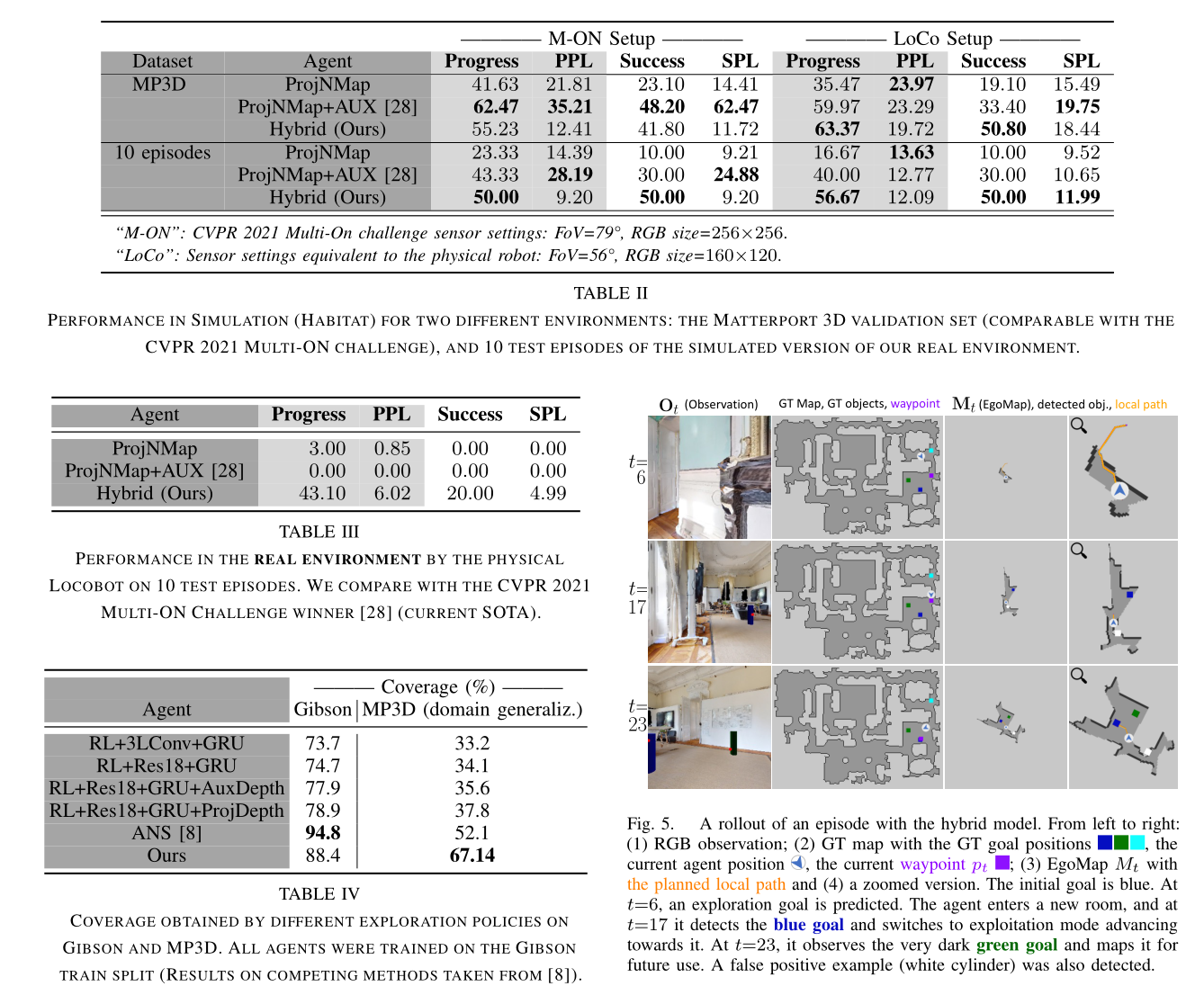
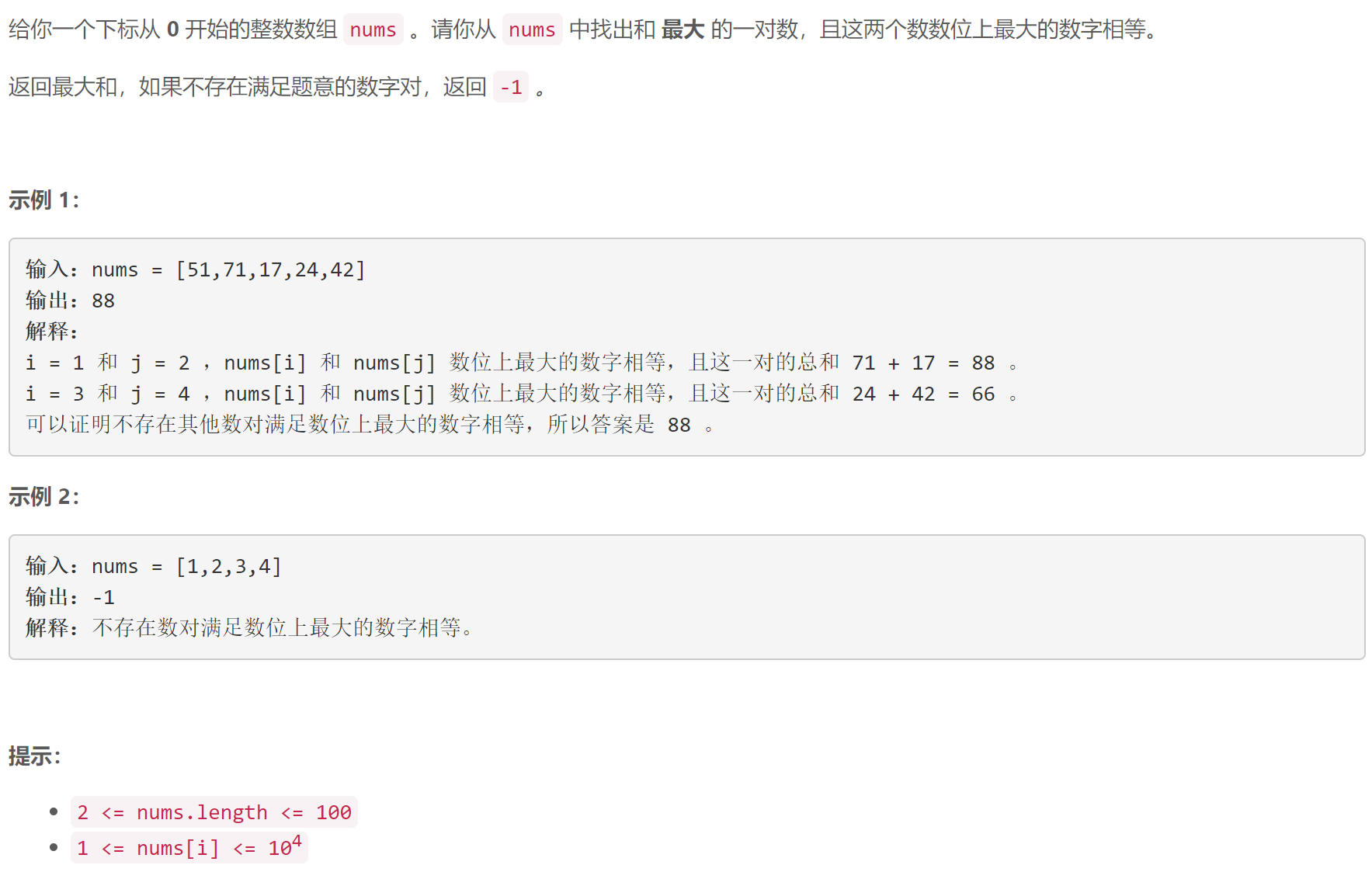
A 数组中的最大数对和
数据范围小,直接暴力枚举数对
class Solution {
public:int mx(int x) {//返回10进制表示的数的最大数字int res = 0;for (; x; x /= 10)res = max(res, x % 10);return res;}int maxSum(vector<int> &nums) {int n = nums.size();int res = -1;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int cur = mx(nums[i]);for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {int temp = mx(nums[j]);if (cur == temp)res = max(res, nums[i] + nums[j]);}}return res;}
};
B 翻倍以链表形式表示的数字

借助栈反序遍历链表,模拟乘2的过程
class Solution {
public:ListNode *doubleIt(ListNode *head) {stack<ListNode *> st;for (ListNode *cur = head; cur; cur = cur->next)st.push(cur);int c = 0;//是否进位while (!st.empty()) {auto t = st.top();st.pop();int nc = (t->val * 2 + c) / 10;t->val = (t->val * 2 + c) % 10;c = nc;}if (c)head = new ListNode(1, head);return head;}
};
C 限制条件下元素之间的最小绝对差

有序集合:设 l < r l<r l<r,枚举 r r r,同时用有序集合维护所有满足 r − l ≥ x r-l\ge x r−l≥x的 n u m s [ l ] nums[l] nums[l],在集合中查找最接近 n u m s [ r ] nums[r] nums[r]的数。
