ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架

工具箱:Lite.AI.ToolKit - 开箱即用的C++ AI 工具箱,包括70+流行的开源模型,如最新的RVM, YOLOX, YOLOP, YOLOR, YoloV5, DeepLabV3, ArcFace等模型,支持ONNXRuntime/NCNN/MNN/TNN
tags:[C++,目标检测,人脸检测,部署]
‘Lite.AI.ToolKit: A lite C++ toolkit of awesome AI models, such as RobustVideoMatting, YOLOX, YOLOP etc.’ by DefTruth
GitHub:http://github.com/DefTruth/lite.ai.toolkit

工具库:Zennit - PyTorch神经网络解释/探索框架
tags:[深度学习,解释,Pytorch]
‘Zennit - a high-level framework in Python using PyTorch for explaining/exploring neural networks using attribution methods like LRP.’ by Christopher
GitHub:http://github.com/chr5tphr/zennit
工具库:PyDaddy - 分析随机时间序列数据
tags:[时间序列]
‘PyDaddy - Package to analyse stochastic time series data’ by TEE Lab
GitHub:http://github.com/tee-lab/PyDaddy

工具库:continual-inference - 用于构建持续推理网络的PyTorch组件库
tags:[持续推理,神经网络,pytorch]
‘continual-inference - PyTorch building blocks for Continual Inference Networks’ by LukasHedegaard
GitHub:http://github.com/LukasHedegaard/continual-inference

工具库:gget - 用于高效查询基因组数据库的开源命令行工具和Python包
tags:[基因组,基因数据,生物医疗]
‘gget - a free and open-source command-line tool and Python package that enables efficient querying of genomic databases’ by Pachter Lab
GitHub:http://github.com/pachterlab/gget

2.项目&代码

项目:Python-Mini-Projects:Python迷你练手项目集锦
tags:[Python,项目]
‘Python-Mini-Projects - A collection of simple python mini projects to enhance your python skills’ by PYTHON WORLD
GitHub:https://github.com/Python-World/python-mini-projects
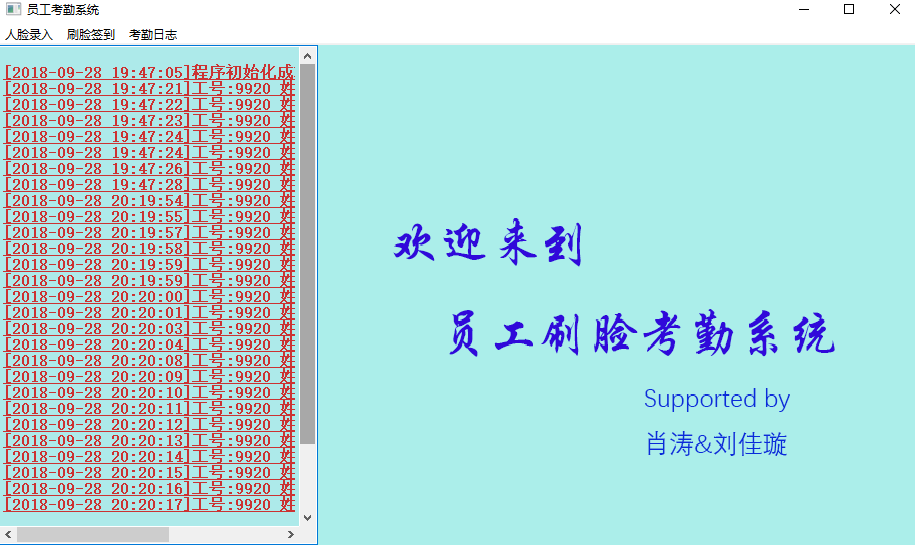
项目:WorkAttendanceSystem - 基于opencv、dilb的员工人脸识别考勤系统
tags:[opencv,dilib,人脸识别,自动考勤]
GitHub:http://github.com/inspurer/WorkAttendanceSystem

3.博文&分享

教程:( ACL 2022 Tutorial Slides): 基于预训练语言模型的零样本和少样本 NLP
tags:[语言模型,少样本学习,自然语言处理]
‘ACL 2022 Tutorial: Zero- and Few-Shot NLP with Pretrained Language Models’ by AI2
GitHub:http://github.com/allenai/acl2022-zerofewshot-tutorial
教程:The System Design Primer:系统设计入门,学习如何设计可扩展系统
tags:[系统设计]
‘The System Design Primer - Learn how to design large-scale systems. Prep for the system design interview. Includes Anki flashcards.’ by Donne Martin
GitHub:http://github.com/donnemartin/system-design-primer/blob/master/README-zh-Hans.md
教程:GitHub为Markdown设置的一些特殊的引用块样式,方便设计
tags:[资讯,工具]
GitHub:http://github.com/github/feedback/discussions/16925
4.数据&资源

数据集:3D人体数据集
tags:[数据集,人体]
‘THUman3.0 Dataset’ by fwbx529
GitHub:http://github.com/fwbx529/THuman3.0-Dataset

资源数据:myosuite:用肌肉骨骼模型解决的环境/任务集合
tags:[数据,任务,肌肉,骨骼]
‘MyoSuite - a collection of environments/tasks to be solved by musculoskeletal models simulated with the MuJoCo physics engine and wrapped in the OpenAI gym API.’ by Meta Research
GitHub:http://github.com/facebookresearch/myosuite

数据集:MuCGEC中文纠错数据集及文本纠错SOTA模型
tags:[纠错,文本纠错,数据集]
GitHub:http://github.com/HillZhang1999/MuCGEC
资源列表:图和表格数据上的联邦学习文献资源列表
tags:[图,表格,结构化,联邦学习]
‘Federated-Learning-on-Graph-and-Tabular-Data - Federated learning on graph and tabular data related papers, frameworks, and datasets.’ by YoungFish
GitHub:http://github.com/youngfish42/Awesome-Federated-Learning-on-Graph-and-Tabular-Data
5.研究&论文

