ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架

工具库:Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn - 通过Intel CPU/GPU优化来加速Scikit-learn(10-100X)的扩展库(补丁)
tags:[sklearn,intel,补丁]
‘Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn* - Intel® Extension for Scikit-learn is a seamless way to speed up your Scikit-learn application’ by Intel
GitHub: https://github.com/intel/scikit-learn-intelex

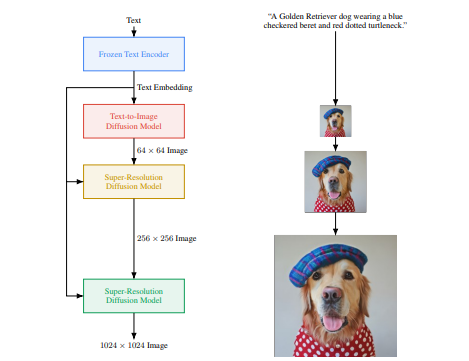
工具库:Diffusers - 跨模态预训练扩散模型
tags:[预训练模型,跨模态,扩散模型]
‘Diffusers - provides pretrained diffusion models across multiple modalities, such as vision and audio, and serves as a modular toolbox for inference and training of diffusion models’ by Hugging Face
GitHub: https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers

工具库:mmap.ninja - 支持Python, C/C++ (Cython), Rust, Java等多种语言的内存映射数据结构
tags:[内存映射,多语言]
‘mmap.ninja - Memory mapped data structures which can be used by multiple languages - Python, C/C++ (Cython), Rust, Java.’ by Hristo Vrigazov
GitHub: https://github.com/hristo-vrigazov/mmap.ninja

工具框架:Horovod - TensorFlow/Keras/PyTorch/MXNet深度学习分布式训练框架
tags:[分布式,框架,训练,深度学习]
‘Horovod - Distributed training framework for TensorFlow, Keras, PyTorch, and Apache MXNet.’
GitHub: https://github.com/horovod/horovod



工具平台:DI-star - OpenDILab星际争霸II决策AI平台
tags:[AI平台,星际争霸]
‘DI-star - OpenDILab Decision AI in StarCraftII’ by opendilab
GitHub: https://github.com/opendilab/DI-star

2.项目&代码

代码:计算机视觉神经网络模型大比拼
tags:[计算机视觉,图像识别,模型,比较]
《Which image models are best? | Kaggle》by Jeremy Howard
Link: https://www.kaggle.com/code/jhoward/which-image-models-are-best
3.博文&分享

免费书籍:机器学习方案手册,内容覆盖自然语言处理、计算机视觉、图像与文字
tags:[机器学习方案,NLP,CV]
《ML Recipe》by Bipin Krishnan P
Link: https://bipinkrishnan.github.io/ml-recipe-book/about.html

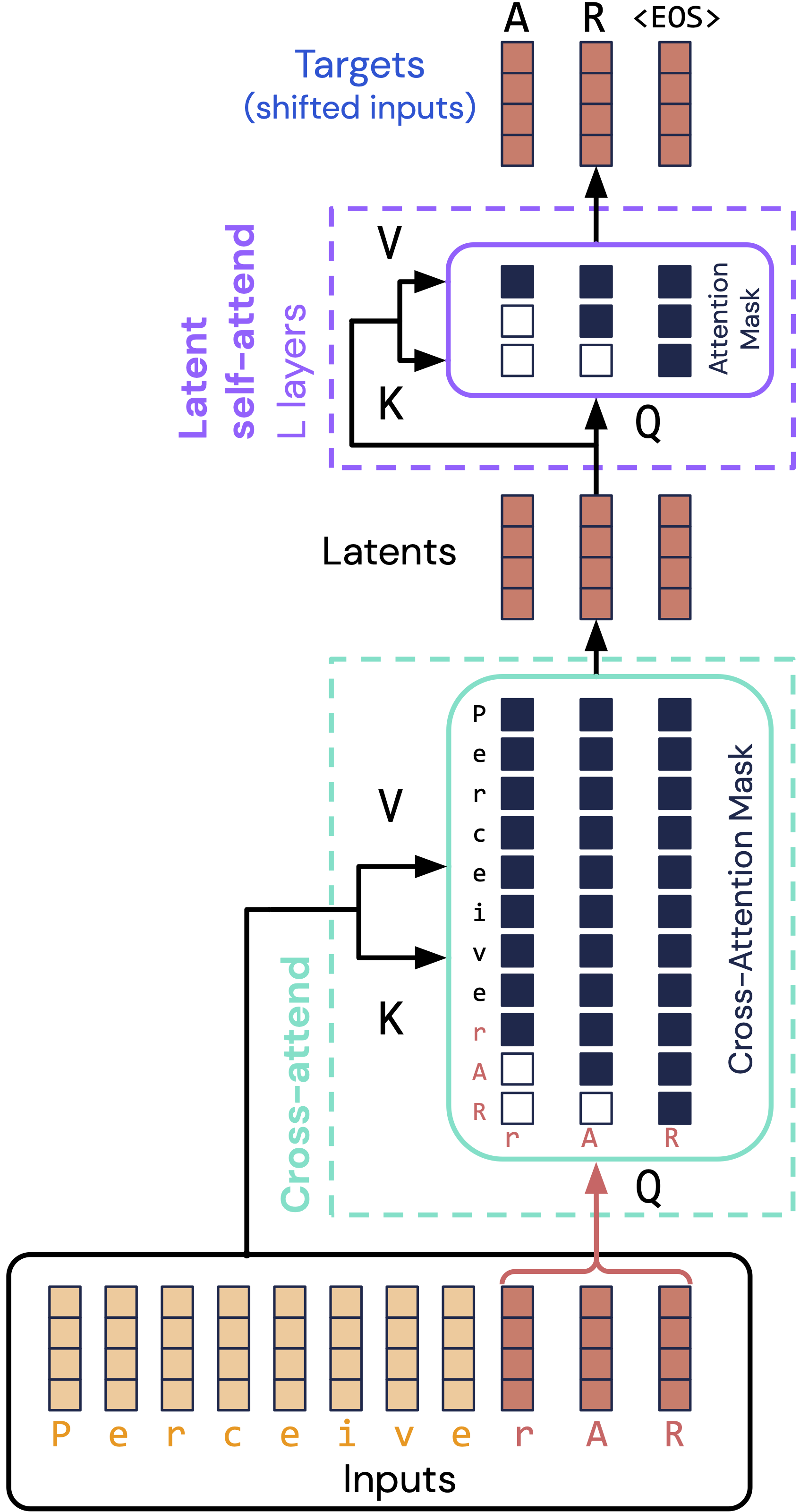
博文:Perceiver AR,通用、长上下文自回归生成
tags:[自回归,上下文]
《Perceiver AR: general-purpose, long-context autoregressive generation》
Link: https://www.deepmind.com/publications/perceiver-ar-general-purpose-long-context-autoregressive-generation

