ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架

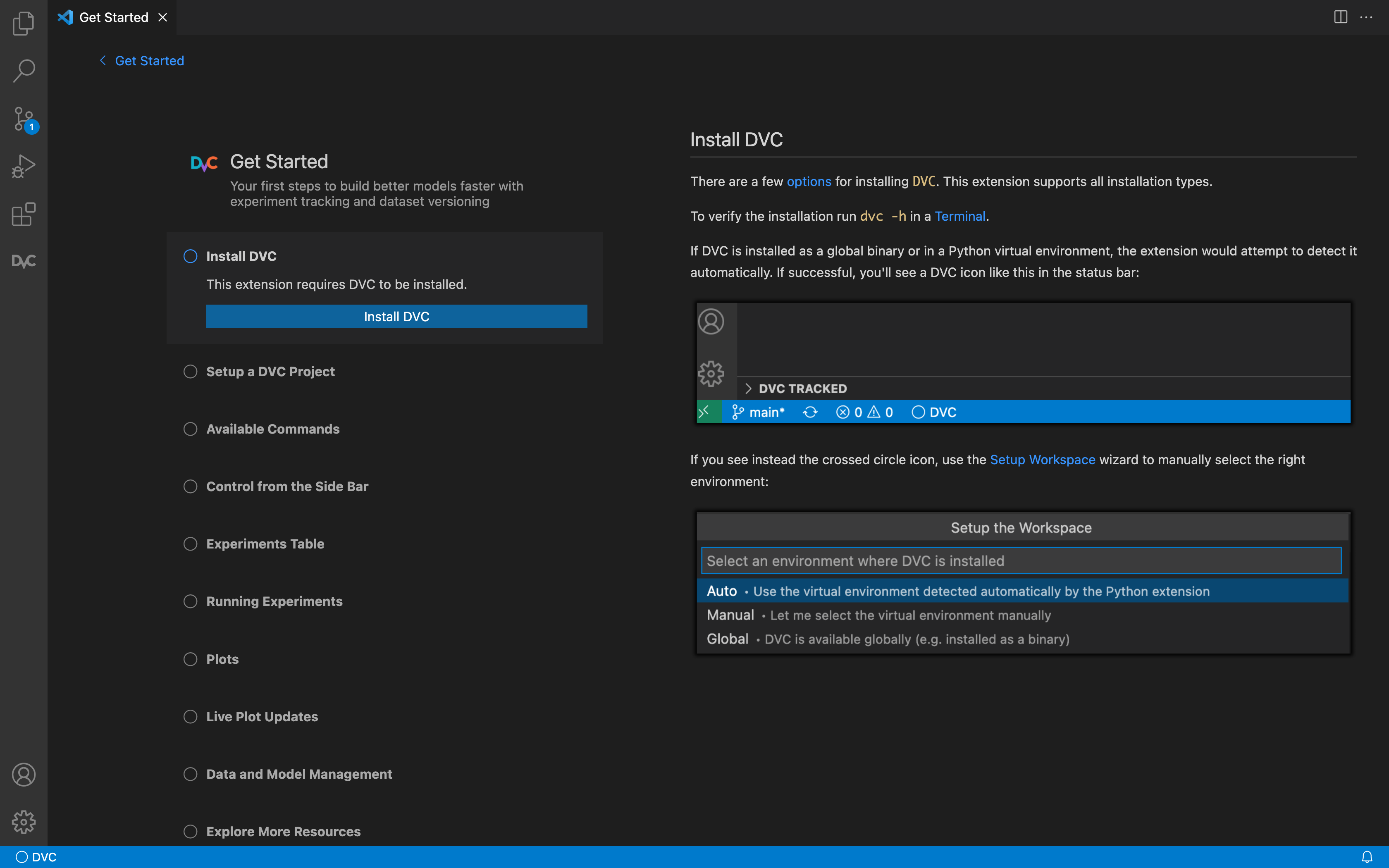
工具:Visual Studio Code的DVC扩展,用于版本管理、实验管理、数据流程可视化
‘DVC Extension for Visual Studio Code - Machine learning experiment tracking and data versioning with DVC extension for VS Code’ by Iterative
GitHub: https://github.com/iterative/vscode-dvc

工具平台:Mage - 开源数据管理平台,可用来清洗数据,为训练AI/ML模型做准备
‘Mage - Mage is an open-source data management platform that helps you clean data and prepare it for training AI/ML models.’
GitHub: https://github.com/mage-ai/mage-ai




工具框架:Torch Points3D - 点云深度学习统一框架
《Torch Points3D — A unifying framework for deep learning on point clouds》by Nicolas Chaulet
GitHub: https://github.com/nicolas-chaulet/torch-points3d


工具库:torchsnapshot - 用于为PyTorch大规模分布式训练工作负载提供容错能力的轻量库
‘torchsnapshot - A light-weight library for adding fault tolerance to large-scale PyTorch distributed training workloads.’ by Meta Research
GitHub: https://github.com/facebookresearch/torchsnapshot


