int(input())
a = [(int(x), _ + 1) for _, x in enumerate(input().split())]
a.sort()
s = 0
for i, (x, idx) in enumerate(a):s += x * (n - i - 1)print(idx, end=' ')
print('')
print('%.2f' % (s / n))
2.6 货仓选址
104. 货仓选址 - AcWing题库
很经典的中位数问题,就是数轴上找到一个点y使得,Σ|x - y|最小
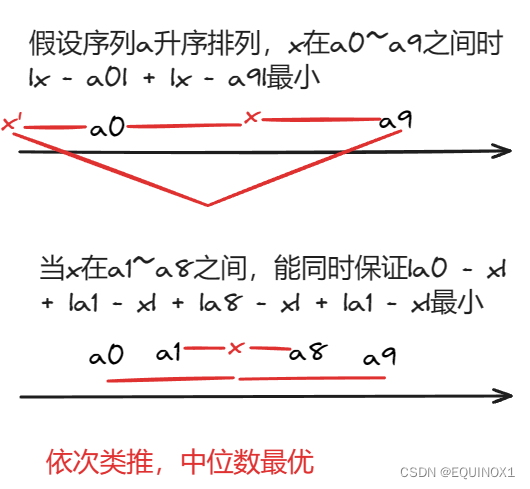
上图其实已经很明白了,当y选在两个数里面的差绝对值和总小于等于在两个数外面的差绝对值
那么我们剥洋葱似的一层一层往里钻,就会落到中位数处
n = int(input())
a = list(map(int, input().split()))
a.sort()mid = a[len(a) // 2]print(sum(abs(x - mid) for x in a))
2.7 防晒
110. 防晒 - AcWing题库
又是区间问题,不过这道题按照左右端点哪个排都能做,其实有点让每个资源发挥其最大作用的意思
怎么思考呢?我们把牛牛的区间按照右端点排序,然后顺序遍历牛牛每次选取在自己区间内最小的那个防晒霜
如何证明我们这样得到的一定是最优解?
我们可以证明对任意最优解按照贪心策略调整不会使得解变差从而得到一个最优解,我们也可以用范围缩放来证明,即我们的局部最优贪心策略对整体影响最小。
我们已经按照右端点排序,那么对于当前枚举奶牛的可用防晒霜x,y,SPF[x] < SPF[y]只有如下三种情况:
- 后面奶牛x,y都能用
- 后面奶牛只能用y
- 后面奶牛x,y都不能用
我们发现我们选择x对后面奶牛影响最小,所以贪心策略正确。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 2510;int n, m;
PII w[N];
map<int, int> mp;int main(){cin >> n >> m;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cin >> w[i].x >> w[i].y;for(int i = 0, a, b; i < m; i ++) cin >> a >> b, mp[a] += b;sort(w, w + n, [](const PII& a, const PII& b){return a.y < b.y;});int res = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){ //cout << w[i].x << ' ' << w[i].y << endl;auto it = mp.lower_bound(w[i].x);if (it != mp.end() && it -> first <= w[i].y) {it -> second --, res ++;if(! it -> second) mp.erase(it);}}cout << res;return 0;
}2.8 畜栏预定
111. 畜栏预定 - AcWing题库
我们将牛按开始时间升序排序,然后枚举牛
如果对于当前牛有可以安排的畜栏(畜栏内最后一头牛结束时间不晚于当前牛的开始时间),那么我们就安排进去
如果没有,就新开一个畜栏
上述做法的正确性:
反证法:我们存在不同于上述策略的方案为更优解,只需m个畜栏,那么我们上述策略建立第m + 1个畜栏时,必然有m个畜栏的结束时间都大于当前牛的开始时间,而由于我们按照开始时间升序,故m个畜栏的最后一头牛都和当前牛区间有交集,等价于m + 1头牛两两有交集,所以我们至少需要m + 1个畜栏,矛盾,故得证。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
const int N = 5e4 + 10;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef pair<PII, int> PIII;
PIII lines[N];
int n, id[N];
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> pq;
int main(){cin >> n;for(int i = 0, a, b; i < n; i ++) cin >> a >> b, lines[i] = { {a, b}, i };sort(lines, lines + n);for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){if(pq.empty() || pq.top().x >= lines[i].x.x)pq.emplace(lines[i].x.y, id[lines[i].y] = pq.size() + 1);else{PII t = pq.top();pq.pop();t.x = lines[i].x.y;pq.emplace(t);id[lines[i].y] = t.y;}}cout << pq.size() << endl;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) cout << id[i] << endl;return 0;
}
2.9 雷达设备
112. 雷达设备 - AcWing题库
对于每个小岛而言,可以覆盖它的点对应x轴上一个区间,那么每个小岛就能够有一个可监测区间
我们只需选择尽可能少的点使得每个区间都被覆盖到即可,这就转化为了区间选点问题
我们将区间按照右端点排序,然后如果当前区间左端点小于覆盖区间的右端点,说明该区间可以被前面覆盖区间的点
否则我们就开一个新区间,所选的点为当前区间的右端点
from math import sqrt
n, d = map(int, input().split())
eps = 1e-6
lines = []
for _ in range(n):x, y = map(int, input().split())if y - d > eps:print(-1)exit(0)dx = sqrt(d * d - y * y)lines.append((x - dx, x + dx))lines.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
ed = -2000
res = 0
for l, r in lines:if l - ed > eps:res += 1ed = r
print(res)
2.10 国王游戏
114. 国王游戏 - AcWing题库