4.数据&资源

数据集:Google Scanned Objects - 高质量日常用品3D扫描数据集
tags:[数据集,3D,日常用品]
《Scanned Objects by Google Research: A Dataset of 3D-Scanned Common Household Items | Google AI Blog》
Link: https://ai.googleblog.com/2022/06/scanned-objects-by-google-research.html
资源列表:图数据增强文献资源列表
tags:[图模型,图,数据增强,资源列表]
‘graph-data-augmentation-papers - A curated list of graph data augmentation papers.’ by Tong Zhao
GitHub: https://github.com/zhao-tong/graph-data-augmentation-papers
5.研究&论文

可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
论文:Discovering Object Masks with Transformers for Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation
论文标题:Discovering Object Masks with Transformers for Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation
论文时间:13 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Semantic Segmentation,Unsupervised Semantic Segmentation,语义分割,无监督语义分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.06363
代码实现:https://github.com/wvangansbeke/MaskDistill
论文作者:Wouter Van Gansbeke, Simon Vandenhende, Luc van Gool
论文简介:This paper presents MaskDistill: a novel framework for unsupervised semantic segmentation based on three key ideas. / 本文介绍了 MaskDistill:一种基于三个关键思想的无监督语义分割新框架。
论文摘要:The task of unsupervised semantic segmentation aims to cluster pixels into semantically meaningful groups. Specifically, pixels assigned to the same cluster should share high-level semantic properties like their object or part category. This paper presents MaskDistill: a novel framework for unsupervised semantic segmentation based on three key ideas. First, we advocate a data-driven strategy to generate object masks that serve as a pixel grouping prior for semantic segmentation. This approach omits handcrafted priors, which are often designed for specific scene compositions and limit the applicability of competing frameworks. Second, MaskDistill clusters the object masks to obtain pseudo-ground-truth for training an initial object segmentation model. Third, we leverage this model to filter out low-quality object masks. This strategy mitigates the noise in our pixel grouping prior and results in a clean collection of masks which we use to train a final segmentation model. By combining these components, we can considerably outperform previous works for unsupervised semantic segmentation on PASCAL (+11% mIoU) and COCO (+4% mask AP50). Interestingly, as opposed to existing approaches, our framework does not latch onto low-level image cues and is not limited to object-centric datasets. The code and models will be made available.
无监督语义分割的任务旨在将像素聚类成具有语义意义的组。具体来说,分配给同一簇的像素应该共享高级语义属性,例如它们的对象或部件类别。本文介绍了 MaskDistill:一种基于三个关键思想的无监督语义分割新框架。首先,我们提倡一种数据驱动的策略来生成对象掩码,作为语义分割的像素分组先验。这种方法省略了手工制作的先验,这些先验通常是为特定的场景组合而设计的,并限制了竞争框架的适用性。其次,MaskDistill 对对象掩码进行聚类以获得用于训练初始对象分割模型的伪真值。第三,我们利用这个模型过滤掉低质量的对象掩码。这种策略减轻了我们之前像素分组中的噪声,并产生了一个干净的掩码集合,我们使用这些掩码来训练最终的分割模型。通过结合这些组件,我们可以在 PASCAL (+11% mIoU) 和 COCO (+4% mask AP50) 上大大优于以前的无监督语义分割工作。有趣的是,与现有方法相反,我们的框架不锁定低级图像线索,也不限于以对象为中心的数据集。代码和模型将可用。