可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
论文:Pretraining is All You Need for Image-to-Image Translation
论文标题:Pretraining is All You Need for Image-to-Image Translation
论文时间:25 May 2022
所属领域:Adversarial/对抗性
对应任务:Image-to-Image Translation,Texture Synthesis,Translation,图图转换,纹理合成,转换
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.12952
代码实现:https://github.com/PITI-Synthesis/PITI
论文作者:Tengfei Wang, Ting Zhang, Bo Zhang, Hao Ouyang, Dong Chen, Qifeng Chen, Fang Wen
论文简介:We propose to use pretraining to boost general image-to-image translation. / 我们建议使用预训练来提高一般的图图转换(Image-to-Image Translation)。
论文摘要:We propose to use pretraining to boost general image-to-image translation. Prior image-to-image translation methods usually need dedicated architectural design and train individual translation models from scratch, struggling for high-quality generation of complex scenes, especially when paired training data are not abundant. In this paper, we regard each image-to-image translation problem as a downstream task and introduce a simple and generic framework that adapts a pretrained diffusion model to accommodate various kinds of image-to-image translation. We also propose adversarial training to enhance the texture synthesis in the diffusion model training, in conjunction with normalized guidance sampling to improve the generation quality. We present extensive empirical comparison across various tasks on challenging benchmarks such as ADE20K, COCO-Stuff, and DIODE, showing the proposed pretraining-based image-to-image translation (PITI) is capable of synthesizing images of unprecedented realism and faithfulness.
我们建议使用预训练来提高一般的图图转换(Image-to-Image Translation)效果。先前的图图转换方法通常需要专门的架构设计和从头开始训练单个翻译模型,难以高质量地生成复杂场景下的图像,尤其是在配对训练数据不丰富的情况下。在本文中,我们将每个图图转换问题视为一个下游任务,并引入了一个简单且通用的框架,该框架采用预训练的扩散模型来适应各种图像到图像的翻译。我们还提出对抗性训练以增强扩散模型训练中的纹理合成,并结合归一化引导采样以提高生成质量。我们在 ADE20K、COCO-Stuff 和 DIODE 等具有挑战性的基准上对各种任务进行了广泛的实证比较,表明所提出的基于预训练的图像到图像转换 (PITI) 能够合成具有前所未有的真实可靠的图像。


论文:Variational Diffusion Models
论文标题:Variational Diffusion Models
论文时间:NeurIPS 2021
所属领域:Methodology
对应任务:Density Estimation,密度估计
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.00630
代码实现:https://github.com/google-research/vdm
论文作者:Diederik Kingma, Tim Salimans, Ben Poole, Jonathan Ho
论文简介:In addition, we show that the continuous-time VLB is invariant to the noise schedule, except for the signal-to-noise ratio at its endpoints. / 此外,我们证明了连续时间 VLB 对噪声调度是不变的,除了端点处的信噪比。
论文摘要:Diffusion-based generative models have demonstrated a capacity for perceptually impressive synthesis, but can they also be great likelihood-based models? We answer this in the affirmative, and introduce a family of diffusion-based generative models that obtain state-of-the-art likelihoods on standard image density estimation benchmarks. Unlike other diffusion-based models, our method allows for efficient optimization of the noise schedule jointly with the rest of the model. We show that the variational lower bound (VLB) simplifies to a remarkably short expression in terms of the signal-to-noise ratio of the diffused data, thereby improving our theoretical understanding of this model class. Using this insight, we prove an equivalence between several models proposed in the literature. In addition, we show that the continuous-time VLB is invariant to the noise schedule, except for the signal-to-noise ratio at its endpoints. This enables us to learn a noise schedule that minimizes the variance of the resulting VLB estimator, leading to faster optimization. Combining these advances with architectural improvements, we obtain state-of-the-art likelihoods on image density estimation benchmarks, outperforming autoregressive models that have dominated these benchmarks for many years, with often significantly faster optimization. In addition, we show how to use the model as part of a bits-back compression scheme, and demonstrate lossless compression rates close to the theoretical optimum.
基于扩散的生成模型已经证明了一种强大的综合能力,但它们也可以是很好的基于可能性的模型吗?我们的回答是肯定的,并引入了一系列基于扩散的生成模型,这些模型在标准图像密度估计基准上获得了最先进的效果。与其他基于扩散的模型不同,我们的方法允许与模型的其余部分一起有效地优化噪声调度。我们表明,变分下限(VLB)在扩散数据的信噪比方面简化为一个非常短的表达式,从而提高了我们对这个模型类的理论理解。利用这一想法,我们证明了文献中提出的几个模型之间的等价性。此外,我们证明了连续时间 VLB 对噪声调度是不变的,除了其端点的信噪比。这使我们能够学习最小化结果 VLB 估计器的方差的噪声调度,从而实现更快的优化。将这些进步与架构改进相结合,我们在图像密度估计基准上获得了最先进的可能性,优于多年来主导这些基准的自回归模型,而且优化速度通常要快得多。此外,我们展示了如何将该模型用作位回压缩方案的一部分,并展示了接近理论最优值的无损压缩率。



论文:Top1 Solution of QQ Browser 2021 Ai Algorithm Competition Track 1 : Multimodal Video Similarity
论文标题:Top1 Solution of QQ Browser 2021 Ai Algorithm Competition Track 1 : Multimodal Video Similarity
论文时间:30 Oct 2021
所属领域:Natural Language Processing/自然语言处理
对应任务:Language Modelling,TAG,Video Similarity,语言建模,视频相似度
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.01677
代码实现:https://github.com/zr2021/2021_qq_aiac_tack1_1st
论文作者:Zhuoran Ma, Majing Lou, Xuan Ouyang
论文简介:In this paper, we describe the solution to the QQ Browser 2021 Ai Algorithm Competition (AIAC) Track 1. / 在本文中,我们描述了 QQ 浏览器 2021 人工智能算法竞赛 (AIAC) Track 1 的解决方案。
论文摘要:In this paper, we describe the solution to the QQ Browser 2021 Ai Algorithm Competition (AIAC) Track 1. We use the multi-modal transformer model for the video embedding extraction. In the pretrain phase, we train the model with three tasks, (1) Video Tag Classification (VTC), (2) Mask Language Modeling (MLM) and (3) Mask Frame Modeling (MFM). In the finetune phase, we train the model with video similarity based on rank normalized human labels. Our full pipeline, after ensembling several models, scores 0.852 on the leaderboard, which we achieved the 1st place in the competition. The source codes have been released at Github.
在本文中,我们描述了 QQ 浏览器 2021 人工智能算法竞赛 (AIAC) Track 1 的解决方案。我们使用多模态转换器模型进行视频嵌入提取。 在预训练阶段,我们用三个任务训练模型,(1)视频标签分类(VTC),(2)掩码语言建模(MLM)和(3)掩码帧建模(MFM)。 在微调阶段,我们根据等级归一化的人类标签训练具有视频相似性的模型。 我们的完整管道在集成了几个模型后,在排行榜上的得分为 0.852,我们在比赛中获得了第一名。 源代码已在 Github 上发布。