本题贪心策略为:将大臣按照左手乘右手升序排序,此时的最大值最小
证明策略:临项交换(微扰)
我们假设最优解不是按照上述策略得到,那么一定存在a[i] * b[i] >= a[i + 1] * b[i + 1]
交换二者不影响其他大臣的收益
我们对比交换前后二者的收益:
交换前:i人:premul(i - 1) / bi i + 1人:premul(i - 1) * ai / bi+1
交换后:i人:premul(i - 1) / bi+1 i + 1人:premul(i - 1) * ai+1 / bi
四个数同乘 bi*bi+1/premul(i - 1):
交换前:i人:bi+1 i + 1人:ai bi
交换后:i人:bi i + 1人:ai+1 bi+1
由于ai * bi >= ai+1*bi+1,ai bi >= bi,则交换后整体的最大值没有变大,甚至变小
那么我们交换所有逆序对可以得到不比最优解差的解,故我们的贪心策略正确。
cpp要手写高精度
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1005;vector<int> mul(vector<int>& a, int x){int n = a.size(), t = 0;vector<int> ret;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){t += a[i] * x;ret.push_back(t % 10);t /= 10;}while(t) ret.push_back(t % 10), t /= 10;return ret;
}vector<int> div(vector<int>& a, int x){int n = a.size(), t = 0;vector<int> ret;for(int i = n - 1; ~i; i --){t = t * 10 + a[i];ret.push_back(t / x);t %= x;}reverse(ret.begin(), ret.end());while(ret.size() && !ret.back()) ret.pop_back();return ret;
}
vector<int> ma(const vector<int>& a, const vector<int>& b){if(a.size() > b.size()) return a;if(a.size() < b.size()) return b;if(vector<int>(a.rbegin(), a.rend()) > vector<int>(b.rbegin(), b.rend())) return a;return b;
}
int n;
PII w[N];int main(){cin >> n, n ++;for(int i = 0, a, b; i < n; i ++) cin >> a >> b, w[i] = { a, b };sort(w + 1, w + n, [](const PII& a, const PII& b){return a.first * a.second < b.first * b.second;});vector<int> cur(1, 1), res(1, 0);for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){ if(i)res = ma(res, div(cur, w[i].second));cur = mul(cur, w[i].first);/*for(int x : vector<int>(cur.rbegin(), cur.rend()))cout << x;puts("");*/} for(int x : vector<int>(res.rbegin(), res.rend()))cout << x;return 0;
}
不想写高精度就用python3
n = int(input())
n += 1
w = [tuple(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(n)]
cur ,res = w[0][0], 0
for a, b in sorted(w[1::], key=lambda x:x[0]*x[1]):res = max(res, cur // b)cur *= a
print(res)
2.11 耍杂技的牛
125. 耍杂技的牛 - AcWing题库
和上一题很像,这题按照w + s升序排序
和上一题同样的证明思路,不再赘述
n = int(input())
ws = [tuple(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(n)]
pre = 0
ans = -1e18
for w, s in sorted(ws, key=lambda x:x[0]+x[1]):ans = max(ans, pre - s)pre += w
print(ans)
2.12 给树染色
115. 给树染色 - AcWing题库
错误的贪心:从根结点开始扩展,每次取当前最小权值的结点
很容易举出反例,可以自己试一下。
我们可以确定的事情是,当前除去根节点的最大权值结点会在其父节点被染色后立即被染色。
那么我们考虑当前最大结点x,父节点y,和任意结点z,染色顺序无非:
x,y,z,代价为x + 2y + 3z
z,x,y,代价为:z + 2x + 3y
二者做差有:2z - (x + y),可见当z大于x+y的平均值时才会先染x+y
那么我们在考虑当前树中剩余结点时,不妨将x,y当成一个结点,其权值为平均权值,然后就有了做法:
选择当前树中的最大权值,进行染色,由于它和父亲染色顺序为一前一后,所以染色后合并到父亲结点后面
我们合并n - 1次就只剩下一个结点,此时整棵树的染色顺序也就知道了
具体实现时,由于我们并不关心具体染色方案,所以为了简便,我们可以在合并时维护答案
考虑x合并到y上,由于要先染色y,所以x的权值要被加上y的sz次(sz为y结点的大小)
可以用并查集+堆优化到O(nlogn),不过这个数据量没必要,重要的还是这道题的思想
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;const int N = 1005;
const double eps = 1e-6;
struct node{int fa, sz, v;double avg;
}nodes[N];
int n, root, res;int nxt()
{double avg = 0;int res = -1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )if (i != root && nodes[i].avg > avg){avg = nodes[i].avg;res = i;}return res;