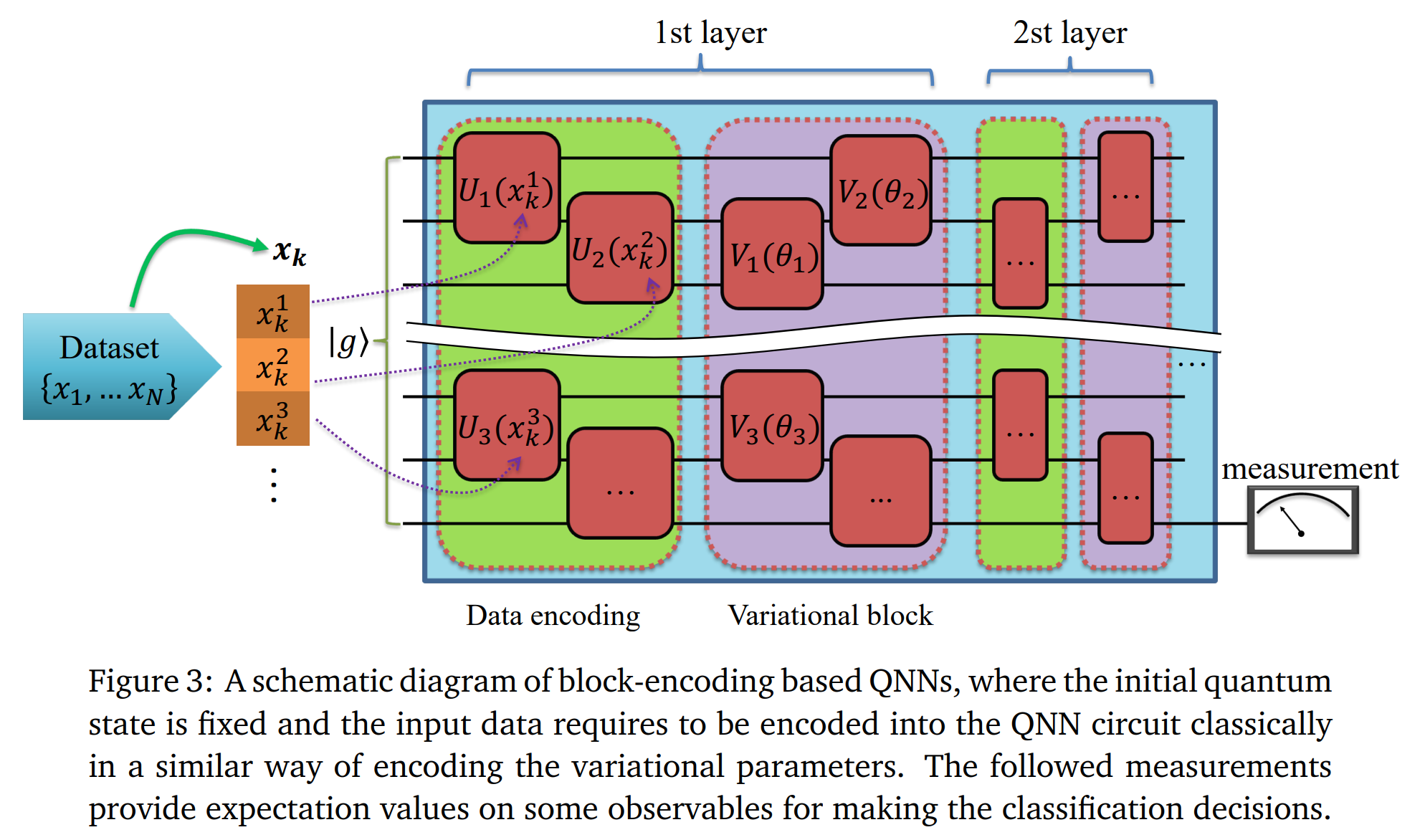
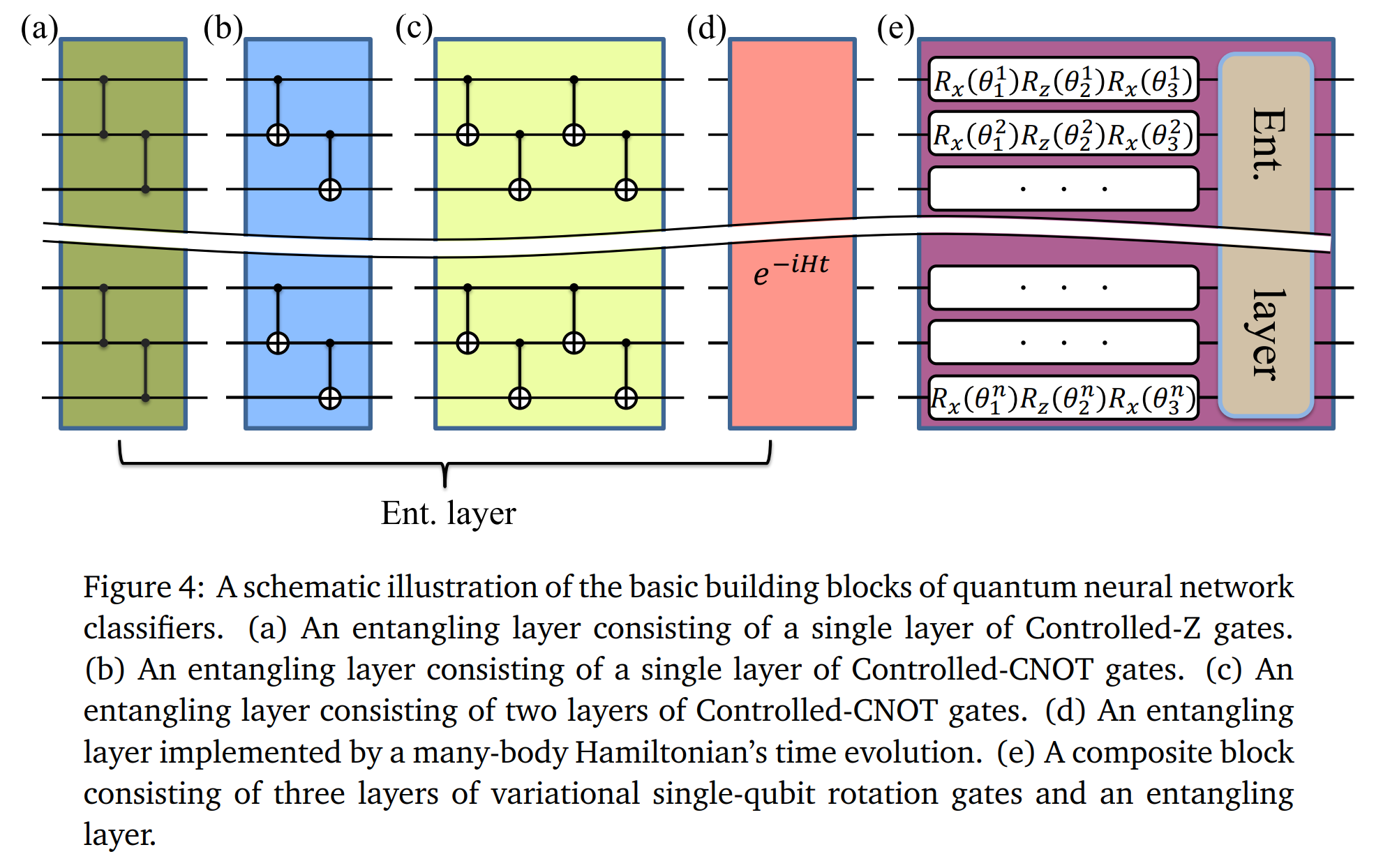
论文:Quantum Neural Network Classifiers: A Tutorial
论文标题:Quantum Neural Network Classifiers: A Tutorial
论文时间:6 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Face Recognition,人脸识别
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02806
代码实现:https://github.com/lwkjjonak/quantum_neural_network_classifiers
论文作者:Weikang Li, Zhide Lu, Dong-Ling Deng
论文简介:Machine learning has achieved dramatic success over the past decade, with applications ranging from face recognition to natural language processing. / 机器学习在过去十年中取得了巨大的成功,应用范围从人脸识别到自然语言处理。
论文摘要:Machine learning has achieved dramatic success over the past decade, with applications ranging from face recognition to natural language processing. Meanwhile, rapid progress has been made in the field of quantum computation including developing both powerful quantum algorithms and advanced quantum devices. The interplay between machine learning and quantum physics holds the intriguing potential for bringing practical applications to the modern society. Here, we focus on quantum neural networks in the form of parameterized quantum circuits. We will mainly discuss different structures and encoding strategies of quantum neural networks for supervised learning tasks, and benchmark their performance utilizing Yao.jl, a quantum simulation package written in Julia Language. The codes are efficient, aiming to provide convenience for beginners in scientific works such as developing powerful variational quantum learning models and assisting the corresponding experimental demonstrations.
机器学习在过去十年中取得了巨大的成功,应用范围从人脸识别到自然语言处理。与此同时,量子计算领域取得了快速进展,包括开发强大的量子算法和先进的量子器件。机器学习和量子物理学之间的相互作用具有将实际应用带入现代社会的迷人潜力。在这里,我们专注于参数化量子电路形式的量子神经网络。我们将主要讨论用于监督学习任务的量子神经网络的不同结构和编码策略,并利用 Yao.jl(用 Julia 语言编写的量子模拟包)对其性能进行基准测试。代码高效,旨在为科学工作的初学者提供便利,例如开发强大的变分量子学习模型和辅助相应的实验演示。