论文:Dataset Condensation via Efficient Synthetic-Data Parameterization
论文标题:Dataset Condensation via Efficient Synthetic-Data Parameterization
论文时间:30 May 2022
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14959
代码实现:https://github.com/snu-mllab/efficient-dataset-condensation
论文作者:Jang-Hyun Kim, Jinuk Kim, Seong Joon Oh, Sangdoo Yun, Hwanjun Song, JoonHyun Jeong, Jung-Woo Ha, Hyun Oh Song
论文简介:The great success of machine learning with massive amounts of data comes at a price of huge computation costs and storage for training and tuning. / 具有大量数据的机器学习的巨大成功是以巨大的计算成本和用于训练和调整的存储为代价的。
论文摘要:The great success of machine learning with massive amounts of data comes at a price of huge computation costs and storage for training and tuning. Recent studies on dataset condensation attempt to reduce the dependence on such massive data by synthesizing a compact training dataset. However, the existing approaches have fundamental limitations in optimization due to the limited representability of synthetic datasets without considering any data regularity characteristics. To this end, we propose a novel condensation framework that generates multiple synthetic data with a limited storage budget via efficient parameterization considering data regularity. We further analyze the shortcomings of the existing gradient matching-based condensation methods and develop an effective optimization technique for improving the condensation of training data information. We propose a unified algorithm that drastically improves the quality of condensed data against the current state-of-the-art on CIFAR-10, ImageNet, and Speech Commands.
海量数据上的机器学习的巨大成功是以巨大的计算成本和用于训练和调整的存储为代价的。最近关于数据集压缩的研究试图通过合成一个紧凑的训练数据集来减少对如此大量数据的依赖。然而,由于合成数据集的可表示性有限,没有考虑任何数据规律性特征,现有方法在优化方面存在根本限制。为此,我们提出了一种新颖的压缩框架,该框架通过考虑数据规律性的有效参数化生成具有有限存储预算的多个合成数据。我们进一步分析了现有基于梯度匹配的压缩方法的缺点,并开发了一种有效的优化技术来改进训练数据信息的压缩。我们提出了一种统一的算法,可以相对于 CIFAR-10、ImageNet 和 Speech Commands 上的当前最先进技术大幅提高压缩数据的质量。


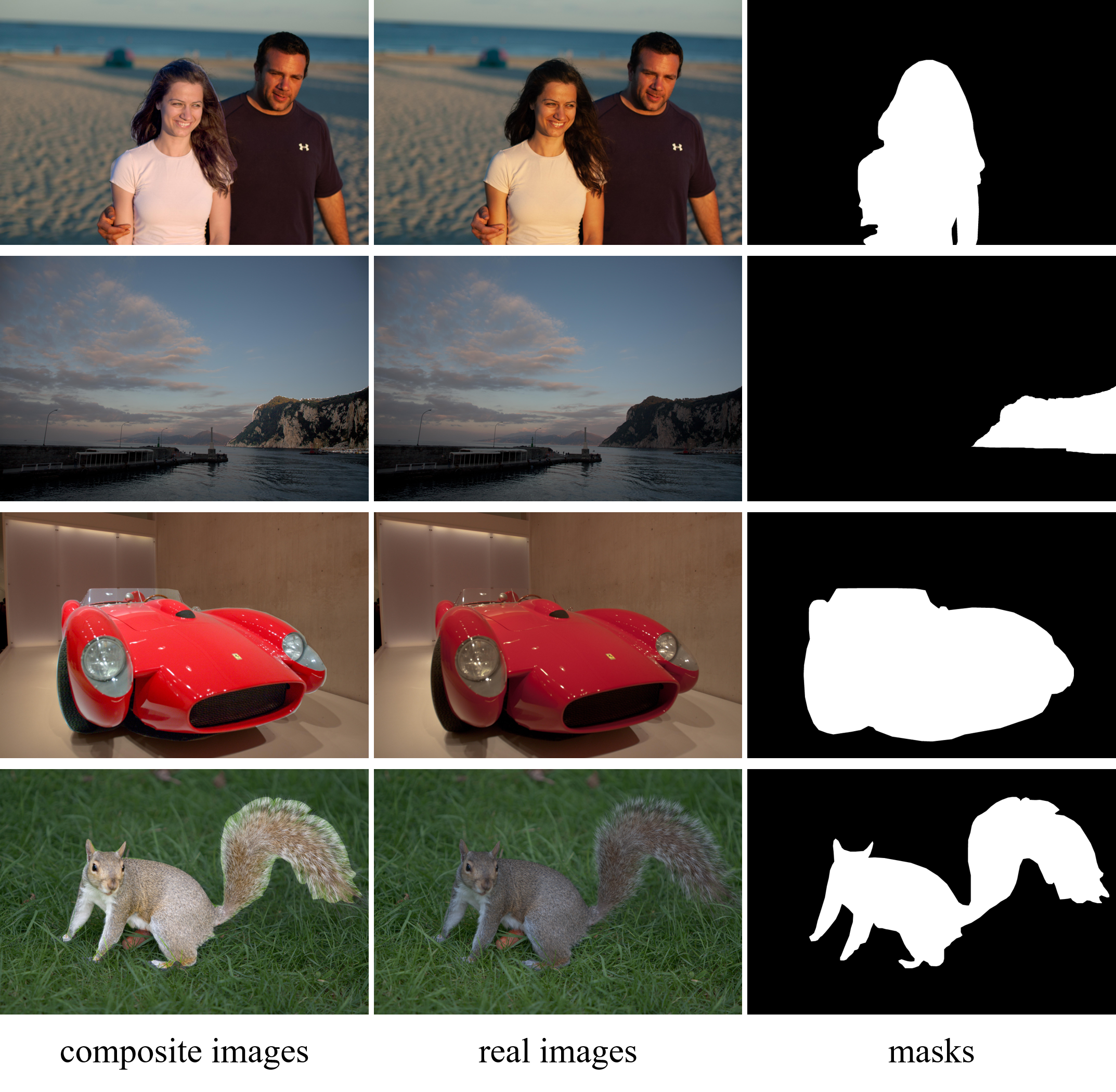
论文:High-Resolution Image Harmonization via Collaborative Dual Transformations
论文标题:High-Resolution Image Harmonization via Collaborative Dual Transformations
论文时间:14 Sep 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06671
代码实现:https://github.com/bcmi/CDTNet-High-Resolution-Image-Harmonization
论文作者:Wenyan Cong, Xinhao Tao, Li Niu, Jing Liang, Xuesong Gao, Qihao Sun, Liqing Zhang
论文简介:Conventional image harmonization methods learn global RGB-to-RGB transformation which could effortlessly scale to high resolution, but ignore diverse local context. / 传统的图像协调方法学习全局 RGB 到 RGB 的转换,可以毫不费力地扩展到高分辨率,但忽略了不同的局部上下文。
论文摘要:Given a composite image, image harmonization aims to adjust the foreground to make it compatible with the background. High-resolution image harmonization is in high demand, but still remains unexplored. Conventional image harmonization methods learn global RGB-to-RGB transformation which could effortlessly scale to high resolution, but ignore diverse local context. Recent deep learning methods learn the dense pixel-to-pixel transformation which could generate harmonious outputs, but are highly constrained in low resolution. In this work, we propose a high-resolution image harmonization network with Collaborative Dual Transformation (CDTNet) to combine pixel-to-pixel transformation and RGB-to-RGB transformation coherently in an end-to-end network. Our CDTNet consists of a low-resolution generator for pixel-to-pixel transformation, a color mapping module for RGB-to-RGB transformation, and a refinement module to take advantage of both. Extensive experiments on high-resolution benchmark dataset and our created high-resolution real composite images demonstrate that our CDTNet strikes a good balance between efficiency and effectiveness. Our used datasets can be found in https://github.com/bcmi/CDTNet-High-Resolution-Image-Harmonization .
给定一张合成图像,图像协调旨在调整前景使其与背景兼容。高分辨率图像协调的需求量很大,但仍未得到探索。传统的图像协调方法学习全局 RGB 到 RGB 转换,可以毫不费力地扩展到高分辨率,但忽略了不同的局部上下文。最近的深度学习方法学习密集的像素到像素的转换,可以产生和谐的输出,但在低分辨率下受到高度限制。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个高分辨率图像协调网络与协作双变换 (CDTNet),以在端到端网络中连贯地结合像素到像素的变换和 RGB 到 RGB 的变换。我们的 CDTNet 包括一个用于像素到像素转换的低分辨率生成器、一个用于 RGB 到 RGB 转换的颜色映射模块,以及一个利用两者的细化模块。高分辨率基准数据集和我们创建的高分辨率真实合成图像的广泛实验表明,我们的 CDTNet 在效率和有效性之间取得了良好的平衡。我们使用的数据集可以在 https://github.com/bcmi/CDTNet-High-Resolution-Image-Harmonization 中找到。