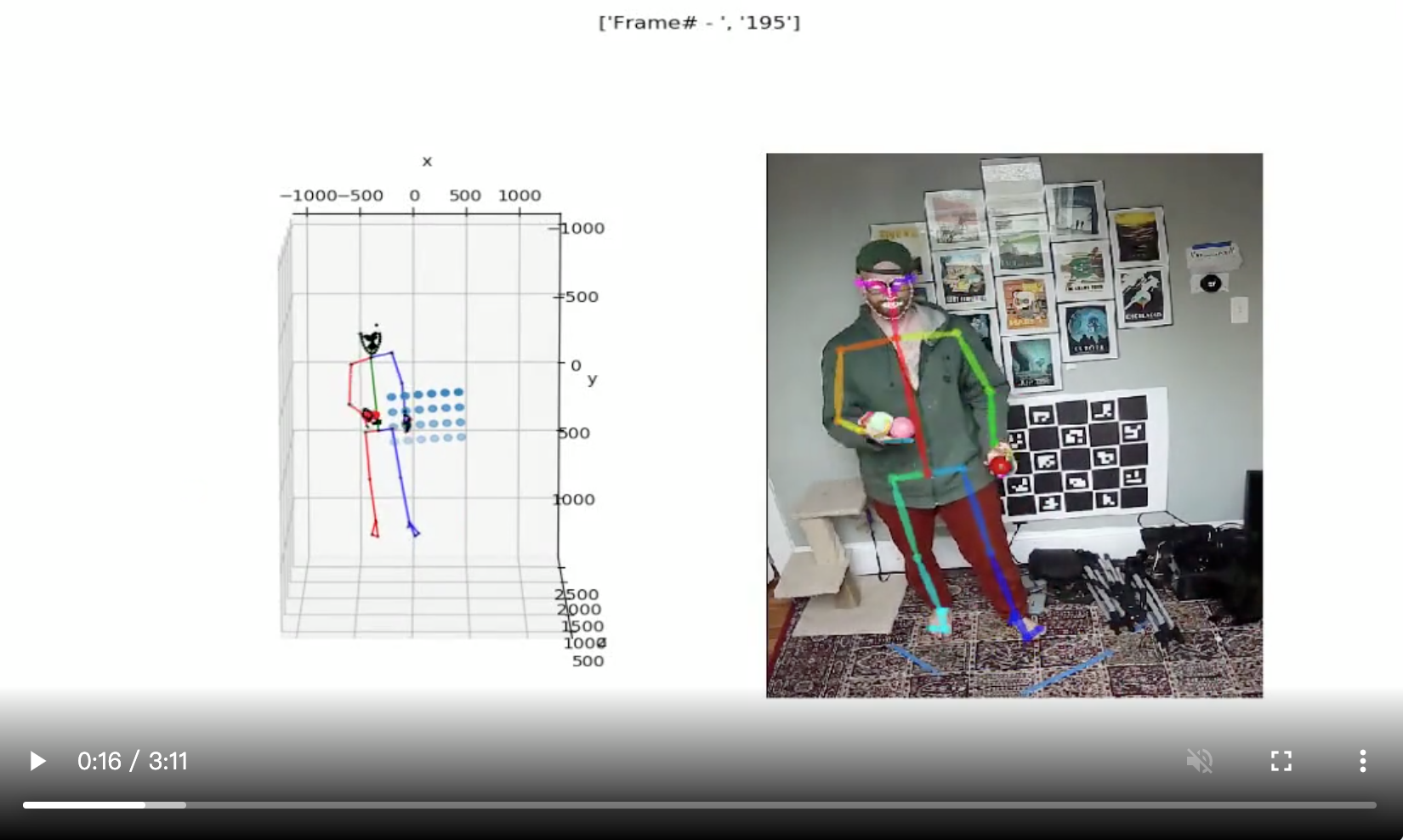
工具库:freemocap - 3D人体骨架检测
‘freemocap - Free like Freedom’ by jonmatthis
GitHub: https://github.com/jonmatthis/freemocap


工具:Beekeeper Studio - 一款开源的跨平台 SQL 编辑器
Beekeeper Studio提供 SQL 语法高亮、自动补全、数据表内容筛选与过滤、连接 Web 数据库、存储历史查询记录等功能。
支持 SQLite、MySQL、MariaDB、Postgres 等主流数据库,并兼容 Windows、macOS、Linux 等桌面操作系统。
GitHub: https://github.com/beekeeper-studio/beekeeper-studio

2.博文&分享

免费书籍:南瓜书PumpkinBook
地址: https://datawhalechina.github.io/pumpkin-book/#/
“周志华老师的《机器学习》(西瓜书)是机器学习领域的经典入门教材之一,周老师为了使尽可能多的读者通过西瓜书对机器学习有所了解, 所以在书中对部分公式的推导细节没有详述,但是这对那些想深究公式推导细节的读者来说可能“不太友好”,本书旨在对西瓜书里比较难理解的公式加以解析,以及对部分公式补充具体的推导细节。”

3.数据&资源

资源列表:计算机视觉最佳实践、代码示例和相关文档
‘Computer Vision - Best Practices, code samples, and documentation for Computer Vision.’ by Microsoft
GitHub: https://github.com/microsoft/computervision-recipes


课程资料:STAT 991 - Topics In Modern Statistical Learning (UPenn, 2022 Spring):UPenn现代统计学习专题课程资料
‘STAT 991: Topics In Modern Statistical Learning (UPenn, 2022 Spring) - focus on uncertainty quantification’ by Edgar Dobriban
GitHub: https://github.com/dobriban/Topics-In-Modern-Statistical-Learning