论文:Referring Image Matting
论文标题:Referring Image Matting
论文时间:10 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Matting,Referring Image Matting,Referring Image Matting (Expression-based),Referring Image Matting (Prompt-based),Visual Grounding,图像抠图,图像抠图(基于表达式),图像抠图(基于提示),图像文字
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.05149
代码实现:https://github.com/jizhizili/rim
论文作者:Jizhizi Li, Jing Zhang, DaCheng Tao
论文简介:Image matting refers to extracting the accurate foregrounds in the image. / 图像抠图是指提取图像中准确的前景。
论文摘要:Image matting refers to extracting the accurate foregrounds in the image. Current automatic methods tend to extract all the salient objects in the image indiscriminately. In this paper, we propose a new task named Referring Image Matting (RIM), referring to extracting the meticulous alpha matte of the specific object that can best match the given natural language description. However, prevalent visual grounding methods are all limited to the segmentation level, probably due to the lack of high-quality datasets for RIM. To fill the gap, we establish the first large-scale challenging dataset RefMatte by designing a comprehensive image composition and expression generation engine to produce synthetic images on top of current public high-quality matting foregrounds with flexible logics and re-labelled diverse attributes. RefMatte consists of 230 object categories, 47,500 images, 118,749 expression-region entities, and 474,996 expressions, which can be further extended easily in the future. Besides this, we also construct a real-world test set with manually generated phrase annotations consisting of 100 natural images to further evaluate the generalization of RIM models. We first define the task of RIM in two settings, i.e., prompt-based and expression-based, and then benchmark several representative methods together with specific model designs for image matting. The results provide empirical insights into the limitations of existing methods as well as possible solutions. We believe the new task RIM along with the RefMatte dataset will open new research directions in this area and facilitate future studies. The dataset and code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/JizhiziLi/RIM
图像抠图是指提取图像中准确的前景。当前的自动方法倾向于不加选择地提取图像中的所有显着对象。在本文中,我们提出了一项名为“Referring Image Matting (RIM)”的新任务,指的是提取最能匹配给定自然语言描述的特定对象的精细 alpha matte。然而,流行的视觉基础方法都仅限于分割级别,这可能是由于缺乏用于 RIM 的高质量数据集。为了填补这一空白,我们建立了第一个具有挑战性的大规模数据集 RefMatte,通过设计一个全面的图像合成和表达生成引擎,在当前公共的高质量抠图前景之上生成具有灵活逻辑和重新标记的不同属性的合成图像。 RefMatte 由 230 个对象类别、47,500 张图像、118,749 个表达式区域实体和 474,996 个表达式组成,将来可以很容易地进一步扩展。除此之外,我们还构建了一个真实世界的测试集,其中包含手动生成的短语注释,由 100 个自然图像组成,以进一步评估 RIM 模型的泛化性。我们首先在两种设置中定义 RIM 的任务,即基于提示的和基于表达的,然后对几种具有代表性的方法以及图像抠图的特定模型设计进行基准测试。结果为现有方法的局限性以及可能的解决方案提供了经验见解。我们相信新任务 RIM 以及 RefMatte 数据集将在该领域开辟新的研究方向并促进未来的研究。数据集和代码将在 https://github.com/JizhiziLi/RIM 公开