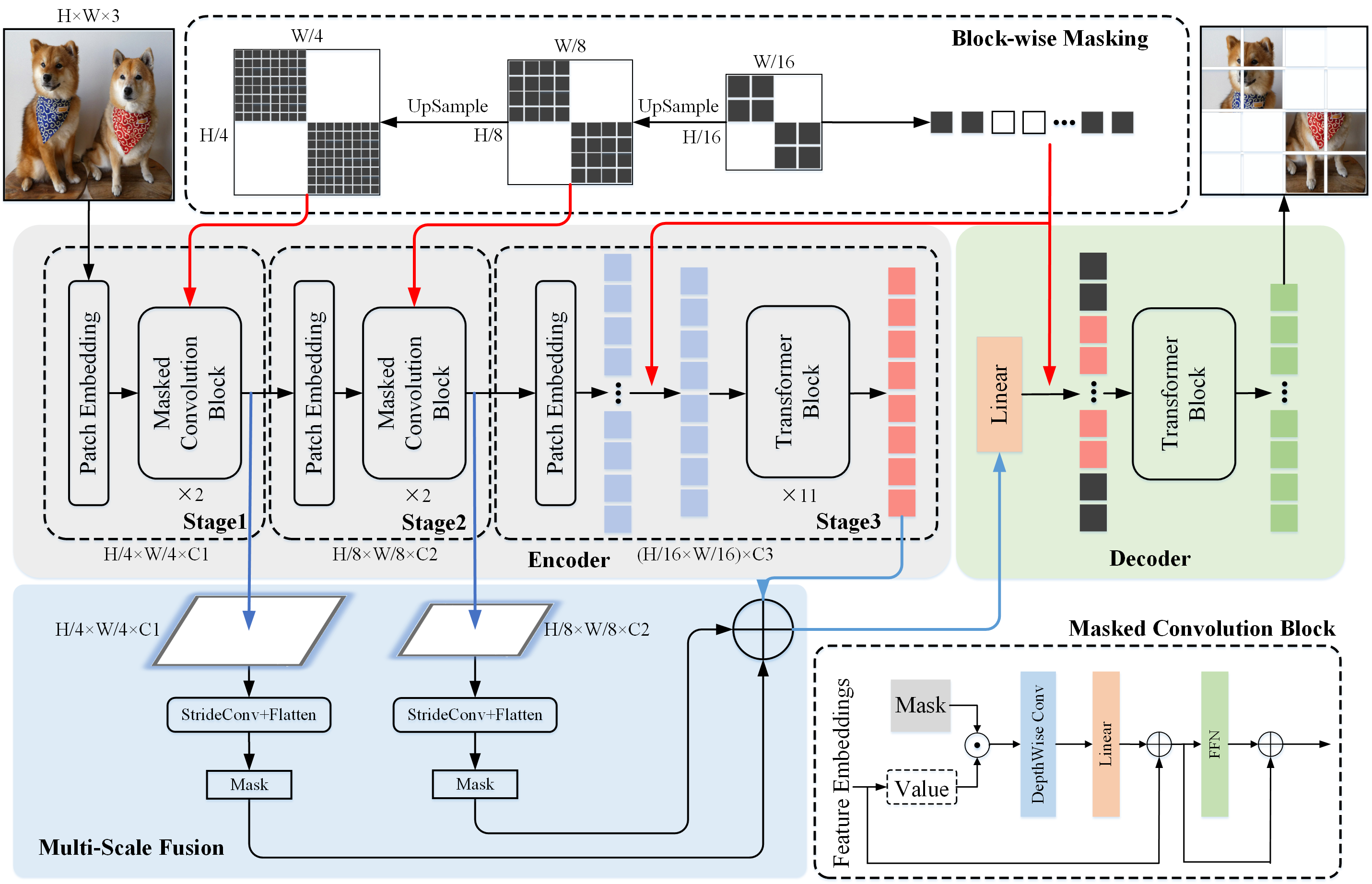
论文:ConvMAE: Masked Convolution Meets Masked Autoencoders
论文标题:ConvMAE: Masked Convolution Meets Masked Autoencoders
论文时间:8 May 2022
所属领域:Natural Language Processing/计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Classification,Object Detection,Semantic Segmentation,图像分类,目标检测,语义分割
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.03892
代码实现:https://github.com/alpha-vl/convmae
论文作者:Peng Gao, Teli Ma, Hongsheng Li, Ziyi Lin, Jifeng Dai, Yu Qiao
论文简介:Masked auto-encoding for feature pretraining and multi-scale hybrid convolution-transformer architectures can further unleash the potentials of ViT, leading to state-of-the-art performances on image classification, detection and semantic segmentation. / 用于特征预训练和多尺度混合卷积变换器架构的掩码自动编码可以进一步释放 ViT 的潜力,从而在图像分类、检测和语义分割方面取得最先进的性能。
论文摘要:Vision Transformers (ViT) become widely-adopted architectures for various vision tasks. Masked auto-encoding for feature pretraining and multi-scale hybrid convolution-transformer architectures can further unleash the potentials of ViT, leading to state-of-the-art performances on image classification, detection and semantic segmentation. In this paper, our ConvMAE framework demonstrates that multi-scale hybrid convolution-transformer can learn more discriminative representations via the mask auto-encoding scheme. However, directly using the original masking strategy leads to the heavy computational cost and pretraining-finetuning discrepancy. To tackle the issue, we adopt the masked convolution to prevent information leakage in the convolution blocks. A simple block-wise masking strategy is proposed to ensure computational efficiency. We also propose to more directly supervise the multi-scale features of the encoder to boost multi-scale features. Based on our pretrained ConvMAE models, ConvMAE-Base improves ImageNet-1K finetuning accuracy by 1.4% compared with MAE-Base. On object detection, ConvMAE-Base finetuned for only 25 epochs surpasses MAE-Base fined-tuned for 100 epochs by 2.9% box AP and 2.2% mask AP respectively. Code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/Alpha-VL/ConvMAE .
视觉Transformer (ViT) 已成为各种视觉任务广泛采用的架构。用于特征预训练和多尺度混合卷积变换器架构的掩码自动编码可以进一步释放 ViT 的潜力,从而在图像分类、检测和语义分割方面取得最先进的性能。在本文中,我们的 ConvMAE 框架证明了多尺度混合卷积变换器可以通过掩码自动编码方案学习更多的判别表示。然而,直接使用原始掩码策略会导致计算成本和预训练-微调差异。为了解决这个问题,我们采用掩码卷积来防止卷积块中的信息泄漏。提出了一种简单的分块屏蔽策略来确保计算效率。我们还建议更直接地监督编码器的多尺度特征以提升多尺度特征。基于我们预训练的 ConvMAE 模型,与 MAE-Base 相比,ConvMAE-Base 将 ImageNet-1K 微调精度提高了 1.4%。在目标检测方面,仅微调 25 个 epoch 的 ConvMAE-Base 比微调 100 个 epoch 的 MAE-Base 分别高出 2.9% 的框 AP 和 2.2% 的掩码 AP。代码和预训练模型可在 https://github.com/Alpha-VL/ConvMAE 获得。