class Solution {
public:int minAbsoluteDifference(vector<int> &nums, int x) {int res = INT32_MAX;set<int> s;for (int r = x, l = 0; r < nums.size(); r++, l++) {s.insert(nums[l]);auto it = s.upper_bound(nums[r]);if (it != s.end())res = min(res, *it - nums[r]);if (it != s.begin())res = min(res, nums[r] - *prev(it));}return res;}
};
D 操作使得分最大


质因数分解+单调栈+快速幂:
1)首先通过质因数分解计算数组中每个元素的质数分数。
2)不妨设一个存在多个最大质数分数的子数组中最大质数分数的贡献来自有最大质数分数且下标最小的一个元素,设当前位置为 i i i,设 i i i左边第一个大于等于 n u m s [ i ] nums[i] nums[i]的位置为 l [ i ] l[i] l[i],设 i i i右边第一个大于 n u m s [ i ] nums[i] nums[i]的位置为 r [ i ] r[i] r[i],则子数组的最大质数分数贡献来自于 n u m s [ i ] nums[i] nums[i]的子数组的个数为 ( i − l [ i ] ) × ( r [ i ] − i ) (i-l[i])\times(r[i]-i) (i−l[i])×(r[i]−i),通过单调栈来求 l l l和 r r r数组。
3)将各项为(元素,元素作为最大质数分数产生贡献的子数组数目)的数组按元素大小降序排序,然后遍历数组,用快速幂更新答案同时更新 k k k。
class Solution {
public:typedef long long ll;ll mod = 1e9 + 7;int maximumScore(vector<int> &nums, int k) {int n = nums.size();vector<int> score(n);//质数分数for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)score[i] = get_score(nums[i]);vector<int> l(n, -1);//初始化边界stack<int> st;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {while (!st.empty() && score[st.top()] < score[i])st.pop();if (!st.empty())l[i] = st.top();st.push(i);}st = stack<int>();vector<int> r(n, n);//初始化边界for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {while (!st.empty() && score[st.top()] <= score[i])st.pop();if (!st.empty())r[i] = st.top();st.push(i);}vector<pair<int, ll>> li(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)li[i] = {nums[i], 1LL * (i - l[i]) * (r[i] - i)};//(元素, 元素作为最大质数分数产生贡献的子数组数目)sort(li.begin(), li.end(), greater<>());//按元素大小降序排序ll res = 1;for (int i = 0; k; i++) {int t = min((ll) k, li[i].second);res = res * fpow(li[i].first, t) % mod;k -= t;}return (res + mod) % mod;}int get_score(int x) {int res = 0;for (int i = 2; i * i <= x; i++)//质因数分解if (x % i == 0) {res++;while (x % i == 0)x /= i;}if (x > 1)res++;return res;}ll fpow(ll x, ll n) {//快速幂ll res = 1;for (ll e = x; n; n >>= 1, e = (e * e) % mod)if (n & 1)res = res * e % mod;return res;}
};