论文:Towards Understanding Sharpness-Aware Minimization
论文标题:Towards Understanding Sharpness-Aware Minimization
论文时间:13 Jun 2022
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.06232
代码实现:https://github.com/tml-epfl/understanding-sam
论文作者:Maksym Andriushchenko, Nicolas Flammarion
论文简介:We further study the properties of the implicit bias on non-linear networks empirically, where we show that fine-tuning a standard model with SAM can lead to significant generalization improvements. / 我们通过经验进一步研究了非线性网络上的隐含偏差的属性,我们表明使用 SAM 微调标准模型可以显着提高泛化能力。
论文摘要:Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) is a recent training method that relies on worst-case weight perturbations which significantly improves generalization in various settings. We argue that the existing justifications for the success of SAM which are based on a PAC-Bayes generalization bound and the idea of convergence to flat minima are incomplete. Moreover, there are no explanations for the success of using m-sharpness in SAM which has been shown as essential for generalization. To better understand this aspect of SAM, we theoretically analyze its implicit bias for diagonal linear networks. We prove that SAM always chooses a solution that enjoys better generalization properties than standard gradient descent for a certain class of problems, and this effect is amplified by using m-sharpness. We further study the properties of the implicit bias on non-linear networks empirically, where we show that fine-tuning a standard model with SAM can lead to significant generalization improvements. Finally, we provide convergence results of SAM for non-convex objectives when used with stochastic gradients. We illustrate these results empirically for deep networks and discuss their relation to the generalization behavior of SAM. The code of our experiments is available at https://github.com/tml-epfl/understanding-sam
Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) 是一种最近的训练方法,它依赖于最坏情况的权重扰动,显着提高了各种设置中的泛化能力。我们认为,基于 PAC-Bayes 泛化界和收敛到平坦最小值的想法的 SAM 成功的现有理由是不完整的。此外,对于在 SAM 中使用 m-sharpness 的成功没有任何解释,这已被证明对于泛化至关重要。为了更好地理解 SAM 的这一方面,我们从理论上分析了它对对角线线性网络的隐含偏差。我们证明 SAM 对于某一类问题总是选择比标准梯度下降具有更好泛化特性的解决方案,并且这种效果通过使用 m-sharpness 得到放大。我们进一步研究了非线性网络隐含偏差的特性,我们证明了使用 SAM 微调标准模型可以显着提高泛化能力。最后,我们提供了与随机梯度一起使用时非凸目标的 SAM 收敛结果。我们从经验上说明了深度网络的这些结果,并讨论了它们与 SAM 泛化行为的关系。我们的实验代码可在 https://github.com/tml-epfl/understanding-sam 获得



