文章目录
- 医学图像分割之 Dice Loss
- 1. Dice coefficient 定义
- 1.1. Dice 系数计算示例
- 1.2. Dice-coefficient loss function vs cross-entropy
- 2. Dice 系数的 Pytorch 实现
- 2.1. Dice 系数
- 2.2. Dice Loss
- 2.3. BCELoss2d
- 3. Dice 系数的 Keras 实现
- 4. Dice 系数的 TensorFlow 实现
- 参考资料
医学图像分割之 Dice Loss
在很多关于医学图像分割的竞赛、论文和项目中,发现 Dice 系数(Dice coefficient) 损失函数出现的频率较多,自己也存在关于分割中 Dice Loss 和交叉熵损失函数(cross-entropy loss) 的一些疑问,这里简单整理.
1. Dice coefficient 定义
Dice系数 - 维基百科
Dice系数, 根据 Lee Raymond Dice[1] 命名,是一种集合相似度度量函数,通常用于计算两个样本的相似度(值范围为 [0, 1]):
s = 2 ∣ X ∩ Y ∣ ∣ X ∣ + ∣ Y ∣ s = \frac{2|X\cap Y|}{|X|+|Y|} s=∣X∣+∣Y∣2∣X∩Y∣
|X⋂Y| - X 和 Y 之间的交集;|X| 和 |Y| 分别表示 X 和 Y 的元素个数. 其中,分子中的系数 2,是因为分母存在重复计算 X 和 Y 之间的共同元素的原因.
语义分割问题而言,X - GT 分割图像, Y - Pred 分割图像.
Dice 系数差异函数(Dice loss):
s = 1 − 2 ∣ X ∩ Y ∣ ∣ X ∣ + ∣ Y ∣ s =1- \frac{2|X\cap Y|}{|X|+|Y|} s=1−∣X∣+∣Y∣2∣X∩Y∣
1.1. Dice 系数计算示例
预测的分割图的 dice 系数计算,首先将 |X⋂Y| 近似为预测图与 GT 分割图之间的点乘,并将点乘的元素结果相加:
[1] - Pred 预测分割图与 GT 分割图的点乘:
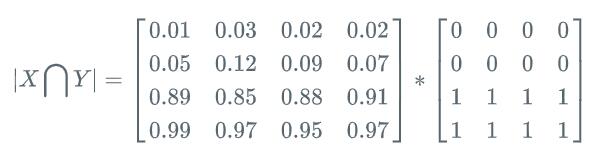
[2] - 逐元素相乘的结果元素的相加和:
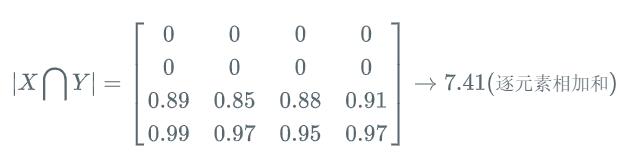
对于二分类问题,GT 分割图是只有 0, 1 两个值的,因此 |X⋂Y| 可以有效的将在 Pred 分割图中未在 GT 分割图中激活的所有像素清零. 对于激活的像素,主要是惩罚低置信度的预测,较高值会得到更好的 Dice 系数.
关于 |X| 和 |Y| 的量化计算,可采用直接简单的元素相加;也有采用取元素平方求和的做法:
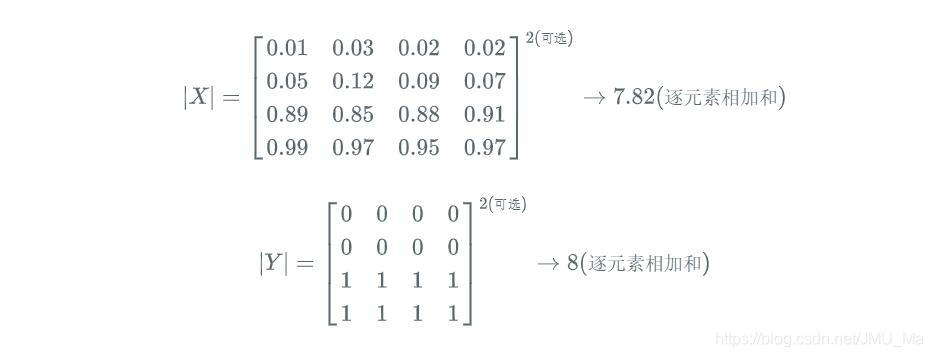
注:dice loss 比较适用于样本极度不均的情况,一般的情况下,使用 dice loss 会对反向传播造成不利的影响,容易使训练变得不稳定.
1.2. Dice-coefficient loss function vs cross-entropy
这是在 stackexchange.com 上一个提问:
Dice-coefficient loss function vs cross-entropy
问题:
在训练像素分割的神经网络时,如 FCN,如何选择交叉熵损失函数还是 Dice-coefficient 损失函数?
回答:
采用交叉熵损失函数,而非 dice-coefficient 和类似 IoU 度量的损失函数,一个令人信服的愿意是其梯度形式更优(the gradients are nicer.)
交叉熵损失函数中交叉熵值关于 logits 的梯度计算形式类似于 p−t ,其中,p 是 softmax 输出;t 为 target.