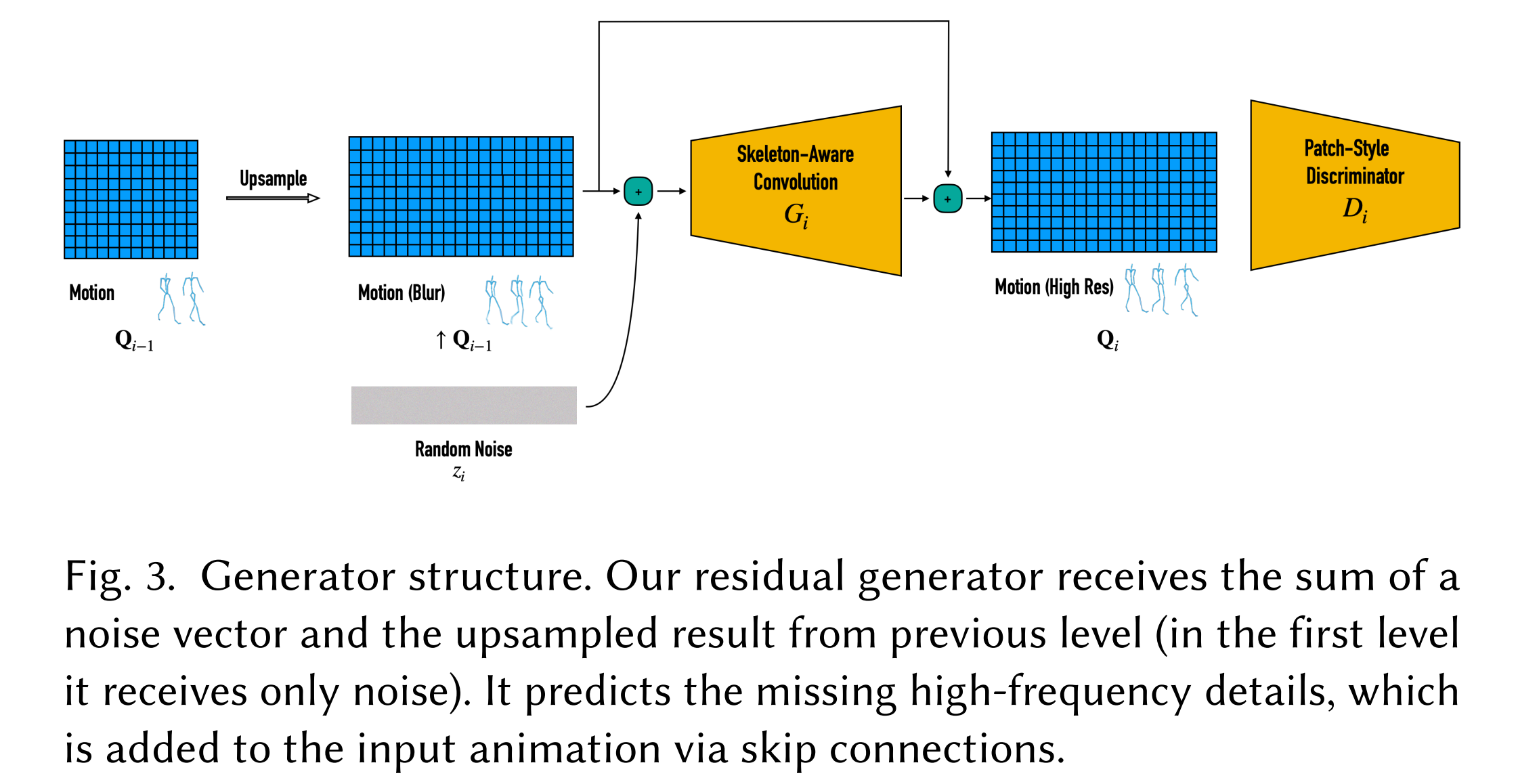
论文:GANimator: Neural Motion Synthesis from a Single Sequence
论文标题:GANimator: Neural Motion Synthesis from a Single Sequence
论文时间:5 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision
对应任务:motion synthesis,Style Transfer,运动合成,风格转移
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.02625
代码实现:https://github.com/PeizhuoLi/ganimator
论文作者:Peizhuo Li, Kfir Aberman, Zihan Zhang, Rana Hanocka, Olga Sorkine-Hornung
论文简介:We present GANimator, a generative model that learns to synthesize novel motions from a single, short motion sequence. / 我们提出了 GANimator,这是一种生成模型,可以学习从单个短运动序列中合成新的运动。
论文摘要:We present GANimator, a generative model that learns to synthesize novel motions from a single, short motion sequence. GANimator generates motions that resemble the core elements of the original motion, while simultaneously synthesizing novel and diverse movements. Existing data-driven techniques for motion synthesis require a large motion dataset which contains the desired and specific skeletal structure. By contrast, GANimator only requires training on a single motion sequence, enabling novel motion synthesis for a variety of skeletal structures e.g., bipeds, quadropeds, hexapeds, and more. Our framework contains a series of generative and adversarial neural networks, each responsible for generating motions in a specific frame rate. The framework progressively learns to synthesize motion from random noise, enabling hierarchical control over the generated motion content across varying levels of detail. We show a number of applications, including crowd simulation, key-frame editing, style transfer, and interactive control, which all learn from a single input sequence. Code and data for this paper are at https://peizhuoli.github.io/ganimator .
我们提出了 GANimator,这是一种生成模型,可以学习从单个短运动序列中合成新的运动。 GANimator 生成类似于原始动作核心元素的动作,同时合成新颖多样的动作。用于运动合成的现有数据驱动技术需要包含所需和特定骨骼结构的大型运动数据集。相比之下,GANimator 只需要对单个运动序列进行训练,从而为各种骨骼结构(例如双足动物、四足动物、六足动物等)实现新颖的运动合成。我们的框架包含一系列生成和对抗神经网络,每个网络负责以特定帧速率生成运动。该框架逐步学习从随机噪声中合成运动,从而能够对生成的运动内容进行分层控制,涵盖不同的细节级别。我们展示了许多应用程序,包括人群模拟、关键帧编辑、样式转换和交互式控制,它们都从单个输入序列中学习。本文的代码和数据在https://peizhuoli.github.io/ganimator。