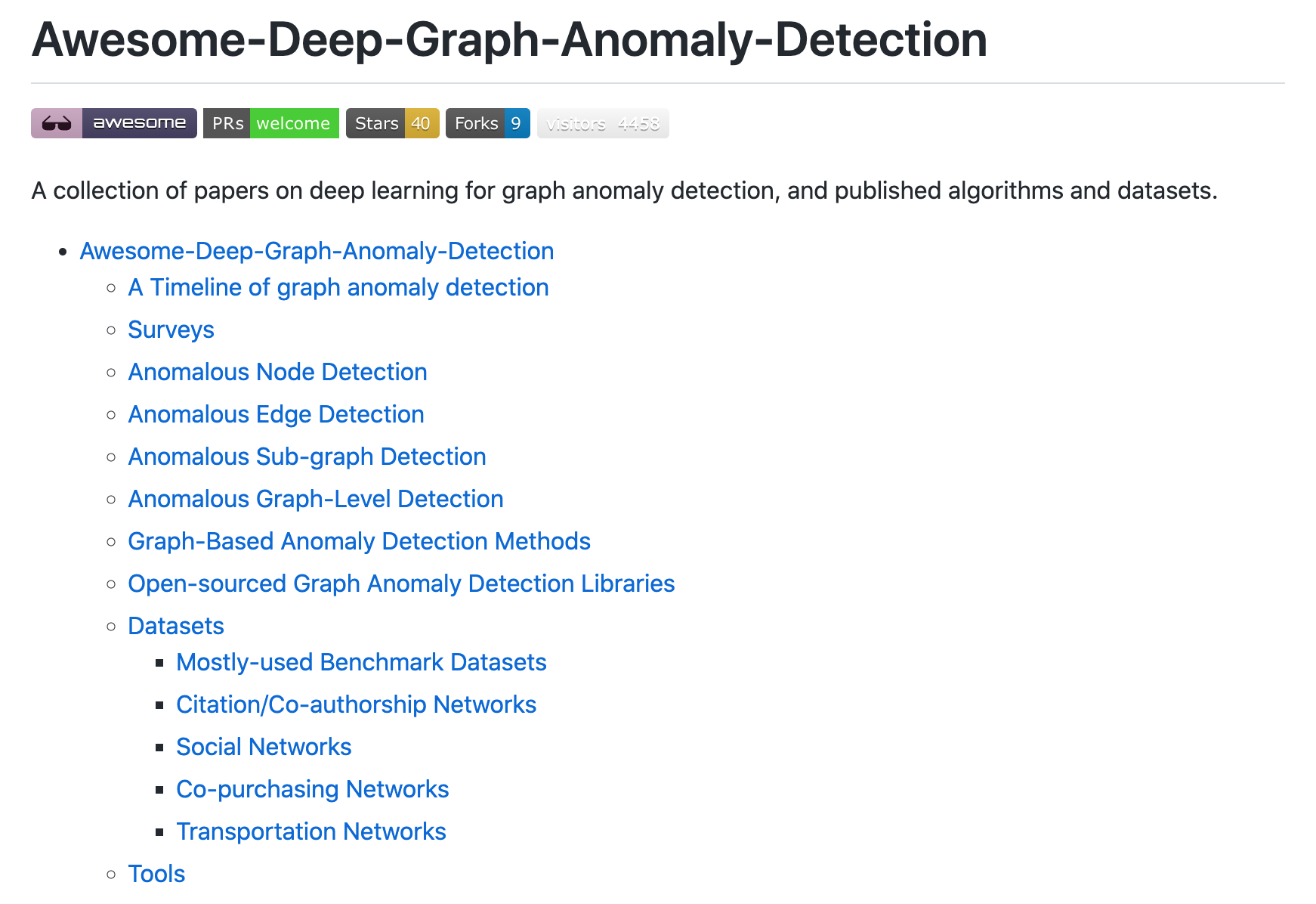
资源列表:深度学习图异常检测文献资源列表
'Awesome-Deep-Graph-Anomaly-Detection - Awesome graph anomaly detection techniques built based on deep learning frameworks. ’ by XiaoxiaoMa-MQ
GitHub: https://github.com/XiaoxiaoMa-MQ/Awesome-Deep-Graph-Anomaly-Detection