而关于 dice-coefficient 的可微形式,loss 值为
2 p t p 2 + t 2 或 2 p t p + t \frac{2pt}{p^2+t^2}或\frac{2pt}{p+t} p2+t22pt或p+t2pt
,其关于 p 的梯度形式是比较复杂的:
2 t 2 ( p + t ) 2 或 2 t ( t 2 − p 2 ) ( p 2 + t 2 ) \frac{2t^2}{(p+t)^2}或\frac{2t(t^2-p^2)}{(p^2+t^2)} (p+t)22t2或(p2+t2)2t(t2−p2)
. 极端场景下,当 p 和 t 的值都非常小时,计算得到的梯度值可能会非常大. 通常情况下,可能导致训练更加不稳定.
直接采用 dice-coefficient 或者 IoU 作为损失函数的原因,是因为分割的真实目标就是最大化 dice-coefficient 和 IoU 度量. 而交叉熵仅是一种代理形式,利用其在 BP 中易于最大化优化的特点.
另外,Dice-coefficient 对于类别不均衡问题,效果可能更优. 然而,类别不均衡往往可以通过简单的对于每一个类别赋予不同的 loss 因子,以使得网络能够针对性的处理某个类别出现比较频繁的情况. 因此,对于 Dice-coefficient 是否真的适用于类别不均衡场景,还有待探讨.
2. Dice 系数的 Pytorch 实现
2.1. Dice 系数
# https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/1249
def dice_coeff(pred, target):smooth = 1.num = pred.size(0)m1 = pred.view(num, -1) # Flattenm2 = target.view(num, -1) # Flattenintersection = (m1 * m2).sum()return (2. * intersection + smooth) / (m1.sum() + m2.sum() + smooth)
2.2. Dice Loss
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as Fclass SoftDiceLoss(nn.Module):def __init__(self, weight=None, size_average=True):super(SoftDiceLoss, self).__init__()def forward(self, logits, targets):num = targets.size(0)smooth = 1probs = F.sigmoid(logits)m1 = probs.view(num, -1)m2 = targets.view(num, -1)intersection = (m1 * m2)score = 2. * (intersection.sum(1) + smooth) / (m1.sum(1) + m2.sum(1) + smooth)score = 1 - score.sum() / numreturn score
2.3. BCELoss2d
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as Fclass BCELoss2d(nn.Module):def __init__(self, weight=None, size_average=True):super(BCELoss2d, self).__init__()self.bce_loss = nn.BCELoss(weight, size_average)def forward(self, logits, targets):probs = F.sigmoid(logits) # 二分类问题,sigmoid等价于softmaxprobs_flat = probs.view(-1)targets_flat = targets.view(-1)return self.bce_loss(probs_flat, targets_flat)
3. Dice 系数的 Keras 实现
From:Dice’s coefficient 实现
smooth = 1. # 用于防止分母为0.
def dice_coef(y_true, y_pred):y_true_f = K.flatten(y_true) # 将 y_true 拉伸为一维.y_pred_f = K.flatten(y_pred)intersection = K.sum(y_true_f * y_pred_f)return (2. * intersection + smooth) / (K.sum(y_true_f * y_true_f) + K.sum(y_pred_f * y_pred_f) + smooth)def dice_coef_loss(y_true, y_pred):return 1. - dice_coef(y_true, y_pred)
4. Dice 系数的 TensorFlow 实现
def dice_coe(output, target, loss_type='jaccard', axis=(1, 2, 3), smooth=1e-5):"""Soft dice (Sørensen or Jaccard) coefficient for comparing the similarity of two batch of data, usually be used for binary image segmentationi.e. labels are binary. The coefficient between 0 to 1, 1 means totally match.Parameters-----------output : TensorA distribution with shape: [batch_size, ....], (any dimensions).target : TensorThe target distribution, format the same with `output`.loss_type : str``jaccard`` or ``sorensen``, default is ``jaccard``.axis : tuple of intAll dimensions are reduced, default ``[1,2,3]``.smooth : floatThis small value will be added to the numerator and denominator.- If both output and target are empty, it makes sure dice is 1.- If either output or target are empty (all pixels are background), dice = ```smooth/(small_value + smooth)``, then if smooth is very small, dice close to 0 (even the image values lower than the threshold), so in this case, higher smooth can have a higher dice.Examples--------->>> outputs = tl.act.pixel_wise_softmax(network.outputs)>>> dice_loss = 1 - tl.cost.dice_coe(outputs, y_)References------------ `Wiki-Dice <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sørensen–Dice_coefficient>`__"""inse = tf.reduce_sum(output * target, axis=axis)if loss_type == 'jaccard':l = tf.reduce_sum(output * output, axis=axis)r = tf.reduce_sum(target * target, axis=axis)elif loss_type == 'sorensen':l = tf.reduce_sum(output, axis=axis)r = tf.reduce_sum(target, axis=axis)else:raise Exception("Unknow loss_type")dice = (2. * inse + smooth) / (l + r + smooth)dice = tf.reduce_mean(dice)return dice
参考资料
医学图像分割常用的损失函数
Dice系数 - 维基百科
图像分割结果的评估—DICE参数