}int main(){cin >> n >> root;for(int i = 1, v; i <= n; i ++){cin >> v, res += v;nodes[i] = { -1, 1, v, v };}for(int i = 1, a, b; i < n; i ++){cin >> a >> b;nodes[b].fa = a;}for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++){int t = nxt(), fa = nodes[t].fa;res += nodes[fa].sz * nodes[t].v;nodes[t].avg = -1;for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)if(nodes[j].fa == t) nodes[j].fa = fa;nodes[fa].sz += nodes[t].sz, nodes[fa].v += nodes[t].v, nodes[fa].avg = (double)nodes[fa].v / nodes[fa].sz;}cout << res;return 0;
}
2.13 任务
127. 任务 - AcWing题库
我们发现式子中x对于利润占主导,所以按x从大到小来进行考虑每个任务。对于每个任务从时间满足的机器中选择等级足够且最小的那个。
具体流程如下:
- 按照x对任务和机器排序
- 按x从大到小遍历任务,把时间充足的机器放入集合
- 如果集合中存在等级足够的机器,那么选择等级最小的那个
- 再处理下一个任务时,集合中的机器的时间都是足够的,我们只需考虑等级
时间复杂度:O(nlogn + mlogn)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using i64 = long long;
using PII = std::pair<int, int>;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, M = 1e5 + 10;
int n, m;
PII a[N], b[M];
int main(){std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false), std::cin.tie(0), std::cout.tie(0);while (std::cin >> n >> m){for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) std::cin >> a[i].first >> a[i].second;for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++) std::cin >> b[i].first >> b[i].second;std::sort(a, a + n), std::sort(b, b + m);std::multiset<int> st;i64 cnt = 0, res = 0;for(int i = m - 1, j = n - 1; ~i; i --){while(~j && a[j].first >= b[i].first)st.insert(a[j --].second);auto it = st.lower_bound(b[i].second);if(it != st.end()){cnt ++;res += 500 * b[i].first + 2 * b[i].second;st.erase(it);}}std::cout << cnt << ' ' << res << '\n';}return 0;
}
2.14 能量石
734. 能量石 - AcWing题库
01背包 + 临项交换
先暴力考虑所有情况,即全排列中依次求01背包
那么最优解是否存在某种特性呢?或者说,我们需要考虑的情况的范围能否缩小?
我们考虑最优解,相邻两个能量石s[i], s[i + 1]
二者的收益为:e’[i] + e’[i + 1] - s[i] * l[i + 1]
交换次序:e’[i] + e’[i + 1] - s[i + 1] * l[i]
由于是最优解,所以交换前的收益不小于交换后的收益:s[i] * l[i + 1] <= s[i + 1] * l[i]
那么说明最优解满足两两之间s[i] * l[i + 1] <= s[i + 1] * l[i]
所以我们将能量石按照s[i] / l[i]升序排序,然后跑01背包即可
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define sc scanf
using i64 = long long;
const int N = 105, M = 1e4 + 10;
struct node{int s, e, l;bool operator<(const node& x) const{return s * x.l < x.s * l;}
}nodes[N];int main(){int _ = 1;std::cin >> _;for(int t = 1, n, m; t <= _; t ++){std::cin >> n;m = 0;for(int i = 0, a, b, c; i < n; i ++) std::cin >> a >> b >> c, nodes[i] = { a, b, c }, m += a;std::sort(nodes, nodes + n);std::vector<i64> f(m + 1, -1e8);f[0] = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){auto [s, e, l] = nodes[i];for(int j = m; j >= s; j --){f[j] = std::max(f[j], f[j - s] + e - (j - s) * l);}}printf("Case #%d: %lld\n", t, *std::max_element(f.begin(), f.end()));}return 0;
}
三、总结
很想从上面的问题中提取出某些东西,但是发现没有套路可言,只是遇到贪心问题时有了几个贪心的方向,区间类试着按端点排序,贪心构造,临项交换等等,但具体还得多做题。
![[JAVASE] 类和对象(二)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/74db2fa9a5554ba69739cf276c93590b.png)