4.研究&论文

可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
论文:ReCo: Retrieve and Co-segment for Zero-shot Transfer
论文标题:ReCo: Retrieve and Co-segment for Zero-shot Transfer
论文时间:14 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Semantic Segmentation,Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation,语义分割,无监督语义分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.07045
代码实现:https://github.com/NoelShin/reco
论文作者:Gyungin Shin, Weidi Xie, Samuel Albanie
论文简介:Semantic segmentation has a broad range of applications, but its real-world impact has been significantly limited by the prohibitive annotation costs necessary to enable deployment. / 语义分割具有广泛的应用,但其对现实世界的应用部署受到所需的高昂注释成本显着限制。
论文摘要:Semantic segmentation has a broad range of applications, but its real-world impact has been significantly limited by the prohibitive annotation costs necessary to enable deployment. Segmentation methods that forgo supervision can side-step these costs, but exhibit the inconvenient requirement to provide labelled examples from the target distribution to assign concept names to predictions. An alternative line of work in language-image pre-training has recently demonstrated the potential to produce models that can both assign names across large vocabularies of concepts and enable zero-shot transfer for classification, but do not demonstrate commensurate segmentation abilities. In this work, we strive to achieve a synthesis of these two approaches that combines their strengths. We leverage the retrieval abilities of one such language-image pre-trained model, CLIP, to dynamically curate training sets from unlabelled images for arbitrary collections of concept names, and leverage the robust correspondences offered by modern image representations to co-segment entities among the resulting collections. The synthetic segment collections are then employed to construct a segmentation model (without requiring pixel labels) whose knowledge of concepts is inherited from the scalable pre-training process of CLIP. We demonstrate that our approach, termed Retrieve and Co-segment (ReCo) performs favourably to unsupervised segmentation approaches while inheriting the convenience of nameable predictions and zero-shot transfer. We also demonstrate ReCo’s ability to generate specialist segmenters for extremely rare objects.
语义分割具有广泛的应用,但其现实世界的应用部署受到所需的高昂注释成本显着限制。放弃监督的分割方法可以回避这些成本,但表现出不方便的要求,即提供来自目标分布的标记示例以将概念名称分配给预测。语言-图像预训练的另一项工作最近证明了生成模型的潜力,这些模型既可以跨大型概念词汇表分配名称,又可以实现零样本迁移以进行分类,但不能表现出相应的分割能力。在这项工作中,我们努力实现这两种方法的结合,综合它们的优势。我们利用这样一种语言图像预训练模型 CLIP 的检索能力,从未标记图像中为任意概念名称集合动态管理训练集,并利用现代图像表示提供的鲁棒对应关系来共同分割实体之间的实体。然后使用合成的分段集合来构建分段模型(不需要像素标签),其概念知识继承自 CLIP 的可扩展预训练过程。我们证明了我们的方法,称为检索和协同分割(ReCo),优于无监督分割方法,同时继承了可命名预测和零样本迁移的便利性。我们还展示了 ReCo 极其稀有的物体生成专业分割器的能力。



论文:DoWhy-GCM: An extension of DoWhy for causal inference in graphical causal models
论文标题:DoWhy-GCM: An extension of DoWhy for causal inference in graphical causal models
论文时间:14 Jun 2022
所属领域:归因分析
对应任务:归因分析
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.06821
代码实现:https://github.com/py-why/dowhy
论文作者:Patrick Blöbaum, Peter Götz, Kailash Budhathoki, Atalanti A. Mastakouri, Dominik Janzing
论文简介:We introduce DoWhy-GCM, an extension of the DoWhy Python library, that leverages graphical causal models. / 我们带来了DoWhy-GCM,它是 DoWhy Python 库的扩展,它利用了图因果模型。
论文摘要:We introduce DoWhy-GCM, an extension of the DoWhy Python library, that leverages graphical causal models. Unlike existing causality libraries, which mainly focus on effect estimation questions, with DoWhy-GCM, users can ask a wide range of additional causal questions, such as identifying the root causes of outliers and distributional changes, causal structure learning, attributing causal influences, and diagnosis of causal structures. To this end, DoWhy-GCM users first model cause-effect relations between variables in a system under study through a graphical causal model, fit the causal mechanisms of variables next, and then ask the causal question. All these steps take only a few lines of code in DoWhy-GCM. The library is available at https://github.com/py-why/dowhy
我们带来了 DoWhy-GCM,它是 DoWhy Python 库的扩展,它利用了图因果模型。 与主要关注效果估计问题的现有因果关系库不同,使用 DoWhy-GCM,用户可以提出广泛的附加因果问题,例如识别异常值和分布变化的根本原因、因果结构学习、归因因果影响以及因果结构的诊断。 为此,DoWhy-GCM 用户首先通过图因果模型对所研究系统中变量之间的因果关系进行建模,然后拟合变量的因果机制,然后提出因果问题。 所有这些步骤在 DoWhy-GCM 中只需要几行代码。 该库位于 https://github.com/py-why/dowhy


