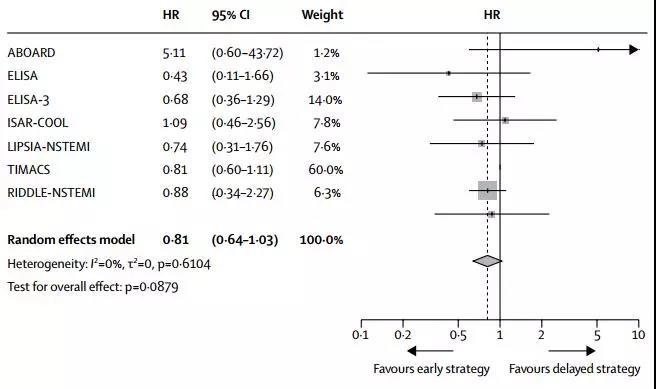
孤立森林算法sklearn实现,源码分析
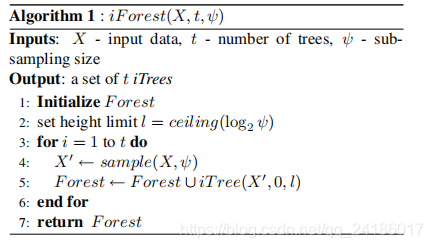
算法一: 首先初始化一些参数
class sklearn.ensemble.IsolationForest(n_estimators=100, max_samples=’auto’, contamination=’legacy’, max_features=1.0, bootstrap=False, n_jobs=None, behaviour=’old’, random_state=None, verbose=0)
参数解释:n_estimators = 构建多少个itree
max_samples=采样数,自动是256
contamination=c(n)默认为0.1
max_features=最大特征数 默认为1
bootstrap=构建Tree时,下次是否替换采样,为True为替换,为False为不替换
n_jobs=fit和perdict执行时的并行数
第二步进行fit训练:def fit(self, X, y=None, sample_weight=None):
其中max_samples:
if self.max_samples == 'auto':
max_samples = min(256, n_samples) #如果输入的采样数大于256,就选择256,小于256选择输入的max_samples
itree的最大路径为:max_depth = int(np.ceil(np.log2(max(max_samples, 2))))
然后将max_samples,max_depth,X,sample_weight 传入
super(IsolationForest, self)._fit(X, y, max_samples,max_depth=max_depth,sample_weight=sample_weight)
进行统计:使用Scipy我们很方便的得到数据所在区域中某一百分比处的数值
self.threshold_ = -sp.stats.scoreatpercentile(-self.decision_function(X), 100. * (1. - self.contamination))
return selffit方法就此结束了,下面是创建树也是进行分类的过程。
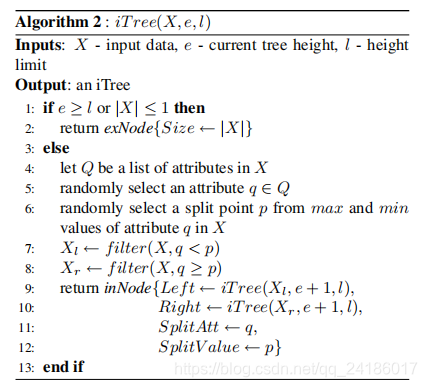
def decision_function(self, X):
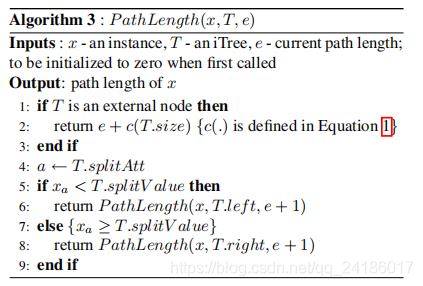
未完待续