论文:MAE-AST: Masked Autoencoding Audio Spectrogram Transformer
论文标题:MAE-AST: Masked Autoencoding Audio Spectrogram Transformer
论文时间:30 Mar 2022
所属领域:Audio/音频
对应任务:Audio Classification,音频分类
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.16691
代码实现:https://github.com/AlanBaade/MAE-AST-Public
论文作者:Alan Baade, Puyuan Peng, David Harwath
论文简介:In this paper, we propose a simple yet powerful improvement over the recent Self-Supervised Audio Spectrogram Transformer (SSAST) model for speech and audio classification. / 在这篇论文中,我们提出了一个简单而强大的改进,对最近用于语音和音频分类的自监督音频频谱图变换器 (SSAST) 模型进行了改进。
论文摘要:In this paper, we propose a simple yet powerful improvement over the recent Self-Supervised Audio Spectrogram Transformer (SSAST) model for speech and audio classification. Specifically, we leverage the insight that the SSAST uses a very high masking ratio (75%) during pretraining, meaning that the vast majority of self-attention compute is performed on mask tokens. We address this by integrating the encoder-decoder architecture from Masked Autoencoders are Scalable Vision Learners (MAE) into the SSAST, where a deep encoder operates on only unmasked input, and a shallow decoder operates on encoder outputs and mask tokens. We find that MAE-like pretraining can provide a 3x speedup and 2x memory usage reduction over the vanilla SSAST using current audio pretraining strategies with ordinary model and input sizes. When fine-tuning on downstream tasks, which only uses the encoder, we find that our approach outperforms the SSAST on a variety of downstream tasks. We further conduct comprehensive evaluations into different strategies of pretraining and explore differences in MAE-style pretraining between the visual and audio domains.
在本文中,我们提出了一个简单而强大的改进,该改进是对最近用于语音和音频分类的自监督音频频谱图Transformer (Self-Supervised Audio Spectrogram Transformer SSAST) 模型。具体来说,我们认为 SSAST 在预训练期间使用非常高的掩码率 (75%) ,这意味着绝大多数自注意力计算都是在掩码令牌上执行的。我们通过将 Masked Autoencoders are Scalable Vision Learners (MAE) 的编码器-解码器架构集成到 SSAST 中来解决这个问题,其中深度编码器仅对未屏蔽的输入进行操作,而浅解码器对编码器输出和掩码令牌进行操作。我们发现,使用当前具有普通模型和输入大小的音频预训练策略,与普通 SSAST 相比,类似 MAE 的预训练可以提供 3 倍的加速和 2 倍的内存使用减少。在对仅使用编码器的下游任务进行微调时,我们发现我们的方法在各种下游任务上都优于 SSAST。我们进一步对不同的预训练策略进行综合评估,并探索视觉和音频领域之间 MAE 式预训练的差异。



