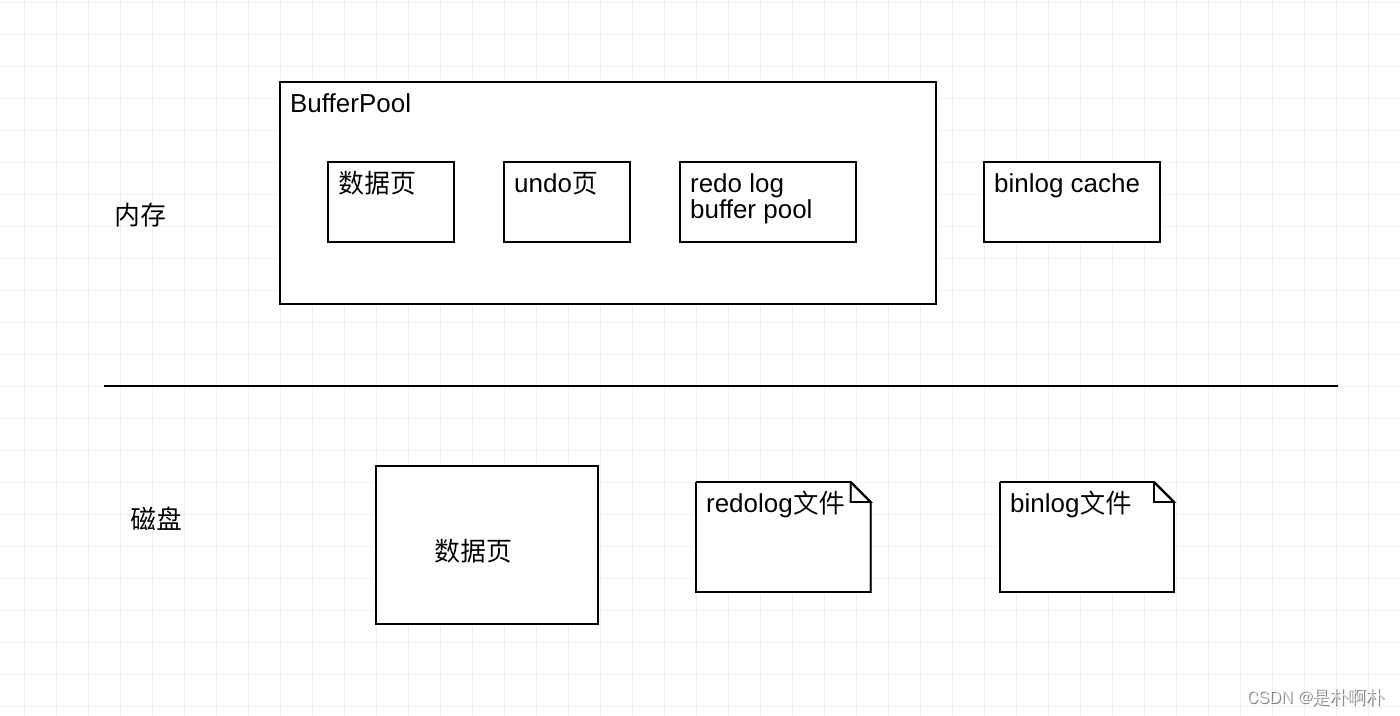
一、准备数据

【效果展示】
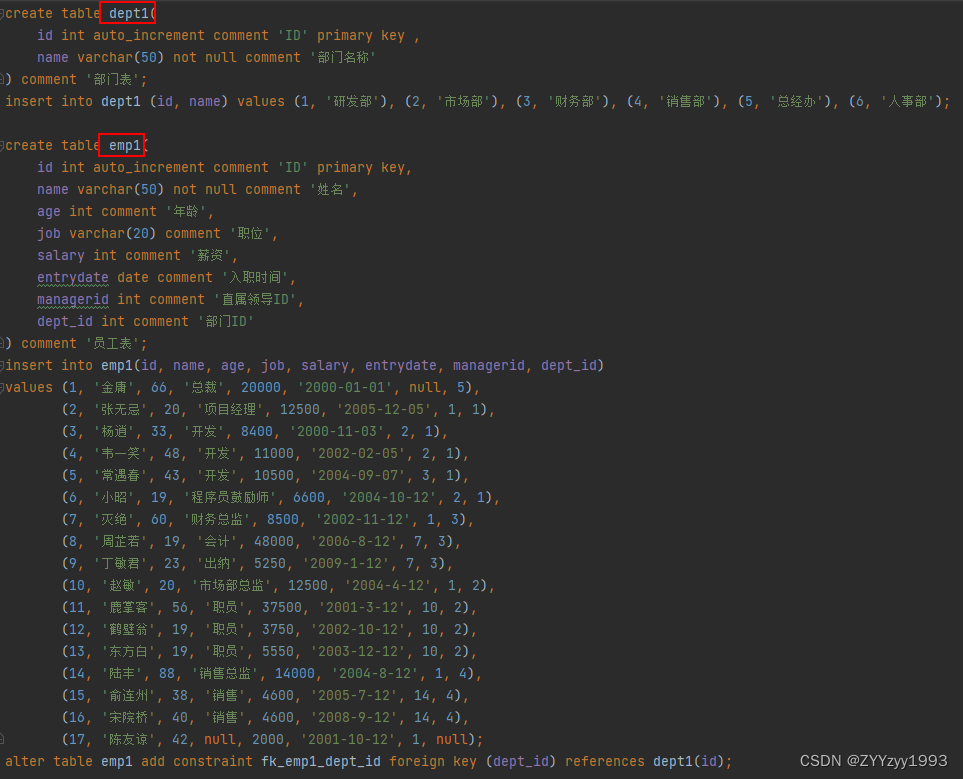
emp1表(员工表):

dept1表(部门表):

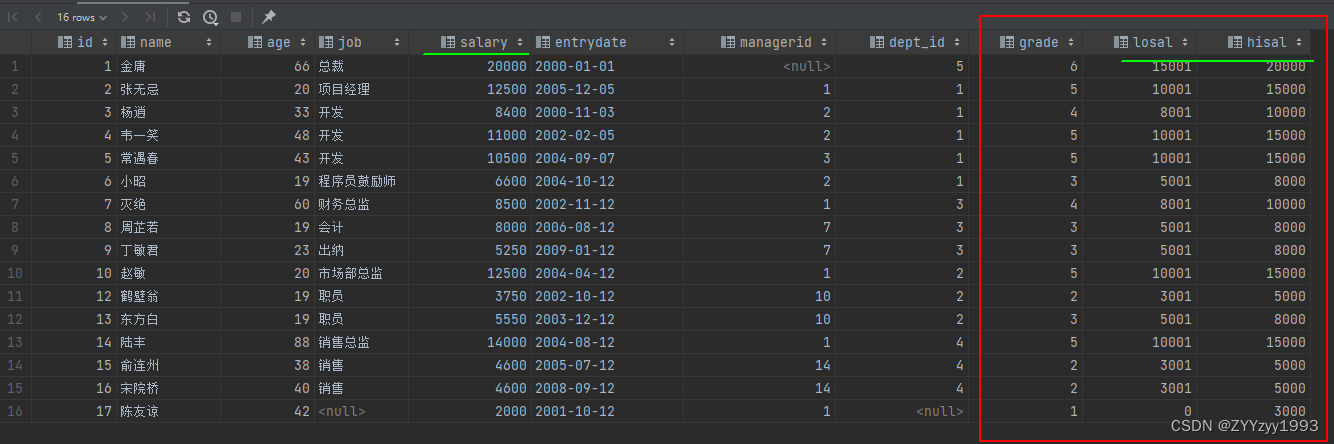
salgrade表(薪资等级表):

二、案例
1、查询员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(隐式内连接) 


2、查询 年龄小于30岁的 员工姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(显式内连接)
![]()


3、查询拥有员工的部门ID、部门名称(内连接)
id为6人事部下没有员工 —> 要查拥有员工的部门信息 —> 部门表和员工表交集部分的数据
(1)查询员工和部门的交集

![]()

(2)对结果去重:distinct

![]()

4、查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工,及其归属的部门名称;如果员工没有分配部门,也需要展示出来(外连接)