论文:Featurized Query R-CNN
论文标题:Featurized Query R-CNN
论文时间:13 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:object-detection,Object Detection,物体检测,物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.06258
代码实现:https://github.com/hustvl/featurized-queryrcnn
论文作者:Wenqiang Zhang, Tianheng Cheng, Xinggang Wang, Shaoyu Chen, Qian Zhang, Wenyu Liu
论文简介:The query mechanism introduced in the DETR method is changing the paradigm of object detection and recently there are many query-based methods have obtained strong object detection performance. / DETR 方法中引入的查询机制正在改变物体检测的范式,最近有许多基于查询的方法获得了强大的物体检测性能。
论文摘要:The query mechanism introduced in the DETR method is changing the paradigm of object detection and recently there are many query-based methods have obtained strong object detection performance. However, the current query-based detection pipelines suffer from the following two issues. Firstly, multi-stage decoders are required to optimize the randomly initialized object queries, incurring a large computation burden. Secondly, the queries are fixed after training, leading to unsatisfying generalization capability. To remedy the above issues, we present featurized object queries predicted by a query generation network in the well-established Faster R-CNN framework and develop a Featurized Query R-CNN. Extensive experiments on the COCO dataset show that our Featurized Query R-CNN obtains the best speed-accuracy trade-off among all R-CNN detectors, including the recent state-of-the-art Sparse R-CNN detector. The code is available at https://github.com/hustvl/Featurized-QueryRCNN
DETR方法中引入的查询机制正在改变物体检测的范式,最近有许多基于查询的方法获得了强大的对象检测性能。然而,当前基于查询的检测管道存在以下两个问题。首先,需要多级解码器来优化随机初始化的对象查询,从而产生很大的计算量。其次,查询在训练后是固定的,导致泛化能力不强。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了在完善的 Faster R-CNN 框架中由查询生成网络预测的特征化对象查询,并开发了一个特征化查询 R-CNN。在 COCO 数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的特征化查询 R-CNN 在所有 R-CNN 检测器(包括最近最先进的 Sparse R-CNN 检测器)中获得了最佳的速度-准确度权衡。代码可在 https://github.com/hustvl/Featurized-QueryRCNN



论文:Counterfactual Inference for Text Classification Debiasing
论文标题:Counterfactual Inference for Text Classification Debiasing
论文时间:ACL 2021
所属领域:自然语言处理
对应任务:Classification,Counterfactual Inference,Fairness,Text Classification,分类,反事实推理,公平,文本分类
论文地址:https://aclanthology.org/2021.acl-long.422.pdf
代码实现:https://github.com/qianc62/corsair
论文作者:Chen Qian, Fuli Feng, Lijie Wen, Chunping Ma, Pengjun Xie
论文简介:In inference, given a factual input document, Corsair imagines its two counterfactual counterparts to distill and mitigate the two biases captured by the poisonous model. / 在推理中,给定一个事实输入文档,Corsair 想象它的两个反事实对应物来提炼和减轻有毒(文本)模型捕获的两个偏差。
论文摘要:Today{‘}s text classifiers inevitably suffer from unintended dataset biases, especially the document-level label bias and word-level keyword bias, which may hurt models{’} generalization. Many previous studies employed data-level manipulations or model-level balancing mechanisms to recover unbiased distributions and thus prevent models from capturing the two types of biases. Unfortunately, they either suffer from the extra cost of data collection/selection/annotation or need an elaborate design of balancing strategies. Different from traditional factual inference in which debiasing occurs before or during training, counterfactual inference mitigates the influence brought by unintended confounders after training, which can make unbiased decisions with biased observations. Inspired by this, we propose a model-agnostic text classification debiasing framework {–} Corsair, which can effectively avoid employing data manipulations or designing balancing mechanisms. Concretely, Corsair first trains a base model on a training set directly, allowing the dataset biases {`}poison{‘} the trained model. In inference, given a factual input document, Corsair imagines its two counterfactual counterparts to distill and mitigate the two biases captured by the poisonous model. Extensive experiments demonstrate Corsair{’}s effectiveness, generalizability and fairness.
今天的文本分类器不可避免地会遭受意外的数据集偏差,尤其是文档级标签偏差和单词级关键字偏差,这可能会影响模型的泛化能力。许多先前的研究采用数据级操作或模型级平衡机制来恢复无偏分布,从而防止模型捕获这两种类型的偏差。不幸的是,他们要么遭受数据收集/选择/注释的额外成本,要么需要精心设计平衡策略。与传统的在训练前或训练过程中去偏的事实推理不同,反事实推理减轻了训练后意外混杂因素带来的影响,可以在有偏见的观察下做出无偏见的决策。受此启发,我们提出了一个与模型无关的文本分类去偏框架Corsair,它可以有效地避免采用数据操作或设计平衡机制。具体来说,Corsair 首先直接在训练集上训练基础模型,从而允许有偏差和毒害的数据集经过训练的模型。在推论中,给定一个事实输入文档,Corsair 想象它的两个反事实对应物来提炼和减轻有毒模型捕获的两个偏差。大量实验证明了 Corsair 的有效性、普遍性和公平性。