论文:Are Transformers Effective for Time Series Forecasting?
论文标题:Are Transformers Effective for Time Series Forecasting?
论文时间:26 May 2022
所属领域:时间序列
对应任务:Anomaly Detection,Relation Extraction,Time Series,Time Series Analysis,Time Series Forecasting,异常检测,关系提取,时间序列,时间序列分析,时间序列预测
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.13504
代码实现:https://github.com/cure-lab/DLinear
论文作者:Ailing Zeng, Muxi Chen, Lei Zhang, Qiang Xu
论文简介:Recently, there has been a surge of Transformer-based solutions for the time series forecasting (TSF) task, especially for the challenging long-term TSF problem. / 最近,针对时间序列预测 (TSF) 任务的基于 Transformer 的解决方案激增,尤其是针对具有挑战性的长期 TSF 问题。
论文摘要:Recently, there has been a surge of Transformer-based solutions for the time series forecasting (TSF) task, especially for the challenging long-term TSF problem. Transformer architecture relies on self-attention mechanisms to effectively extract the semantic correlations between paired elements in a long sequence, which is permutation-invariant and anti-ordering to some extent. However, in time series modeling, we are to extract the temporal relations among an ordering set of continuous points. Consequently, whether Transformer-based techniques are the right solutions for long-term time series forecasting is an interesting problem to investigate, despite the performance improvements shown in these studies. In this work, we question the validity of Transformer-based TSF solutions. In their experiments, the compared (non-Transformer) baselines are mainly autoregressive forecasting solutions, which usually have a poor long-term prediction capability due to inevitable error accumulation effects. In contrast, we use an embarrassingly simple architecture named DLinear that conducts direct multi-step (DMS) forecasting for comparison. DLinear decomposes the time series into a trend and a remainder series and employs two one-layer linear networks to model these two series for the forecasting task. Surprisingly, it outperforms existing complex Transformer-based models in most cases by a large margin. Therefore, we conclude that the relatively higher long-term forecasting accuracy of Transformer-based TSF solutions shown in existing works has little to do with the temporal relation extraction capabilities of the Transformer architecture. Instead, it is mainly due to the non-autoregressive DMS forecasting strategy used in them. We hope this study also advocates revisiting the validity of Transformer-based solutions for other time series analysis tasks (e.g., anomaly detection) in the future.
最近,针对时间序列预测 (TSF) 任务的基于 Transformer 的解决方案激增,尤其是针对具有挑战性的长期 TSF(时间序列预测) 问题。 Transformer 架构依靠自注意力机制来有效提取长序列中配对元素之间的语义相关性,这在一定程度上是置换不变和反序的。然而,在时间序列建模中,我们要提取一组有序的连续点之间的时间关系。因此,尽管这些研究显示了性能改进,但基于 Transformer 的技术是否是长期时间序列预测的正确解决方案是一个值得研究的有趣问题。在这项工作中,我们质疑基于 Transformer 的 TSF 解决方案的有效性。实验中,比较的(非 Transformer)基线主要是自回归预测解决方案,由于不可避免的误差累积效应,它们的长期预测能力通常很差。相比之下,我们使用了一种非常简单的架构,名为 DLinear,它进行直接多步 (DMS) 预测进行比较。 DLinear 将时间序列分解为趋势序列和余数序列,并采用两个单层线性网络对这两个序列进行建模以用于预测任务。令人惊讶的是,在大多数情况下,它大大优于现有的基于 Transformer 的复杂模型。因此,我们得出结论,现有作品中基于 Transformer 的 TSF 解决方案相对较高的长期预测精度与 Transformer 架构的时间关系提取能力关系不大。相反,这主要是由于其中使用了非自回归 DMS 预测策略。我们希望这项研究还提倡在未来重新审视基于 Transformer 的解决方案对其他时间序列分析任务(例如异常检测)的有效性。