论文:LST: Ladder Side-Tuning for Parameter and Memory Efficient Transfer Learning
论文标题:LST: Ladder Side-Tuning for Parameter and Memory Efficient Transfer Learning
论文时间:13 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉,自然语言处理
对应任务:Transfer Learning,Visual Question Answering,VQA,迁移学习,视觉问答
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.06522
代码实现:https://github.com/ylsung/ladder-side-tuning
论文作者:Yi-Lin Sung, Jaemin Cho, Mohit Bansal
论文简介:LST saves 69% of the memory costs to fine-tune the whole network, while other methods only save 26% of that in similar parameter usages (hence, 2. 7x more memory savings). / LST 为微调整个网络节省了 69% 的内存成本,而其他方法在类似的参数使用情况下仅节省了 26%(因此,节省了 2. 7 倍的内存)。
论文摘要:Fine-tuning large pre-trained models on downstream tasks has been adopted in a variety of domains recently. However, it is costly to update the entire parameter set of large pre-trained models. Although recently proposed parameter-efficient transfer learning (PETL) techniques allow updating a small subset of parameters (e.g. only using 2% of parameters) inside a pre-trained backbone network for a new task, they only reduce the training memory requirement by up to 30%. This is because the gradient computation for the trainable parameters still requires backpropagation through the large pre-trained backbone model. To address this, we propose Ladder Side-Tuning (LST), a new PETL technique that reduces training memory requirements by more substantial amounts. Unlike existing parameter-efficient methods that insert additional parameters inside backbone networks, we train a ladder side network, a small and separate network that takes intermediate activations as input via shortcut connections (ladders) from backbone networks and makes predictions. LST has significantly lower memory requirements than previous methods, because it does not require backpropagation through the backbone network, but instead only through the side network and ladder connections. We evaluate our method with various models (T5, CLIP-T5) on both NLP (GLUE) and vision-language (VQA, GQA, NLVR2, MSCOCO) tasks. LST saves 69% of the memory costs to fine-tune the whole network, while other methods only save 26% of that in similar parameter usages (hence, 2.7x more memory savings). Moreover, LST achieves higher accuracy than Adapter and LoRA in a low-memory regime. To further show the advantage of this better memory efficiency, we also apply LST to larger T5 models (T5-large, T5-3B), attaining better GLUE performance than full fine-tuning and other PETL methods. The exact same trend also holds in our experiments on VL tasks.
最近,各种领域都采用了对下游任务的大型预训练模型进行微调。但是,更新大型预训练模型的整个参数集的成本很高。尽管最近提出的参数高效迁移学习 (PETL) 技术允许在预训练的骨干网络中为新任务更新一小部分参数(例如,仅使用 2% 的参数),但它们最多只能将训练内存需求减少30%。这是因为可训练参数的梯度计算仍然需要通过大型预训练骨干模型进行反向传播。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了 Ladder Side-Tuning (LST),这是一种新的 PETL 技术,可大幅减少训练内存需求。与现有的在骨干网络中插入额外参数的参数有效方法不同,我们训练了一个梯形侧网络,这是一个小型且独立的网络,它通过来自骨干网络的快捷连接(“梯子”跳接)将中间激活作为输入并进行预测。 LST 比以前的方法具有显着降低的内存需求,因为它不需要通过骨干网络进行反向传播,而只需要通过侧网络和跳跃“梯子”连接。我们在 NLP (GLUE) 和视觉语言 (VQA, GQA, NLVR2, MSCOCO) 任务上使用各种模型 (T5, CLIP-T5) 评估我们的方法。 LST 为微调整个网络节省了 69% 的内存成本,而其他方法在类似的参数使用情况下仅节省了 26%(因此,节省了 2.7 倍的内存)。此外,LST 在低内存状态下实现了比 Adapter 和 LoRA 更高的精度。为了进一步展示这种更好的内存效率的优势,我们还将 LST 应用于更大的 T5 模型(T5-large,T5-3B),获得比完全微调和其他 PETL 方法更好的 GLUE 性能。在我们对 VL 任务的实验中也存在完全相同的趋势。



论文:Neural Prompt Search
论文标题:Neural Prompt Search
论文时间:9 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Few-Shot Learning,Neural Architecture Search,Prompt Engineering,Transfer Learning,小样本学习、神经架构搜索、迁移学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04673
代码实现:https://github.com/Davidzhangyuanhan/NOAH
论文作者:Yuanhan Zhang, Kaiyang Zhou, Ziwei Liu
论文简介:The size of vision models has grown exponentially over the last few years, especially after the emergence of Vision Transformer. / 视觉模型的规模在过去几年呈指数级增长,尤其是在 Vision Transformer 出现之后。
论文摘要:The size of vision models has grown exponentially over the last few years, especially after the emergence of Vision Transformer. This has motivated the development of parameter-efficient tuning methods, such as learning adapter layers or visual prompt tokens, which allow a tiny portion of model parameters to be trained whereas the vast majority obtained from pre-training are frozen. However, designing a proper tuning method is non-trivial: one might need to try out a lengthy list of design choices, not to mention that each downstream dataset often requires custom designs. In this paper, we view the existing parameter-efficient tuning methods as “prompt modules” and propose Neural prOmpt seArcH (NOAH), a novel approach that learns, for large vision models, the optimal design of prompt modules through a neural architecture search algorithm, specifically for each downstream dataset. By conducting extensive experiments on over 20 vision datasets, we demonstrate that NOAH (i) is superior to individual prompt modules, (ii) has a good few-shot learning ability, and (iii) is domain-generalizable. The code and models are available at https://github.com/Davidzhangyuanhan/NOAH
视觉模型的规模在过去几年呈指数级增长,尤其是在 Vision Transformer 出现之后。这推动了参数高效调整方法的开发,例如学习适配器层或视觉提示标记,它们允许只训练一小部分模型参数,而从预训练中获得的绝大多数参数被冻结。然而,设计合适的调优方法并非易事:可能需要尝试一长串设计选择,更不用说每个下游数据集通常都需要定制设计。在本文中,我们将现有的参数有效调整方法视为“提示模块”,并提出了神经提示搜索(NOAH),这是一种新方法,可以通过神经架构搜索算法学习大型视觉模型的提示模块的优化设计,特别是针对每个下游数据集。通过对 20 多个视觉数据集进行广泛的实验,我们证明 NOAH (i) 优于单个提示模块,(ii) 具有良好的小样本学习能力,以及 (iii) 是域泛化的。代码和模型可在 https://github.com/Davidzhangyuanhan/NOAH 获得。