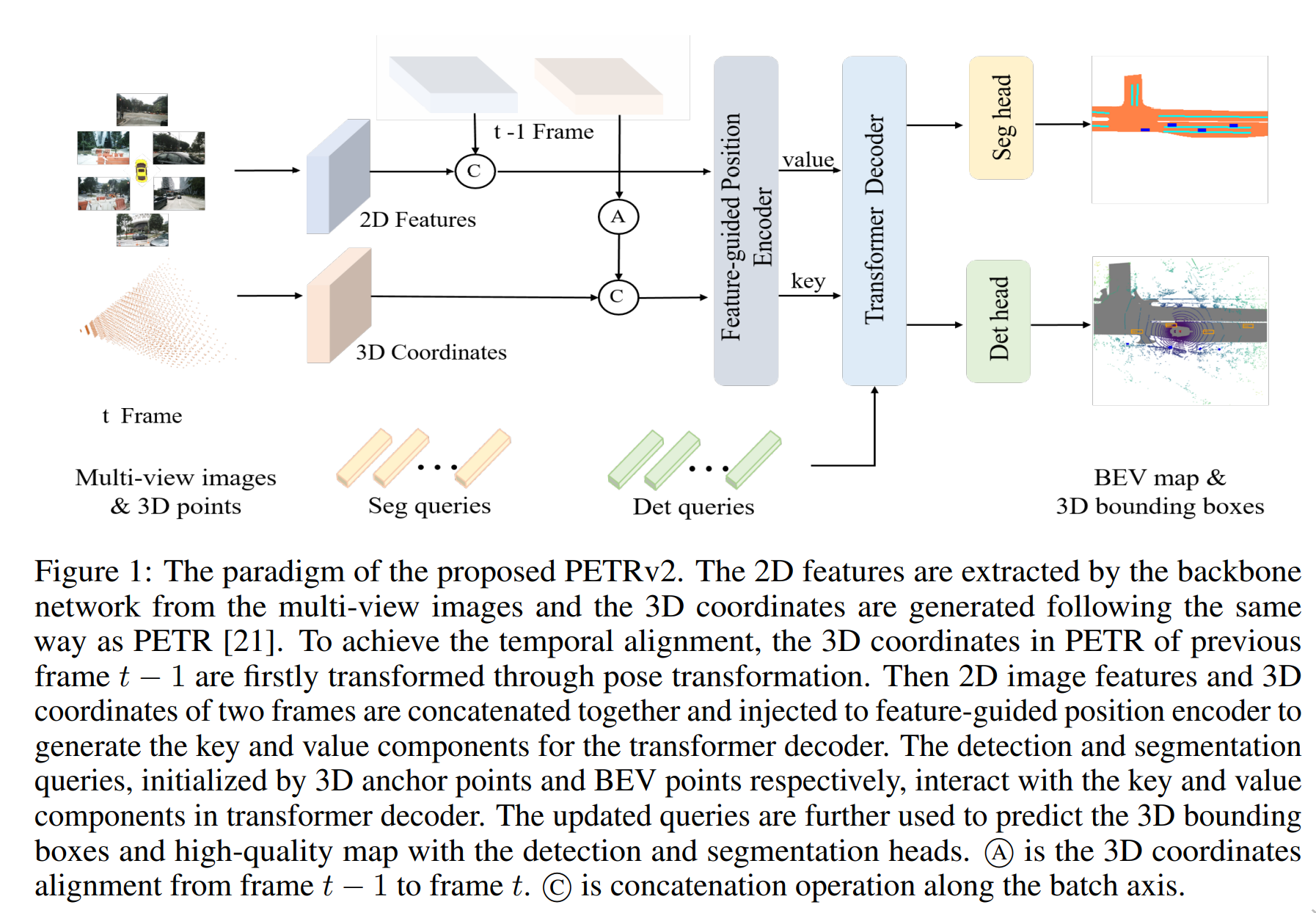
论文:PETRv2: A Unified Framework for 3D Perception from Multi-Camera Images
论文标题:PETRv2: A Unified Framework for 3D Perception from Multi-Camera Images
论文时间:2 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:3D Object Detection,object-detection,Object Detection,3D物体检测,物体检测,物体检测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01256
代码实现:https://github.com/megvii-research/petr
论文作者:Yingfei Liu, Junjie Yan, Fan Jia, Shuailin Li, Qi Gao, Tiancai Wang, Xiangyu Zhang, Jian Sun
论文简介:More specifically, we extend the 3D position embedding (3D PE) in PETR for temporal modeling. / 更具体地说,我们扩展了 PETR 中的 3D 位置嵌入 (3D PE) 用于时间建模。
论文摘要:In this paper, we propose PETRv2, a unified framework for 3D perception from multi-view images. Based on PETR, PETRv2 explores the effectiveness of temporal modeling, which utilizes the temporal information of previous frames to boost 3D object detection. More specifically, we extend the 3D position embedding (3D PE) in PETR for temporal modeling. The 3D PE achieves the temporal alignment on object position of different frames. A feature-guided position encoder is further introduced to improve the data adaptability of 3D PE. To support for high-quality BEV segmentation, PETRv2 provides a simply yet effective solution by adding a set of segmentation queries. Each segmentation query is responsible for segmenting one specific patch of BEV map. PETRv2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on 3D object detection and BEV segmentation. Detailed robustness analysis is also conducted on PETR framework. We hope PETRv2 can serve as a strong baseline for 3D perception. Code is available at https://github.com/megvii-research/PETR
在本文中,我们提出了 PETRv2,这是一个从多视图图像中进行 3D 感知的统一框架。在 PETR 的基础上,PETRv2 探索了时间建模的有效性,它利用先前帧的时间信息来提升 3D 对象检测。更具体地说,我们扩展了 PETR 中的 3D 位置嵌入 (3D PE) 以进行时间建模。 3D PE 实现了不同帧对象位置的时间对齐。进一步引入了特征引导的位置编码器,以提高 3D PE 的数据适应性。为了支持高质量的 BEV 分段,PETRv2 通过添加一组分段查询提供了一个简单而有效的解决方案。每个分割查询负责分割一个特定的 BEV 图块。 PETRv2 在 3D 对象检测和 BEV 分割方面实现了最先进的性能。还对PETR框架进行了详细的稳健性分析。我们希望 PETRv2 可以作为 3D 感知的强大基线。代码可在 https://github.com/megvii-research/PETR