5、查询所有员工的工资等级 没有外键关联
-- 表结构:emp1, salgrade
-- 连接条件:emp1.salary >= salgrade.losal and emp1.salary <= salgrade.hisal
-- 内连接:select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件
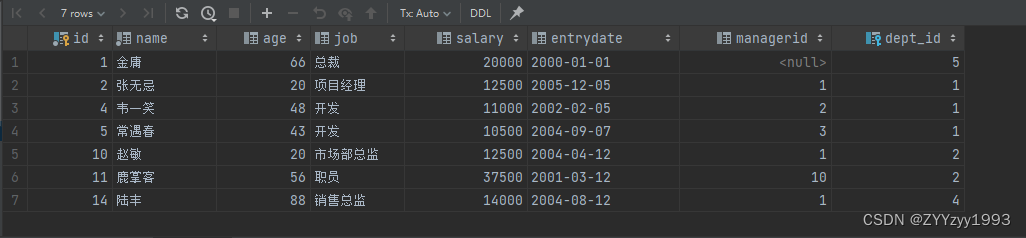
6、查询“研发部”所有员工的信息及工资等级
-- 表结构:emp1, dept1, salgrade
-- 连接条件:emp1.salary between salgrade.losal and salgrade.hisal, emp1.dept_id = dept1.id
-- 内连接:select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件
-- 查询条件:dept1.name = '研发部'
【代码格式化】

7、查询“研发部”员工的平均工资(聚合函数avg())
-- 表结构:emp1, dept1
-- 连接条件:emp1.dept_id = dept1.id
-- 内连接:select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件
-- 查询条件:dept1.name = '研发部'
-- 平均数的聚合函数:avg()
![]()

【聚合函数复习】

8、查询工资比“灭绝”高的员工信息(子查询-标量子查询)
-- a.查询灭绝的薪资
![]()

-- b.查询比她工资高的员工数据
9、查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
-- a.查询平均薪资 聚合函数avg()
![]()

-- b.查询比平均薪资高的员工信息 子查询-标量子查询
10、查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
-- a.查询指定部门平均薪资(特殊值:1)![]()
-- b.查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息

11、查询所有的部门信息,并统计部门的员工人数(select后-子查询)
-- a.统计ID为1的部门的员工人数 聚合函数count()![]()
-- b.查询所有部门信息![]()
-- c.统计所有部门的员工人数 子查询-标量子查询

12、查询所有学生的选课情况,展示出学生名称、学号、课程名称 (三表联查)
-- 表结构:student, course, student_course
-- 连接条件:student.id = student_course.studentid, course.id = student_course.courseid
-- 内连接:select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件 ![]()
【数据准备】
-- 多表关系演示(多对多)
create table student(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '姓名',no varchar(10) comment '学号'
) comment '学生表';
insert into student
values (null, '黛绮丝', '2000100101'),(null, '谢逊', '2000100102'),(null, '殷天正', '2000100103'),(null, '韦一笑', '2000100104');create table course(id int auto_increment primary key comment '主键ID',name varchar(10) comment '课程名称'
) comment '课程表';
insert into course
values (null, 'Java'),(null, 'PHP'),(null, 'MySQL'),(null, 'Hadoop');create table student_course(id int auto_increment comment '主键' primary key ,studentid int not null comment '学生ID',courseid int not null comment '课程ID',constraint fk_courseid foreign key (courseid) references course(id),constraint fk_studentid foreign key (studentid) references student(id)
) comment '学生课程中间表';
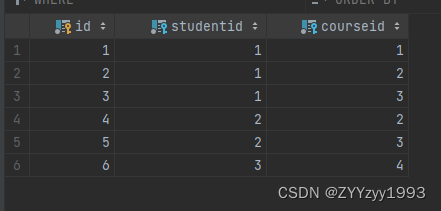
insert into student_course
values (null, 1, 1),(null, 1, 2),(null, 1, 3),(null, 2, 2),(null, 2, 3),(null, 3, 4);【效果】
student表:

course表:

student_course表:
【表关系查看】


【代码】
-- -------------------------------- 多表查询练习 --------------------------------
-- 准备数据
create table salgrade(grade int,losal int,hisal int
) comment '薪资等级表';insert into salgrade values (1, 0, 3000);
insert into salgrade values (2, 3001, 5000);
insert into salgrade values (3, 5001, 8000);
insert into salgrade values (4, 8001, 10000);
insert into salgrade values (5, 10001, 15000);
insert into salgrade values (6, 15001, 20000);
insert into salgrade values (7, 20001, 25000);
insert into salgrade values (8, 25001, 30000);-- 1、查询员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(隐式内连接)
-- select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件
select e.name, e.age, e.job, d.name from emp1 e, dept1 d where e.dept_id = d.id;-- 2、查询 年龄小于30岁的 员工姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(显式内连接)
-- select ... from 表1 join 表2 on 连接条件
select e.name, e.age, e.job, d.name from emp1 e join dept1 d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age < 30;-- 3、查询拥有员工的部门ID、部门名称(内连接)
-- a.查询员工和部门的交集——内连接
select d.id, d.name from emp1 e, dept1 d where e.dept_id = d.id;
-- b.对结果去重:distinct
select distinct d.id, d.name from emp1 e, dept1 d where e.dept_id = d.id;-- 4、查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工,及其归属的部门名称;如果员工没有分配部门,也需要展示出来(外连接)
-- select ... from 表1 left join 表2 on 连接条件
select e.*, d.name from emp1 e left join dept1 d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age > 40;-- 5、查询所有员工的工资等级 没有外键关联
-- 表结构:emp1, salgrade
-- 连接条件:emp1.salary >= salgrade.losal and emp1.salary <= salgrade.hisal
-- 内连接:select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件
select e.*, s.grade, s.losal, s.hisal from emp1 e, salgrade s where e.salary >= s.losal and e.salary <= s.hisal;
select e.*, s.grade, s.losal, s.hisal from emp1 e, salgrade s where e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal;-- 6、查询“研发部”所有员工的信息及工资等级
-- 表结构:emp1, dept1, salgrade
-- 连接条件:emp1.salary between salgrade.losal and salgrade.hisal, emp1.dept_id = dept1.id
-- 内连接:select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件
-- 查询条件:dept1.name = '研发部'
select e.*, s.grade
from emp1 e,dept1 d,salgrade s
where e.dept_id = d.idand (e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal)and d.name = '研发部';-- 7、查询“研发部”员工的平均工资
-- 表结构:emp1, dept1
-- 连接条件:emp1.dept_id = dept1.id
-- 内连接:select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件
-- 查询条件:dept1.name = '研发部'
-- 平均数的聚合函数:avg()
select avg(e.salary) from emp1 e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id and d.name = '研发部';-- 8、查询工资比“灭绝”高的员工信息
-- a.查询灭绝的薪资
select salary from emp1 where name = '灭绝'; -- 返回8500
-- b.查询比她工资高的员工数据
select * from emp1 where salary > (select salary from emp1 where name = '灭绝');-- 9、查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
-- a.查询平均薪资
select avg(emp1.salary) from emp1; -- 返回10308.8235
-- b.查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
select * from emp1 where salary > (select avg(emp1.salary) from emp1);-- 10、查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
-- a.查询指定部门平均薪资(特殊值:1)
select avg(e.salary) from emp1 e where e.dept_id = 1; -- 返回9800
-- b.查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
select emp1.*, (select avg(e.salary) from emp1 e where e.dept_id = emp1.dept_id) '平均薪资'
from emp1
where emp1.salary < (select avg(e.salary) from emp1 e where e.dept_id = emp1.dept_id);-- 11、查询所有的部门信息,并统计部门的员工人数(select后-子查询)
-- a.统计ID为1的部门的员工人数
select count(*) from emp1 where dept_id = 1; -- 返回5
-- b.查询所有部门信息
select id, name from dept1;
-- c.统计所有部门的员工人数
select dept1.id, dept1.name, (select count(*) from emp1 where emp1.dept_id = dept1.id) '人数' from dept1;-- 12、查询所有学生的选课情况,展示出学生名称、学号、课程名称 (学生和课程是多对多的关系)1个学生可以选多个课程,1个课程也可以被多个学生选择
-- 表结构:student, course, student_course
-- 连接条件:student.id = student_course.studentid, course.id = student_course.courseid
-- 内连接:select ... from 表1, 表2 where 连接条件
select s.name, s.no, c.name from student s, course c, student_course sc where s.id = sc.studentid and c.id = sc.courseid;