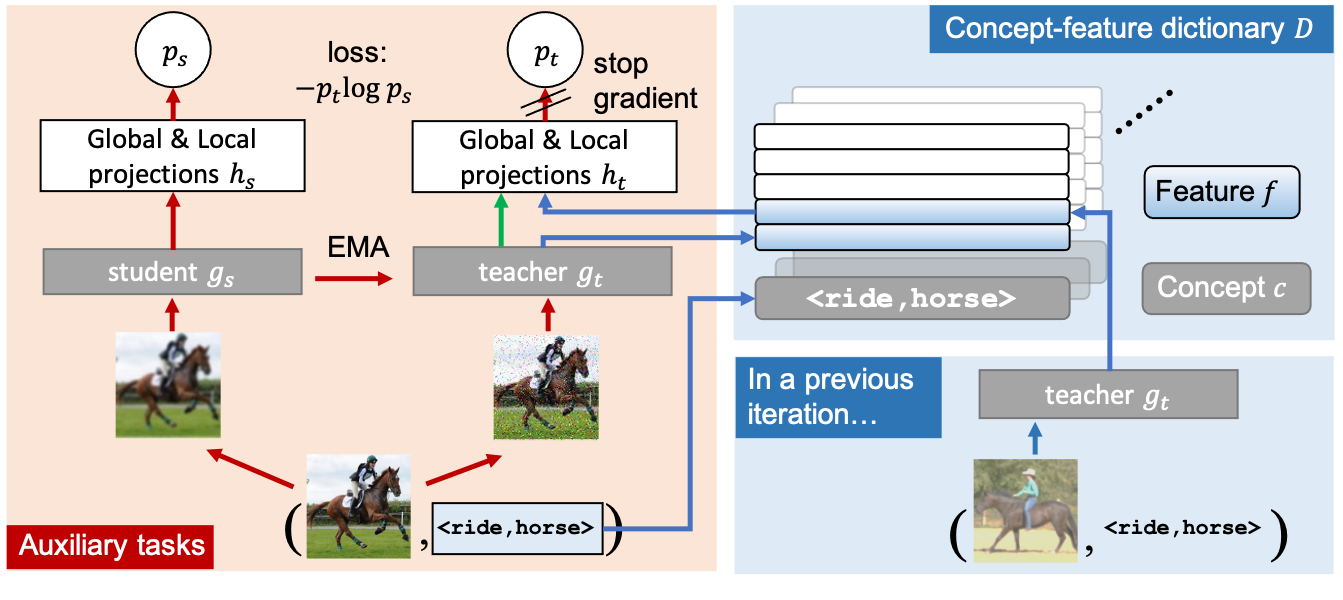
论文:RelViT: Concept-guided Vision Transformer for Visual Relational Reasoning
论文标题:RelViT: Concept-guided Vision Transformer for Visual Relational Reasoning
论文时间:ICLR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Human-Object Interaction Detection,Systematic Generalization,Visual Question Answering,Visual Reasoning,Zero-Shot Human-Object Interaction Detection,人机交互检测、系统泛化、视觉问答、视觉推理、零样本人机交互检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.11167
代码实现:https://github.com/NVlabs/RelViT
论文作者:Xiaojian Ma, Weili Nie, Zhiding Yu, Huaizu Jiang, Chaowei Xiao, Yuke Zhu, Song-Chun Zhu, Anima Anandkumar
论文简介:This task remains challenging for current deep learning algorithms since it requires addressing three key technical problems jointly: 1) identifying object entities and their properties, 2) inferring semantic relations between pairs of entities, and 3) generalizing to novel object-relation combinations, i. e., systematic generalization. / 这项任务对于当前的深度学习算法仍然具有挑战性,因为它需要共同解决三个关键技术问题:1)识别对象实体及其属性,2)推断实体对之间的语义关系,以及 3)推广到新的对象关系组合,也即“系统性泛化”。
论文摘要:Reasoning about visual relationships is central to how humans interpret the visual world. This task remains challenging for current deep learning algorithms since it requires addressing three key technical problems jointly: 1) identifying object entities and their properties, 2) inferring semantic relations between pairs of entities, and 3) generalizing to novel object-relation combinations, i.e., systematic generalization. In this work, we use vision transformers (ViTs) as our base model for visual reasoning and make better use of concepts defined as object entities and their relations to improve the reasoning ability of ViTs. Specifically, we introduce a novel concept-feature dictionary to allow flexible image feature retrieval at training time with concept keys. This dictionary enables two new concept-guided auxiliary tasks: 1) a global task for promoting relational reasoning, and 2) a local task for facilitating semantic object-centric correspondence learning. To examine the systematic generalization of visual reasoning models, we introduce systematic splits for the standard HICO and GQA benchmarks. We show the resulting model, Concept-guided Vision Transformer (or RelViT for short) significantly outperforms prior approaches on HICO and GQA by 16% and 13% in the original split, and by 43% and 18% in the systematic split. Our ablation analyses also reveal our model’s compatibility with multiple ViT variants and robustness to hyper-parameters.
关于视觉关系的推理是人类如何解释视觉世界的核心。这项任务对于当前的深度学习算法仍然具有挑战性,因为它需要共同解决三个关键技术问题:1)识别对象实体及其属性,2)推断实体对之间的语义关系,以及 3)推广到新的对象关系组合,即,系统性泛化。在这项工作中,我们使用视觉transformers (ViTs) 作为视觉推理的基础模型,并更好地利用定义为对象实体及其关系的概念来提高 ViTs 的推理能力。具体来说,我们引入了一种新颖的概念特征字典,以允许在训练时使用概念键进行灵活的图像特征检索。该词典支持两个新的概念引导辅助任务:1)促进关系推理的全局任务,以及 2)促进以语义对象为中心的对应学习的局部任务。为了检查视觉推理模型的系统概括,我们为标准 HICO 和 GQA 基准引入了系统拆分。我们展示了由此产生的模型,Concept-guided Vision Transformer(或简称 RelViT)在原始分割中显着优于 HICO 和 GQA 的先前方法 16% 和 13%,在系统分割中分别优于 43% 和 18%。我们的消融分析还揭示了我们的模型与多种 ViT 变体的兼容性以及对超参数的鲁棒性。