论文:Implicit Sample Extension for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
论文标题:Implicit Sample Extension for Unsupervised Person Re-Identification
论文时间:CVPR 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Person Re-Identification,Unsupervised Person Re-Identification,人重识别,无监督人重识别
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06892
代码实现:https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas
论文作者:Xinyu Zhang, Dongdong Li, Zhigang Wang, Jian Wang, Errui Ding, Javen Qinfeng Shi, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Jingdong Wang
论文简介:Specifically, we generate support samples from actual samples and their neighbouring clusters in the embedding space through a progressive linear interpolation (PLI) strategy. / 具体来说,我们通过渐进线性插值(PLI)策略从嵌入空间中的实际样本及其相邻簇生成支持样本。
论文摘要:Most existing unsupervised person re-identification (Re-ID) methods use clustering to generate pseudo labels for model training. Unfortunately, clustering sometimes mixes different true identities together or splits the same identity into two or more sub clusters. Training on these noisy clusters substantially hampers the Re-ID accuracy. Due to the limited samples in each identity, we suppose there may lack some underlying information to well reveal the accurate clusters. To discover these information, we propose an Implicit Sample Extension (\OurWholeMethod) method to generate what we call support samples around the cluster boundaries. Specifically, we generate support samples from actual samples and their neighbouring clusters in the embedding space through a progressive linear interpolation (PLI) strategy. PLI controls the generation with two critical factors, i.e., 1) the direction from the actual sample towards its K-nearest clusters and 2) the degree for mixing up the context information from the K-nearest clusters. Meanwhile, given the support samples, ISE further uses a label-preserving loss to pull them towards their corresponding actual samples, so as to compact each cluster. Consequently, ISE reduces the “sub and mixed” clustering errors, thus improving the Re-ID performance. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method is effective and achieves state-of-the-art performance for unsupervised person Re-ID. Code is available at https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas
大多数现有的无监督行人重识别 (Re-ID) 方法使用聚类来生成用于模型训练的伪标签。不幸的是,聚类有时会将不同的真实身份混合在一起,或者将相同的身份拆分为两个或多个子集群。在这些嘈杂的集群上进行训练大大阻碍了 Re-ID 的准确性。由于每个身份中的样本有限,我们认为可能缺少一些基础信息来很好地揭示准确的聚类。为了发现这些信息,我们提出了一种隐式样本扩展方法来生成我们所说的围绕集群边界的支持样本。具体来说,我们通过渐进线性插值(PLI)策略从嵌入空间中的实际样本及其相邻簇生成支持样本。 PLI 用两个关键因素控制生成,即 1)从实际样本到其 K-最近集群的方向和 2)混合来自 K-最近集群的上下文信息的程度。同时,给定支持样本,ISE进一步使用标签保留损失将它们拉向对应的实际样本,从而压缩每个集群。因此,ISE 减少了“子和混合”聚类错误,从而提高了 Re-ID 性能。大量实验表明,所提出的方法是有效的,并且在无监督人员 Re-ID 方面取得了最先进的性能。代码可在 https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleClas



我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。

- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处 - 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~