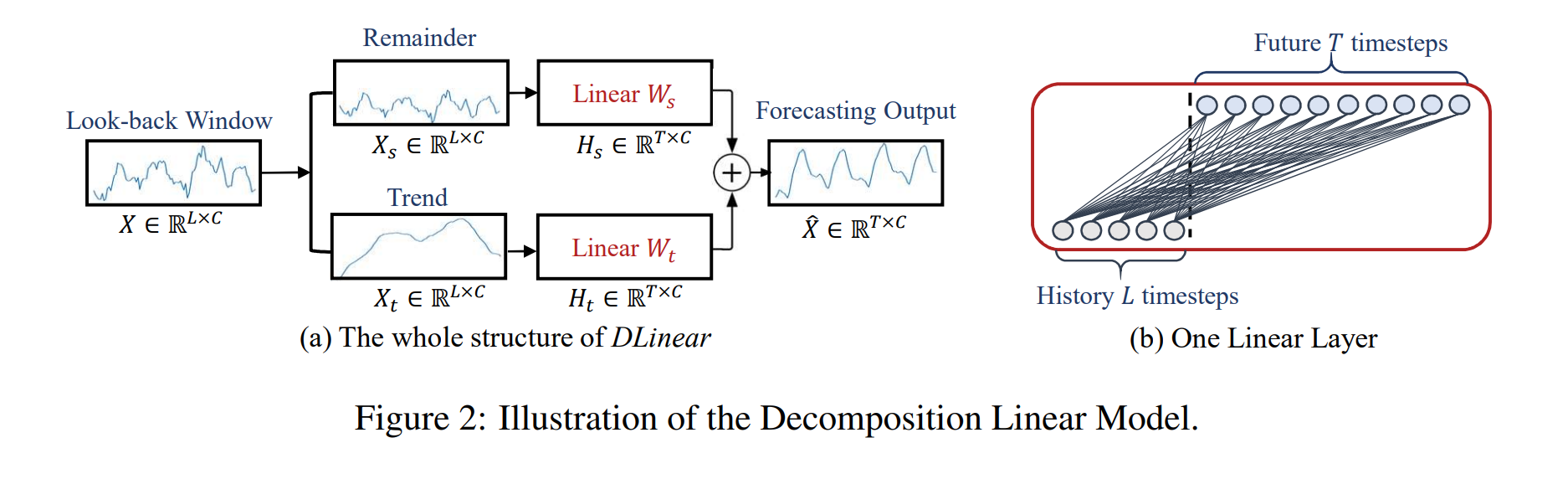
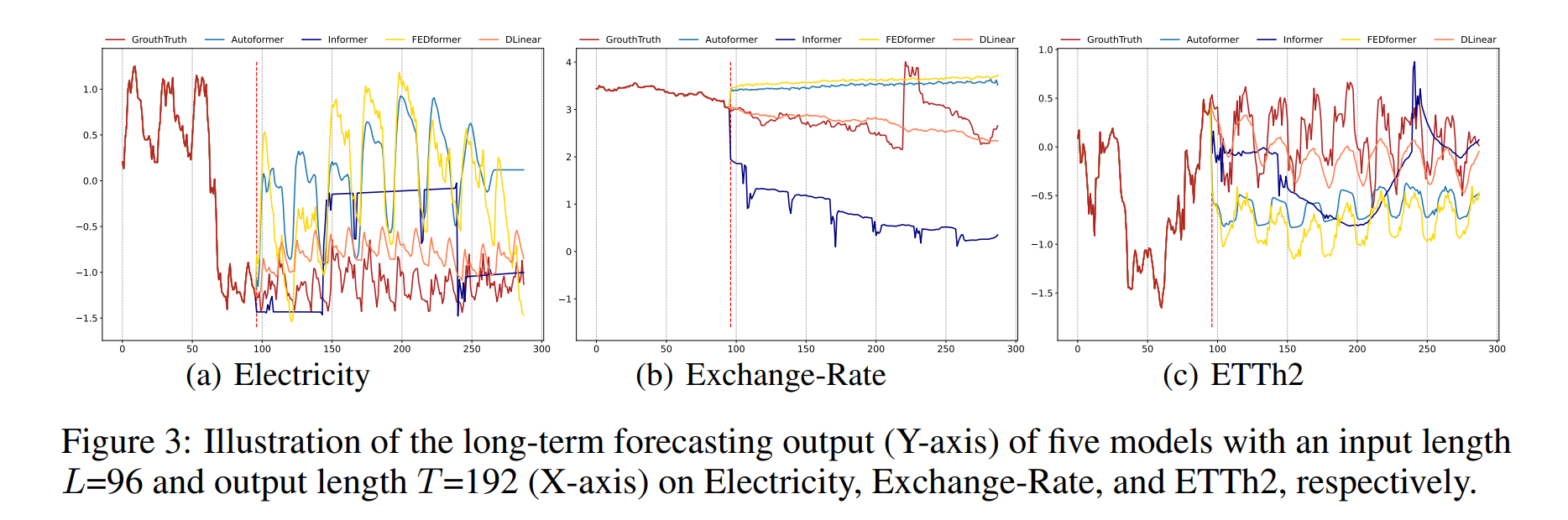
论文:Multimodal Image Synthesis and Editing: A Survey
论文标题:Multimodal Image Synthesis and Editing: A Survey
论文时间:27 Dec 2021
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Generation,图像生成
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.13592
代码实现:https://github.com/fnzhan/mise
论文作者:Fangneng Zhan, Yingchen Yu, Rongliang Wu, Jiahui Zhang, Shijian Lu
论文简介:We start with an introduction to different types of guidance modalities in image synthesis and editing. / 我们首先介绍图像合成和编辑中不同类型的引导模式。
论文摘要:As information exists in various modalities in real world, effective interaction and fusion among multimodal information plays a key role for the creation and perception of multimodal data in computer vision and deep learning research. With superb power in modelling the interaction among multimodal information, multimodal image synthesis and editing have become a hot research topic in recent years. Different from traditional visual guidance which provides explicit clues, multimodal guidance offers intuitive and flexible means in image synthesis and editing. On the other hand, this field is also facing several challenges in alignment of features with inherent modality gaps, synthesis of high-resolution images, faithful evaluation metrics, etc. In this survey, we comprehensively contextualize the advance of the recent multimodal image synthesis & editing and formulate taxonomies according to data modality and model architectures. We start with an introduction to different types of guidance modalities in image synthesis and editing. We then describe multimodal image synthesis and editing approaches extensively with detailed frameworks including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), GAN Inversion, Transformers, and other methods such as NeRF and Diffusion models. This is followed by a comprehensive description of benchmark datasets and corresponding evaluation metrics as widely adopted in multimodal image synthesis and editing, as well as detailed comparisons of different synthesis methods with analysis of respective advantages and limitations. Finally, we provide insights into the current research challenges and possible future research directions. A project associated with this survey is available at https://github.com/fnzhan/MISE.
由于现实世界中信息以各种模态存在,多模态信息之间的有效交互和融合对于计算机视觉和深度学习研究中多模态数据的创建和感知起着关键作用。凭借对多模态信息交互建模的强大能力,多模态图像合成与编辑成为近年来的研究热点。与传统的提供明确线索的视觉引导不同,多模态引导在图像合成和编辑方面提供了直观灵活的手段。另一方面,该领域在特征与固有模态差距的对齐、高分辨率图像的合成、真实性的评估指标等方面也面临着一些挑战。在本次调查中,我们全面介绍了最近多模态图像合成的进展,以及根据数据模式和模型架构编辑和制定分类法。我们首先介绍图像合成和编辑中不同类型的引导方式。然后,我们使用详细的框架广泛描述多模态图像合成和编辑方法,包括生成对抗网络 (GAN)、GAN 反转、Transformers 和其他方法,例如 NeRF 和扩散模型。随后对多模态图像合成和编辑中广泛采用的基准数据集和相应的评估指标进行了全面描述,并对不同的合成方法进行了详细比较,并分析了各自的优缺点。最后,我们提供了对当前研究挑战和未来可能的研究方向的见解。与此调查相关的项目可在 https://github.com/fnzhan/MISE 获得



我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。

- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处
- 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~