论文:Optimal Transport Tools (OTT): A JAX Toolbox for all things Wasserstein
论文标题:Optimal Transport Tools (OTT): A JAX Toolbox for all things Wasserstein
论文时间:28 Jan 2022
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.12324
代码实现:https://github.com/ott-jax/ott
论文作者:Marco Cuturi, Laetitia Meng-Papaxanthos, Yingtao Tian, Charlotte Bunne, Geoff Davis, Olivier Teboul
论文简介:Optimal transport tools (OTT-JAX) is a Python toolbox that can solve optimal transport problems between point clouds and histograms. / 最优传输工具(OTT-JAX)是一个 Python 工具箱,可以解决点云和直方图之间的最优传输问题。
论文摘要:Optimal transport tools (OTT-JAX) is a Python toolbox that can solve optimal transport problems between point clouds and histograms. The toolbox builds on various JAX features, such as automatic and custom reverse mode differentiation, vectorization, just-in-time compilation and accelerators support. The toolbox covers elementary computations, such as the resolution of the regularized OT problem, and more advanced extensions, such as barycenters, Gromov-Wasserstein, low-rank solvers, estimation of convex maps, differentiable generalizations of quantiles and ranks, and approximate OT between Gaussian mixtures. The toolbox code is available at https://github.com/ott-jax/ott
最优传输工具(OTT-JAX)是一个 Python 工具箱,可以解决点云和直方图之间的最优传输问题。 该工具箱建立在各种 JAX 功能之上,例如自动和自定义反向模式区分、矢量化、即时编译和加速器支持。 该工具箱涵盖基本计算,例如正则化 OT 问题的解决,以及更高级的扩展,例如重心、Gromov-Wasserstein、低秩求解器、凸图估计、分位数和秩的可微泛化以及之间的近似 OT 高斯混合。 工具箱代码可以在 https://github.com/ott-jax/ott 取到


论文:SaRNet: A Dataset for Deep Learning Assisted Search and Rescue with Satellite Imagery
论文标题:SaRNet: A Dataset for Deep Learning Assisted Search and Rescue with Satellite Imagery
论文时间:26 Jul 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Humanitarian,object-detection,Object Detection,人道主义,物体检测,物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.12469
代码实现:https://github.com/michaelthoreau/SearchAndRescueNet
论文作者:Michael Thoreau, Frazer Wilson
论文简介:Access to high resolution satellite imagery has dramatically increased in recent years as several new constellations have entered service. / 近年来,随着几个新卫星的投入使用,高分辨率卫星图像的获取显着增加。
论文摘要:Access to high resolution satellite imagery has dramatically increased in recent years as several new constellations have entered service. High revisit frequencies as well as improved resolution has widened the use cases of satellite imagery to areas such as humanitarian relief and even Search and Rescue (SaR). We propose a novel remote sensing object detection dataset for deep learning assisted SaR. This dataset contains only small objects that have been identified as potential targets as part of a live SaR response. We evaluate the application of popular object detection models to this dataset as a baseline to inform further research. We also propose a novel object detection metric, specifically designed to be used in a deep learning assisted SaR setting.
近年来,随着几个新卫星的投入使用,对高分辨率卫星图像的访问急剧增加。 高重访频率和更高的分辨率已将卫星图像的用例扩大到人道主义救济甚至搜救 (SaR) 等领域。 我们提出了一种用于深度学习辅助 SaR 的新型遥感对象检测数据集。 该数据集仅包含作为实时 SaR 响应的一部分被识别为潜在目标的小对象。 我们评估流行的对象检测模型在该数据集上的应用,作为进一步研究的基准。 我们还提出了一种新颖的对象检测指标,专门设计用于深度学习辅助 SaR 的场景。


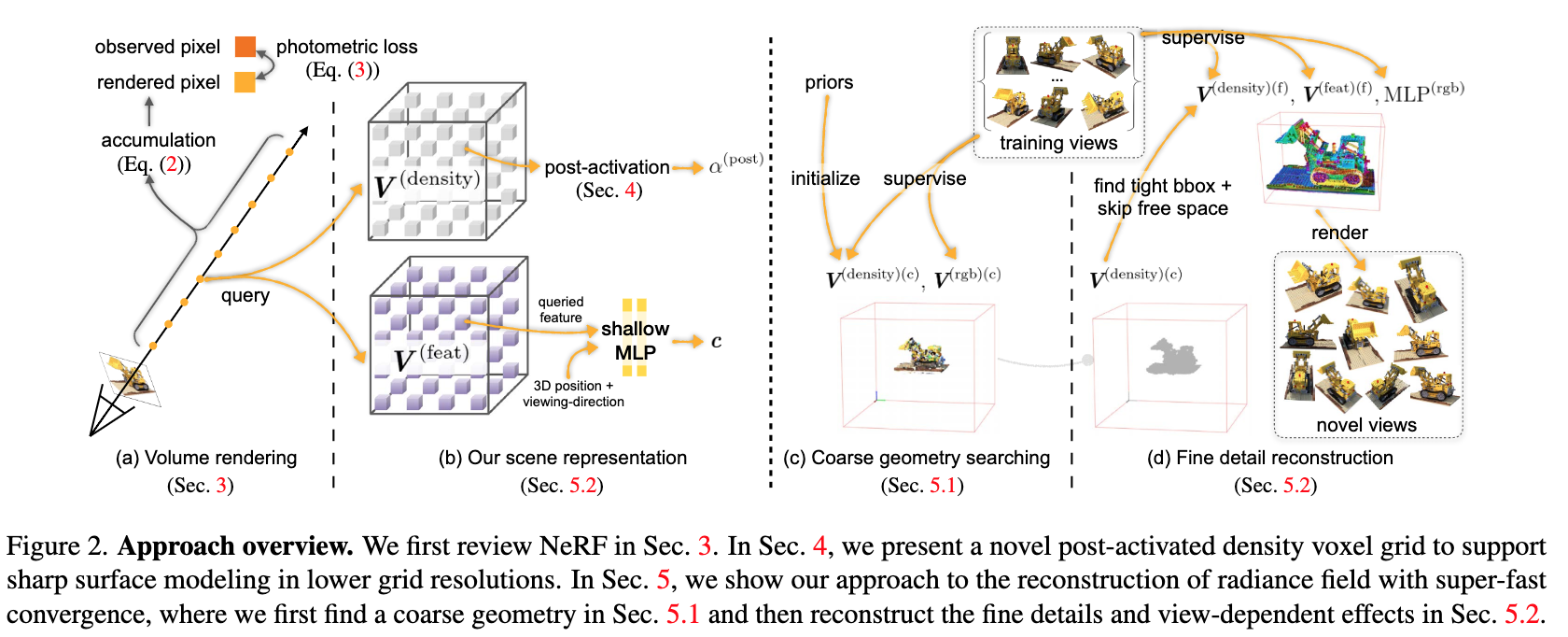
论文:Direct Voxel Grid Optimization: Super-fast Convergence for Radiance Fields Reconstruction
论文标题:Direct Voxel Grid Optimization: Super-fast Convergence for Radiance Fields Reconstruction
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Novel View Synthesis,新视图合成
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11215
代码实现:https://github.com/sunset1995/directvoxgo
论文作者:Cheng Sun, Min Sun, Hwann-Tzong Chen
论文简介:Finally, evaluation on five inward-facing benchmarks shows that our method matches, if not surpasses, NeRF’s quality, yet it only takes about 15 minutes to train from scratch for a new scene. / 最后,对五个内向基准的评估表明,我们的方法与 NeRF 的质量相匹配,甚至超过,但从头开始训练新场景只需要大约 15 分钟。
论文摘要:We present a super-fast convergence approach to reconstructing the per-scene radiance field from a set of images that capture the scene with known poses. This task, which is often applied to novel view synthesis, is recently revolutionized by Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) for its state-of-the-art quality and flexibility. However, NeRF and its variants require a lengthy training time ranging from hours to days for a single scene. In contrast, our approach achieves NeRF-comparable quality and converges rapidly from scratch in less than 15 minutes with a single GPU. We adopt a representation consisting of a density voxel grid for scene geometry and a feature voxel grid with a shallow network for complex view-dependent appearance. Modeling with explicit and discretized volume representations is not new, but we propose two simple yet non-trivial techniques that contribute to fast convergence speed and high-quality output. First, we introduce the post-activation interpolation on voxel density, which is capable of producing sharp surfaces in lower grid resolution. Second, direct voxel density optimization is prone to suboptimal geometry solutions, so we robustify the optimization process by imposing several priors. Finally, evaluation on five inward-facing benchmarks shows that our method matches, if not surpasses, NeRF’s quality, yet it only takes about 15 minutes to train from scratch for a new scene.
我们提出了一种超快速收敛方法,用于从一组捕获具有已知姿势的场景的图像中重建每个场景的辐射场。这项任务通常应用于新颖的视图合成,最近因其最先进的质量和灵活性而被神经辐射场 (NeRF) 彻底改变。然而,对于单个场景,NeRF 及其变体需要很长的训练时间,从数小时到数天不等。相比之下,我们的方法实现了与 NeRF 相当的质量,并在不到 15 分钟的时间内仅凭单个 GPU 从头训练可以完成快速收敛。我们采用由用于场景几何的密度体素网格和具有浅层网络的特征体素网格组成的表示,用于复杂的依赖于视图的外观。使用显式和离散化的体积表示进行建模并不新鲜,但我们提出了两种简单但非实用的技术,有助于快速收敛和高质量输出。首先,我们介绍了体素密度的激活后插值,它能够以较低的网格分辨率产生锐利的表面。其次,直接体素密度优化容易出现次优几何解决方案,因此我们通过强加几个先验来加强优化过程。最后,对五个内向基准的评估表明,我们的方法与 NeRF 的质量相匹配,甚至超过,但从头开始训练新场景只需要大约 15 分钟。


我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。

- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处
- 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~